Osteoarthritis of the elbow joints is a disease that is accompanied by degenerative changes in cartilage, which leads to their deformation, the formation of osteophytes, and synovitis.
The pathological process is accompanied by pain, dysfunction of the joints, decreased quality of life, and in severe cases disability is assigned. The disease affects approximately 12% of all people, with incidence increasing after age 55–60 years.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the elbow joint may appear earlier if the patient’s activities are associated with physical activity.
general information
Osteoarthritis begins with microdamage to cartilage against a background of increased load or reduced ability to regenerate. As a result, the tissue becomes thinner and becomes denser and less smooth. The movement of bones relative to each other becomes difficult, and certain areas of the articular surfaces begin to experience constant overload.
The process is accompanied by a change in the properties of the synovial fluid, which becomes thicker. Bone growths – osteophytes – appear inside the joint cavity. As the disease progresses, their number increases and the distance between the bones decreases. The pathological process spreads to surrounding tissues: ligaments, muscles. Ultimately, all elements of the joint grow together, and movement is completely blocked.
Make an appointment
Content
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease of cartilage tissue, most often developing in the joints of the legs and spine. However, there are also atypical cases when the elbow joint is affected.
The pain occurs in the very center of the elbow, just below the bend. At the same time, it intensifies when the arm is extended.
The pathology is localized in the elbow in people due to frequent physical activity. Due to hormonal changes, osteoarthritis of the elbow joint appears in women after 40 years of age. Doctors classify this disease as an occupational disease. Constant and monotonous flexion and extension of the arm leads to the progression of osteoarthritis of the elbow. Builders, musicians, athletes and heavy physical labor workers are at risk. As a result of the costs of the profession, microtraumas form in the elbow joint. Vibration can also have a negative impact, for example, if a person has to work with a jackhammer every day.
Advice! People at risk for osteoarthritis of the elbow joint should especially monitor proper nutrition and remember to take breaks from work to prevent the development of the disease.
The professional factor is not the only one that negatively affects and causes osteoarthritis of the elbow joint. Other factors include:
- improper metabolism;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- previous joint surgery;
- severe injuries;
- elbow bruises.
Remember! Although mechanical influences cause the disease, doctors attribute it to genetic pathologies. When someone in the family is sick, in 70% of cases the descendants also develop osteoarthritis of the elbow joint.
Kinds
Most often, the disease is classified depending on the location of the pathological process. Osteoarthritis can be unilateral or bilateral and deform almost any joint:
- knee;
- hip;
- ankle;
- brachial;
- temporomandibular;
- elbow;
- small joints of the foot and hand;
- intervertebral joints.
Depending on the cause, osteoarthritis can be primary (occurs on its own) or secondary (develops against the background of another pathology or injury).
ethnoscience
Against the background of the main therapy for the first and second stages of the disease, traditional methods can also be used. The use of a salt compress on the affected area (elbow) has gained considerable popularity.
The solution is prepared at the rate of 3 tablespoons of salt per liter of water. A moistened gauze bandage is applied to the elbow joint, tied with a woolen cloth and left overnight. The course is 5-7 such procedures, then a break is taken.
Causes
The development of osteoarthritis can be triggered by any disease or condition that increases the load on the joint or worsens its regeneration processes. Most often, pathology occurs against the background of:
- joint injury or surgery;
- past inflammatory process;
- excess body weight;
- regular excessive physical activity (standing work, professional sports, heavy lifting);
- hormonal shocks (pregnancy, menopause);
- congenital pathologies of the musculoskeletal system (flat feet, congenital hip dislocation, etc.);
- autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis);
- connective tissue dysplasia (a condition in which its structure changes);
- endocrine diseases and metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, gout);
- vascular diseases (atherosclerosis, thrombophlebitis, etc.).
Heredity, as well as age over 45 years, significantly increases the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
Non-drug methods
The main methods are physiotherapy, physical therapy, massage, diet. They help very well in the initial stages of the disease and are carried out during periods of remission.
Physiotherapeutic procedures include electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, cryotherapy, laser, darsonvalization, diadynamic currents, etc.
