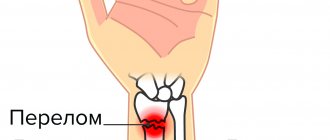
A fracture is an injury that is accompanied by complete or partial disruption of the integrity of the bone due to excessive load on it. One of the most common injuries of the lower extremities is a fracture of the fibula. Like other fractures, it can be either the result of a gross traumatic impact that exceeds the strength characteristics of the bone, or a consequence of any disease accompanied by changes in the structure of bone tissue.
Fracture of the fibula: causes
This fracture can be caused by many reasons:
- impaired coordination of movements;
- increased body weight;
- Various injuries resulting in a fracture of the tibia;
- falls from different heights;
- passive lifestyle;
- Smoking cigarettes (smokers have much lower bone density than people who do not have this bad habit; their recovery period is almost 2 times longer than that of non-smokers);
- calcium deficiency in the body;
- osteomyelitis;
- malignant tumors;
- osteoporosis.
A fibula fracture can be caused by excess body weight.
Rehabilitation period
Carrying out rehabilitation measures after a fracture of the fibula guarantees the restoration of the functions of the lower leg. The duration of rehabilitation is primarily related to the nature of the injury, the body’s ability to recover, and the rate of bone tissue fusion. On average, the recovery period takes six months.
As rehabilitation measures, the doctor will prescribe therapeutic massage and physiotherapeutic procedures at the site of injury. After the patient is allowed to stand up, walking with a moderate load on the broken leg is prescribed, and special exercises are recommended, which are done while wearing a cast. If you experience pain, your doctor will prescribe painkillers.
One of the means of rehabilitation is to follow a special diet rich in calcium, meat products and vitamins.
Neglect of doctor’s recommendations, as well as early and long periods of walking on the injured leg, and failure to follow a diet contribute to the development of complications. These include:
- improper fusion and, as a result, shortening of the broken leg,
- long fusion of tissue fragments,
- further development of joint diseases such as arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Read also: The danger of hip fracture in older people
Fracture of the fibula: types
Depending on the severity of the force influencing the ongoing process, there are:
- stable or fracture of the fibula without displacement - there is a slight displacement relative to the cut axis of the damaged bone without the formation of small fragments;
- displaced (displaced fracture of the fibula) - characterized by the formation of bone fragments displaced along the axis, preventing the patient from moving without assistance;
- transverse - there is a fracture line transverse to the axis of the bone, which makes it difficult for the patient to move;
- oblique - occurs as a result of force acting on the bone at an angle, mostly displaced fractures, sometimes stable
- Spiral or helix - Caused by twisting of the leg during an injury.
- Single - no more than 2 fractures are observed in the fracture;
- Crush - occurs when the bone is broken into several fragments, the fragments can protrude and damage surrounding tissue, and are most difficult to treat.
Non-displaced fibular fracture
- Combined fracture, in which fractures of the tibia and fibula fuse
- In combination with other injuries (for example, burns, wounds).
Depending on the nature of the damage, open and closed fractures are distinguished.
Closed
In this case, small fractures of the bone, its fragments do not come out from under the epithelium. Sometimes bone fragments can be felt under the skin, so do not allow them to come out. Externally, even with palpation, fractures and the fracture line are not easy to detect. No deformation is observed. The patient may mistake this type of fracture for a bruise.
Open
In this most severe type of bone fracture, the wound is open and fragments are visible. Seek medical attention immediately. Most often this is accompanied by shock. If the wound gets infected, the course of the disease will become more complicated.
Rehabilitation
For fractures of various types with displacements, it is rehabilitation that is mandatory and the main component of the entire treatment. This is necessary to reduce treatment time and reduce the likelihood of complications. A large part of rehabilitation consists of physical exercises carried out to restore blood supply to the fracture area.
Exercises are prescribed individually for each patient; classes can be carried out at home. The duration of rehabilitation varies for different cases, up to 3 months.
A set of physical training exercises of a therapeutic type consists of the following exercises:
- Rotate the foot in different directions for 10 repetitions. This exercise can be performed within a week after the plaster is removed.
- Deviation of the injured leg by 30 degrees from the plane of the body, followed by holding it in this position for several seconds (up to 5). Number of repetitions – 10, performed with both legs.
- Swing your legs alternately to the side and back. The number of repetitions is 10, performed with each leg.
- Standing on your toes. At first, this exercise should be performed on both legs, after 2 weeks on one, the number of repetitions is 10.
- Swing your legs in a lying position with alternate crossing of your legs. Number of repetitions – 10.
- Walking every day is mandatory.
To help the patient relax his muscles better during recovery, baths with sea salt are recommended. A pre-created solution of 100 g of salt in one liter of water will help you prepare a bath; then you need to mix it with a filled warm bath. You can put your feet on a platform.
These measures are designed to improve the recovery of the lymphatic and circulatory system at the site of injury.
Signs of fractures
Symptomatology varies depending on the location of the fibula fracture.
| Fracture location | Symptoms |
| Neck fracture and other isolated fractures | Discomfort in the knees, moderate pain, no movement disorders, since the main load falls on other parts of the lower limb. |
| Ankles | Severe pain syndromes in the ankle joint, in many cases accompanied by damage to the epithelium and muscles, painful when stepping |
| Fracture of the third lower (oblique) with subluxation of the foot | Visceral hematoma and swelling, inability to move, pain increases with palpation |
| joint | Severe pain syndromes with a characteristic cracking sound when bone fractures rub against each other. |
In general, the following symptoms are characteristic of this fracture:
- Bleeding occurs from ruptured vessels, which leads to swelling of the adjacent soft tissues, the pressure of which corresponds to severe pain;
- Fractures are the periosteum and connective tissue that forms the endosteal canal and lines the tubular bones from the inside;
- shortening the length of the limb during a fracture as a result of displacement of fragments;
- Significant deformation of the lower limb caused by displacement of bone fragments.
