Periarthritis of the ankle joint is a pathological lesion of the synovial capsules, muscle and tendon apparatus. Inflammation occurs in the pericartilaginous tissues and is characterized by a specific course. The disease is serious and causes great physical discomfort to the person.
However, ankle arthritis, due to its anatomical features, is not a common orthopedic pathology and accounts for only 13% of the total number of cases. The disease affects older people and predominantly females. The inflammation is treatable, but requires long-term therapy.
Pathogenesis
Periarthritis develops from infection of the soft tissues enveloping large joints of the upper and lower extremities. Degenerative processes can affect any interosseous joints of the foot. The pathology is based on degradation followed by secondary infection and visible changes in the cartilaginous surfaces, synovial bursae and tendons.
Clinically, the disease manifests itself as severe attacks of pain at the site of inflammation, limited joint mobility and regional muscle spasms.
In the case of periarthritis progression, partial or complete destruction of the cartilage fragment and immobilization of the limb are observed. It is difficult for the patient to move and perform even the simplest actions. In the advanced form of the disease, the fibrous tissues of the affected joints grow together, leading to a permanent disruption of the functionality of the organ.
Most often, the prognosis of ankle periarthritis is favorable and is characterized by gradual resorption of calcifications and foci of inflammation, as well as complete restoration of ankle mobility.
Diagnostic features
Treatment of joint diseases, periarthritis of the foot, in particular, begins with a complete examination of the person, including procedures such as:
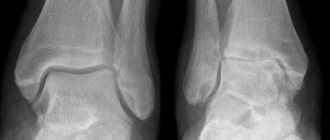
- X-ray. Thanks to it, the presence of other pathologies is excluded.
- Ultrasound (swelling of the tendons is determined).
- MRI or CT. Such research is considered the most informative. Specialists have the opportunity to examine the affected tissue layer by layer and assess their condition. Tomography allows you to determine the causes of the development of the pathological process.
- Laboratory tests of blood and urine. They detect inflammation in the body. In this case, rheumatic tests must be negative.
The specialist also records the patient’s complaints and collects his anamnesis.
Types
There are several forms of development of inflammation of the ankle joint:
Due to education
- Primary;
- Secondary.
According to duration
- Simple. The pain is mild, but slight discomfort is already felt when moving. The joint is swollen and has small seals inside, clearly visualized upon palpation of the inflamed area;
- Spicy. The pain is very severe, intensifying after physical activity. The patient tries to immobilize the leg to prevent its mobility;
- Chronic. The course is sluggish, with aching pain in the affected areas. Also added to the symptoms of the acute phase are increased body temperature, severe fatigue, weakness and progressive stiffness of the ankle joint.
Inflammation can be complicated by the following degenerative processes:
- Fasciitis - inflammation of the muscular system;
- Tendonitis - tendon lesion;
- Bursitis - inflammation of the interarticular space;
- Capsulitis - inflammation of the synovial bursa;
- Tenosynovitis - an inflammatory process in the tendon sheath;
- Enthesopathy - damage to the joints of the ligaments at the point of attachment to the bone.
Possible complications
After periarthritis occurs, it is better to begin treatment immediately, otherwise it may become chronic. She is dangerous:
- constant pain syndrome,
- acute pain that occurs with any unsuccessful movement or careless turn of the leg.
Lack of attention to the problem can lead to loss of mobility in the ankle.
Reasons for development
Periarthritis of the ankle develops due to:
- Dysfunction of the vascular system;
- Improper metabolism;
- Immunological diseases - diabetes mellitus, endocrine pathologies, etc.;
- Previous rheumatoid arthrosis, spondylosis or arthritis;
- Systematic hypothermia of joints or prolonged exposure to damp conditions;
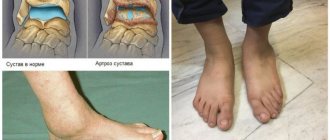
- Skeletal anomalies - flat feet, improper fusion of bone tissue after a fracture, hallux valgus, etc.;
- Excess weight putting pressure on the ankle cartilages;
- Poor circulation of the extremities;
- Lung and heart diseases;
- Microtrauma of the joint due to professional activities;
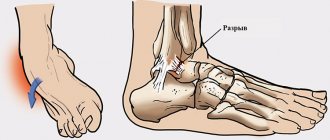
- Various mechanical injuries to the ankle - blows, bruises, dislocations, sprains, etc.;
- Complications due to previous infectious diseases.
Symptoms
The most typical sign of the disease is sharp pain at the site of the lesion. However, periarthritis does not have its own specific symptoms, which is why inflammation can be easily confused with other orthopedic pathologies.