Manual therapy with massage helps to gently and gradually increase the range of motion in the affected limb. Prevents the development of atrophy of the muscles surrounding the joint. Improve blood circulation and eliminate muscle spasms.
A set of exercise therapy exercises is carried out in a medical institution or performed independently by the patient at home. The technique is selected individually by the doctor, and the patient is taught how to perform the exercises.
It is especially important to stick to your diet. Often people suffering from osteoarthritis are overweight. Therefore, review your diet and adhere to the following principles:
- eat in small portions;
- food should not be high in calories (do not abuse carbohydrates, fats, reduce the consumption of baked goods, especially those made from premium flour);
- add vegetables and fruits to your diet;
- reduce consumption of salt and spices;
- give up alcohol.
Degrees
Orthopedists distinguish 4 degrees of the disease:
- Grade 1: there are no symptoms, but with exertion a person may notice slight pain or discomfort; all cartilage damage occurs at the microscopic level;
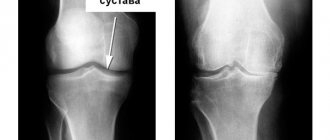
- 2nd degree: pain occurs not only during exercise, but also at rest; x-rays reveal a narrowing of the joint space and isolated bone growths;
- 3rd degree: destruction reaches its peak, surrounding tissues are involved in the pathological process; the pain becomes constant, and the pictures clearly show deformation, narrowing of the joint space and numerous osteophytes; Often at this stage, dislocations and subluxations of the joint occur due to weakening of the ligaments;
- 4th degree: bone growths completely block the joint, movement is impossible.
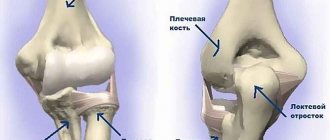
Stages and symptoms of elbow osteoarthritis
The clinical picture of the disease is such that first there are periodic pains in the affected area. In the future, if no treatment is taken, the disease progresses. Osteoarthritis of the elbow joint is divided into three degrees. The rating is given according to the level of damage.
When affected by arthrosis, osteophytes form on the ulna. This is already an advanced stage, treatment action must be taken immediately.
Osteoarthritis of the elbow joint of the 1st degree is manifested by mild pain during exercise and a decrease in the cartilage gap between the two end parts of the humerus and ulna by a third of normal. Roughness appears on the cartilage.
Osteoarthritis of the elbow joint grade 2 is characterized by constant pain that gets worse at night. Mobility in the elbow decreases. The gap between the subchondral plates is reduced by half compared to normal.
The x-ray shows that the bones are touching each other at the junction. There is no cartilage gap.
Osteoarthritis of the elbow joint of the 3rd degree is characterized by thickening of the ulnar and radial ligaments, the absence of synovial (articular) fluid in the joint capsule and a decrease in joint mobility by 80%. When trying to load the arm, acute pain appears. The x-ray shows that the cartilage is no longer there, the bones are thickened and deformed, and the cartilage tissue has been replaced by osteophytes.
Osteoarthritis of the elbow has signs that separate it from other lesions of the joint capsule and cartilage tissue. At the first manifestations, the patient does not pay attention to them. However, the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the elbow joint appear more often over time and create severe painful discomfort. Signs of progression include the following:
- pain when bending and straightening the elbow under load;
- pain at rest if the disease is at a late stage;
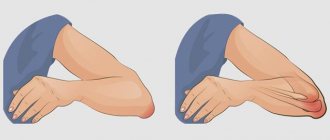
- redness and swelling;
- crunching when bending and straightening the elbow;
- joint stiffness in the morning;
- decreased mobility;
- external deformation;
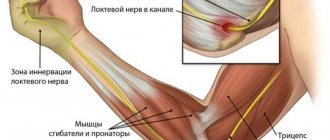
- numbness or anemia of the fingers on the affected hand.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the elbow joint in this form develop over decades. At first, the patient experiences only mild discomfort, which is perceived as fatigue after heavy exertion. But when the cartilage is already half erased, the symptoms become more pronounced.