Treatment
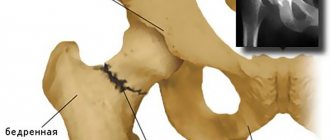
Treatment is not particularly difficult if there is no displacement. Even if there is a fracture of the fibula and tibia, but there is no displacement, treatment will be faster and easier. In this case, treatment consists of applying plaster. The cast is placed on the area of the leg that needs to be immobilized. This placement of the plaster helps prevent displacement of bone fragments.
If there is displacement of bone fragments, especially if there has been displacement of the large and small bones, treatment consists primarily of restoring their correct position. In case of transverse impacts, bone plates may be applied. The insertion of pins slightly below and above the fracture during the treatment process is carried out in case of displacement that occurred as a result of an impact, except transverse. These needles fix and stretch the restoration site.
Fracture of the fibula: diagnosis
Performed in the following sequence:
- Visual examination of the leg and determination of the ability to move it;
- talk with the patient about the cause of the injury;
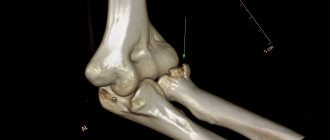
- X-ray in 2 projections to clarify the nature of the injury and its type (recommended for closed fractures).
X-ray is one of the methods for diagnosing fibula fractures.
In case of a fracture of the head of the fibula, the doctor prescribes, in addition to X-rays, an MRI or computed tomography to clarify damage to the tendons, ligaments and muscles. X-rays are taken twice: immediately after the injury and after applying a cast to prevent improper fusion of the damaged bone.
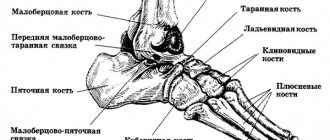
Anatomy
The fibula is simple in structure, has a posterior, lateral and medial surface. In addition, the edge of the bone tissue is distinguished:
- rear,
- front,
- medial.
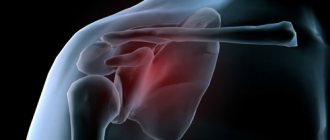
At the top, the head of the fibula is united with the tibia by a joint capsule. The lower (distal) end forms the lateral malleolus, to which the peroneal tendons are attached. Separately, damage to the fibula is rare, but under certain circumstances such an injury together with the tibia is possible. Common injuries to the lower leg include a fracture of the head of the fibula.
First aid
First aid plays an important role in further effective treatment of a fracture. A person with a broken leg bone is usually helpless, so those around him should know certain rules of first aid. Nobody knows when this might come in handy. Basic steps:
- Call a medical team.
- Lay the victim on a flat surface in a horizontal position.
- The body and limbs need to be immobilized as much as possible.
- Shoes must be removed.
- If the victim is suffering from unbearable pain, it is permissible to give a non-narcotic pain reliever.
- If the fracture is closed, it is recommended to apply ice to the injured area
- The next step is to fix the leg from heel to thigh using a splint. To do this, you can use two planks or something else, the main thing is that the objects are made of solid material. Secure the splints with a bandage or scarf.
- If there is a bleeding wound, all pieces of tissue should be removed from it and a tourniquet or aseptic bandage should be applied.
- The tourniquet is applied for no more than 2 hours, so the exact time of application should be recorded.
The patient is hospitalized using a stretcher only in a supine position. Based on the above, it becomes clear that in case of a fracture, the victim needs to be provided with complete rest. And questions such as “is it possible to step on the leg if the fibula is fractured” are absurd.
Etiology of injury
From an anatomical point of view, the above bone is relatively thin, slightly spirally twisted in the shape of a triangular spoke, which is “attached” to the tibia from the outside.
Despite its title, the video in this article emphasizes that without the fibula, the tibia or ankle joint could not form. With its help, the outer malleolus of the above joint is formed.
Thus, the main causes of damage may be:
- falls from a significant height with the person resting on the lower limb (pronation/supination or external or internal twisting of the foot occurs);
- receiving a direct ramming blow to the area of the outer half of the shin (most often such a blow occurs when the human body hits a car bumper, when there is strong compression of the foot);
- the implementation of a movement of “screwing” origin, in which the lower leg remains in a fixed position (most often, the injury occurs when the leg is damaged while wearing a ski, since it involves a forced rotation of the foot).
Often, pathological health problems such as osteomyelitis, osteoporosis or sarcoma of the bone structure have a significant impact on how a fracture of the fibula heals.
If you suspect such an injury, you should immediately call an ambulance. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that self-correction of damage is prohibited in order to prevent associated complications.
At the same time, it should be noted that the provision of first aid is desirable in order to prevent the possible consequences of the damaged integrity of the fibula.
Violation of the integrity of the bone structure of the lower limb at the site of the fibula
Complications
When physical therapy after a fracture of the fibula was followed, but the treatment itself was prescribed incorrectly, complications arise:
- Arthritis;
- Various limb lengths;
- Infection entering the bloodstream through a wound;
- Peroneal nerve injury.
Avoiding self-medication will help protect yourself from unwanted consequences.
If you notice the first symptoms of a fracture, you should immediately consult a doctor who can make a diagnosis and carry out effective treatment.