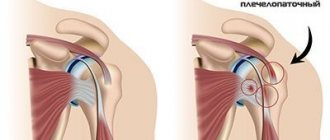
A disease such as glenohumeral periarthrosis is a degenerative process with thinning and destruction of tissues - capsules, ligaments, tendons that surround the joint. Periarthrosis, with structural changes in tissues, in contrast to periarthritis - an inflammatory process, is characterized by complications in the form of deformations, in the absence of proper treatment. Rapidly developing periarthritis can develop into glenohumeral periarthrosis, the cause of which will be the initial inflammation.
With this disease, a person experiences pain that intensifies when pressing on the affected area, difficulty sleeping, and the disease leads to great inconvenience in everyday life. With periarthrosis, there is a significant limitation in the motor ability of the arm on the affected side, difficulties arise when lifting it, and it is difficult to place the arm behind the back, as this causes a significant increase in pain.
It is quite possible to successfully treat an ailment such as periarthrosis, but timely seeking medical help will be a very important point. The doctor, having studied the symptoms, will select the correct treatment package for glenohumeral periarthrosis. Traditional therapy for the disease can be supplemented with traditional methods, with a preliminary discussion of these methods with the treating doctor.
Periarthrosis is treated by neurologists, orthopedists or rheumatologists, when pathology develops as one of the symptoms of rheumatic lesions. Surgery is resorted to in cases where conservative treatment of the disease does not bring results, for example, with extensive growth of fibrous tissue in the joint capsule.
Treatment of glenohumeral periarthritis
To treat glenohumeral periarthrosis, we use the following methods:
- Medical massage;
- Isometric kinesiotherapy;
- Kinesiotherapy using the Exart installation;
- Acupuncture;
- Kinesio taping;
- Limiting the load on the shoulder joint;
- Drug therapy.
If you suffer from glenohumeral periarthrosis and delay treatment, the situation will only get worse, and it will become more and more difficult to correct it. The fact is that over time, in the absence of treatment, the joint capsule and ligaments become less elastic, the joint loses mobility, and pain increases.
Symptoms of the disease
The disease is accompanied by persistent aching pain in the shoulder joint.
As a rule, it affects one side - in right-handed people, it is more often the right. In the joint areas of the shoulder, muscle contracture may form, which, along with pain, limits movement. Rotation of the shoulder, moving the arm to the side and behind the back (frozen syndrome) are especially painful; stiffness of movements in the sternum and scapular muscles is felt.
The inflammatory process is accompanied by elevated temperature. At night and during hypothermia, the pain intensifies; the patient cannot sleep on the affected side.
The disease can radiate (give) to the cervical and occipital region, as well as to the arm and shoulder blades.
Shoulder periarthritis: diagnosis and treatment
Periarthritis affects all periarticular tissues with further formation of an inflammatory process in the nearest mobile joints. It is defined as a rheumatic disease.
Causes of occurrence and development
Shoulder periarthritis can occur as a result of:
- micro/macro injuries;
- hypothermia;
- regular injury to a particular joint, which results in the formation of reflex contracture;
- professional/sports intensive loads;
- metabolic disorders (excess weight);
- menopause and other endocrine changes;
- pathologies at birth;
- acute cerebral circulatory disorder;
- disorders in the gallbladder;
- damage to the serosa/lungs;
- ischemic myocardial necrosis;
- age-related changes;
- other diseases.
Stages of development and diagnosis of periarthritis of the shoulder joint
- At first, mild pain appears in the joints
when moving your arm. Then stiffness, swelling appears, pain intensifies, radiating to the arm and cervical spine, and insomnia appears. - In most cases, the disease progresses to chronic brachial periarthritis. This is the next stage in the development of the disease. Moderate pain syndrome with shooting pain, severe pain, sleep disturbance. Long duration of the disease.
- In approximately 30% of patients, the second stage progresses to the third - ankylosing brachial periarthritis. A dull ache with more severe stiffness in the shoulder, which feels quite tight.
During the initial history taking, palpation and visual examination are performed. If acute pain appears from various movements of the arm, topical diagnoses can be established: inflammation/pathology in the subacromiaotic bursa, teres minor and infraspinatus/supraspinatus muscles.