Symptoms
The main signs of osteoarthritis develop gradually, intensifying as the disease progresses. Most patients note:
- pain: associated with friction of the articular surfaces of bones from each other, intensity and duration depend on the stage;
- crunching when moving: is one of the first signs of the disease, as it progresses it is accompanied by pain;
- stiffness: as the cartilage is destroyed and osteophytes appear, the range of motion of the joint is reduced until complete blocking (ankylosis);
- joint deformation due to bone growths;
- changes in surrounding tissues: especially noticeable when affecting the limbs and fingers, which appear noticeably curved.
Damage to large joints significantly changes a person’s lifestyle, as he loses the ability to move independently and take care of himself.
Diagnostics
If you have problems with your joints, you should seek help from an orthopedist-traumatologist. Its tasks include identifying the symptoms of osteoarthritis, determining the extent of the disease and selecting treatment.
Radiography remains the main way to visualize changes occurring inside the joint. The image allows you to see the size of the joint space, the number and size of osteophytes, and bone deformation. If it is necessary to visualize soft tissues, ultrasound or MRI is performed. According to indications, arthroscopy is performed: a puncture of the joint capsule, followed by the introduction of a miniature camera into the cavity, allowing one to see the joint from the inside. This technique can be supplemented by the administration of drugs.
Laboratory diagnostics are of an auxiliary nature. A general blood test can show an active inflammatory process if arthritis has joined osteoarthritis. If the disease is secondary in nature, tests, examinations and consultations with specialists are prescribed to diagnose the original pathology.
Treatment of osteoarthritis
Treating osteoarthritis of the joints takes time and patience. At an early stage, doctors successfully stop the pathological process with the help of medications and physiotherapy, but in advanced cases the disease can only be dealt with surgically. All treatment methods are divided into:
- medicinal;
- non-medicinal;
- surgical.
Drug treatment is aimed at reducing pain and restoring cartilage tissue. Pain due to osteoarthritis significantly reduces the patient’s quality of life, making it difficult to move freely, which is why analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs are at the top of the list of prescriptions. Depending on the clinical situation, drugs from the following groups are prescribed:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs): stop inflammation and reduce pain;
- corticosteroids: hormonal drugs that block inflammation;
- antispasmodics: relieve reflex muscle spasms.
Preparations of these groups are available in the form of ointments for topical use, tablets and capsules, suppositories or solutions for injections. Some are injected directly into the joint cavity, acting as efficiently as possible. The dose, duration and frequency of administration are selected only by a doctor, since long-term use can accelerate the destruction of joints.
The second group of drugs is aimed at restoring or slowing down the destruction of cartilage. The debate about the effectiveness of chondroprotectors is still not over, but at the moment their use is mandatory. Preparations based on chondroitin, glucosamine or their combination are used in long courses of 3-6 months.
In addition to basic therapy, the doctor may prescribe drugs to improve blood circulation and anti-enzyme drugs. Warming ointments have a good effect.
Non-drug treatment methods help enhance the effect of drugs. They are aimed at improving microcirculation in the affected area, stimulating muscles and reducing stress on the joint. For this purpose the following are used:
- massage;
- physical therapy and mechanotherapy;
- joint traction;
- physiotherapy: shock wave therapy, electrophoresis, ultraphonophoresis, ozone therapy, various applications, etc.
The help of surgeons is necessary in the final stages of the disease, when drugs can no longer stop or slow down the pathological process. The most effective method at the moment is endoprosthetics. The affected joint is removed and replaced with a modern prosthesis that can function for decades. This technique is especially often used to restore knee and hip joints.
In some cases, operations are performed to alleviate the patient's condition:
- corrective osteotomy: excision of part of the bone tissue followed by fixation of the remains at a different angle; allows you to reduce the load on the sore joint;
- arthrodesis: fastening bones together; this completely blocks movement in the joint, but the patient is able to lean on the leg without pain.
Make an appointment
Surgical intervention
At stage 3 of the disease, the patient experiences severe pain, and there is practically no effect from medications. In such circumstances, only surgery will help. Osteotomy is used - excision of the bone at the site of the lesion and fixing it in an advantageous position. If osteophytes are present, they are removed.
In advanced cases, endoprosthesis replacement of the elbow joint or the head of the radial bone is performed. It is indicated for severe contracture or ankylosis (complete immobilization of the elbow). The affected bone areas are excised and a prosthesis is installed in their place. Its parts are attached to the bone tissue of the person being operated on using medical cement.
