Hip injuries lead in traumatology statistics. The legs literally take the first blow in a variety of situations: sports, falls, car accidents. We will talk about sprained muscles and ligaments of the thigh - an injury that cannot be called severe, but it requires quite a long treatment.
Author of the article / Site experts Shulepin Ivan Vladimirovich, traumatologist-orthopedist, highest qualification category
Total work experience over 25 years. In 1994 he graduated from the Moscow Institute of Medical and Social Rehabilitation, in 1997 he completed a residency in the specialty “Traumatology and Orthopedics” at the Central Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics named after. N.N. Prifova.
Types and severity of sprains
Injuries to the muscles and ligaments of the thigh are classified by location, degree of damage and severity.
Hamstring strain
There are three muscles located here (semitendinosus, semimembranosus and biceps), responsible for flexion of the leg at the knee and extension at the hip joint. Intense movements on insufficiently warmed or unprepared muscles lead to their damage.
Hip adductor strain
The internal group of muscles is responsible for bringing the legs together and flexing the knee joint. Injured when trying to do the splits without preparation, squats and strong swings of the legs. The adductor longus muscle is most susceptible to stretching, which happens in sports such as fencing, football, speed skating, handball, skiing, and athletics (high jump).
Quadriceps strain
Since this muscle (quadriceps) is the most massive in the human body, it is injured only under strong impact (usually excessive load in professional sports) - contraction of muscle tissue when trying to sharply slow down a high speed of movement. The rectus muscle of this group is most often damaged, which, unlike the others, is attached to two joints: the hip and knee.
Hip muscle injuries
In the area of the hip joint there is a whole group of hip muscles that provide complex movements of the leg (flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, rotation). These are the gluteal, gluteus medius, deep gluteus, biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, quadratus femoris and others. Their damage occurs quite often, and not only during sports. The main mechanism is an unexpected contraction, which happens during a fall, impact, or excessive physical activity in physically unprepared people.
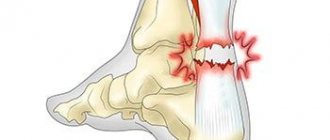
Hip sprain
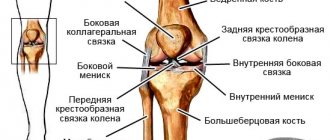
This is a more severe injury than a muscle strain. It is preceded by prolonged tension in the connective tissue, which leads to thinning of the fibers and loss of their elastic properties. Sprains are possible in the hip and knee areas.
The ligaments of the hip joint are injured in the following situations:
- Lifting weights with legs wide apart. A typical injury in track and field athletes.
- Repeated blows to the legs and falls in team sports.
- Stretching under intense loads in untrained people.
A characteristic feature of this injury is that symptoms appear not at the moment of impact, but with repeated stress.
Severity of tendon sprain:
- Light when single fibers are torn.
- Average degree. Most of the ligament is injured, and the fibers begin to separate from each other.
- Severe degree. Tear and complete rupture of the ligamentous apparatus.
The first two degrees are not considered complex and are treated conservatively.
Severe degrees are dangerous due to complications and incomplete restoration of movement, and therefore require hospitalization and surgical treatment.
Rehabilitation after a hamstring muscle tear
Rehabilitation for a hamstring muscle tear includes:
- Exercise therapy. The exercises are designed to restore muscle elasticity and mobility, prevent muscle fiber atrophy, and increase muscle strength and endurance.
- Electrophoresis. Prescribed to relieve pain and accelerate the regeneration process.
- Magnetotherapy. It is prescribed to activate metabolic processes and increase blood flow, which has a beneficial effect on the tissue healing process.
- Acupuncture. Returns sensitivity of the skin over the injured area.
- Massage. Prescribed 3-7 days after injury. The procedure is carried out once a day for an average of 2 weeks. Its action is aimed at improving the supply of oxygen to cells, restoring local metabolism and increasing tissue elasticity.
Exercise therapy exercises begin with simple movements - flexion and extension of the knee joint in a standing position or lying on the stomach. With the doctor's permission, exercises using weights are added. It is important to perform movements in full amplitude to prevent shortening of the muscle length and the formation of contracture. Exercise increases blood microcirculation and ensures the delivery of nutrients to damaged tissues. After 3-5 days, you can add stretching to the exercises to restore elasticity and flexibility.
Symptoms and diagnosis of hip sprain
Regardless of the location and type of injury (muscle or ligament), hip injury has common symptoms:
- Click. The patient feels it at the time of injury. This is muscle fibers tearing.