The development of degenerative processes in the ankle is assumed in the presence of the following manifestations:
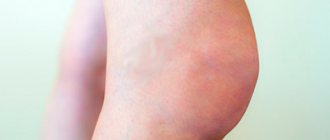
- Local swelling of the ankle or spreading to the heel and foot;
- Stiffness of movement in the joint area;
- Formation of painful knot-type lumps in the area of inflammation;
- Severe pain when walking;
- Constant muscle tension in the ankle area;
- Lameness and visible changes in gait;
- Heel spurs are bone growths that can reach a size of 2 to 12 mm.
The tightening of the heel tendon causes significant inconvenience to the patient and does not have the best effect on his quality of life.
Diagnostic methods
Identifying periarthritis of the ankle is not easy. The reason for this is that the clinical picture is similar to other joint pathologies.
In order to avoid mistakes and make an accurate diagnosis when examining an inflamed joint, a differentiated approach is used using various laboratory and instrumental methods.
Among the most informative technologies for identifying and studying periarthritis of the ankle joint are:
- Visual examination of the patient and collection of medical history;
- X-ray, which allows you to record the source of degenerative processes in the joint;
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging (CT and MRI), providing a detailed image of ligaments and tendons, places of their damage, ruptures or sprains;
- Ultrasound examination (US) of the foot, which allows to detect characteristic changes in the structure of the tendons;
- Thermography is the study of temperature values (gradients) of inflammatory tissues.
Laboratory blood parameters in periarthritis are usually normal and not changed. For maximum diagnostic effectiveness, an integrated approach is used with the appointment of several types of examinations at once.
In a situation with periarthritis, it is very important not to confuse ankle inflammation with synovitis, chronic arthritis, exostosis, arthropathy, chondromatosis of the bursa, post-traumatic deformities and myofascial pain syndrome.
Treatment with folk remedies
You can fight pathology not only with medications, but also with folk remedies. They are able to reduce the intensity of inflammation, improve metabolic processes and tissue nutrition. But before using this treatment method, you need to consult a specialist.
The following recipes will be useful:
- You will need a bucket of water and half a kilogram of hay dust. The raw materials need to be boiled over low heat for several minutes. It takes half an hour to infuse. The liquid is filtered and poured into a basin. The product is used for foot baths. You need to take them for 30 minutes. In this case, you need to ensure that the water is always warm.
- Honey. This remedy contains a huge amount of useful substances that can not only eliminate symptoms, but also restore the affected tissue. A compress is made from honey, which is fixed on the ankle overnight and tied with a warm scarf.
- Horseradish based compress. It has a warming effect. It must be used carefully so as not to burn the skin. First, the vegetable is rubbed, and then laid out on a napkin and fixed over the affected tissues. It should be kept for no more than an hour.
- Infusion using calendula or nettle. You need 1 tbsp. l. Pour a liter of boiling water over the selected crushed plant. It takes 20 minutes to infuse. Next, the liquid is filtered and used for grinding. It can also be used internally.
Folk remedies are not a panacea. They cannot always completely cope with the disease, so they are used in combination with medications prescribed by a doctor.
Therapy
Treatment of periarthritis is based on a number of therapeutic measures to ensure rapid and maximum results. To eliminate the inflammatory process in the ankle joint, they resort to:
Treatment with medications
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - Ketoprofen, Nimesulide, Ibuprofen;
- Corticosteroids (hormonal drugs);
- Analgesics in the form of tablets, creams, ointments and gels for severe joint pain;
- Vitamin complex;
- Sedatives for psychological discomfort - motherwort, St. John's wort, valerian;
- Chondroprotectors.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
In addition to medications, the patient is prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Mud applications. They can eliminate pain in the affected part of the limb and improve local immunity.
- Pharmacopuncture. This procedure involves the targeted administration of medications.
- Laser and magnetic therapy. Treatment in this way allows you to improve your defenses, reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process, stimulate blood circulation and lymph outflow. These procedures help reduce swelling.
- Electric and vibration massage. It normalizes muscle tone, therefore reducing the severity of pain.
- UVT. Here, the affected tissues are cleansed of harmful substances and lymph outflow is restored.
- Electrophoresis with medications. Thanks to the electrical effect, the medicine enters deep into the tissue and acts more effectively.
Acupuncture and acupressure are considered a good method of combating periarthritis. Thanks to these procedures, metabolism in the affected tissues is improved and limb mobility is improved.
Surgery is rarely performed, since the disease can be managed using traditional methods.
Prevention of periarthritis
To prevent inflammation, it is important:
- Monitor your body mass index;
- Choose the right shoes for everyday wear and sports;
- Use orthopedic insoles and arch supports for hallux valgus and flat feet;
- Avoid overloading the joints;
- Regularly engage in therapeutic exercises and carry out preventive massage of the top and ankles;
- Lead a healthy and active lifestyle;
- Eat rationally and balanced. The diet must include the entire complex of vitamins (especially A, B, E) and microelements that promote cell regeneration and stimulate the immune system;
- Treat diseases in a timely manner.