Causes of sternum fracture
The breastbone is strong enough to successfully perform the functions assigned to it by nature. It can break only under the influence of a large force.
In most cases, it is caused by a car accident in which the chest is suddenly compressed by a seat belt or hits the steering wheel hard. You can get a rib cage fracture from a direct punch or kick to the chest while practicing various martial arts. Also, similar injuries occur during natural disasters, falls from a height onto a hard surface, severe beating, or pinching of the chest between two hard surfaces.
In old age, sternal fractures occur more often. This is due to changes in hormonal levels, disruption of metabolic processes in bone tissue and an increase in its fragility. These age-related fractures take longer to heal due to decreased bone mineral density.
Classifications of sternal fractures
Fractures of the chest are very diverse, as are their classifications. The latter are compiled to help traumatologists and allow them to accurately make a diagnosis, prescribe the correct treatment, prevent possible complications, and decide on rehabilitation measures.
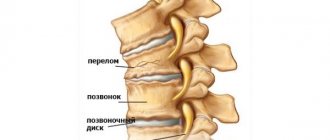
Based on the number of injuries, a distinction is made between multiple sternum fractures, in which several bones are injured at the same time, and single fractures, in which one bone is broken.
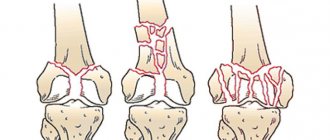
Based on the nature of the fracture line, fractures are divided into transverse, longitudinal, oblique, T-shaped, cruciform, and mixed.
Depending on the location of the bone fragments, the injury can be either displaced or non-displaced. In the first case, the bone fragments are in the usual anatomical position, in the second they diverge to the sides due to muscle tension. The last type of sternum fracture is the most dangerous, since displaced bones can injure surrounding tissues and internal organs. Depending on the damage to certain organs and tissues, fractures of the chest can be uncomplicated or complicated. In uncomplicated injuries, only bone fragments are affected, soft tissues are not affected. A complicated fracture is characterized by the fact that in addition to the bones, the respiratory organs are also damaged.
Also, for fractures of the sternum, a classification is used based on the presence or absence of skin damage: closed fractures - the skin is not broken, open fracture - there is a rupture of the skin.
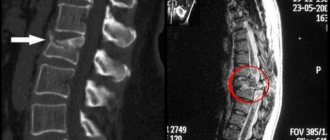
Diagnostics
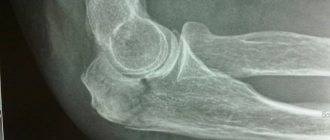
After clarifying all the circumstances of the injury and external examination of the fracture area with palpation, the patient must have an x-ray taken in two projections. This will allow you to determine the type of displacement, fracture line, number of fragments and the presence of associated damage.
In case of doubt, the result of a computed tomogram will be relevant as a more informative study. A cardiac injury can be ruled out or confirmed using an ECG.
Symptoms of a sternal fracture
The following signs can help identify a dangerous fracture.
- Pressing pain. With a deep breath, movement or coughing, it intensifies, and therefore the victim tries to breathe shallowly. In a bent sitting position, the muscles relax, the pressure on the broken bone decreases, and the pain subsides; in a lying position, on the contrary, it intensifies.
- Labored breathing
- Swelling at the site of injury , growing at a high rate.
- Hematoma in the anterior mediastinum. It has a bluish-purple color and has clear contours.
- Crunch. It manifests itself at the moment of breathing and is caused by the displacement of bone fragments.
- Hemoptysis. Occurs when the membrane covering the lungs is damaged.
- Subcutaneous emphysema is the accumulation of air in the subcutaneous tissue from damaged bronchi and lungs and its spread under pressure to other areas of the body.
- Vomiting, dizziness and loss of consciousness occur when internal organs and nerve fibers are damaged.
- The chest appears depressed. This is observed with displaced fractures of the sternum.
- Movement of fragments. It is especially noticeable during breathing.
- Rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath.
The appearance of such symptoms should be a reason to immediately call an ambulance. It is also worth contacting a doctor if, after a strong blow to the chest, your health has practically not worsened. A crack in the sternum (partial fracture) may not manifest itself in any way, but at the same time pose a threat to health!
How long does recovery take?
Bruised ribs recover fairly quickly with proper treatment, although the pain may persist for a long time. It is difficult to say in advance how long the treatment will take. This process usually takes from 30 to 50 days. Some people, even after a mild injury, feel discomfort for several weeks, and a moderate injury can last 2-3 months or more. If the pain does not ease, but intensifies, go to the doctor. In rare cases, the treatment regimen may need to be repeated. You should not endure severe pain, especially after a fracture. A third-degree rib bruise can take up to 3-4 weeks to recover, and mild discomfort can last up to six months, but a lot depends on rehabilitation. Physical therapy, massage, physiotherapy and breathing exercises can speed up healing.
Providing first aid for a sternum fracture
Providing first aid for a chest fracture is aimed at maintaining the victim’s well-being until doctors arrive and preventing possible complications.
First of all, it is necessary to relieve pain in order to prevent a state of shock and return the person to the ability to breathe fully. To do this, it is recommended to sit the victim down and make sure that he moves less and does not talk. Ice, which should be wrapped in a cloth and briefly pressed against the site of injury, will also have an analgesic effect. Cold will also help prevent swelling and hematoma from spreading. If the pain does not subside, the victim is given two tablets of an anesthetic.
