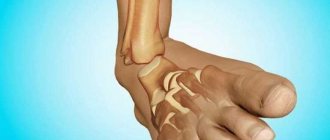
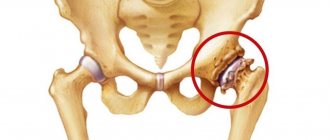
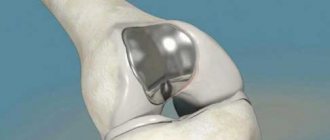
Diagnosis by X-ray.
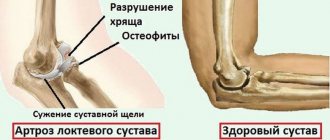
Damage to the left joint, absence of joint space. Arthrosis of the ankle joint is a chronic pathology of the cartilage of the joint, which develops gradually. At the same time, the tissues become thin and are destroyed. If treatment is not started on time, the patient’s function of the presented joint is completely impaired, which leads to disability.
Massage and manual therapy
Massage for arthrosis, like exercise therapy and therapeutic exercises, is aimed at strengthening muscles and ligaments, improving blood supply and tissue trophism. Therefore, not only the joint is worked out, but also the foot, lower leg, and thigh. The massage is performed in an upward direction, starting from the toes. It is recommended to take 3 two-week massage courses, consisting of sessions lasting 15-20 minutes, taking 2 weeks breaks between them. The patient can learn self-massage techniques and practice them at home.
Manual therapy for arthrosis is carried out using 2 techniques:
- manipulation - a sharp movement, as a result of which the deformity of the joint is eliminated;
- mobilization – smooth, gradual stretching of bones.
In case of arthrosis of the ankle joint, they resort mainly to mobilization or precede manipulation with it. As a result of mobilization, the load on the articular cartilage is reduced and its destruction is stopped. And if degenerative-dystrophic changes in the joint were associated not with metabolic disorders, but with its mechanical trauma, cartilage restoration is possible after mobilization. There is an alternative to manual mobilization - computer-assisted bone traction.
Manual therapy is not used for arthrosis in the terminal stage, its complications with arthritis, osteoporosis, or unhealed injuries. There are other contraindications to manual therapy and massage, so osteoarthritis of the ankle joint can be treated with these methods only after a detailed examination.
One of the alternative methods of treating crusoarthrosis - Shiatsu, influencing biologically active points - can be considered a type of massage or manual therapy. Unlike acupuncture, the effect is performed using the fingers of a specialist. There are many pressure points concentrated on the lower leg, foot, ankle, and heel tendon.
Development mechanism
Normally, the articular surfaces are smooth and elastic. They slide smoothly relative to each other during movements and provide effective shock absorption when loaded. As a result of mechanical damage (trauma) or metabolic disorders, cartilage loses its smoothness, becomes rough and inelastic.
Cartilage “rubs” during movements and increasingly injure each other , which leads to worsening pathological changes. Due to insufficient depreciation, excess load is transferred to the underlying bone, and degenerative-dystrophic disorders also develop in it: the bone is deformed and grows along the edges of the articular area.
Due to secondary trauma and disruption of the normal biomechanics of the joint, not only the cartilage and bone suffer, but also the surrounding tissues. The joint capsule and synovial membrane thicken, and foci of fibrous degeneration form in the ligaments and periarticular muscles.
The ability of the joint to participate in movements and withstand loads decreases. The joint becomes unstable, contractures occur, and pain progresses. In severe cases, the articular surfaces are destroyed, the supporting function of the limb is impaired, and movements become impossible.
Causes of formation and treatment of bone islands of enostosis
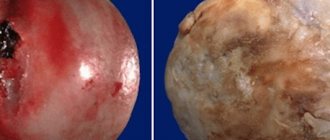
Enostosis (also called a bone island) is a tumor-like benign formation, in the form of a kind of nodule like a tumor.
Its size can reach from 2 to 20 mm, and very rarely - up to 50 mm.
This nodule is associated with the bony cortical layer, consists of lamellar tissue and has a fairly well-developed system of Haversian canals. Its development occurs in the inner part of the bone. Most often occurs in children and young people under 35 years of age.
It can be either single or fill the entire intraosseous cavity, for example, with a diagnosis of osteopoikilosis or spotted bone.