- Pain. Very intense, usually occurs immediately. The pain forces the patient to stop moving, sometimes painful shock develops. Injuries in the area of the hip joints are especially painful, since this is where bundles of nerve fibers are concentrated.
- Pain on palpation. It is impossible to touch the affected area. This immediately allows you to clarify the location of the injury.
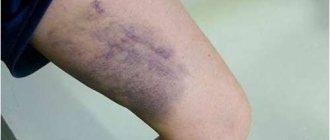
- Hematoma. It is formed if blood vessels are damaged and hemorrhage occurs in the tissue and under the skin.
- Edema. Characteristic for stretching the biceps femoris.
The prevalence of edema and hematoma, the severity of pain are additional criteria for the severity of the injury.
Diagnosis begins with a detailed questioning of the patient about the circumstances of the injury. It is important not only to find the place of greatest intensity of symptoms, but also to find out how the patient pulled the muscles and tendons. Sometimes, due to severe swelling and pain, palpation of the injury site is difficult, so it is the patient’s story that serves as the basis for making a diagnosis. The surgeon flexes and extends the leg and asks the patient to lean on it. After these manipulations, the diagnosis becomes clear. To exclude bone fractures, joint dislocations, and ligament ruptures, radiography and computed tomography are prescribed.
Urgent Care
This type of care is appropriate when a person's life is in danger due to a hip injury. In the presence of painful shock, it is important to direct all efforts to maintaining the basic processes of life: breathing and heartbeat. This can be done while lying on your side, placing a cushion under your head and legs. Inhaling ammonia vapor and vigorously massaging the ear canals will help bring the person to consciousness.
If vomiting occurs, keep your head down as vomiting can block your airway. A weak thread-like pulse requires chest compressions and CPR.
Before making a diagnosis, it is recommended to apply ice to the area of pain. The use of warm or warm bandages should be avoided as this will cause additional blood flow to the painful area, increasing swelling and bleeding.
The patient should be as calm and limited in mobility as possible. A locking splint can be used to immobilize the hip during transport. This will reduce the intensity of the pain and help avoid further injury.
Treatment of hip muscle and ligament injuries
The success of therapy for sprained muscles and ligaments of the hip depends on timely and correctly provided first aid. In the future, tactics are determined by the severity of the damage.
First aid
For injuries of any location, there is a clear first aid algorithm. For sprains and tears of the muscles and ligaments of the thigh, it is as follows:
- The main principle of treatment is rest and cold. To do this, the victim is placed on his back in a semi-lying position with a bolster under the knee. This eliminates additional tension on muscles and ligaments.
- Any load on the leg should be avoided.
- Cold is applied to the injury site (a towel soaked in cold water, ice cubes in a bag, any item from the refrigerator). The duration of this effect is 15 minutes, which reduces pain, swelling and the spread of hematoma.
- For severe pain, any painkiller in tablets is allowed.
- If there is a suspicion of a sprain in the knee joint, apply a tight bandage (you can use an elastic bandage). It is important not to crush the tissue or cause circulatory problems.
In any case, the victim is taken to the hospital to clarify the diagnosis and exclude more serious pathologies (fractures, complete rupture of muscles and ligaments).
Semimembranosus muscle rupture
The semimembranosus femoris muscle is located under the semitendinosus muscle and performs the same functions. With its help, flexion and internal rotation of the lower leg occurs, as well as extension and adduction of the thigh.
As a rule, a sprain of the semimembranosus muscle occurs due to poor warming up before training, excessive tension, or sudden movement. Symptoms of injury are severe pain, swelling, noticeable weakness in the muscle, and subcutaneous hemorrhage.
In case of partial tear of the semimembranosus muscle, rest is recommended for 2-3 weeks and drug therapy and rehabilitation are prescribed. If a complete rupture of the semimembranosus muscle occurs, surgical intervention is required to restore the integrity of the tissue, followed by the application of a cast for 6 weeks, medication and rehabilitation.
Treatment after confirmation of diagnosis
With the first and second severity of muscle and ligament injuries (when there is no complete rupture of muscle fibers and ligaments), the patient is treated independently at home. He must strictly follow the following recommendations:
- Complete rest of the affected area. Moving only on crutches. If these recommendations are not followed, the recovery period is significantly prolonged and complications may arise. For example, inflammation of the ligaments of the hip joint. A child may be given a plaster splint to prevent movement, since it is difficult to explain to young children the need for complete rest.