After such treatment, the patient will have a recovery period, which is carried out in rehabilitation centers or at home under the supervision of a doctor.
Prevention
Like most diseases, osteoarthritis is much easier to prevent than to cure. Simple rules will help maintain healthy joints and stop the process at an early stage if it has already occurred:
- sufficient physical activity: amateur sports are a good prevention of physical inactivity, help improve microcirculation and form a good muscle frame;
- normalization of body weight: excess weight creates increased stress on the joints, especially the knee, hip and ankle;
- minimizing traumatic factors: vibration, standing work, heavy lifting contribute to the development of joint diseases;
- correct posture and shoes to distribute the load on the joints;
- timely treatment of diseases that can cause secondary osteoarthritis.
Diet
Proper nutrition is not the main factor in the prevention of osteoarthritis, but it will also make its contribution to maintaining healthy joints. Recommended:
- a diet balanced in calories, macro- and micronutrients;
- sufficient amounts of vitamins and minerals;
- exclusion of spicy, canned, excessively fatty foods, alcohol, as well as products with artificial flavors and dyes;
- minimizing fast carbohydrates.
Collagen and omega-3 acids have a good effect on the condition of cartilage, which is why aspic and sea fish and olive oil should always be present in the diet.
Consequences and complications
Without timely treatment, osteoarthritis can cause disability, especially with bilateral damage.
It causes:
- severe joint deformation;
- bone curvature;
- loss of mobility;
- shortening of the limb (with coxarthrosis and gonarthrosis).
When the large joints of the legs are affected, a person’s gait and posture change so much that this inevitably leads to problems with the spine, pain in the neck and lower back.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is performed if there is no effect from conservative therapy for deforming osteoarthritis of the elbow joint. The main treatment method for DOA is endoprosthetics. It is important to consider that the procedure does not have a lifelong effect; after twenty years the prosthesis will need to be changed.
Surgery is performed in case of ineffective conservative treatment
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
If you begin to notice a suspicious crunch in your joints, you should not quickly search the Internet for how to treat osteoarthritis with folk remedies. It is better to seek help from professionals from the Energy of Health clinic. We use modern means of cartilage tissue restoration and offer each patient:
- individual selection of a drug regimen;
- constant monitoring and control of treatment effectiveness;
- various physiotherapeutic procedures;
- massage and physical therapy;
- puncture of the joints followed by the administration of painkillers or artificial synovial fluid;
- drug blockades for quick and effective pain relief.
How does osteoarthritis of the elbow joint manifest?
At the initial stages, the symptoms of osteoarthritis are expressed by rare pain, which only bothers you after prolonged and intense physical activity. The joints of the elbow and shoulder hurt, it is painful to lift and twist the arm, extension and flexion causes severe discomfort. The elbow area swells, turns red, and becomes hot. In the morning there is stiffness, but after 15-20 minutes the elbow releases. By evening, the pain may intensify.
Sometimes symptoms may disappear, but this is not a sign of recovery, but a short-term remission, after which, according to statistics, the condition worsens.
Advantages of the clinic
“Health Energy” is a multidisciplinary clinic with modern equipment and experienced staff. We are always aware of new developments in the field of treatment and prevention of diseases and offer our patients not only time-tested methods, but also modern, advanced methods.
Come to us if you need:
- fast and effective diagnostics;
- assistance from experienced doctors;
- an integrated approach to the treatment of diseases;
- comfortable conditions in the clinic;
- affordable prices for all medical services.
Osteoarthritis is a disease that begins gradually, develops slowly, but ultimately often leads to disability. Don’t let it change your life, sign up for a consultation with the orthopedists at Energy of Health.
Is disability issued for arthrosis, and in what cases?
According to the international classification of diseases ICD-10, arthrosis is assigned the code M15-M19. The patient is granted disability in several cases:
- if after surgery there are disturbances in the functioning of the joint that interfere with the patient’s normal functioning;
- when a person suffers from exacerbations more than three times a year;
- obvious impairment of the left or right hand.
This category of people is sent for a special examination. You will need to undergo it periodically; it is this that determines the disability group.