All joint diseases have a terrible prognosis because they lead to disability. A person cannot independently perform basic household tasks. Periarthritis of the elbow joint differs from other diseases in that only elements of the periarticular tissues are involved in the inflammatory process: the joint capsule, the synovial bursa, areas of tendons and muscles. With proper treatment of this disease, a person can remain healthy longer. But inflammation of the elbow joint with any mechanism of manifestation is extremely dangerous.
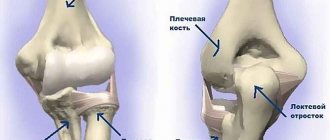
The structure of the elbow joint
Features of the development of periarthritis of the elbow
If once in a lifetime a diagnosis of periarthritis has been made, it will be a person’s companion for life, because... occurs chronically. Any provoking factor can cause an exacerbation. Therefore, the joint must be protected and attention should be paid to the slightest symptoms in order to prevent the development of the disease in time.
Periarthritis happens:
- Primary. As a result of fractures or ruptures of tendons and muscles.
- Secondary. Inflammation develops against the background of other diseases of the musculoskeletal system, chronic infections, and systemic autoimmune diseases.
Interesting fact! Statistical studies have shown that periarthritis of the elbow joint ranks second in frequency. And the first is inflammation of the soft tissues of the shoulder - the scapular joint.
If periarthritis is identified and treated promptly, serious disorders in the functioning of the joints can be avoided. If not, development will be like a snowball. First, a focus of inflammation will form in the tissue (possibly in both tendons and muscles), then salt deposits occur, collagen fibers merge (due to which they do not perform their functions), and infiltrates are formed. All this leads to malnutrition of the periarticular tissues, which causes their atrophy. These processes are accompanied by unpleasant symptoms that significantly reduce the quality of life.
Causes
One of the main reasons why periarthritis may begin to develop is inflammation in the areas where the ligaments connect to the bone. This is preceded by the appearance of microtraumas in the form of partial ruptures and sprains of the ligaments in the joint area. Any person can get such an injury by performing not only any forceful actions that damage the tendons. In some cases, it is enough to simply perform atypical work, which will affect the condition of these tissues.
In addition to injuries, the following factors may influence:
- Person's age . The lack of physical activity to maintain the general tone of the joint elements, together with the lack of preventive actions, weakens both the joints and the periarticular elements over the years, which leads to consequences.
- Frequent hypothermia . Exposure to low temperatures has the most negative effect on the development of inflammatory processes in various tissues and leads to disruption of their functions.
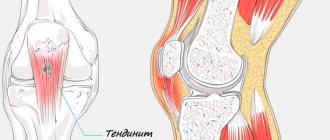
- Diseases of the periarticular elements . In the event of constant physical activity associated with the characteristics of a person’s life, the following diseases can become more active: bursitis (synovial cavities are affected), tendonitis (inflammation in the tendon fibers), fasciitis (a disease of the connective membrane)
- Lack of muscle nutrition . The flow of insufficient blood into the joint and its surrounding space provokes edematous processes and the further development of many pathologies.
Causes of elbow periarthritis
The causes of periarthritis are varied, but they all cause inflammation in the tissue, which occurs due to:
- Injuries or chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system
- Frequent hypothermia and being in a damp room. Any person has had colds. Some viruses and bacteria continue to circulate in the body, but due to the correct immune response, they do not cause harm. When hypothermia occurs, the immune defense decreases, the infection develops and is transmitted through the bloodstream to the joint tissue. Where trophism is already impaired due to vasospasm. All this leads to the formation of inflammatory reactions (redness, swelling, pain) and, as a result, periarthritis
- Diseases of one of the periarticular elements (bursitis, tendinitis, fasciitis) caused by other reasons
- Impaired blood flow. Poor circulation does not allow regular removal of metabolic products. This causes tissue swelling to form, which provokes the immune system to a false-inflammatory reaction.
