This article will discuss how to treat heel spurs at home. This is a rather unpleasant disease, accompanied by pain when walking. According to medical statistics, every tenth person experiences heel spurs. The disease progresses rapidly and constantly. Ligaments, tendons and muscles become inflamed. All this causes unbearable pain. At home, you can use FitoHeel phytocream for heel spurs. It has proven its effectiveness in numerous clinical trials. Positive reviews confirm high performance. Orthopedic doctors also talk about the unique effect of Phyto Heal balm.
general information
The spur develops against the background of chronic inflammation of the plantar (plantar) fascia. This is a thin but very strong piece of connective tissue that connects the toes and heel bone. It is responsible for the formation of the arch of the foot and experiences significant stress during walking.
These loads often cause microdamage to the tissue, which heals on its own during the night's rest. If this process does not happen quickly enough, the trauma is repeated in the morning. When a person gets out of bed, he feels pain of varying intensity. Regular damage to the fascia inevitably leads to the development of an inflammatory process, which gradually increases.
Inflammation begins to involve nearby tissues, in particular bone and tendons. On the surface of the bone tissue, the deposition of calcium salts and the growth of a process (osteophyte), which is called a heel spur, begins. It further damages the fascia, and the pathological circle closes. Without the help of a doctor, walking becomes unbearably painful.
A spur can form on only one heel, or it can affect both feet. It all depends on the individual predisposition of the person.
Make an appointment
Causes
A heel spur, as well as the plantar fasciitis that causes it, is a multifactorial disease. Its occurrence is due to the complex influence of several reasons:
- old age (the risk of the disease increases after 45-50 years of age due to changes in metabolism and decreased blood supply to the lower extremities);
- obesity (excess body weight causes excessive load on the fascia);
- flat feet, incorrect gait (the load on the foot is distributed unevenly, which leads to increased trauma to its individual areas);
- wearing shoes that are incorrect from an orthopedic point of view (excessively tight, high heels, etc.);
- curvature of the spine (scoliosis) and some other diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- pregnancy (shift in the center of gravity, changes in hormonal levels and metabolism);
- features of the profession due to which a person is on his feet for a long time (salespeople, waiters, promoters, many blue-collar professions) or is often forced to carry heavy loads;
- professional sports;
- hereditary predisposition;
- metabolic disorders associated with increased deposition of salts in tissues (in particular, gout);
- vascular diseases, in particular, atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, obliterating endarteritis (increase the risk of developing spurs due to impaired blood supply to tissues and deterioration of regeneration processes);
- injuries of the spine, lower extremities;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the bones and joints of the legs (arthrosis, rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis, etc.), as well as the use of hormonal agents for their treatment.
Physiotherapy
There are several physiotherapeutic methods of treatment, but medications are used only for one of them (phonophoresis), the rest are listed below:
- treatment with high and low frequency current;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser exposure;
- shock wave treatment.
Phonophoresis using medications
This technique involves using ultrasound to introduce medications into soft tissue. During phonophoresis, medications that relieve inflammation are used (mainly Hydrocortisone ointment). Ultrasound waves have a beneficial effect on the damaged heel area, and the procedure itself is somewhat similar to injections of NSAID drugs into soft tissues.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a heel spur depend not on the cause of the disease, but on the location and size of the bone growth, as well as the degree of neglect of the process.
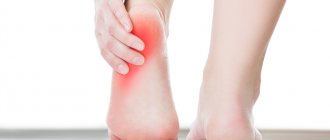
The first sign of trouble is pain. At the initial stage of development of the disease, it is felt at the level of mild discomfort and only in the morning hours. Many people report a feeling of a nail in the heel while walking, which soon disappears.
As the disease progresses, pain begins to appear after prolonged use of the legs and gradually intensifies. The intensity of sensations depends not so much on the size of the process, but on its location. The closer the osteophyte is to the nerve endings, the more painful the leg is. An acute attack can be provoked by sudden support on the heel (when getting up from a chair or bed) or climbing stairs. In rare cases, the disease is practically asymptomatic, but inflammation is still present, and a bone spike is detected during examination.
If acute inflammation of the plantar fascia joins the process, patients note:
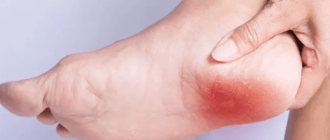
- constant tingling and feeling of heat in the heel area;
- redness of the skin in the affected area;
- roughening of the skin of the feet;
- increased pain when walking.
