How often a bruise is mistakenly considered a minor injury! The problem is that it is in the area of the lower extremities that developed fatty tissue and a massive muscle group are concentrated. Specifics of a hip joint bruise: the skin remains intact, but subcutaneous hemorrhage causes acute pain and can cause damage to the thigh muscles. Moreover, outwardly the injury is completely invisible.
Author of the article / Site experts Shulepin Ivan Vladimirovich, traumatologist-orthopedist, highest qualification category
Total work experience over 25 years. In 1994 he graduated from the Moscow Institute of Medical and Social Rehabilitation, in 1997 he completed a residency in the specialty “Traumatology and Orthopedics” at the Central Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics named after. N.N. Prifova.
General information
In case of a hip injury, recovery methods depend on the mechanical impact indicators - in some cases, the only treatment option will be surgical correction.
The disease is divided according to the severity of the damage received:
- The first stage is when a minor hematoma forms in the area of damage, which is accompanied by unpleasant sensations. Key sources of development include accidental contact with hard objects and a light blow.
- The second is accompanied by muscle damage; upon examination, swelling and bruising are visible. Patients complain of painful sensations, the condition requires contacting a medical facility.
- Third, any attempts to move provoke pain. In the affected area, pronounced swelling of the tissues is determined, a hematoma is a deviation that occurs when the fibers of the connective tissues rupture.
- The fourth refers to complex injuries, with acute pain, swelling of the skin, and local hemorrhages. In the impact zone, an increase in temperature is detected, enlarged lymph nodes, and any movements of the affected limb are limited.
Is rehabilitation necessary?
Recovery after a bruise of the hip joint begins on the third day, if the pathology is without complications.
If hemarthrosis occurs along with a bruise of the hip joint, then exercises can be started after removing the fixation bandages. It is important to develop the hip joint. Before this, it is recommended to do only static exercises, in which the thigh muscles tense but do not move. You can strain them daily, 2-3 approaches. This will help improve blood flow in the affected area and prevent stagnation.
The exercises can be found in this article.
Exercise videos
Check out the exercises you can do after a hip injury to avoid chronic pain.
Elderly people and athletes often suffer from bruises of varying severity. The injury is accompanied by bruising and swelling. The sharp pain at the time of injury is replaced by dull and aching pain. Ignoring a bruise and not treating it can lead to complications. Timely diagnosis will help determine the condition of the bones and exclude cracks and fractures. Adequate treatment will speed up recovery time after injury.
Symptoms
Traumatologists pay attention to the key signs of a hip injury:
- severe pain – the level of discomfort depends on the severity of the injury;
- subcutaneous hemorrhage with hematoma formation;
- swelling of the skin in the area of damage;
- violation of free movements of the lower limb;
- increased local temperature, enlarged lymph nodes.
Severe injuries can cause prolonged bleeding that continues throughout the day. A concomitant complication of a hip bruise can be a fracture of its neck.
Rehabilitation period
During rehabilitation, the patient is shown performing exercises from therapeutic physical culture complexes. A number of exercises are useful and must be performed as follows:
- Lie on your side so that your sore hip is on top. Gently move your leg back. You need to perform the exercise very slowly, repeat 5-6 times;
- lie down on your back. Begin to make gentle circular movements with the injured limb - first inward, then outward. Repeat the exercise up to 8 times;
- stand against the wall with the side of your body with a healthy lower limb. Move the affected leg slightly to the side and slowly lift it. The arm should be kept straight and to the side. Repeat up to 10 times.
The patient’s performance of exercises to develop the damaged joint should be supervised by a doctor at the initial stages to prevent additional damage.
Also, during the recovery period, the patient may be prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures: laser therapy, magnetic therapy, massage, electrophoresis. The purpose of such procedures is to accelerate regenerative processes in damaged structures.
Difference from fracture
The main symptom of a fracture is bone deformation; with every attempt to move, bursts of acute pain occur in the leg. The main signs of a fracture are:
- the outbreak of pain that occurred during the injury does not disappear and may intensify over time;
- swelling and bruising form almost instantly;
- when you move your fingers, leg or try to lean on it, pain occurs;
- in the affected area, bone fragments are displaced, the limb may increase or decrease in size;
- pronounced crunching in the injured hip;
- if the fracture occurs with displacement, then pathological mobility is observed;
- in the open form, bone fragments break through the skin.