Features of the pathology
A distinctive feature of enostosis is also considered to be the presence of spicules around it - these are small peculiar “spikes” that resemble a brush-like border growing from the outer layer of the bone.
These “spikes” can consist of fibrous or lamellar bone, and there are cases of a combination of both types.
Enostosis can appear in any bone:
- often found in the spine;
- thigh bones;
- in the ilium;
- in the phalanges of the fingers.
Another name for this tumor is osteoma. It can consist of spongy bone tissue - spongy osteoma, or compact, dense bone - compact.
Some sources indicate that enostosis is also called focal osteosclerosis. This is a disease in which there is a noticeable increase in bone density due to thickening of its substance itself and bone septa and plates.
The cause of its development can be inflammatory processes of bones, intoxication, arthrosis, a number of genetically determined diseases and as a result of skeletal injuries.
Where is the true cause of the disease hidden?
The disease develops as a result of a number of diseases associated with pathologies of bone tissue: syphilis, chronic osteomyelitis, marble disease and others.
The cause of enostosis can also be a genetic predisposition in half of the cases, since it is inherited from close relatives.
It can also develop with injuries and increased mechanical stress.
Enostosis is the first symptom of disorders when a patient has all kinds of bone diseases. By the appearance of this bone nodule, you can determine the nature of the existing disease.
For example, if enostosis is limited and has no structure, with blurred contours, this is a sign of the osteoplastic form of osteogenic sarcoma; With the development of marble disease, a sharp narrowing in the bone cavity is observed or the medullary canal completely disappears.
If the spongy substance has a multifocal compaction of the structure, this indicates the development of osteopoikolia.
When examined by a specialist, not only the presence of bone islands is determined, but also, based on their appearance and structure, a conclusion is drawn about the disease that provoked its occurrence.
Difficulties of symptoms
Usually, enostosis is asymptomatic and is found by chance during X-ray, radionuclide and other types of examination. Often, the doctor prescribes the procedure without knowing about the existence of a bone tumor.
And if detected, a specialist must study the image and determine the characteristics of this bone nodule.
This will help in subsequently making the correct diagnosis and identifying the true causes of tumor formation.
When is treatment needed?
Treatment when enostosis is detected is not prescribed, since this symptom does not pose a danger. If it grows, it does so very slowly.
Enostosis is considered a benign disease and does not cause discomfort to the patient. Moreover, it does not develop on its own.
It is necessary to apply treatment for the disease that caused it.
The formation does not clinically pose a threat, it does not cause concern, pain or discomfort.
The pathology develops over a long period, so the disease it indicates may be in a progressive state.
Modern research centers continue to conduct research and further study of the disease, its clinical characteristics and developmental features.
Patients with focal enostosis are also examined to determine the causes of its occurrence.
Concept of crusarthrosis
Crusarthrosis of the ankle is a pathological phenomenon in the cartilage that occurs in a chronic form. It develops gradually, affecting tissues: over time they become thinner and destroyed. When treatment for ankle crus arthrosis is delayed, the person gradually loses important ankle functions , which significantly impacts their quality of life.
Crusarthrosis without proper treatment can lead to loss of leg function
According to the international classification of diseases, arthrosis has the code M19. Crusarthrosis is more difficult to find on this list because it is a subtype of the disease. It is in a group called “Other arthrosis.” This is where you need to look for the exact definition of crusarthrosis according to ICD 10.
When is surgery needed?
If arthrosis of the ankle joint cannot be cured using conservative methods, surgical therapy is performed:
- sanitation arthroscopy;
- arthrodesis;
- endoprosthetics.
During arthroscopy, the doctor removes the affected cartilage tissue and bone growths through small punctures. If no complications arise during the postoperative period, the disease will not bother you for a long time. With arthrodesis, the joint is completely removed, after which the bone structures of the foot and leg are fused. Endoprosthetics involves removing the joint and replacing them with an artificial implant.
How and how to treat ankle arthrosis?
The specific manifestation of arthrosis is not an obstacle to its effective elimination. The disease can be treated and adjusted with medication:
- The first degree, if detected in a timely manner, is completely curable, but this requires leading a healthy lifestyle and following preventive measures, otherwise relapses are possible;
- The second stage is characterized by several treatment outcomes - complete recovery or relief of a chronic destructive process;
- The third stage is complex, irreversible processes can lead to disability;
- The fourth is associated with adjusting the structure and motor ability of the joint using artificial substitutes.