Over time, the pain syndrome becomes habitual, and the person’s gait changes. He begins to place his foot so as not to touch the affected area and rests mainly on the toe and side of the foot. This often causes the development of transverse flatfoot, which further aggravates the course of the disease.
In severe cases, the ability to walk independently is completely lost due to unbearable pain when supporting the leg.
Characteristics of the disease
Plantar fasciitis is a fairly common pathological process, the peak of activity of which has occurred in the last 10 years. Most often, heel spurs are observed in women over 40 years of age.
However, cases of plantar fasciitis also occur in younger people. Removing a heel spur does not cause difficulties for specialists if the disease is in its initial stage.
Diagnostics
An orthopedic surgeon diagnoses and treats heel spurs. The main way to identify pathology and assess the degree of its development is radiography. The image clearly shows the bone growth, its shape, location and size.
Additional examination techniques include:
- general and biochemical blood test to identify the inflammatory process, assess the level of uric acid (important for diagnosing gout) and some other indicators;
- Analysis of urine;
- Ultrasound of the foot to assess the condition of soft tissues and identify a possible abscess;
- duplex examination of the vessels of the lower extremities (detects possible circulatory disorders);
- MRI of the foot to determine the condition of all anatomical structures of the foot, including nerve fibers.
If there are concomitant diseases, appropriate laboratory and instrumental studies and consultations with specialists are prescribed.
It is important to remember that heel pain does not necessarily indicate the development of a heel spur. Similar symptoms can be caused by:
- gout;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- osteomyelitis (inflammation of bone tissue);
- Bekhterev's disease;
- bone tuberculosis;
- injuries, etc.
You should not self-medicate or take painkillers uncontrollably. Only a doctor can choose the appropriate regimen.
Heel spur treatment
Treatment for heel spurs largely depends on its causes and symptoms and is prescribed on an individual basis. Doctors use several techniques:
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapy - shock wave exposure; laser treatment;
- X-ray therapy;
- massage;
- physical therapy and gymnastics;
The patient is required to adjust their lifestyle and diet, as well as wear orthopedic shoes.
Drug treatment
Medicines used in the treatment of heel spurs are aimed at relieving inflammation and pain. Most in demand:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): products based on indomethacin, diclofenac, ibuprofen in the form of tablets, injections and local products (creams, ointments, pain-relieving patches);
- long-acting corticosteroid drugs (diprospan and its analogues) are injected directly into the fascia to stop the inflammatory process;
- antibiotics in the presence of purulent inflammation or in the infectious nature of the disease.
If there are concomitant diseases, drugs are prescribed to treat them, for example, drugs to normalize blood flow, anti-gout drugs, etc. Only a doctor is responsible for selecting specific medications, their dosage and regimen.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is aimed at improving blood supply and tissue regeneration, as well as enhancing the effect of medications. For this we use:
- electrophoresis: introduction of drugs into tissue using electric current;
- sonophoresis: treatment of tissues with ultrasonic waves that improve the penetration of drugs;
- ultrasound therapy: heating tissues and reducing inflammatory reactions using ultrasonic waves;
- mud and mineral baths.
Shock wave therapy
Shock wave therapy is one of the most effective methods for treating heel spurs in the early stages of development. The technique is based on the influence of ultrasonic waves of a certain frequency, which promotes:
- destruction of calcium deposits;
- reducing inflammation and swelling;
- activation of tissue regeneration.
If the size of the heel spur is small, the technique allows you to get rid of it completely, and in advanced cases it slows down or stops its growth.
Laser exposure
Warming up the deep layers of tissue with a laser helps improve blood flow in them. As a result, the quality of supply of oxygen and nutrients to cells improves, metabolic processes and restoration of affected tissues are activated.
X-ray therapy
This method of treating heel spurs is only suitable for people under 40 years of age and is used extremely rarely if other methods do not work. The affected area is exposed to x-rays in a certain dosage. As a result, persistent pain relief and improvement in condition are achieved.
Surgery
All previous techniques are aimed at relieving pain and inflammation, as well as improving the patient’s condition. A correctly selected set of techniques helps to slow down the process of spur growth or even stop it completely, but it does not allow you to get rid of it completely. The exception is shock wave therapy, but it destroys only very small growths.