X-ray helps to exclude injuries, as well as determine:
- decreased bone density of the proximal epiphysis;
- cystic restructuring of the structure of the greater tubercle of the humerus;
- inflammation of the periosteum;
- calcification of the shoulder joint.
The doctor can determine the main articular diseases and lesions of the acromioclavicular joint through simple manipulations.
Ultrasound examines tissue in the shoulder area, determining echo transparency, swelling, thinning of the structure, discontinuity of the contour, calcifications/fibrosis.
MRI and arthroscopy are rarely performed in order to clarify the diagnosis for the correct prescription of a treatment course.
Types of conservative therapy for periarthritis
Treatment is prescribed to:
- eliminate symptoms;
- restore muscle mobility;
- prevent relapse and complications;
- eliminate destructive joint changes.
Periarthritis can become chronic, so it is necessary to carry out treatment until the patient recovers completely. Usually, to remove the maximum load from the sore shoulder during the period of acute inflammation, the limb is fixed. Sometimes a cast is also applied in severe cases.
For complex therapy, the following is prescribed:
- oral NSAIDs;
- psycholeptics;
- muscle relaxants.
Local localization of the disease is carried out for a long time using warm compresses, warming/NSAID ointments. Pain points are soaked in a solution of novocaine/lidocaine with glucocorticosteroids. This is necessary to quickly relieve inflammation and suppress the immune system.
Physiotherapy is prescribed in the post-acute inflammatory period. For brachial periarthritis, drug electrophoresis is usually prescribed, which has proven itself in the treatment of many diseases.
Exercise therapy for periarthritis
During the period of remission, therapeutic exercises are prescribed that relieve pain, restore normal nutrition to damaged joints and shoulder mobility.
Exercise therapy can be done in a group or at home on your own. The main thing to remember is that movements should not be sudden, since you cannot put a lot of stress on the sore joint. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Diagnosis of periarthritis (periarthrosis):
The main complaints for periarthritis (periarthrosis):
For pain in the joint area and associated movement restrictions.
Upon palpation, local areas of pain are determined, corresponding to inflamed soft tissue anatomical structures.
Laboratory tests for periarthritis (periarthrosis):
In the acute phase, changes in the blood are characteristic - an increase in ESR and CRP.
X-ray examination for periarthritis (periarthrosis):
An X-ray of the diseased joint and the corresponding part of the spine is taken.
Typically, radiological changes are detected in advanced chronic forms of periarthritis (periarthrosis). Typically, they are characterized by periarticular deposits of calcium microcrystals (ossification or calculous bursitis); local osteosclerosis and osteoporosis can also be determined.
Other instrumental studies for periarthritis (periarthrosis):
To clarify the diagnosis, an ultrasound or MRI of the joint can be performed.
Invasive diagnostic methods (arthrography, arthroscopy) are justified when deciding on surgical treatment.
The use of shockwave therapy in the treatment of glenohumeral periarthritis: a review of scientific literature
A group of Russian researchers studied the effectiveness of shockwave therapy for chronic glenohumeral periarthritis. They selected 30 patients for the study. All of them received 5-6 sessions of shockwave therapy with an interval of 1 week. After completion of treatment, patients noted relief of pain and restoration of mobility in the joint. Subsequently, they underwent 1 course of anti-relapse shock therapy for a year. There were no relapses of the disease.
German scientists tested the effectiveness of shockwave therapy for glenohumeral periarthritis in 512 patients. Already after the first procedure, almost all of them had relief of pain, and after completing the course, 52% of patients showed a significant improvement in functional indicators of mobility in the joint.
A group of scientists from the USA conducted a study using shockwave therapy for calcifying processes accompanying glenohumeral periarthritis. They divided all patients into two groups: the first received shockwave therapy sessions, the second received a placebo effect. After completion of treatment, patients from the first group showed more pronounced improvements compared to patients from the second group - reduction and relief of pain, destruction of calcifications, restoration of mobility in the joint.
Rice. 4. Treatment of glenohumeral periarthritis using the UVT method
Causes of shoulder periarthritis
Inflammation affects tendons, muscles, joint capsule, and mucous membranes. In cases of degenerative changes in these structures, they speak of periarthrosis of the shoulder; treatment in both cases is similar. Due to the greater load on the dominant hand, the right side is more likely to be injured. Cartilage tissue is usually not affected.