Treatment of ankle arthrosis is a comprehensive program:
- 1st degree – analgesic therapy, preventive exercise therapy;
- 2nd degree – anti-inflammatory therapy, physiotherapy, targeted physical therapy;
- 3rd degree – medicinal, surgical therapy, restorative physical therapy;
- 4th degree – endoprosthetics, rehabilitation course of exercise therapy.
Important!
The result of treatment for ankle arthrosis directly depends on the choice of the right tactics. The prescribed therapy is aimed at relieving negative symptoms at a certain stage of the disease and eliminating the cause that provokes its progress.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy for deforming arthrosis of the ankle joint is a standard treatment regimen for arthrosis. When prescribing drugs, there is no difference in which limb is being treated (right, left). Medicines for the treatment of arthrosis are broad-spectrum drugs that simultaneously affect all joints of the patient’s musculoskeletal system, improving its general condition.
Analgesics
Treatment of grade 1 ankle arthrosis begins with taking simple painkillers. Anesthesia of the affected joint is performed with the help of Analgin, Baraglin, Revalgin, Spasmoblock, Citramon, Trinalgin, Maxigan, prescribed in the form of capsules, tablets, injections.
Analgesics and NSAIDs for osteoarthritis
NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
In the treatment of grade 2 ankle arthrosis, the simplest analgesics are unable to relieve persistent painful syndrome. This task is accomplished by NSAIDs that have antipyretic, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory effects - Brufen, Diclofenac, Dicloplus, Dolomed, Piroxicam, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, Meloxicam, Ketoprofen, Movalis. Prescribed in the form of tablets, injections, ointments, gels.
Corticosteroids (glucocorticoids)
For grade 3 ankle arthrosis, strong anti-inflammatory hormonal painkillers are prescribed. Their use is also possible for grade 2 arthrosis in situations where NSAID therapy is ineffective. Corticosteroids eliminate swelling of the periarticular tissues and help stop autoimmune processes that cause joint destruction.
Glucocorticoids Hydrocortisone, Prednisone, Prednisolone, Medopred, Prednisolone Elfa, Triamcinolone, Diprospan, Dexamethasone are prescribed in the form of intra-articular injections, tablets, ointments, gels.
The blockade practice of severe pain is widely used in the treatment of ankles - complex injections (a combination of steroid hormones with Novocaine, Ledocaine).
Chondroprotectors
At all stages of arthrosis of the ankle joint, it is important to prevent complete destruction of the cartilage lining, provide restorative support, and start the process of natural renewal of cartilage tissue. For this purpose, chondroprotectors are prescribed: Artradol, Dona, Chondrolon, Structum, Chondrograd, Mucosat, Chondroxide, Rumalon, Arteparon, Glucosamine. For arthrosis of the 1st degree - tablets, injections, 2-3 degrees - intra-articular injections. These drugs are also applicable for preventive purposes in case of high risks of developing ankle pathologies.
Synovial Fluid Protectors
Since the start of ankle arthrosis is a decrease in the production of synovium and a deterioration in its quality, at all stages of the disease it is appropriate to prescribe synovial fluid protectors Elbona, Stoparthrosis, Fermatron Plus, Ostenil, Armaviscon, Suplazin, Hymovis, Gialurom, Giruan Plus, Sinokrom in the form of intra-articular injections.
Synovial fluid protectors and vasodilators
Vasodilators
The effect of chondroprotectors, synovial fluid protectors, painkillers and hormonal prescribed medications is improved by conductor drugs Trental, Nikospan, Cynaresin, Teonicol, Cavinton, Profilaktin S. Vasodilators are taken in the form of tablets.
They help improve the nutrition of joint tissues and blood circulation, due to which it is possible to relieve pain (at night), eliminate swelling, and accelerate the regeneration of ankle tissue.
Muscle relaxants
With ankle arthrosis, cramps, atrophy of the ligaments, muscles of the foot and leg are observed. In order to restore tone to the ligamentous-muscular system, it is appropriate to prescribe the muscle relaxants Sirdalud, Mydocalm, Tizanil, Tizanidin, Miaxil, Toccata, Midostad Combi, Baklosan, No-shpa in the form of tablets. These drugs relieve muscle spasms and improve blood circulation in the extremities at the level of small vessels.