Key symptoms for a hip injury:
- a sharp flash of pain upon impact, weakening over time;
- increasing swelling within 24 hours - when the leg is elevated, its volume decreases;
- problems with free movement of the limb - due to discomfort and swelling.
The clinical picture of a fracture or bruise may be blurry; a diagnostic examination is necessary to accurately determine the type of injury.
Possible complications and consequences
A joint bruise is a minor injury, but without treatment complications arise:
- Formation of bone formations (ossifications) in damaged muscles. The problem area becomes swollen and dense. The pathology is treated conservatively or by surgical removal.
- The development of secondary arthrosis, provoked by the impact of a bruise. The cartilage tissue of the joint becomes thinner and exfoliates. There is limited mobility of the hip.
- Morel-Lavallee disease - the epidermis, together with subcutaneous adipose tissue, is sharply separated from the fascia. The resulting cavity is filled with blood or another type of fluid.
- Purulent infection of the hemorrhage area caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Symptoms of complications: increasing pain, fever, weakness.
Sources of development
Damage to the lower limb can occur anywhere: at home, at work, in a sports complex, on the street.
Common causes of hip bruises include:
- Impacts to the problem area with blunt objects;
- Car crashes;
- Falls on a slippery surface - in the cold season, on wet linoleum, tiles;
- Playing sports without the necessary equipment;
- Neglect of workplace safety rules.
In childhood, most injuries occur due to playing in inappropriate places: construction sites, quarries, roofs of low buildings. Elderly people, due to poor coordination, are injured when falling on ice.
Causes
Injuries to the hip joints are possible both at home and as a result of professional activities associated with increased physical activity. Most often, damage occurs due to external influences, for example, a strong impact on a foreign object. It is also possible to injure the hip joint when falling from a height.
It should also be noted that external damage to the joint by people suffering from various types of diseases of cartilage and bone tissue is possible even when the tissue is subjected to a minor impact. As a rule, these types of injuries are especially difficult to treat and require a long period of rehabilitation.
Diagnostics
Determining the type of damage begins in the trauma room. The doctor collects an anamnesis: with examination of the injured hip, palpation examination, determining the time and place of injury. The mandatory program includes testing the affected leg: the patient is asked to bend it, straighten it, and move his fingers. After making a preliminary diagnosis, the patient undergoes several procedures:
- X-ray images - will confirm or refute the presence of a fracture, show where exudate has accumulated;
- CT or MRI - prescribed for questionable radiographic results, they allow you to find out the exact location of hidden hematomas, bleeding, bone cracks, soft tissue ruptures, and the ligamentous-tendon apparatus.
Based on the information received, the traumatologist recommends a suitable treatment regimen.
Main signs
Accompanied by symptoms:
- The bruised area is swollen;
- There was an outpouring of blood under the skin;
- The thigh is enlarged;
- The bruised area hurts when touched;
- The function of the knee joint is impaired.
Fall on the thigh Due to a severe bruise, the hemorrhage continues for about a day. The consequence is damage to internal organs located in close proximity to the impacted area.
Due to a serious injury, after a few hours the temperature rises and the lymph nodes become enlarged. Possible hardening of the muscle, pressing down on the swollen muscles by inelastic bones.
A doctor is competent to make a diagnosis of such an injury. It will be necessary to diagnose the patient, palpate the affected area and near it, and check the joints for movement. If, during the examination, the doctor suspects a serious injury, for example, a hip fracture, he has the right to prescribe an x-ray or MRI to examine the soft tissues.
Treatment
A hip bruise requires emergency measures to prevent the development of complications. The algorithm includes the following provisions:
- giving the injured limb the most comfortable position - the patient is seated or laid down, the leg is slightly raised with a small bolster;
- scratches and small wounds are treated with an antiseptic solution and hydrogen peroxide;
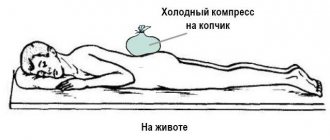
- a heating pad with ice and bags of frozen food are applied to the damaged area - before the procedure they must be wrapped in cotton cloth so that there is no direct contact with the skin;
- Cold treatment is carried out according to the following scheme: 20 to 20 minutes; longer exposure to ice can lead to a cold burn;
- To reduce swelling, the affected limb is tightly bandaged with an elastic bandage - after the bandage, the skin should not change its natural color.