The next step is to free the chest from constricting clothing, a tie, a belt and apply a pressure bandage to it. The latter will reduce the range of movement of this part of the body and bone fragments during breathing, and will help reduce pain. But you should not tighten the chest too tightly. This is fraught with even greater displacement of the bones. Instead of a bandage, strips of wide adhesive tape can be applied from side to side to prevent bone separation.
If the sternum fracture is open, it is important to treat the wound with an antiseptic as quickly as possible to reduce the risk of infection. If gas bubbles are released from the wound and the skin swells, it should be covered with oilcloth or a plastic bag. Otherwise, air may enter the pleural cavity.
In case of loss of consciousness, the victim is placed on his back and his head is turned to the side so that vomit does not enter the respiratory tract. If calling an ambulance is impossible for one reason or another, you must transport the victim yourself to the nearest traumatology department, always in a sitting position.
When providing first aid, it is strictly forbidden to independently remove bone fragments or remnants of clothing from a wound, shift the victim to the injured side, or give any medications, foods or liquids to an unconscious person.
Complications
Complications of a sternal fracture arise only against the background of concomitant injuries. As a result of injury, the following pathologies most often develop:
- traumatic shock against the background of pain - a violation of blood microcirculation in small vessels;
- trauma of varying severity to mediastinal organs: heart, bronchi, trachea, pulmonary arteries and veins, esophagus;
- infectious inflammation of the wound surface as a result of an open fracture;
- pulmonary embolism;
- unstable spine syndrome;
- curvature of the spine - kyphosis - in elderly patients;
- periodic numbness and decreased sensitivity in different parts of the body;
- weakness of muscle strength;
- frequent shortness of breath even at rest;
- when the spinal cord is damaged by bone fragments, neurological pathologies appear;
- complete or partial paralysis due to ruptures of nerve roots by fragments.
But the most dangerous consequences caused by a fracture of the sternum are pneumothorax, hemothorax and hemopericardium.
Pneumothorax
The level of pressure in the pleural cavity in the normal state is below atmospheric. The penetrating air increases the pressure, as a result of which the lung is compressed and collapses, causing partial or complete collapse. Together with the large veins, the heart is also compressed, shifting in the opposite direction.
The development of pneumothorax can be recognized by the victim's panic, excessive sweating, bluish skin, shortness of breath and sharp chest pain. The patient's condition is assessed as potentially fatal. Pneumothorax requires decisive action and urgent medical intervention.
Hemothorax
As a result of rupture of the pulmonary vessels, blood accumulates in the pleural area. Normally, it contains very little serous fluid. Under the pressure of the cavity filled with blood, the thymus gland, trachea and aortic arch are displaced in the opposite direction, and the lung is compressed. The amount of blood sometimes exceeds 2 liters. The condition is life-threatening due to the development of respiratory failure.
Treatment of a chest fracture
The choice of treatment methods depends on the severity of the fracture and the presence or absence of complications.
If a closed fracture of the sternum without displacement is diagnosed, and the internal organs are not damaged, conservative therapy is preferred. The patient is prescribed analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ointments to relieve swelling, and expectorants. The chest is fixed with a wide adhesive plaster for 2–4 weeks.
When a slight displacement of bone fragments without damage to internal organs is detected, they are first carefully aligned with their hands, placing the patient on a flat, hard surface with a roller between the shoulder blades, and only after that they are fixed. Open fractures, as well as injuries with significant displacement of bone fragments or a large number of fragments are treated surgically. The fragments are removed, and the parts of the bones are connected to each other using special metal screws. Plaster or any other tight bandages are not applied for a fracture of the sternum, since they contribute to the development of stagnation - pneumonia and inflammation of the pleural layers. Only wide adhesive plasters are used. With the most favorable prognosis, complete recovery from injury takes about two months.
How to recover faster after a sternum fracture
The longer the recovery period for a sternum fracture takes, the greater the number of complications that can develop. Bones take a particularly long time to heal in old age. This is facilitated by a slowdown in metabolic processes in bone tissue and a decrease in the number of bone cells that ensure the restoration of bone structures after a fracture.
However, scientists have figured out how to influence the rate of bone fusion. The founder of the Volga Region Center for Osteoporosis, V.I. Strukov, has developed a means to increase bone density without the use of bisphosphonates and hormone replacement therapy. This is the drug Osteomed Forte .
It differs from other similar products in that it contains not only a building material for bones (calcium), vitamins D3 and B6, but also a component that ensures the direction of the mineral into bone tissue - HDBA organic complex. The latter is a natural substance with an anabolic effect - drone homogenate. It helps to increase the number of bone cells, which take calcium from the bloodstream and integrate it into the collagen framework of the bone. Tests of the Russian development were carried out at the Penza Institute for Advanced Medical Studies. They showed that Osteomed Forte accelerates bone healing in case of fracture by an average of 2 weeks. And it does it safely.
Anatomical features
The sternum is an elongated dagger-like bone, slightly convex on the outside and slightly concave on the lung side. This is the central bone of the anterior part of the chest, which consists of the manubrium, the body itself and the xiphoid process. At the top of the manubrium are the jugular and clavicular notches. Along the edges of the body of the sternum on both sides there are symmetrical costal notches, and the appearance of the xiphoid process can be different: deviated to the side, forked, and even with a hole. This segment of the bone is the most mobile.
All three parts are connected by cartilage tissue, which completely ossifies over the years. In general, the structure of the sternum is characterized by a large amount of spongy substance with many blood vessels.
In case of urgent need, this significant factor provides the opportunity to perform intrathoracic blood transfusion. And the abundance of bone marrow in the sternum during the treatment of radiation sickness allows it to be removed from this very bone.