The only way to get rid of a large heel spur is through surgery. When choosing the classic version of the operation, the surgeon cuts the fascia completely and immediately removes the bony protrusion. With complete tissue transection, the patient's foot anatomy and gait change significantly, which becomes the reason for assigning a disability group.
A more modern and gentle technique is radiofrequency microtenotomy. The essence of the operation is to eliminate damaged tissue using radio frequency waves.
On the Internet and popular literature you can find a large number of home methods for treating heel spurs using herbs and homemade compresses. Using them without prior approval from a doctor is strictly prohibited. At best, the patient’s condition will remain unchanged, at worst, complications will arise, for example, burns.
Make an appointment
Conservative therapy
As a rule, conservative treatment methods are effective, but much depends on the size of the spur itself. Sometimes surgery is necessary, but this is rare. Moreover, no operation is comparable to conservative therapy, since it will not eliminate the reasons for the formation of spurs.
This treatment consists of:
- wearing orthopedic insoles;
- physical exercises, massage;
- diet (it is necessary to stabilize the patient’s weight and remove salts from the body); prescribed by a doctor on an individual basis;
- mud procedures;
- physiotherapy (more about it in the next paragraph), aimed at eliminating inflammatory processes and acute pain.
It is worth noting that during conservative treatment, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, which are described above, are taken in parallel.
Gymnastics for heel spurs
Physical therapy exercises are one of the important factors in the treatment of heel spurs. It helps improve blood circulation in the affected area, which means it stimulates tissue restoration, subject to regular exercise. The minimum complex includes the following exercises:
- squats: the patient bends one leg and puts it forward, takes the other back, feet are on the same line, palms rest on the wall; from this position, squats are performed without lifting the heel off the floor;
- rolling an object: in a sitting position, the patient rolls a small ball or water bottle with his foot for 5 minutes;
- “step”: feet are placed on a threshold, step or stack of books so that the heels hang in the air, bends forward with support on a chair to stretch the muscles of the ankle joint; in the maximum tilt position, you need to freeze for 5-20 seconds, and then return to the starting position;
- collecting objects: using your toes, you need to lift small objects from the floor: peas, beads, beans, etc.; Ideally, the exercise is performed standing, but a sitting position is also allowed;
- stretching: the patient sits on a chair, places the foot of one leg on the knee of the other and with his hands pulls the toes toward himself, while simultaneously turning the foot outward; the exercise stretches the heel fascia well;
- cool-down: the final exercise is performed using a jump rope, a rubber expander, a towel, the patient stretches his legs forward in a sitting position, passes the band under the feet and pulls them towards himself.
The ideal time to practice is in the morning, when the feet are not yet overloaded.
Removing a spur using an endoscope
Endoscopic fasciotomy was first performed in 1991 and has since been considered the preferred method for removing heel fasciitis.
Endoscopic surgeries usually do not require large incisions. The insertion of surgical instruments to remove a spur is carried out using an endoscope - a long and flexible hollow tube equipped with special optics. To insert the endoscope into the operated area, it is enough to make two or three punctures less than a centimeter long.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia, with the installation of a compressive tourniquet under the lower leg. An incision 5 millimeters long is made on the medial surface of the heel region - it is located approximately a centimeter distal to the area of attachment of the aponeurosis.
The endoscopic trocar and cannula are inserted superficially in relation to the location of the spur, to the opposite edge of the heel area - there is an exit hole. Next, the surgeon removes the cannula and inserts an endoscopic camera into the medial opening and a retrograde cutting scalpel into the lateral portal. A dissection is made with a scalpel. The entire process is carried out under the control of the endoscope camera – it displays on the device’s monitor a picture of what is happening in the surgical field.
Massage
Massage is another way to improve blood circulation in the feet with heel spurs. The simplest complex can be done independently. The feet are first warmed up by intense rubbing, after which the active effect begins:
- small pinches with gradual movement from the tips of the fingers to the heel;
- rubbing the heel: performed with the pads of the fingers with force in different directions;
- circular rubbing: first the outer radius of the heel is grabbed, then the circles are concentrated on the spike area;
- kneading: the spur area is intensively kneaded with the thumbs;
- light tapping with the edge of the palm.
The exposure cycle is repeated 2-3 times and ends with rubbing and stroking. At the end, if necessary, an anesthetic ointment is used.
