A heel spur injection (called a blockade) is an effective way to treat inflammation of the heel fascia by injecting a drug based on artificial hormones directly into the heel spur.
The peculiarity of this method is that the active substance is injected into the affected fascia and begins to act instantly. Steroid injections have many contraindications; only a doctor can prescribe and administer them.
Attention: this article is for informational purposes only. Self-treatment of heel spurs with steroid injections is strictly prohibited!
What types of blockades are there?
Local
The doctor gives an injection exactly in the area where there is damage. The drug can be administered near or under it, hoping to get into the area of the inflammatory focus. When an injection is administered into the periarticular tissues, the blockade is called periarticular, and into the nerve trunks - perineural.
Segmental
The segmental method involves injecting an anesthetic into a specific spinal segment. This means that the medicine must enter the projection zone of this segment, corresponding to a specific nerve, vertebra or muscle.
Vertebral
The term "vertebral" means "vertebral, which refers to a vertebra" and is derived from the Latin vertebra - vertebra. The specialist inserts the needle subcutaneously into the space between the spinous processes of the vertebra (insertion depth - 2-4 cm) or into the vertebral body (depth - 8-10 cm).
Blockage in the spine for pain
A blockade in the spine for pain is carried out when nerve roots are pinched due to osteochondrosis, herniated intervertebral discs, neuralgia, spondyloarthrosis. Pain relief is achieved by temporarily “switching off” nerve conduction in a particular area. The introduction of anesthetics blocks the transmission of signals along the nerve fibers, and the pain recedes almost instantly. There is also a decrease in vascular spasm, swelling goes away, tissue self-healing processes are accelerated, and intracellular metabolism is normalized.
Diagnostics
An orthopedic surgeon diagnoses and treats heel spurs. The main way to identify pathology and assess the degree of its development is radiography. The image clearly shows the bone growth, its shape, location and size.
Additional examination techniques include:
- general and biochemical blood test to identify the inflammatory process, assess the level of uric acid (important for diagnosing gout) and some other indicators;
- Analysis of urine;
- Ultrasound of the foot to assess the condition of soft tissues and identify a possible abscess;
- duplex examination of the vessels of the lower extremities (detects possible circulatory disorders);
- MRI of the foot to determine the condition of all anatomical structures of the foot, including nerve fibers.
If there are concomitant diseases, appropriate laboratory and instrumental studies and consultations with specialists are prescribed.
It is important to remember that heel pain does not necessarily indicate the development of a heel spur. Similar symptoms can be caused by:
- gout;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- osteomyelitis (inflammation of bone tissue);
- Bekhterev's disease;
- bone tuberculosis;
- injuries, etc.
You should not self-medicate or take painkillers uncontrollably. Only a doctor can choose the appropriate regimen.
When are blockades used?
Heel spurs
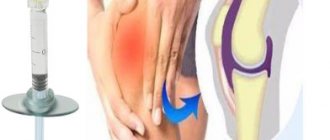
Blockades in traumatology and orthopedics are most often performed for heel spurs, using corticosteroid hormones. The maximum effect is provided by drugs such as Diprospan, Kenalog and Hydrocortisone.
Joints
The main indications for pain-relieving “blocking” of joints are exacerbations of arthritis and arthrosis. An anesthetic injection is given into the joint capsule, or less often into the muscle, after which relief quickly occurs.
Nerves
The medicine is injected directly into the area where the nerve trunk passes to quickly relieve inflammation and spasms. This type of pain relief is often the optimal solution for tunnel syndromes, neuralgia, neuritis, and oncological tumors.
When is an injection against a heel spur contraindicated?
Even with the most unbearable pain, spur blockade is contraindicated in the presence of the following pathologies:
- tuberculosis, bronchitis and other infections;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- endocrine disorders;
- calcium absorption disorders;
- skin diseases of the feet;
- obesity, etc.
Also contraindicated in women are taking COCs, pregnancy, and gynecological diseases. In each specific case, the decision on how to treat a heel spur is made by the doctor.
How does a spinal block block work?
First, the doctor examines the patient and, based on the examination and examination data, selects the optimal method. Then the injection site is disinfected, and local anesthesia is performed if necessary. Once the anesthesia has taken effect, the medicine itself is administered. Since the disease can affect any part, the injection is given in the lumbar region, shoulder blades or neck, that is, in the place where the pain is localized. At the end of the procedure, the injection site is once again treated with an antiseptic, and a sterile bandage is applied. To consolidate the effect, the patient remains lying on the couch for at least an hour.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a heel spur depend not on the cause of the disease, but on the location and size of the bone growth, as well as the degree of neglect of the process.
The first sign of trouble is pain. At the initial stage of development of the disease, it is felt at the level of mild discomfort and only in the morning hours. Many people report a feeling of a nail in the heel while walking, which soon disappears.
