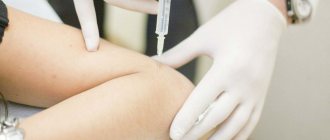
One of the most effective methods for eliminating pain and treating the spine is paravertebral blockade. It is aimed at a specific segment and, in addition to pain relief, performs a therapeutic function. The most important thing is the right choice of a specialist who will carry out the procedure. You should also pay attention to the equipment used in the clinic. In most cases, the injection is well tolerated by patients and adverse reactions are possible if the injection technique is violated.
Description and features
Paravertebral blockade is used to eliminate pain near the spine, so that the disease does not become chronic. In addition, using this procedure, medicine is injected into the pathological focus. Often, only after such manipulation the patient recovers.
The injection is given near the spine in the place where the pain is felt the most. This is where the nerve endings pass. After the blockade, the patient's swelling disappears and nerve trophism improves. Paravertebral blockade is also practiced to prevent muscle spasms.
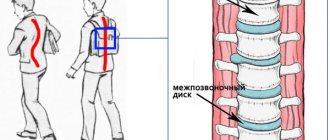
The medicine is administered into the paravertebral space (PVS) using manipulation. It is a gap limited at the thoracic level by the parietal pleura, the internal intercostal membrane, the posterolateral surface of the vertebra and intervertebral disc, and above and below by the heads of the ribs. In the lumbar region, the PVP is limited to the vertebral bodies, intervertebral discs and intervertebral foramina, the iliopsoas muscle, and the transverse processes of the vertebrae.
The paravertebral spaces are connected to each other through the transverse processes, as well as the heads and necks of the ribs. In addition, the PVP has a connection with the epidural space, in the thoracic space with the intercostal space, and in the lumbar region with the transverse abdominal space. The anesthetic can spread from the thoracic to the lumbar region and vice versa.
Thanks to the injection, nocireceptors are blocked in the area where the drug was injected. To relieve inflammation, in addition to the blockade, an injection of corticosteroids is given. Paravertebral blockade is also carried out into the joint cavity or joint capsule.
This method of treatment is used only as prescribed by a doctor, when the patient has passed all the necessary tests.
REVIEWS FROM OUR PATIENTS
“ We are sincerely grateful for every review you leave! ”
Add a comment
Artem 03/18/2021 02:22:53
Tell me, does this injection correct the problem itself or can it only temporarily relieve pain? Will it be necessary to undergo a full examination and continue treatment after this procedure?
Show answer
LITVINENKO Andrey Sergeevich 03/22/2021 11:31:33
Hello Artem! the blockade helps reduce pain, the course may include from 1 to 5 injections with different drugs, in some cases this is the only way to help the patient. The effectiveness and need for follow-up treatment, as well as the prescription of additional medications, depend on the severity of the patient’s pain. If the pain has decreased but not completely disappeared, additional appointments will be required.
Lily 03/17/2021 12:06:35
I would like to ask, what methods are used for patients with low blood pressure and diseases of the central nervous system for urgent relief of pain when the sciatic nerve is pinched?
Show answer
MOISEENKO Alexey Yurievich 03/22/2021 11:26:14
Good afternoon Lily! All treatment methods are selected based on indications and contraindications. If some method is contraindicated, then it can be replaced with another, there is always a way out).
Valeria 03/13/2021 22:58:57
Good afternoon Please tell me how to alleviate the condition. I have osteochondrosis of the lumbar region in the acute stage. I experience severe discomfort and pain while moving. Treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs does not help much, or for a short period of time.
Show answer
LITVINENKO Andrey Sergeevich 03/17/2021 09:35:33
Good afternoon Valeria! If the pain is severe, we recommend doing an MRI of the lumbar region and consulting a doctor. It may be necessary to take a drug blockade to relieve severe pain.