It is important to remember that the massage should not be overly painful, but slight pain is a sign that the exercises are being performed correctly. For additional stimulation of the affected area, you can use a massage mitt.
In addition to classic manual massage, the use of special relief mats and electric massagers is allowed.
Diet
Nutrition for heel spurs has several goals:
- reduce body weight and prevent its increase;
- minimize inflammatory processes;
- remove excess salts from the body.
Doctors recommend adhering to the following rules:
- control the daily caloric intake of food, prevent overeating;
- in the absence of contraindications, drink at least 2-3 liters of clean water daily (tea, coffee, juices and other drinks do not count);
- balance the menu in terms of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, provide a sufficient amount of vitamins;
- do fasting days regularly;
- minimize the consumption of spicy, hot, smoked, salty foods, sauces, canned food, as well as products containing artificial flavors;
- exclude strong broths, mushrooms, offal, coffee, alcohol from the diet;
- reduce the amount of salt;
Prevention
The development of heel spurs can be prevented and significantly slowed down by lifestyle changes. To avoid problems associated with inflammation of the plantar fascia, you must:
- wear comfortable shoes with small, comfortable heels (recommended height 2-4 cm);
- use orthopedic insoles with arch support;
- maintain body weight at a normal level, prevent obesity;
- provide a complete, balanced diet, drink enough clean water;
- engage in recreational sports that bring pleasure;
- minimize overload of the feet (long walking or standing);
- periodically massage the feet (the exercises are similar to the therapeutic effect);
- promptly and fully treat postural disorders and flat feet.
At the first sign of pain in the heel area, you should consult a doctor for examination. Many physiotherapeutic techniques are effective at an early stage and allow you to completely get rid of the spur before it makes life unbearable.
How is the classic operation performed?
The open type of intervention is today considered the most traumatic, outdated and inappropriate. It is prescribed quite rarely.
Classic open surgery can be performed in any surgical department - a clinic, hospital or specialized medical institution. In any case, it is carried out only in a hospital setting.
Open surgery is possible only with the use of local anesthesia, and in some cases general anesthesia. In the process, the surgeon makes a skin incision in the area of the Achilles tendon or heel bone, through which the tumor is removed. Postoperative rehabilitation can take up to 2-4 months.
Consequences and complications
When a heel spur develops, the patient must rest on the toes or side of the foot. This can lead to complications:
- swelling and pain in the ankle joint;
- arthritis and arthrosis of the big toe joint;
- development or worsening of flat feet;
- pronounced violations of posture.
Without treatment, the heel spur grows so large that it completely deprives the patient of the ability to put weight on his foot. The quality of life deteriorates significantly.
Minimally invasive technique with X-ray control
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
To perform a minimally invasive operation, you only need one incision up to 3 millimeters long. A triangular sharpened scalpel is inserted through the hole - it cuts off the fascia at the point of attachment to the heel bone. The spur itself is removed with a cutter, which is inserted into the same puncture.
The process causes virtually no injury to the person being operated on - after 2-3 days he can get back on his feet. In addition, there is no need to apply a cast during rehabilitation.
X-ray equipment in this case is used to monitor the operation - it performs a role similar to an endoscope camera in endoscopic surgery.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
If you are worried about pain or discomfort in your heel, come for an appointment at the Health Energy clinic. An experienced orthopedic doctor will listen and examine you, and also prescribe the necessary examinations. After making a diagnosis, we will offer modern methods of treating pathology:
- blockades for quick pain relief;
- all types of physiotherapy;
- professional therapeutic massage;
- training in physical therapy exercises and exercises under the supervision of a trainer.
Additionally, we will prescribe drug treatment in accordance with modern standards, and also monitor the effect of therapy.
Advantages of the clinic
“Health Energy” is a modern multidisciplinary medical center that offers its patients comprehensive services for the treatment and prevention of diseases. Here are the benefits of contacting us:
- review and expansion of early disease detection programs;
- modern diagnostic equipment;
- qualified medical staff who regularly improve their skills;
- an integrated approach to diagnosis and treatment.
We do everything to provide each patient with maximum comfort from the first minutes of their stay in the clinic. Adequate prices make quality medicine accessible.
A heel spur is just a small bony growth that can, however, completely change a person's life. Don’t delay in seeing a doctor, make an appointment with an Energy of Health orthopedist.