Innovative methods of anti-arthrosis therapy
The most difficult task in the treatment of ankle arthrosis is stopping the inflammatory process, which is directly a consequence of the influence of a specific cause, which is not always possible to identify. In such situations, a completely new method of treating ankle disease comes to the rescue - plasma lifting (blood plasma treatment). The so-called PRP therapy is an intra-articular injection of platelets, which are taken from the patient. The procedure is effective for grade 1 and 2 arthrosis.
If the body's immune system fails, it is difficult to start the natural processes of renewal of cartilage and bone tissue. In such cases, treatment of arthrosis with stem cells (own, donor) from bone marrow or adipose tissue is effective. The material is injected into the site of inflammation using injections or surgically.
Plasmolifting in the treatment of crusarthrosis
Physiotherapeutic treatment
An auxiliary method of treatment is physiotherapy, recommended for ankle arthrosis of stages 2-3 of the disease:
- Electrophoresis - relieves acute, prolonged aching pain (15 procedures for 20 minutes);
- Magnetic therapy - improves blood circulation by dilating blood vessels (10 procedures for 5-10 minutes);
- Ultraphonophoresis - stops the inflammatory process of soft periarticular tissues, stimulates collagen production (10 procedures for 5 minutes);
- UHF - reduces the threshold of inflammation, accelerates tissue regeneration (10 procedures for 5-8 minutes);
- Applications of coolants (peat mud, ozokerite, paraffin) – improve the metabolism of cartilage tissue, accelerate regeneration processes (15 procedures for 20 minutes);
- Cryotherapy – improves blood circulation in the ankle, nourishes it with useful substances, eliminates swelling (10 procedures, 3 minutes each);
- Laser therapy - improves metabolic processes that promote regeneration of ankle tissue (10 procedures for 20 minutes).
Physiotherapy
Exercise therapy is an auxiliary method of treatment, useful for arthrosis of the ankle joint in that it improves blood circulation in the foot and lower leg, strengthens the muscles, which helps restore the full functions of the limb.
Therapeutic exercise is advisable at all stages of ankle disease, for each of which the optimal set of individual exercises is selected.
The basic program consists of simple exercises:
- Grasping objects with your toes;
- Movement of the foot up and down, in the direction and counterclockwise;
- Rolling the foot from heel to toe and back;
- Holding stand with support – lifting the feet onto the toes.
Massage
During periods of remission and relief of the inflammatory process, massage of the ankle joint along an ascending guide (foot, lower leg, thigh) is allowed. The procedure improves the condition of the ligamentous-muscular system of the ankle joint.
Massage and joint traction
Joint traction
In the treatment of arthrosis of the extremities, manual and hardware traction of the joints is practiced, preventing surgical intervention. Manual traction is performed by a doctor using physical effort, while hardware traction is performed through the use of special training devices. Due to these procedures, it is possible to widen the interarticular space, improve blood circulation, and ensure the flow of nutrients into the joint cavity. Traction is performed at the initial stage of the disease or during remission, when the inflammatory process is stopped.
Anti-arthrosis devices
At the initial stage of ankle disease, it is recommended to use special devices:
- Orthopedic (shoes, insoles, half-insoles, correctors for the foot, fingers) – reduce pain syndrome, prevent further deformation of the foot;
- Corrective (fixing bandages, orthoses) – correct the internal and external displacement of the ankle joint, improve the mobility of the joint in accordance with the anatomical properties of functioning.
Kinesio taping
Taping the ankle for grade 1-2 arthrosis reduces the pain threshold and corrects the position of the ankle joint. Plastic adhesive tapes act as a temporary bandage, take on the main load when moving the limb and resting the foot, and create favorable conditions for the restoration of the ligamentous-muscular apparatus of the leg.
Nutrition correction
Throughout the treatment of ankle arthrosis, you need to follow a low-calorie diet (table No. 8). Restrictions apply to salt, quickly digestible carbohydrates, animal fats, semi-finished products, fried, smoked, and canned foods. Products high in B vitamins are recommended.
Dietary nutrition for illness
Small balanced meals (5-6 times a day), drinking plenty of fluids help improve metabolism and reduce body weight.