- The affected leg is placed above the level of the body, placing a pillow under it. This is done to prevent edema.
- It is advisable to fix the injury site with an elastic bandage without disrupting the blood supply to the tissue.
- For the first three to four days, cold is applied every 4 hours for 15 minutes, then you can lubricate the injured area with warming ointments. The criterion for the safety of their use is the disappearance of tissue edema. In addition to warming ones, there are other local drugs that alleviate the patient’s condition. We give a brief description of them in the table.
| Mechanism | Titles | Peculiarities |
| Cooling of tissues. Reducing pain and swelling | Heparin ointment, "Nikovena" | Does not affect body temperature |
| Warming | "Dolpik", "Nicoflex" "Capsoderm" | Use only after swelling disappears. Many contain bee venom, which is contraindicated in children and those with allergies. |
| Anesthesia | "Traumel S", "Fastumgel", "Lioton" | Contains ibuprofen and diclofenac. Effective from the first days. |
- If the injury site hurts even after the acute period, painkillers are prescribed. It is better to check the specific drug with your doctor, since, for example, in case of extensive hematoma and edema, aspirin and ibuprofen are contraindicated.
- During the recovery period, which depends on the severity of the injury, massage and physiotherapy are used. You can start doing massage already on the fifth day after a minor sprain of muscles and ligaments. Physiotherapy procedures are prescribed by a doctor on an individual basis.
In case of severe injury with complete rupture of muscles and tendons, surgical treatment is indicated. Such damage takes much longer to heal and can leave consequences - lameness, limited mobility in the joints.
Recovery time after a hamstring muscle tear
On average, recovery from a hamstring muscle tear takes 2-3 weeks, depending on the location and extent of the damage. Unfortunately, there is a relatively high risk of injury recurrence, especially in the first two weeks after returning to activity. This is why correct diagnosis and timely treatment of hamstring muscle rupture is so important in order to avoid long-term complications: chronic pain syndrome and decreased physical performance.
Stretching while lying down
There are also many gymnastics complexes for stretching in a lying position. To stretch while lying down, lie on one side, bend your knee, and pull your heel as close to you as possible. The other leg can be left straight.
The foot should reach towards the buttocks, but you should not be overzealous so as not to injure the ligaments. You shouldn't move your pelvis. It is better to try to keep it in place by pressing it to the floor. After completing the movement, the foot can be slowly returned to its place, after which the exercise can be continued on the other leg.
Thanks to this complex, not only the front surface of the thigh will be stretched, but also the lumbar and gluteal regions.
Causes
Muscle rupture occurs when a cut wound or blow is received. But in more than 50% of cases, the injury occurs due to severe spraining and overexertion. This happens for 3 reasons:
- Muscle atrophy in old age.
- Changes in muscle structure due to disease.
- Pathological muscle weakness.
Often rupture occurs in weightlifters who work with critical weights. The likelihood of injury increases if you do not spend enough time warming up and warming up before physical exercise.
Stretching while standing on one leg
Stretching the front of the thigh can be done in different ways. The classic version involves the position of the person’s body standing on two legs, while stretching in different directions, similar to how one would want to sit on the cross splits.
If you perform stretching on one leg, the rectus muscle will be stretched most strongly and effectively. It should be taken into account that it will be necessary to maintain balance. To do this, you can either stand at a support or control your movements.
Bend one leg at the knee and take it back, holding it with your hand from behind. At the same time, the second leg, which is located on the floor, should remain level and straight. The knee should not be bent. You will feel a stretch in your thigh muscles, including your glutes.
Clinical manifestations
Most often, ruptures of the calf muscles and other parts of the body occur in professional athletes: gymnasts, wrestlers, volleyball players, weightlifters, rowers, etc.
Symptoms of a muscle rupture, first of all, consist of intense pain that is localized in the damaged muscle. In addition, the following is observed:
- muscle dysfunction;
- the presence of a muscle defect that can be detected by examination and palpation;
- bulging of the muscle in the opposite direction from its separation in the form of a roller (with a complete rupture);
- the appearance of hematoma and edema at the site of injury.
Sprain treatment
In the first and second degrees, the patient is prescribed rest. It is necessary to avoid any physical activity until muscle tissue and ligaments are completely restored. After pain relief, the patient is prescribed physiotherapy and physical therapy.
In the third degree of severity of damage, treatment may require more radical measures: in case of a rupture, surgery is performed on the damaged muscle tissue. Recovery can last up to six months, depending on the characteristics of the body.
