Goals of drug treatment Drugs for effective treatment of osteochondrosis: release form What drugs should be taken for osteochondrosis?
Conservative treatment of osteochondrosis includes various therapeutic measures - from massage and diet to therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy. All of them help improve the patient’s condition and prevent the development of complications. But the leading method has been and remains the use of pharmaceutical drugs for osteochondrosis.
Drugs for osteochondrosis are the main way to combat the disease.
Description of the drug and its properties
Doctors prescribe it for any stage of osteochondrosis.
It is also quite effective in cases of advanced disease in various locations. Mexidol is an antioxidant and antihypoxant (increases the body's resistance to lack of oxygen metabolism). The active ingredient is ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate. The component removes unstable oxygen molecules and increases the immune response to pathogenetic factors.
Mexidol is used to treat cerebral circulatory problems, which may cause cervical osteochondrosis. The side effects of Mexidol are minor.
Pharmacological properties of the drug:
- improvement of enzyme activity;
- an increase in the amount of dopamine in brain cells;
- activation of the movement of lymph and blood in the blood vessels of the microvasculature;
- reducing viscosity and increasing the fluidity of membrane shells;
- normalization of lipid-protein bonds;
- platelet fusion;
- restoration of normal myocardial contractility.
The active substance is highly absorbent, so it quickly combines with the protein components of the plasma, and then penetrates into tissues and organs.
Mexidol is a drug with a diverse mechanism of action. Its main effect is considered to be the fight against free radicals - reactive oxygen species that destroy body cells. Other mechanisms of the therapeutic effect of the drug are:
- increasing energy production;
- stimulation of blood flow;
- increasing the survival of nerve cells under conditions of oxygen starvation;
- acceleration of impulse transmission through nerve cells;
- normalization of metabolism.
The medicine is available in tablet form of 125 mg and in the form of a solution of 2 and 5 ml, which is administered intravenously or into the muscle.
Mexidol is widely used for diseases of the cardiovascular and nervous systems. It has few contraindications: kidney and liver dysfunction, childhood, pregnancy, lactation, individual intolerance.
Contraindications
The drug Mexidol is prescribed in the following cases:
- treatment and prevention of acute and chronic circulatory disorders in the brain;
- rehabilitation after head injuries;
- non-inflammatory brain diseases;
- dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system;
- disorders, diseases of the nervous system, stress conditions;
- complex therapy of coronary heart disease and chronic arterial disease of the elastic and muscular-elastic type;
- poisoning with various kinds of toxins, antipsychotic drugs;
- withdrawal syndrome;
- a group of eye diseases in which intraocular pressure constantly or periodically increases;
- pancreatitis.
A less common indication for use is the prevention of pathologies arising from constant extreme stress.
Indications for the use of the drug Mydocalm are:
- an inflammatory disease in which the mobility of the spinal column decreases;
- chronic disease of the spine, causing deformation of the vertebrae due to the proliferation of bone tissue;
- pain in the cervical spine, lower part of the head and muscle girdle of the shoulders;
- spastic cerebral palsy;
- pathologically increased tone of the striated muscles, resulting from the action of organic neurological diseases;
- rehabilitation treatment after traumatological and orthopedic operations.
When using Mydocalm as part of combination therapy, other indications for use are possible.
The drug Mexidol has the following contraindications:
- age up to 14 years;
- period of pregnancy and lactation;
- disorders of the kidneys, inflammatory diseases of the excretory system;
- hepatitis and other liver diseases;
- high blood pressure;
- asthma.
Mydocalm cannot be used under the following conditions:
- period of pregnancy and lactation;
- severe myasthenia;
- hypersensitivity to one of the components of the drug;
- children under 1 year;
- hypotension.
When taking the medicine during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Indications for its use are:
- the presence of a constant low-frequency squeak in the ears (tinnitus);
- frequent dizziness;
- constant headache caused by pinched nerve endings in the spinal column;
- visual artifacts due to osteochondrosis (spots, blurred vision);
- severe pain symptoms;
- severe dystrophic, degenerative and inflammatory process in the spinal column;
- brain hypoxia caused by muscle spasms in the cervical spine and compression (squeezing) of the vertebral arteries;
- disruption of the metabolic process in the tissues of the spine.
In addition, Mexidol is recommended for use for paresthesia in the fingertips, memory impairment and coordination of movements.
Mexidol is a fairly effective drug, which is extremely rarely accompanied by negative consequences, especially when compared with the effects of muscle relaxants and glucocorticosteroids.