- Systemic infectious diseases. Some infections spread massively throughout the body, forming foci. During the healing process, they may not be completely cured, but fall into a state of “hibernation.” And any provoking factor can “awaken” the infection.
Interesting fact! Periarthritis of the elbow is often called “tennis elbow” because 99% of tennis players suffer from inflammation of this joint.
First of all, those at risk are athletes and people whose professional activities involve regular stress on their elbows: tennis players, blacksmiths, painters. As a result of the load on the ligaments, micro tears regularly form, followed by inflammation. In this case, the presence of stress and the progression of the disease are directly related.
Elbow tendon tear
Elderly people are also at risk. The musculoskeletal and immune systems do not work so well, trophism is impaired. These factors can also cause periarthritis of the joint.
There are so-called indirect causes of periarthritis. One of them is considered to be endocrine disruptions, which can “confuse” and disrupt the functioning of the immune system.
Symptoms of elbow periarthritis
The following symptoms will help determine the inflammatory process of tendons and muscles in the elbow:
- Pain in the elbow area that spreads towards the hand and shoulder. Redness of the skin and an increase in the size of the joint. When bending and straightening the joint, the pain increases. Which leads to decreased movements.
- Swelling, which patients describe as “a constant feeling of tension in the elbow.” And difficulty in bending, as if the tissues were rubbing tightly against each other.
- On palpation, the pain intensifies, most of all in the area of the epicondyle. The doctor feels something like a cushion of water due to swelling. Sometimes lumps can be detected - these are inflamed and enlarged lymph nodes.
Pain in the elbow
The first symptoms of periarthritis should force the patient to consult a specialist. After all, the reasons for its development are not always clearly clear. The less advanced the process, the easier and faster the recovery will be. And if a systemic infection is detected during examination, early treatment will save a person’s life.
Note! Changes in weather can cause joint pain. The synovial fluid in the periarticular bursa reacts to changes in atmospheric pressure, which causes increased pain. This can also trigger the development of periarthritis.
Types and causes of periarthritis
The following clinical and pathomorphological forms of periarthritis are distinguished:
- Tendinitis is inflammation of the tendon;
- Tenosynovitis – inflammation of the tendon sheath;
- Bursitis is inflammation of the synovial bursa;
- Enthesopathy is inflammation of the attachment site of a ligament or tendon to a bone or joint capsule;
- Aponeurositis, fasciitis - damage to aponeuroses and fascia;
- Capsulitis is damage to the joint capsule.
The anatomical relationships of the periarticular structures are quite close. The pathological process can cover several anatomical formations adjacent to each other, be limited or spread to other parts of the tendon and its sheath, synovial bursae. The ligaments through which the tendons pass and the fibrous capsule of the joint itself may be affected primarily or secondarily. This severely limits its function.
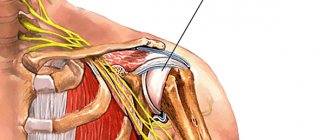
The structures of the joints of the upper extremities are most often affected. This is due to the variety of functions of the hand, which lead to almost constant tension in the tendons. In most cases, periarthritis is localized in the shoulder area, where the short rotators of the shoulder and biceps tendons are constantly exposed to high functional load in difficult conditions (the tendons pass through a narrow space). It is a common cause of tendoperiostitis of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles, tenosynovitis of the long head of the biceps muscle, and subacromial tendobursitis. Post-traumatic periarthritis can develop after damage to periarticular tissues during physical activity or sports.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis always begins with a survey, history taking and examination. The symptoms of periarthritis, arthritis and arthrosis are similar and can be confused. Especially if the stage has not started. Therefore, there is a comparison table:
| Criterion | Periarthritis | Arthritis | Arthrosis |
| Appearance of pain | Manifest when the patient independently makes movements with his hands and during palpation | Appear spontaneously, intensify during movements and palpation of tissue | Pain occurs with any movement, sudden pain is absent upon palpation |
| Swelling | Not significant | Diffuse, painful, without clear boundaries | No |
| External changes in joints | Absent | Not significantly expressed, occurs due to changes in muscles and ligaments | Expressed due to bone deformation |
| Isolated increase in tissue temperature over the joint | Sometimes, not much | Always, clearly expressed | Absent |
Comparison of arthritis and arthrosis
But additional examination methods will determine the stage of development and confirm the diagnosis. Also, some infectious diseases (acute or sluggish) can aggravate the course of periarthritis or be its cause. Therefore, it is important to determine the type of infection for subsequent comprehensive treatment. For this purpose, general and special laboratory tests are prescribed. Then an X-ray, ultrasound of the joint and MRI are prescribed. Which also helps with differential diagnosis.