After the visit to the trauma center, they move on to therapeutic measures. During the first seven days, the patient is recommended to rest in bed with minimal stress on the bruised hip. On the fifth day, the schedule includes exercises with wiggling the toes, bending and straightening the toes.
Exercise helps stabilize blood circulation and speed up the healing process.
While sleeping, place a small pillow or cushion under your leg - this will reduce the amount of swelling. Suppression of painful sensations is achieved by taking NSAID medications; they help get rid of discomfort, inflammation, and tissue swelling. It is recommended to use local products - Fastum-gel, Diclak, Febrofide. Ointments are applied three times a day to reduce discomfort. General systemic medications of the same subgroup are represented by Ibuprofen, Nise, Nimesil, Movalis.
After suppression of the main symptomatic signs, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed:
- electrophoresis - exposure to electrical impulses helps accelerate the absorption of drugs, increases their effectiveness;
- UHF - heat treatment ensures resorption of hematomas and improves blood supply to the diseased area;
- Magnetic therapy - used for most injuries, can be performed both at home and in hospital.
These manipulations can reduce rehabilitation time and restore normal mobility to a bruised hip. Massage sessions and a course of exercise therapy are included in the scheme last - they are used to develop muscles, joints, and increase motor activity. In difficult cases, surgical correction may be required - large hematomas are opened, their contents are removed by pumping out the accumulated blood clots.
The duration of therapy depends on the degree of damage, the general condition of the body, and contraindications to certain treatment methods. For minor injuries, recovery occurs within 2-3 weeks.
How to treat
There are two treatment methods - conservative and surgical. When choosing the first option, treatment includes: first aid and further following the doctor’s recommendations. If you follow your doctor's instructions, pain symptoms can be reduced quickly. During the first week, you cannot put any weight on the leg; the limb remains at maximum rest.
To reduce swelling, the leg should be kept in an elevated position. For example, at night you can put a pillow. The outflow of blood will increase, and swelling will not appear in the morning.
Pain distracts, interferes, brings discomfort to life, so the doctor prescribes painkillers. Now doctors are more inclined to drugs of non-steroidal origin: ibuprofen, Nise and others. They relieve pain, swelling, and reduce the inflammatory response. It is possible to use ointments: fastum, febrofid - they act directly on the lesion.
When these symptoms begin to decrease, the doctor writes a recommendation for physical therapy. This includes electrophoresis using potassium iodide, magnetic therapy, and UHF. After undergoing the procedures, blood flow improves and hematomas resolve.
Preventive actions
To prevent hip bruising, traumatologists advise adhering to general principles:
- Exercise extreme caution in the workplace, while exercising or moving during the cold season. Patients should use protective equipment during competitions, choose shoes with non-slip soles, and remember to follow safety rules.
- Reducing injuries is achieved by constant training: walking, training in sports clubs. Control of body weight plays an important role - excess weight creates additional stress on the lower limbs.
Hip bruise is a common injury among patients of all age groups. Immediately after the injury, the patient should visit the trauma center in order to determine the extent of the injury and exclude a possible fracture. Ignoring the symptoms of the pathology can cause the development of serious complications.
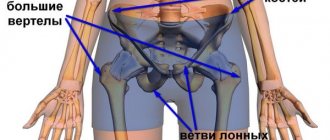
Specifics of injury in the hip joint
A fall on the side or buttocks in most cases results in injury - a bruise or fracture. A person cannot get up on his own or it is difficult for him to do so and is accompanied by severe pain. It is believed that a bruise should not be taken as a serious circumstance. Just rest for a couple of days and the pain will go away. But in practice, such bruises of the hip joint have complications that prevent the victim from leading an active lifestyle for another 1-3 months. For older people, a pelvic injury can be a reason for complete limitation of mobility and lack of independence until complete recovery.
When the pelvis is contused, depending on the force of the fall or impact, both soft tissue and bone are injured. A symptom of a bruise is acute pain and the formation of a hematoma at the site of impact.
If a pelvic contusion is not accompanied by the formation of a crack, displacement of articular elements or a fracture, then treatment requires following the doctor’s recommendations and staying at home in bed.