Conservative therapy
Treatment for hip muscle strain involves:
- Limiting physical activity is mandatory for effective healing of the thigh muscles: on the first day it is recommended to remain in bed, and in the next few days, use crutches to move around, which will reduce the load on the damaged muscles.
- Applying ice packs to treat a strained thigh muscle: Apply ice packs to the affected area two to three times a day for at least half an hour. An alternative is to use a heating pad filled with cold water.
- Wearing an elastic bandage or compression stockings.
- Fixing the limb in a position that facilitates the outflow of blood from the damaged area: to get rid of swelling, the leg must be positioned above the level of the heart. You can achieve the desired effect by placing a pillow or bolster under your foot.
- Oral intake of antispasmodics (No-spa, Mydocalm) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ketoprofen, Piroxicam).
- Topical medications should initially be applied with massage movements before bedtime. Subsequent treatment tactics are three times a day. The most effective pharmaceutical drugs: Lyoton-1000, Heparin ointment, Actovegin, Nicoflex, Voltaren Emulgel, Indomethacin.
Traditional methods
Treatment of thigh muscle strain at home using folk remedies is an addition to the main treatment prescribed by the doctor.
Below are the most popular recipes used in muscle fiber strain therapy:
- Beer decoction. Heat the drink in a water bath without letting it boil. Soak a towel or gauze bandage in it, wring it out and sprinkle ground pepper on top. Apply the compress to the damaged area for 15 minutes.
- Treatment with barberry. Pour a tablespoon of branches, roots and bark of the plant with a glass of water and cook over low heat. Let the liquid cool slightly, dip a piece of cloth into it, squeeze it out and apply it to the sore area.
- Onion therapy. Finely chop the onion head. Mix with sugar to form a thick mixture. Wrap everything in gauze, place it on the damaged area and leave for an hour. Apply the compress once every 2 days.
- Treatment with blue clay. Combine clay powder with water until you get a thick mixture. Put it in the refrigerator. Then apply the hardened clay to the affected area. Repeat the procedure every 4-5 hours.
- Compresses with milk. Dampen a cloth with the liquid and apply it to the damaged area of the thigh. Change the compresses every time after they have cooled completely.
- Treatment with pine branches. Fill the enamel container halfway with pine branches. Fill to the top with water and cook for 30 minutes. Use the resulting decoction for a medicinal bath.
Alternative medicine methods are aimed at eliminating painful symptoms, but not at treating the underlying disease. Before using traditional recipes, you need to consult a specialist.
Lunge Stretch
Another version of hip exercises is the lunge. To do this, lunge on one leg, bending the other at a right angle and placing it so that the knee does not go beyond the toe.
Next, move your pelvis forward to feel the stretching of the muscles. The heel should not be lifted off the floor.
During this exercise, not only the front part, but also the gluteal region works well. If you perform the exercise at the same interval and the same degree of load on both legs, you can eliminate the appearance of asymmetry. It has long been known that asymmetrically developed and stretched legs will lead to the appearance of scoliosis in humans.
Also a good complex would be exercises from the famous Suzanne Bowen. She suggests doing the lunge this way. Having transferred the weight of your own body to one leg, you need to feel a slight tingling sensation in the opposite thigh. If you place one leg behind you, stretching it across the floor, and bring the other one forward as much as possible, then stretching will be more effective. But this exercise option will not be available for people who have severely stiff areas of the anterior thigh and buttocks.
The back should remain straight, the torso should be kept strictly symmetrical, without leaning forward, backward or to the sides. You can breathe every five counts, replacing the position of your body with each exhalation.
Carrying out diagnostics
An experienced surgeon or traumatologist can accurately determine the presence of disorders during an external examination of the patient. The location of the bruises and the soreness of the injured area indicate the intensity of the impact that led to the sprain.
A qualified specialist will conduct a survey to clarify all the circumstances of the injury, flex and extend the injured leg in the joints, and also use palpation to determine the integrity of the joints, and only after that will be able to make the correct diagnosis. In some cases, additional examination may be necessary. In addition, a possible fracture or dislocation can be excluded using x-rays or computer diagnostics.
Recovery period
After therapy, it is imperative to carry out rehabilitation measures. They include procedures such as:
- physiotherapy;
- swimming;
- physiotherapy;
- massage.
The rehabilitation period largely depends on the degree of complexity of the injury; for example, with a minor muscle strain, it lasts no more than 10 days. In more complex cases, when muscles, ligaments or tendons are torn, it may take six months to fully recover.