Invasive methods (arthrography, arthroscopy) are prescribed only if the patient has an advanced stage of periarthritis, or a case that is not amenable to conservative treatment. In such cases, these examinations are needed for subsequent surgery.
Carrying out arthroscopy on the elbow joint
Treatment strategy
After the examination, the doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis and prescribes general treatment. Then the patient undergoes a comprehensive examination (tests, hardware examinations) to identify concomitant diseases that could provoke or may aggravate the course of periarthritis. And only after the examination the final tactics are determined.
Throughout the treatment, you need to create rest for the joint using a plaster cast or splint, this already reduces inflammation. These procedures are performed taking into account the possibility of edema development. Anti-inflammatory ointments and gels for external use are also prescribed.
It is important to know! If periarthritis is caused by injury, the probability of developing bursitis is 100%.
Medication tactics
The treatment of periarthritis necessarily includes anti-inflammatory and painkillers: meloxicam, ibuprofen (nurofen), diclofenac. If the pain does not decrease while taking these drugs, it is possible to perform a periarticular joint block. Using a syringe, anti-inflammatory drugs (kenalog or diprospan) are injected into the inflammation site. The result after the blockade is noticeable after 24 hours: pain and swelling decrease, mobility is restored.
Periarticular block of the elbow joint
Physiotherapy sessions
Once the inflammation around the joint and pain symptoms are relieved, the patient is prescribed restorative physical therapy, which includes:
- Massage. Reduces joint stiffness, restores range of motion and blood circulation in periarticular tissues after periarthritis.
- Magnet and laser therapy. Penetrates into the deep layers of tissue and helps reduce inflammation.
- Electrophoresis. Thanks to this method, it is possible to ensure rapid delivery of anti-inflammatory substances into the deep tissues of the joints. This ensures quick results and pain reduction.
- Hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches). Ideal for circulatory problems.
- Therapeutic baths improve the functioning of all joints, not just the elbows. They add sea salt without dyes and additives, and a decoction of pine needles.
- The procedure and duration of the course are prescribed by the doctor, based on the severity of the particular case.
Electrophoresis of the elbow joint
Folk remedies
All recommendations of traditional medicine should be taken in consultation with a doctor. And it is important to remember that curing periarthritis with traditional medicine recipes is impossible. They can be an addition to the main treatment of the joint, used to consolidate treatment and for preventive purposes. Substances included in compresses, rubbing and applications are able to penetrate deep tissues (the source of inflammation). Improves blood circulation and restoration of damaged tissues.
Cabbage leaves are considered highly popular for treating any joints. Cabbage that grows in late spring or summer is best, rather than one that has been sitting through the winter. The cabbage leaf needs to be mashed until the juice appears, then grease one surface of the leaf with honey and apply it to the joint, securing it with a bandage. After complete drying, the sheet is removed. You can finely chop a cabbage leaf, mix it with honey and apply the grounds to the joint, wrap the top with film and a bandage. Thanks to the film, heat will be concentrated around the joint, which also promotes healing.
Cabbage leaf compress
It is also recommended to use compresses for the treatment of periarthritis:
- With sea salt. A tablespoon of salt (white) is dissolved in 500 milliliters of warm water, and two drops of iodine are added. Moisten a piece of natural fabric and wrap it around the joint.