Advantages
Paravertebral blockade, in addition to pain, relieves swelling and spasm. The main advantages of the technique are:
- speed of action, since the medicine is injected directly into the affected area;
- minimal side effects, which is due to the introduction of the drug into the lesion, bypassing the bloodstream;
- more noticeable effect;
- the possibility of repeated administration of the drug;
- using a lower dosage of the drug;
- complex impact.
Paravertebral blockade lasts about 12 hours. After this time, the pain may return, but it will be less severe.
If a paravertebral blockade is used during surgery, patients are less likely to experience nausea, vomiting, and urinary retention. This speeds up their discharge from the medical facility.
Indications for use
Paravertebral blockade is recommended for pathologies of the spine and muscular system, when other methods of pain relief have not shown results.
This method of treating the spine is prescribed to patients diagnosed with the following diseases:
- spinal injuries;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- pinched nerve;
- rib fracture;
- shootings in the back;
- arthrosis;
- spinal hernia;
- radiculitis;
- lower back pain;
- osteochondrosis;
- muscle inflammation;
- renal and hepatic colic;
- chronic pain.
Paravertebral blockade is used after surgical interventions on the mammary gland or chest. The procedure is also performed for postoperative pain relief.
This pain relief technique is used during childbirth instead of epidural analgesia.
Our clinics in St. Petersburg
Structural subdivision of Polikarpov Alley Polikarpov 6k2 Primorsky district
- Pionerskaya
- Specific
- Commandant's
Structural subdivision of Zhukov Marshal Zhukov Ave. 28k2 Kirovsky district
- Avtovo
- Avenue of Veterans
- Leninsky Prospekt
Structural subdivision Devyatkino Okhtinskaya alley 18 Vsevolozhsk district
- Devyatkino
- Civil Prospect
- Academic
For detailed information and to make an appointment, you can call +7 (812) 640-55-25
Make an appointment
Paravertebral blockade is widely used in neurology not only to provide analgesia in the treatment of spinal diseases, but also for rib fractures, chronic or post-traumatic pain and various types of surgical interventions.
Contraindications
Paravertebral blockade is contraindicated if the patient is overly sensitive to the components of the drug used and analgesics. The injection is not given for skin lesions or infectious processes. Other contraindications include:
- pregnancy;
- low blood pressure;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- lactation period;
- renal failure;
- liver failure;
- high body temperature;
- suppuration in the pleural cavity;
- the presence of neoplasms in the paravertebral space;
- epilepsy;
- problems with blood clotting.
This method of therapy is not prescribed to patients undergoing heparin treatment. The blockade is placed with caution in cases of spinal curvature, chest deformities and postural disorders. If there is scar tissue or inflammation in the area where you plan to inject, it is recommended that you choose a different treatment method.
Paravertebral blockade is also not used for osteoporosis, since the patient’s condition may worsen in this case. In patients with osteomyelitis, there is a risk of the drugs used getting into the nerve tissue, which leads to an abscess.
In patients in shock, paravertebral blockade is contraindicated.
Medical indications
Having figured out what it is, many patients, with any manifestation of pain, require a paravertebral blockade. But the patient’s desire does not play a primary role here, since the final decision is made by the attending physician. He necessarily takes into account the patient’s current well-being, medical history, as well as recent test results.
The main indications for such a powerful intervention were the following pathologies:
- neuralgia;
- osteochondrosis;
- radiculitis;
- myositis;
- lumbago;
- protrusion.
A prescription for the purchase of pharmacological agents for the blockade will also be issued to those who suffer from intervertebral hernias or have encountered a pinched peripheral nerve. Spinal injuries are considered separately, since it is not always possible to use a similar technique when they are detected.
Based on the situation, decisions are made by a specialist when the patient has been diagnosed with chronic pain syndrome of almost any localization. The same applies to the severe discomfort that arose due to swelling followed by extensive inflammation. The primary source in this case should be a nerve root that has ceased to function as expected.