However, it is not recommended to take Mexidol during pregnancy and breastfeeding, since no studies have been conducted in this group of patients for the presence of side effects.
It is prescribed to children with extreme caution; if it is possible to avoid its use, then this should be done. You should not take Mexidol if you are prone to allergic reactions, as well as with renal and liver failure.
How should you take the drug? Optimal dose and duration of treatment
Mexidol relatively recently entered protocols for the treatment of osteochondrosis and therefore many still have no idea about its pharmacological properties. You ask. What is this drug for? I answer. To participate in the complex treatment of advanced forms of osteochondrosis.
Mexidol is used when it is urgently necessary to localize inflammation of cartilage and bone tissue, when there are clear signs of impaired blood flow and metabolism in the body. For example, when pathology develops in the neck area, the drug eliminates hypoxia of neighboring tissues.
The same effect is achieved in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar and thoracic spine. The pharmacological effect is exerted on all affected areas of the spinal column, regardless of the stage and degree of the disease.
The main component of the drug, ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate, enters the bloodstream, neutralizes free radicals that arise during inflammation, and promotes the rapid removal of breakdown products from the body.
Doctors prescribe treatment with Mexidol in the following cases:
- with dizziness and frequent headaches of a spastic nature;
- in the presence of pronounced pain syndrome;
- in the presence of dystrophic and degenerative disorders in the segments of the spinal column, in particular when a spinal hernia is detected;
- with inflammatory processes in the vertebral region;
- for muscle spasms in the neck and chest area.
As can be seen from the long list, there are quite a lot of indications for the use of Mexidol.
Despite the fact that taking this medication is extremely rarely accompanied by complications and side effects, it is not recommended to prescribe Mexidol yourself. Can Mexidol be used in the presence of systemic diseases, kidney problems and other serious pathologies.
In this case, you need to contact a neurologist for an answer. A comprehensive examination of the body will allow you to choose an acceptable course of treatment and select the correct dosage of the treatment component. The only restriction for taking the drug may be pregnancy and breastfeeding.
You should not exaggerate the situation, read reviews of patients who, after taking the medicine, constantly felt sick, felt worse and experienced hair loss. In most cases, this is a natural reaction of the body to the abundance of medications taken during the treatment of osteochondrosis.
Tablets can have the desired effect in the initial stages of the disease. The patient is recommended to take 1-2 tablets twice a day. How to take the drug when it comes to an advanced form of osteochondrosis.
A liquid form of the drug is provided, especially for intravenous infusions and intramuscular injections. As a rule, this method of administering medications is used for cervical osteochondrosis, when it is necessary to quickly bring blood vessels back to normal.
Do you still think that it is impossible to cure your joints?
Judging by the fact that you are now reading these lines, victory in the fight against inflammation of cartilage tissue is not yet on your side...
Have you already thought about inpatient treatment? This is understandable, because joint pain is a very dangerous symptom, which, if not treated in a timely manner, can result in limited mobility. Suspicious crunching, stiffness after a night's rest, the skin around the problem area is stretched, swelling in the sore spot... All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand.
What rules should you follow if you have been prescribed hormone injections into a joint?
If you cannot do without hormone injections, remember this:
- Keep a break of at least 2 weeks between injections. The drug does not start working instantly, so you need to wait a while for the doctor to evaluate its effectiveness.
- Remember that the first injection is the most effective. If there is no relief after the first injection, avoid repeated injections in the same place. It would be more correct to change the injection site or choose a different drug.
- You should not give hormone injections to one knee more than 4-5 times, as the risk of complications increases. Each time, the likelihood of needle injury, infection, or ligament damage increases.
Hormone injections are a last resort for arthrosis
In the video you will see how a synovial fluid prosthesis is injected into the knee joint in a medical office:
Side effects and overdose
In most cases, the use of Mexidol occurs without any adverse reactions, but they can still occur. This phenomenon can happen due to non-compliance with the doctor's instructions and prolonged use.
The following manifestations are possible:
- thirst;
- dry mouth;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dysfunction of the digestive system;
- bloating and gas formation;
- flatulence;
- dizziness;
- darkening of the eyes;
- tinnitus;
- allergic reactions.
The symptoms of an overdose of Mexidol are not precisely known; when consuming a large amount of the drug, it may be accompanied by the symptoms described above, which are more intense. The patient becomes lethargic, drowsy, performance deteriorates, apathy appears, and blood pressure rarely increases.