As the disease progresses, pain begins to appear after prolonged use of the legs and gradually intensifies. The intensity of sensations depends not so much on the size of the process, but on its location. The closer the osteophyte is to the nerve endings, the more painful the leg is. An acute attack can be provoked by sudden support on the heel (when getting up from a chair or bed) or climbing stairs. In rare cases, the disease is practically asymptomatic, but inflammation is still present, and a bone spike is detected during examination.
If acute inflammation of the plantar fascia joins the process, patients note:
- constant tingling and feeling of heat in the heel area;
- redness of the skin in the affected area;
- roughening of the skin of the feet;
- increased pain when walking.
Over time, the pain syndrome becomes habitual, and the person’s gait changes. He begins to place his foot so as not to touch the affected area and rests mainly on the toe and side of the foot. This often causes the development of transverse flatfoot, which further aggravates the course of the disease.
In severe cases, the ability to walk independently is completely lost due to unbearable pain when supporting the leg.
Advantages
- fast, complete and long-lasting pain relief;
- additional therapeutic effect due to the acceleration of recovery processes;
- possibility of repeated use;
- minimum of adverse reactions.
For tonic syndromes caused by muscle tension, blockades can relieve discomfort for several months or even years. For more serious diseases, anti-inflammatory and hormonal agents are added to the anesthetics, as well as chondroprotectors for cartilage regeneration. When introduced into a sore spot, they are much more active than droppers, tablets or ointments. Therefore, therapeutic blockades in neurology are much more effective than pharmaceutical drugs and physiotherapy.
Drugs
Anesthetics
Injections with Novocaine are given into nerves and soft tissues. After administration, nerve innervation is blocked, nutrition and cell resistance to allergens are improved. Novocaine has a bacteriostatic effect and has a high safety profile, rarely causing adverse reactions. Lidocaine provides a longer and more pronounced effect compared to Novocaine. It is based on the inhibition of voltage-gated sodium channels, due to which nerve signals cease to be generated and their transmission to the brain stops. Lidocaine dilates blood vessels and relaxes muscles. The pain disappears a few minutes after it enters the tissue.
Important! Lidocaine is less toxic than Novocaine.
Hormones
Dexamethasone is a fast-acting anti-inflammatory drug with prolonged action. It suppresses the activity of the immune system and has an antihistamine effect. Dexamethasone is one of the drugs of choice for diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Eliminates unwanted reactions to local anesthetics and is ten times more effective than hydrocortisone. Diprospan is used for joint diseases and heel spurs. Quickly relieves pain and discomfort, relieves allergic manifestations. Bone growths on the heel disappear after 1-2 procedures. The product can be used for epidural and perineural blockades. The only drawback is the possible side effects common to all corticosteroids. However, compared to analogues, the risk is lower.
Vitamin B12
The use of cyanocobalamin is justified by its ability to have a ganglion-blocking effect, that is, to inhibit nerve conduction. Vitamin B12 is usually administered in combination with B1 and Novocaine. The main indications are neuritis and polyneuropathy.
Causes of spurs
The cause of spurs is flat feet and wearing poor-quality shoes, as well as injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system. The mechanism is associated with damage to the plantar fascia, a ligament that connects the heel bone to the bones of the toes. Normally, minor injuries heal on their own. But if they happen frequently, the tissues do not have time to recover. Inflammation of the fascia develops, and due to the deposition of calcium salts, osteophytes are formed - bone growths.
The risk of developing fasciitis is high in people with excess weight, flat feet, diseases of the musculoskeletal system, and gout. In the same group are athletes and patients with circulatory disorders - diabetes, varicose veins, atherosclerosis.
Blockade in the spine: consequences and their prevention
Complications occur only in 0.5% of cases. These may include unexpected reactions to medications such as dizziness, vomiting, or increased heart rate. Damage to blood vessels at the injection point with the formation of a hematoma, infection and bleeding is also possible. Allergic reactions are possible. For preventive purposes, additional injections are given, and a test test is performed to prevent allergies. Our center has all the conditions for safely performing therapeutic blockades that will relieve you of debilitating pain for a long time. You don't have to worry about possible consequences or poor quality pain relief.
We employ high-level specialists with extensive experience, making patients feel comfortable and confident. If necessary, you will be prescribed one or more intra-articular injection procedures and a drug will be selected based on the indications.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
If you are worried about pain or discomfort in your heel, come for an appointment at the Health Energy clinic. An experienced orthopedic doctor will listen and examine you, and also prescribe the necessary examinations. After making a diagnosis, we will offer modern methods of treating pathology:
- blockades for quick pain relief;
- all types of physiotherapy;
- professional therapeutic massage;
- training in physical therapy exercises and exercises under the supervision of a trainer.
Additionally, we will prescribe drug treatment in accordance with modern standards, and also monitor the effect of therapy.