The method of administering drugs directly to the point of injury is ideal if it is necessary to get rid of compression of the nerve trunk, which is characteristic of muscle spasm.
Complications
Complications with paravertebral blockade are rare and are practically impossible when using ultrasound during manipulation. Studies show that this is possible in only 10% of patients. Several cases of nerve damage, puncture of the inferior vena cava and aorta have been recorded.
A slight swelling and hematoma may appear at the injection site. During an injection, the doctor may accidentally damage surrounding tissue if he moves the needle too much. An unqualified specialist may accidentally touch muscles, ligaments, tendons, and periosteum.
As with any procedure that involves puncturing tissue, the patient may experience bleeding. It poses a danger if blood enters a confined space, compressing neighboring structures.
When performing a paravertebral block, tissue infection is unlikely, since the procedure takes place under sterile conditions and the injection is administered into an area treated with an antiseptic. If the rules of asepsis are violated, patients experience suppuration of the joint and epidural abscess.
Anesthetics used for paravertebral blockade are sometimes difficult to tolerate by patients. Convulsions, breathing problems, loss of consciousness, and epileptic seizures are possible. There is also a chance of death, especially if injected in the neck. Cases of anaphylactic shock and malignant hypertension have been recorded.
Treatment with glucocorticosteroids is accompanied by problems with sleep, metabolic disorders, and increased blood pressure. A high dosage of the drug aggravates the ulcer, and long-term treatment leads to adrenal insufficiency.
In 10% of adult patients, paravertebral blockade was not effective. In children this figure is 6%.
Who carries out the procedure and how
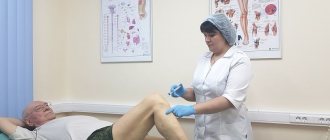
A spinal block for a hernia should only be done in a medical facility. The procedure can only be entrusted to a highly qualified neurologist. Any mistake can immobilize the patient, damage nerves, cause tremors, spinal cord ischemia, and other problems.
The blockade is performed by a neurologist after examining the patient.
Before the procedure, you must undergo a full medical examination or at least make sure there are no contraindications. Be sure to tell your doctor if you have any illness. There is no need to prepare for blockade of a herniated disc. The main condition is not to eat 3 hours before the injection.
The procedure goes like this:
- The patient takes the starting position (depending on the type of injection).
- The doctor makes a solution, draws it into a syringe, and feels the spinal column and nearby tissues.
- He slowly injects the medicine into the desired area, and treats the injection site with an antiseptic.
The procedure is quick, the pain disappears within 5 minutes. The effect lasts from several hours to a couple of days, depending on the type of medicine.
Where is the injection given?
The doctor chooses the injection site, taking into account the location of the intervertebral hernia:
- Paravertebral
- the injection is not injected into the spine, but near it into the area that directly interacts with the affected area (segmental blockade). This can be subcutaneous, muscular, radicular and other types of injections. - Vertebral
- the drug is administered intradermally, into the area of the vertebral body or between the processes to a depth of 2-4 cm. - Intraosseous
- injection into the bony protrusions, processes of the thoracic, cervical, lumbar and sacral vertebrae. - Spinal
- the needle is inserted into the subarachnoid space, at the level of the nerve roots.
A complex injection is the injection of medication into the epidural space, located between the hard shell of the spinal cord and the periosteum of the vertebrae. Epidural blockade of intervertebral hernia includes:
- intralaminar anesthesia
- the needle enters the central axis of the spinal column between the processes; - transforaminal injection
- the medicine is administered through the foraminal opening, from which nerve fibers and veins emerge.
Technique
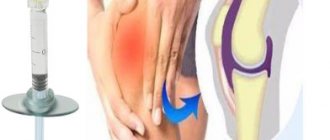
A paravertebral block is performed by a specialist neurologist or neurosurgeon, since it requires complex technical skills. The room where the injection will be given must be sterile. The injection technique depends on the part of the spine where the disease is localized. The main landmark is the midline running along the spinous processes. The paravertebral line runs 25 mm to the side.