Surgical intervention
Surgery on the ankle joint is performed when the joint is temporarily and completely immobilized. In medical practice, three surgical methods are used to treat ankle arthrosis:
- Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that allows you to remove damaged areas of cartilage tissue from the internal cavity of the joint (applicable at stage 2 of the disease);
- Arthrodesis of the joint – removal of remnants of cartilage, fixation of the joint in accordance with the anatomical features. After fusion of the bones (ankylosis), movement of the joint is impossible. This operation is performed when endoprosthesis replacement is contraindicated, which eliminates inflammatory processes;
- Endoprosthetics is the replacement of a joint with an implant, returning the limb to full functions.
Traditional treatment method
With 1st and early 2nd degree ankle arthrosis, pain can be relieved and ankle inflammation can be curbed with the help of:
- Potato compress (grate 1 potato on a fine grater, apply the paste to the joint area, secure the ankle with a bandage, leave for half an hour, rinse with warm water, do 1-2 times a day);
- Comfrey-based ointment (mix ½ cup of melted beeswax, 1 cup of crushed comfrey leaves, ½ cup of sunflower oil, simmer over low heat, cool, add 1 capsule of vitamin E, apply a thin layer to the area of the sore joint 2 times a day).
By localization, phase, stage
Taking into account the location of the disease, a diagnosis of arthrosis of the right or arthrosis of the left ankle joint is made. Unilateral localization is typical for static, dysplastic, post-traumatic osteoarthritis of the ankle joint. Idiopathic is often bilateral. Arthrosis of the joints is a chronic disease that occurs with periodic exacerbations. Therefore, acute arthrosis of the ankle is not a separate form of the disease, which is opposed to chronic arthrosis. Depending on the severity of clinical symptoms, acute and subacute periods of the disease are distinguished. It is an acute illness that is meant when they talk about acute arthrosis of the ankle.
loading…
This classification is important for developing a treatment regimen. In the acute period of ankle arthrosis, treatment is primarily aimed at relieving pain through NSAIDs. It is necessary to use orthopedic devices or an elastic bandage to fix the ankle. In the subacute period, more attention is paid to joint restoration with the help of chondroprotectors, hyaluronic acid preparations, and drugs to improve blood circulation. Physiotherapeutic procedures, exercise therapy, massage and manual therapy are required to mobilize the joint and restore range of motion.
With arthrosis of the ankle joint, the symptoms increase gradually; based on the combination of clinical and radiological signs, 3 degrees (stages) of the disease are distinguished:
- 1 – destruction of cartilage, the onset of pathological processes in bone tissue, occurs without pronounced clinical changes;
- 2 – bone deformations become more pronounced, the disease is accompanied by pain;
- 3 – pronounced clinical manifestations, distinct deformities, limited mobility up to complete immobility (ankylosis). Disability due to arthrosis, as a rule, is assigned precisely at this stage.
Symptoms of ankle arthrosis
At first, fatigue and mild pain occur after significant exertion. Subsequently, the pain syndrome becomes more intense. Pain appears not only after exercise, but also at night.
A visible deformation gradually forms, the range of movements in the joint decreases, and a crunching sound is heard during movements. In the later stages, movements are sharply limited, support becomes difficult, and patients are forced to use crutches or a cane when moving.
Distinctive features of pain and other symptoms in arthrosis:
- Characteristic are initial pains that arise after a state of rest, and then gradually disappear with movement.
- There is increased pain with exertion and rapid fatigue of the joint.
- When moving, crunching, squeaking or clicking noises may occur.
- Night pain usually appears in the morning.
- During an exacerbation, the joint area may be swollen and red.
- Due to instability of the joint, the patient often twists his leg, causing sprains and tears in the ligaments.
- Stiffness and limitation of movements are noted.
- In the later stages, severe deformation of the joint is revealed; the lower leg sometimes bends and takes on an X- or O-shape.
Traumatic injury
Against the background of injuries of varying severity, pathological biochemical degenerative-dystrophic processes begin to occur in the tissues that form the joint, leading to the gradual destruction of cartilage tissue and other elements of the joint. Injuries that often cause the development of arthrosis include:
- sprains and ligament tears;
- intra-articular fractures;
- dislocations;
- cartilage damage;
- subluxations.
In addition, previous surgical interventions on the ankle joint can create conditions for the further development of arthrosis. Even microtraumas of the joint, which are not accompanied by severe symptoms, can cause the appearance of this pathology after 5–15 years.