- Ready solution with bischofite. Sold in a pharmacy, ready-made. Contains large amounts of magnesium, iron, phosphorus and copper chlorides. Applies the same way.
- Medical bile solution. It is better to use it for the first time by diluting it with water.
Has a powerful anti-inflammatory and regenerative effect.
Similar compresses for joints are used for 10-15 days.
Therapeutic applications at home can be carried out using ozokerite or paraffin, which are sold in pharmacies. It is sold in bulk form, so before use you need to heat it in a water bath and then apply it to the joint.
Garlic balm for joints has proven itself well. You need to grind 2 cloves of garlic and one medium-sized lemon through a meat grinder. Mix with honey (200 milliliters). And drink one teaspoon 3 times a day.
All about symptoms and treatment.
With such an unpleasant problem as periarthritis, the symptoms manifest themselves as aching pain, their intensity increases with movement. Characterized by muscle tension in the area of the affected joint, the formation of swelling, causing partial immobility. A tactile examination reveals compactions and nodules - pressing on them is painful. In general, there are several forms of periarthritis: primary, acute, chronic.
With a diagnosis such as periarthritis of the elbow joint, treatment is carried out comprehensively: medication, hardware, hirudotherapy, acupuncture, acupressure (acupressure), traditional medicine, mud applications.
In the overwhelming majority, the list of such measures helps to achieve a significant improvement in the patient’s well-being. Therapy restores a person’s ability to work and returns him to a normal quality of life. A condition for achieving success is a timely visit to a specialist who will advise how to treat periarthritis.
The causes of the disease, the nature of the ailment, the presence of various concomitant diseases, the individual characteristics of the patient’s body - all this will be taken into account by the doctor when choosing a prescription for treating periarthritis in each specific case. The disease can last from a month to several years. Relapses are possible if periarthritis becomes chronic. That is why you cannot waste a minute, and at the first symptoms you should immediately seek help from qualified specialists.
This disease can be defeated if you follow the following treatment principles:
- Immobilization of injured fingers and hands (a gauze bandage is applied to the limb and fingers, which is not removed until obvious signs of the inflammatory process are eliminated);
- Surgical intervention (this method of treatment is used only if the disease is very advanced and the patient experiences severe aching pain in the damaged area);
- Treatment with medications and special medications (medicines can only be prescribed by a specialist; painkillers are mainly prescribed to relieve unpleasant aching sensations and anti-inflammatory drugs);
- Therapeutic exercise and physiotherapy of the injured limb and fingers (all kinds of physiotherapy will relieve pain and help reduce the inflammatory process, which ultimately will allow the patient not only to feel better, but also to be completely healed from the scourge);
- Treatment with folk remedies (decoctions of chamomile, plantain and mint, calendula tincture and even hirudotherapy will allow a person to feel relief).
Treatment of periarthritis of the fingers with traditional methods.
In folk medicine, herbal remedies based on herbal preparations, ointments, and compresses are mainly used to treat periarthritis. The conduct of each course is an individual matter and must be approved by the attending physician. As a rule, traditional medicine preparations have a restorative, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory effect, and improve metabolic processes and blood circulation.
An excellent therapeutic effect is achieved by rubbing methods and massages with decoctions of burdock root, chamomile flowers, plantain, St. John's wort, and nettle.
Gymnastics, exercise therapy
All doctors recommend starting to do joint exercises immediately after pain stops and inflammation stops. Regular exercise helps reduce swelling and stiffness of the joint, which always occurs after periarthritis. Allows you to increase the range of joint movements.
Gymnastics should be carried out in a warm room where there are no drafts. But we carried out ventilation in advance. Clothes chosen are loose-fitting and made from natural materials. When performing exercise therapy, you should not make sudden movements, bend over, or lift heavy objects. Classes need to be done every day. The main goal of therapeutic exercises is to gradually increase loads until the joints begin to fully function.