Paravertebral blockade occurs in several stages. First, the patient's skin is treated with an antiseptic, then anesthesia is administered. Only after this the blockade is placed directly, using a thick needle. The administered drugs help relieve swelling and inflammation and dilate blood vessels.
Repeated introduction of the blockade is allowed for 3-4 days. It is recommended to prescribe the patient no more than 3 injections for 4-6 months.
To carry out paravertebral blockade, prepare the following instrument:
- syringes 20 ml;
- puncture needle;
- needle for local anesthesia of the skin;
- marker;
- sterile wipes;
- sterile gloves.
There are several methods for carrying out this blockade. Sometimes the needle is inserted blindly, and the doctor focuses on the loss of resistance. It is taken into account that a distance of 25-30 mm should remain between the midline and the injection site. This method leads to complications in 13% of cases. In addition, there is no exact data on how to calculate the injection site for a child from the midline.
Another blind method is to focus on the contact of the needle with the transverse process, after which it is bypassed by 15-20 mm from above and below. This does not take into account the characteristics of the patient’s build and anatomical structure, which leads to complications.
Doctors have come to the conclusion that the most successful outcome of paravertebral blockade is possible if during the procedure the doctor controls the exact position of the needle tip.
For this, it is recommended to use radiological methods or ultrasound. The sensor in relation to the transverse processes is installed along the midline or laterally. The direction is chosen oblique, transverse or sagittal. The needle is positioned longitudinally or transversely in relation to the sensor.
The most difficult technique is the transverse position of the needle relative to the sensor, when the sensor is placed parallel to the vertebra directly above the transverse processes. In this case, there is a risk of puncture of the pleural cavity, since the doctor cannot visualize the entire length of the needle. The safest method, in which you can completely follow the movement of the needle, is transverse insertion, when the sensor is positioned perpendicular to the spine. The puncture is made slightly to the side of the transverse process. In this case, the likelihood of the drug entering the epidural space is reduced.
A method that relies on pressure at the tip of a needle is also common. During its passage, it is higher when the patient inhales, and lower when he exhales. Once in the paravertebral space, the tip of the needle records a lower pressure during inhalation and a higher pressure during exhalation.
In some cases, it is practiced to introduce a blockade through a catheter, but even with the use of ultrasound, adverse reactions in the patient are possible. This is due to the twisting of the catheter in the paravertebral space. The procedure is successful only in half of the cases. The likelihood of complications is reduced with the use of flexible catheters.
The infusion rate for adults should be 0.1 ml per kg body weight per hour. For catheterization, the needle is most often inserted at an angle of 45 degrees, its movement is fully visible on the monitor. In this case, the puncture is made between the transverse processes.
When is a blockade prescribed?
A spinal block for a hernia is resorted to when acute, sharp pain occurs during which a person cannot sit, lie, or stand. While the anesthesia is in effect, the doctor can determine the cause, prescribe treatment, and physical procedures. The patient will be able to work calmly and complete projects.
Anesthesia helps to make an accurate diagnosis, since acute pain prevents a person from taking the desired position. As a result, the pictures turn out blurry and incomprehensible. The block helps the doctor to manipulate the vertebra in the area of the diseased segment - relieve pain, take a puncture, administer antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs.
Each type of intervertebral hernia has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easy it is to get rid of a hernia in 10 sessions
Drugs used for blockade
The excitability of the receptors is suppressed using an anesthetic. For this purpose, a solution of novocaine and icecaine is used. Their concentration is selected taking into account the degree of pain and the location of the blockade. To prolong their action, ropivacaine is added. A more noticeable result is obtained when they are combined with corticosteroids, which eliminate swelling and inflammation. To reduce the likelihood of allergies, the patient is also given antihistamines.
To restore cartilage tissue, chondroprotectors are added to these drugs. The condition of the joints is improved by products containing hyaluronic acid. For nerve trophism during blockade, B vitamins are administered.