Causes of foot disease
The main provoking factors for the development of crusarthrosis include:
- Autoimmune, infectious, metabolic, endocrine, genetic diseases;
- Limb injuries (dislocations, fractures, stretch marks);
- Flat feet (congenital, acquired);
- Excess weight, which increases the load on the legs;
- Natural wear of connections;
- Involvement in bad habits (smoking, alcohol, unhealthy diet);
- Arthritis of the extremities;
- Poor blood supply to the extremities;
- Unregulated physical activity.
Non-drug treatment
The doctor determines how to treat arthrosis of the ankle joint, taking into account its stage and the presence of acute manifestations. Most non-drug therapy methods are used outside of an exacerbation, after acute pain and inflammation have been relieved. These include:
- physiotherapy;
- exercise therapy;
- massage and self-massage;
- manual therapy;
- spa treatment, including balneotherapy (baths, healing mud);
- alternative methods - acupuncture, hirudotherapy.
In the acute period, orthopedic treatment of deforming arthrosis of the ankle joint is necessary. To redistribute the load on the joint and prevent subluxation, it is fixed using an elastic bandage and a semi-rigid orthosis. An orthosis must be worn when a hallux valgus or varus deformity of the foot develops. All patients with ankle arthrosis are advised to wear orthopedic shoes or insoles.
Physiotherapeutic procedures include electrophoresis with medications, laser, and magnetic therapy. Outside of exacerbation, thermal procedures are prescribed: wraps, applications, baths with paraffin, ozokerite, mud. Compresses with medical bile, bischofite and dimexide give a good effect.
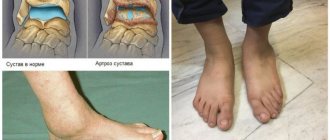
How to tell if you have crusarthrosis
Orthopedists accurately identify this disease by destructive processes in the cartilage and the presence of osteophytes on X-ray images. You may suspect something is wrong if you notice the following symptoms:
- pain during dynamic loads;
- increased pain after exercise;
- discomfort due to mechanical pressure on the joint;
- swelling and redness;
- burning under the skin.
You can find out in your youth whether you are at risk of cruzarthrosis in old age. If your foot falls inward, it’s hard for you to stand on tiptoes, the degree of flexion is reduced, and you hear a crunching sound when you rotate your foot, don’t delay your visit to an orthopedist.
With crusarthrosis, the pain disappears after prolonged rest.
There are a lot of joint diseases. Some of them are curable. Others, such as osteoarthritis, are treated long-term with synovial fluid grafts. In the case of hydrarthrosis, a completely different treatment is required. Therefore, you should never experiment and risk your own health: ask an orthopedist for advice!
Pharmacy drugs
Drug treatment allows you to quickly eliminate the existing acute manifestations of the disease and improve joint mobility. When treating arthrosis of the ankle joint, ointments, creams, and tablets are most often used, but intra-articular injections may also be required.
Since it is necessary to relieve swelling and inflammation first of all, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to eliminate pain. Such medications include:
- Movalis.
- Ibuprofen.
- Diclofenac.
- Nimesulide, etc.
In addition, in cases of severe pain, antispasmodics and analgesics are often prescribed. Local remedies used to eliminate discomfort and improve nutrition of joint tissues include:
- Capsicam.
- Finalgon.
- Diclak gel.
- Apizartron.
- Viprosal.
- Espol.
- Efkamon.
To improve the condition of the joint, Glucosamine injections are often prescribed. In severe cases of the disease, glucocorticoid injections may be indicated. In the presence of severe spasm of smooth muscles, muscle relaxants are prescribed in short courses, including Baclofen, Tizanidine.
To improve local blood circulation, vasodilators and angioprotectors are often introduced into the treatment regimen. Additionally, chondroprotectors and multivitamins may be prescribed.
Preventive actions
Prevention of ankle arthrosis consists of following a healthy lifestyle:
- Avoiding excessive physical stress on the legs;
- Maintaining a balanced diet;
- Daily physical activity in the fresh air;
- Treatment of endocrine diseases, diseases of the circulatory system;
- Wear comfortable shoes made from natural elements;
- Quitting bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- Avoiding limb injuries.
Arthrosis is a slowly progressive disease, the treatment of which cannot be postponed until tomorrow. The earlier therapy is started, the greater the chance of maintaining limb health.