In orthopedics, 2 points of view of the development of the disease dominate:
- Neurodystrophic
. Caused by osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, displacement of the vertebrae and compression of the nerve roots. As a result, neurodystrophy develops in the tendon fibers. The vessels undergo a reflex spasm. Blood circulation in the shoulder area noticeably deteriorates, which leads to degenerative processes and inflammation.
- Mechanical damage
soft tissues. The injury can be either single or cyclic associated with constant physical overload of the tendons. The tendon fibers are torn (enthesopathy), tissue swelling appears, and the blood supply to the tissues is affected. With scapulohumeral periarthritis, treatment often begins with effective pain relief, since the injured tissues hurt very much. Often occurs in tennis players, painters and plasterers working with one hand.
Among the main causes of glenohumeral periarthritis, it is worth highlighting the following:
- Physical overload – causes overstrain of tendons and ligaments
- Hypothermia of the joint - disrupts blood supply
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- Congenital weakness of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the joint;
- injuries (dislocations and subluxations, fractures and bruises);
- Diseases of the endocrine system, for example, symptoms of scapulohumeral periarthritis, often bother middle-aged and older women;
- Parkinson's syndrome;
- congenital anatomical anomalies;
- bacterial or viral infection in the body.
The same causes cause similar joint diseases, for example, shoulder arthritis.
Insufficient blood supply to the joint leads to tissue ischemia and necrotic changes. Necrosis subsequently leads to the formation of scars and the deposition of calcium salts. This is easily proven by pathological studies conducted in individuals with periarthritis of the shoulder.
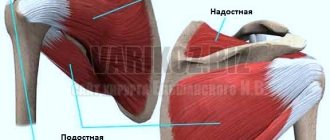
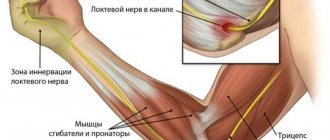
Localization of pain in the shoulder: 1 - supraspinatus muscle, 2 - infraspinatus muscle, 3 - subscapularis muscle, 4 - biceps muscle, 5 - deltoid muscle, 6 - triceps muscle.
Sign up for treatment
Humeroscapular periarthrosis
Pain in the shoulder joint in 80% of cases is associated with a disease such as glenohumeral periarthritis.
Humeral periarthritis (periarthrosis) is an inflammatory (aseptic) inflammation of the tendons, ligaments, joint capsule, etc. surrounding the shoulder joint.
What are the causes of glenohumeral periarthritis?
In young people under the age of 30, the development of the disease is often associated with the consequences of injuries, and in older people - with degenerative processes in the tendons of the shoulder muscle cuff.
The pain is constant , aching, and intensifies with movements of the upper limbs . In the absence of qualified treatment, over time the disease can lead to significant limitation of mobility.
What are the symptoms of scapulohumeral periarthritis?
The disease is characterized by 3 stages of development:
• The initial stage or “freezing” phase is characterized by aching pain and acute inflammation of the shoulder joint and nerve, even at rest, which worsens at night. Lasts from 2 to 9 months.
• The frozen or “sticky” phase is characterized by restriction of shoulder movement in almost all directions, especially when rotating the arm. The second phase can last from 3 to 9 months.
• The unfreezing or regression phase is characterized by a deceptive decrease in shoulder pain, while the limitation in movement increases and can lead to complete locking of the shoulder - sclerosing capsulitis. The third phase can last from 12 to 24 months.
How do we treat glenohumeral periarthrosis at the Center for Spine Strengthening and Joint Rehabilitation at the Institute of Vertebrology and Rehabilitation?
If pain occurs, you should make an appointment with a professional vertebrologist. After consultation, the doctor individually prescribe shock wave therapy or laser therapy or electrotherapy for tissue regeneration, injection therapy to relieve inflammation, or therapeutic massage to relieve stiffness in the neck muscles.
If the doctor sees during the treatment process that the inflammatory processes have stopped, then, if necessary, he can recommend the Finnish-German David movement treatment method. The David Method helps the muscles of the upper limb to be toned, and the ligaments and joints receive enough nutrients from controlled physical activity .