Rehabilitation exercises for the elbow joint
Here are a few exercises that can be performed both in the hospital and at home. But be sure to notify your doctor first and seek advice. All exercises are repeated 10 times, performed in a sitting position:
- Place your hands on your knees so that your palms touch the inner thighs. Then gradually, we “walk” with our palms along the legs and torso to the armpits and back.
- Extend your arms and lock them together. Alternately move the lock to the left and right shoulder.
- Place your palms on your shoulders and gradually, smoothly perform rotational movements.
- Place your palms on your knees and smoothly bend your torso towards your knees.
- Alternating hands, lift and lower in the following order: up, at the shoulder, to the heart, up, on the knee.
- Taking a light stick in one hand, straighten your hand, place it in the center and rotate for 10 seconds. Then we change hands.
There are many exercises, tactics, and proprietary programs. A FC and exercise therapy doctor will help you choose a suitable program and tell you how to carry it out correctly.
Prevention of periarthritis
There are several recommendations to prevent the occurrence of inflammation in the area of periarticular tissues:
- Correctly calculate the intensity of loads during training.
- Avoid hypothermia and prolonged stay in damp rooms.
- In the gym, avoid frequent and excessive same loads.
- Try to avoid any injuries, big or small.
- If you have chronic infectious diseases, undergo preventive examination and treatment in a timely manner.
People whose work involves stress on the elbow joints will not be able to perform these points. Here you can help your joints in another way: wear an elastic bandage or a fixing bandage to reduce the load on the joint. In your free time, ensure complete rest and undergo regular massage. If the first signs of pain or stiffness appear, do not delay, but seek medical help and begin treatment.
Elbow bandage to reduce stress on the joint
It is important to know. Any inflammation is dangerous because it causes irreversible changes in tissues. As a result, full functioning of the joint is not possible and the person becomes disabled.
Treatment of periarthritis
When choosing the appropriate treatment, the doctor must take into account the presence of concomitant diseases and various health features of your body that affect the course of the disease.
Periarthritis (periarthrosis) of the elbow joint is also called tennis players' disease, since constant work of the hand and elbow joint often leads to the development of this disease.
An x-ray usually helps to identify the onset of periarthritis of the elbow joint, which clearly shows the changes that have occurred in the joint and the tissues around it. The image may show swelling of the tissues of the joint and its bursa, which indicates the beginning of the inflammatory process in the elbow area.
When diagnosing periarthritis of the joint, the doctor prescribes the necessary course of treatment. Treatment for hyperarthritis should be varied. Usually a complex treatment is prescribed, which includes taking medications to reduce pain and relieve internal inflammation that has arisen in the joint capsule or periarticular tissues, conducting a course of physiotherapy, massage, acupuncture, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, using various anti-inflammatory ointments, and mud bath treatment. , shock wave therapy.
Treatment of periarthritis begins with the fact that the diseased area must be immobilized and all stress on it must be reduced as much as possible. To do this, you can use a plaster cast on which the arm is placed, thereby preventing all its movements. In serious cases, a plaster splint is used, which fixes the elbow joint and promotes the gradual healing of its tissues.
Next, anti-inflammatory ointments are prescribed, which reduce pain and help restore the functioning of periarticular tissues. The ointment is used throughout the treatment of periarthritis. If necessary, you can change the ointment after some time. For persistent pain in the joint, steroidal anti-inflammatory hormones are used, which are injected directly into the affected area.
Elbow periarthritis is accompanied by the development of elbow bursitis - inflammation of the periarticular bursa, where the main tendons of the arm are attached and which allows movement of the shoulder joint and hand. Inflammation of the joint capsule usually occurs due to injury; it increases in size and causes swelling and injury to adjacent tissues.
Unlike periarthritis of the shoulder, which can develop as a result of dysfunction of the cervical-scapular apparatus, periarthritis of the shoulder or elbow joint is rarely associated with dysfunction of the skeleton.