Physiotherapy
To alleviate the existing symptoms of arthrosis, the patient requires special physical exercise. A set of exercises must be specially selected by a physical therapy instructor, taking into account existing damage to the structures of the joint and adjacent ligaments and muscles. There are a number of simple and effective exercises that can restore mobility to the affected joint.
An exercise that involves rising on tiptoes and returning to the starting position helps a lot. If the patient has too much pain, this exercise can be performed in a lying position. In 1 approach, it is enough to perform this movement 25 times.
To strengthen the muscles and ligaments surrounding the ankle joint, walking on your toes helps. It is advisable to allocate 15 minutes every 2 hours to perform this exercise. If you experience severe pain during the exercise, you should reduce the time you walk on your toes to 5–10 minutes.
To develop mobility of the damaged joint, it is recommended to rotate the foot clockwise and counterclockwise. This exercise should be performed slowly, avoiding the appearance of strong crunching and pain in the joint. It is advisable to perform this exercise for 15 minutes every 2-3 hours.
Another effective exercise for developing the ankle joint is the weighted foot lift. First you need to take a sitting position and place one foot on top of the other. In this case, the lower joint bears the load of 2 joints at once. After this, the foot is lifted off the floor with the heel to the maximum possible distance, while the toe should be in contact with the floor. This exercise should be performed as slowly as possible. For 1 approach you need to do 10 repetitions on each leg.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/oImpcB4du7c
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/oImpcB4du7c
Other exercises may be recommended to safely strengthen the ligaments and muscles and restore mobility to the joint.
Ankle exercises
1. I.p. - standing, arms down along the body, legs together. Walk in place for 2-3 minutes at a moderate pace.
2. I.p. - sitting, hands on hips, legs straight, together. Pull your socks towards you. Keep them in this position for up to 1 minute.
3. I. p. - sitting, emphasis - on your arms placed back (you can rest on your elbows), legs straight, together. Raising your left leg, make several circular movements in the ankle joint clockwise, then counterclockwise. Return to i.p. Repeat the exercise with your right leg.
4. I.p. - standing, hands on hips, feet shoulder-width apart. Simultaneously bending your legs at the ankle joints, stand either on the outer or inner edges of your feet. Change position 8-10 times.
5. I.p. - standing, arms down along the body, legs shoulder-width apart. Rise on your toes, return to standing position. Perform the exercise 10-12 times.
6. I.p. - standing, arms down along the body, legs together. Remaining standing on your right leg, take your left leg back, grab your foot with your left hand and pull your foot up. Return to i.p. Then, remaining standing on your left leg, perform the exercise with your right leg.
7. I.p. - standing, arms down along the body, legs together. Rock from heel to toe. Perform 15-20 of these swings.
8. Finish the set of exercises by walking in place at a moderate pace.
Symptoms
The severity of clinical manifestations of deforming arthrosis of the ankle joint depends on the neglect of pathological processes occurring in the tissues of the joint. In the first degree, the disease does not manifest itself with significant symptoms. In this case, the patient experiences severe stiffness in the joint in the morning. Aches and discomfort occur periodically.
Already in the early stages of development of the pathological process, swelling in the foot area may be observed. Periodically, the patient experiences pain in the joint when trying to lean on the leg, sudden movements, or prolonged periods without physical activity. Later, as the disease progresses, the following symptoms of arthrosis appear:
- pain in the lower leg after physical activity;
- ankle muscle cramps;
- swelling of the surrounding soft tissues
- skin redness;
- clicks and crunching sounds when moving;
- aches and pain at night;
- gait changes;
- increasing impairment of joint mobility.
Supporting the leg becomes impossible due to the constantly present pain syndrome. When the inflammatory process activates, the skin in the area of the affected joint becomes hot.
What is hydrarthrosis
Sometimes excess synovial fluid accumulates in the joint, causing its volume to increase. People call this pathology “ articular dropsy ,” but its official name is hydrarthrosis. The disease develops more often in the knee, less often in several joints at the same time. Not very often it affects the elbows, wrist, ankle and hip joints.
Like gonarthrosis, as well as other chronic diseases, hydrarthrosis occurs with periods of exacerbation and remission. Progresses in winter and spring - against the background of decreased immunity, stress, overwork and exposure to viruses.
Middle-aged women are more likely to develop hydrarthrosis