Paravertebral blockade of the cervical spine
A paravertebral block in the cervical spine is given to the patient in a supine position. His head turns away from the injection site. After applying the antiseptic to the skin, a needle is inserted. Its direction should be perpendicular to the skin.
During a cervical procedure, there is a risk of subdural, subarachnoid and epidural insertion. This error causes hypotension and respiratory arrest. If the medicine enters the vertebral artery, the patient will lose consciousness and have seizures. Other complications include blockade of the phrenic and laryngeal nerves.
Paravertebral blockade of the thoracic spine
A feature of the thoracic spine is that between T4-T9 the spinous process is located at the level of the transverse process of the lower vertebra. Paravertebral blockade of the thoracic region is performed for lesions in the sternum or abdominal wall. The procedure is also prescribed for patients with herpes zoster, rib fractures, and compression fractures of the spine.
The patient should lie on his stomach or side during the procedure. The blockade is placed after identifying the spinous process of the desired vertebra. Then the skin is pulled back along the midline by 3-4 cm. To perform a paravertebral blockade in the thoracic region, a puncture needle with a limiter is required. It is inserted in the median plane at an angle of 45 degrees until it contacts the transverse process. After this, the doctor removes the needle a little and directs it under the indicated process. During manipulation, it is important that the needle does not move beyond the stopper by more than 2 cm. The anesthetic is administered at the level of each segment in an amount of 5 ml.
To reduce the risk of pneumothorax, the puncture needle is inserted 1.5 cm further from the midplane, maintaining a sagittal direction. The injection is administered at the level of the spinous process above the located vertebra, moving to contact with the lateral edge. After this, the doctor removes the needle to the subcutaneous tissue and then points it 0.5 cm laterally. In this case, the sagittal direction should be maintained.
Paravertebral blockade of the thoracic spine can cause the following complications:
- pneumothorax;
- entry of the drug into the bloodstream;
- subdural, epidural or subarachnoid administration of the drug;
- spinal nerve injury;
- decrease in blood pressure.
If a high concentration of medication is administered to the patient during the procedure, the likelihood of sympathetic blockade increases.
After performing such a manipulation on the thoracic region, it is recommended to send the patient for radiography.
Preparatory stage
To perform paravertebral blockade, the patient is placed on the couch on his stomach. The doctor gently palpates your back to determine the most painful areas. Having found them, the specialist treats the suspected injection sites with an antiseptic solution.
Then 4 injections are made with a thin needle to numb the skin. These injections are given at targeted points on the sides of the spinous process. When this anesthesia takes effect, the administration of blockade drugs begins directly.
Paravertebral blockade for the treatment of children
For children, this method of pain relief is used only under ultrasound guidance in order to accurately determine the site of drug administration. It should be taken into account that they require a smaller amount of the drug - 0.5 ml per kg of body weight. If the administration takes place at several levels, inject 0.1 ml at each level.
Carrying out a paravertebral blockade through a catheter involves setting the infusion rate to 0.2 ml per kg of body weight per hour.
Paravertebral blockade is given to children during removal of appendicitis, urological operations and interventions on the kidneys.
Paravertebral blockade, with the correct administration technique and the absence of contraindications, is absolutely safe for the patient and allows you to quickly relieve pain. When using a course of several injections, a therapeutic effect is noticeable. Complications after the procedure are rare and are practically impossible with the professionalism of the doctor.
Prices for blockades for back pain
| Services | Price | Sign up |
| Piriformis muscle block | 3000 rub | Sign up |
| Block of the sacroiliac joint | 3000 rub | Sign up |
| Blockade at home + doctor visit | 6000 rub | Sign up |
| Blockade of the lumbar region | 3000 rub | Sign up |
| Blockade for lumbar hernia | 3000 rub | Sign up |
| Paravertebral spinal block | 3000 rub | Sign up |