Athletes receive blows to the hip joints due to the specifics of their profession, and people involved in a traffic accident. Regardless of the cause of the injury, the degree of damage to the hip joint varies, as evidenced by the symptoms that the victim complains about.
Frequently asked questions
How to get rid of a hematoma using traditional methods?
Folk remedies only help with minor and non-dangerous superficial damage. To speed up resorption, you can apply a compress of mashed cabbage leaves, bodyagu mixed with Vaseline, or tampons soaked in a mummy solution to the bruise. For deep or extensive injuries, you should consult a doctor.
Why is a hematoma dangerous?
The greatest danger to health, and sometimes to life, are hematomas that form deep in the tissues, inside organs or joints. Large hemorrhage is dangerous due to the possible development of infection, inflammation and suppuration. If the joint is damaged, bursitis, synovitis or hemarthrosis may develop, resulting in disability. Blood in the peritoneal cavity leads to peritonitis. Brain hematomas lead to dysfunction of this organ with serious consequences in the form of deterioration of cognitive functions, paralysis of body parts, etc.
How to treat a hematoma in the first hours after injury?
Immediately after a bruise, it is necessary to provide first aid to the victim: apply ice to the injured area, then tightly bandage the injured limb to block the flow of blood into the tissue. The dressing should not remain on for more than two hours. During this time, it is necessary to get to the emergency room, where the patient will receive the necessary professional help.
Urgent Care
If there are no medical facilities nearby, the victim must be given first aid.
Actions should occur in the following sequence:
- The victim should be placed in a comfortable position, eliminating any load on the injured limb, placing it on an elevation. To do this, you can use any available means (a roller, a pillow, rolled clothes).
- Cold should be applied to the damaged area. The bleeding can continue for a long time, but thanks to the cold, the blood vessels narrow and it stops. If you don't have ice on hand, you can use a bottle filled with cold water.
- To reduce swelling and pain, it is necessary to bandage the limb tightly, provided that there are no open wounds and bone fragments do not protrude from the skin. The skin should retain its color; redness or blueness means that the bandage is too tight and needs to be loosened.
- If there are scratches, it is advisable to treat them with antiseptic agents (iodine, brilliant green). If a person complains of severe pain, it is recommended to give him a painkiller.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine recipes allow for additional treatment at home, and are recommended for primary use only in the absence of post-traumatic complications. Here are some of them:
- infuse 30 g of camphor oil and 300 g of water. Then moisten the bandage and apply it to the bruise until it is dry. Repeat several times.
- 1 tbsp. l. cinquefoil pour 1 liter of boiling water and leave for 2-3 hours. After first straining the broth, the pulp is used for a compress, and the infusion is divided into 5 equal parts and drunk throughout the day.
- A beaten, softened cabbage leaf works well. It is applied to the site of injury for 6 hours.
- Crushed aloe leaves are mixed with honey. Apply to the site of injury and keep overnight.
- Boiled potatoes and beans are crushed, the resulting pulp is placed in gauze and applied to the area of injury. Raw potatoes, cut into rings, are applied to the damaged area.
Hematoma
An accumulation of clots or liquid blood in the soft tissues of the body, formed due to rupture of blood vessels, is called a hematoma. The most common type of pathology is an ordinary bruise. However, this concept includes much more severe and complex cases that cannot be left without qualified medical care. Blood flowing from the vessel irritates the tissues surrounding it, resulting in pain, tissue swelling and other signs of developing inflammation. In addition, the hematoma compresses the tissues or organs located next to it, which can lead to the development of complications.
What a doctor should do when detecting a hip bruise
Diagnosing a hip bruise is not difficult. But to prevent complications, the doctor is forced to conduct additional studies:
• Inspection of the affected area. Touching the skin increases the pain. The doctor makes sure that the bones are intact and determines the size of the hematoma.
• The doctor may ask you to walk, lift, or bend a limb. This is how active movements are assessed. The passive ones are checked by a doctor. He bends, lifts, and rotates his limb with his own strength.
• To exclude a fracture, it is recommended to take an x-ray.
• If the patient is experiencing severe pain, movement is limited, and external signs of injury are minimal, an MRI should be done. Such symptoms indicate rupture of ligaments, muscles, skin detachment, intramuscular hematomas - all changes that are not visible on x-rays.