During the initial visit to the Center for Strengthening the Spine and Joints for recovery from glenohumeral periarthritis, the patient, under the guidance of a rehabilitation specialist, undergoes computer testing on specialized medical simulators . After testing, a movement treatment program with an individual weight load is developed for a specific patient according to the Finnish-German David method.
To treat glenohumeral periarthrosis, we use the David Shoulder Concept , which consists of 6 medical simulators aimed at working with the patient’s upper extremities. All simulators are specialized, making it possible to secure the joints of the upper limbs at the correct angle for intense but safe physical activity.
What medical simulators do we use for the treatment of glenohumeral periarthrosis at the Center for Spine Strengthening and Joint Rehabilitation?
All exercise machines use an inertial mechanism that allows you to control the acceleration, deceleration and speed of movements during exercise.
What complaints bother you the most?
Symptoms and treatment of periarthritis of the shoulder joint depend on the stage of the disease:
There are 3 main stages:
- Initial or subacute
. The patient complains of pain only during movements. There is a limitation of rotational movements in the joint. It becomes difficult to put your hand behind your back. The tendons are inflamed and swollen, but their structure is not damaged. Lasts up to 3 weeks and either goes away completely or progresses to the next stage.
- Acute
. The pain becomes stronger and may bother you even at night. Movement in the joint is limited, possible within 90-120 degrees. Particularly affected is the abduction of the arm to the side. A scar is formed in the thickness of the tendon at the site of inflammation. Lasts from 3 weeks to 2 months.
- Chronic
. At this stage, the symptoms of scapular periarthritis occur in waves, sometimes they hardly bother you, or the joint hurts day and night. The range of motion in the joint is significantly reduced, abduction is possible up to 60 degrees. There is weakness and atrophy of the shoulder muscles. Calcium salts are deposited in the tendon scar.
If you do not consult a doctor in time and do not start treatment, a “frozen” (capsulitis) or blocked shoulder may develop when the range of motion in the joint does not exceed 30 degrees. This condition usually ends with surgical treatment.
It is important to know that periatritis is not as dangerous as arthritis or arthrosis of the shoulder joint, so timely consultation with a doctor can count on a full recovery.
| Abduction of the shoulder to the side up to 60-120 degrees causes severe pain. | Critical zone - 1 - supraspinatus muscle, 2 - biceps muscle, 3 - subscapularis muscle. |
Causes of pathology
The occurrence of glenohumeral periarthrosis as an independent disease is quite rare. The development of the disease is facilitated by other pathologies, such as:
- glenohumeral periarthritis;
- osteochondrosis;
- fasciitis is a disease in which the muscle membrane becomes inflamed and there is swelling with a characteristic “orange peel” symptom in the area of inflammation;
- adhesive capsulitis - an inflammatory process of the synovial membrane and joint capsule;
- tendonitis is a disease in which the ligaments of a joint become inflamed;
- bursitis is a pathology with an inflammatory process in the joint capsule.
The cause of inflammatory processes in the joints and tissues that surround them are injuries, frequent hypothermia, decreased immunity as a result of stress, poor diet and bad habits. Pathology also occurs when there are disturbances in the circulatory system in the shoulder and scapular areas. Often, the manifestation of glenohumeral periarthritis occurs after women undergo surgery to remove the mammary glands, or patients suffer from diseases such as myocardial infarction.
Also, the development of such a pathological process as periarthrosis is possible against the background of rheumatic lesions, the cause of which is disturbances in the functioning of the immune system. Excessive loads on the shoulder joint area can lead to glenohumeral periarthrosis, as an independent disease, which most often affects athletes involved in sports such as rowing, tennis, and activities where there is active work of the glenohumeral area.
Side effects in the treatment of glenohumeral periarthritis diseases
The procedure is well tolerated; mild side effects sometimes manifest themselves in the form of pain and slight swelling at the procedure site and disappear by the 2nd day after the procedure. When trigger points are exposed, the pain pattern often changes (the pain moves to another place), sometimes a temporary distortion of a particular body segment may occur, and there are various autonomic reactions associated with trigger points. Based on the experience of our clinic, we can say that the pain syndrome, if successfully hit by the focal spot, can practically go away for some time, but after the first or second procedure, it most often quickly recurs. Therefore, we recommend long courses of shock wave therapy, from 10 procedures.