Both dosage forms of Mexidol are well tolerated by the body. Side effects when taking them are extremely rare. Experts often associate their appearance with the consequences of long-term or improper use of the drug. Most often, when using these drugs, patients complain of the following symptoms:
- dry mouth and thirst;
- nausea;
- dyspepsia;
- gas formation.
If there is intolerance to certain components of the dosage forms, allergic reactions may occur in the form of rash, redness, and swelling. When administering the drug in the form of an injection solution, an unpleasant taste in the mouth, a feeling of constriction in the throat, incomplete breathing, and palpitations may occur. The discomfort disappears a few seconds after the injection.
There are no known cases of overdose with Mexidol. If recommended doses are exceeded many times, symptoms characteristic of side effects may appear. Their intensity may be higher. Also, while taking increased doses of the drug, patients experience lethargy, apathy, and increased drowsiness. In rare cases, surges in blood pressure are recorded.
We advise you to study - Remedies for chondrosis
How to increase the effectiveness of treatment: useful tips
Visiting the treatment room and taking pills is not enough. You should show interest in your own body and start doing physical therapy.
Proper organization of the sleeping area is also important: you need to sleep on a rigid base. It is optimal to choose an orthopedic mattress and pillow.
If you have to work in a static position, every 1-2 hours you need to do a light warm-up, using muscles that are stiff or constantly tense.
You need to pay close attention to your workplace - the height of the table and chair should correspond to your height as much as possible.
It's good to swim in the pool - it will help activate all the muscles and ligaments of the spine and increase blood circulation.
Regularly update your diet to ensure it contains all the minerals and vitamins a person needs.
Compatibility of Mexidol and Mydocalm
Mexidol and Mydocalm have the same active substance, and therefore their simultaneous use allows you to develop a synergistic effect, and this will enhance the effect on the desired area in the body.
Taking these drugs simultaneously improves the transport of oxygen through the blood vessels to the brain area.
The combined use of drugs will not have any negative effects on the body, but will only make the treatment more effective.
These drugs have low toxicity, and therefore the occurrence of side effects when using them is rare. However, in some cases the following may occur:
- nausea, vomiting;
- pain in the stomach;
- spastic pain;
- bloating;
- constipation, diarrhea;
- allergic reactions;
- headache;
- erythematous rash.
Mexidol is quite compatible with certain groups of medications that are used for complex treatment of osteochondrosis. While taking Mexidol, it is necessary to use anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs (Diclogen, Ortofen, Ibuprofen, etc.) that stop the inflammatory process.
Step-by-step therapy, in addition to antioxidants, which include Mexidol, requires taking vitamin preparations (Kombilipen, Milgamma, Neuromultivit, etc.).
Therapy involves taking painkillers (Revalgin, Baralgin, Analgin, etc.), muscle relaxants (Mydocalma, Sirdaluda, Tizanil, etc.), as well as venotonics (Pentoxifylline, Actovegin, Trental, etc.).
The new generation antioxidant combines well with painkillers, such as Paracetamol. However, it is not recommended to combine Mexidol with the drug Ketanov, since there is a high risk of developing side effects from the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, a good combination of the drug is observed when taken simultaneously with Mydocalm.
How to measure your B vitamin levels?
A deficiency of B vitamins can occur due to a number of reasons:
- nutritional deficiencies due to a strict vegetarian diet;
- problems with the absorption of vitamins in the intestines due to atrophy of the mucous membrane or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- helminthiasis;
- Smoking and alcohol also reduce the level of B vitamins in the body.
You can measure your vitamin B12 and vitamin D levels with a simple blood test. A referral for this test can be issued by a physician, or the patient can do it independently at any medical clinic in St. Petersburg that provides laboratory testing services.
How to use for cervical osteochondrosis?
The medicine can be used in the early stages of the pathology in the form of tablets, and in the form of injections in later stages.
Pills
Use 1-2 tablets once or twice a day. Gradually, depending on the severity of the therapeutic effect, the dosage may be increased at the discretion of the attending physician. But it should not be more than 800 mg per day, which corresponds to 6 tablets.
Injections
It can be administered either with a syringe or with a dropper; it can be administered into a vein or into a muscle. For drip administration, you need to prepare a solution in 0.9% sodium chloride. The composition is administered in a stream for 5-7 minutes, with drip administration - 1 drop per second, or slower. Maximum daily dosage (therapeutic) 1200 mg.
For osteochondrosis, such a drug in the form of injections is prescribed only in the presence of severe circulatory disorders (in combination with other methods). In this case, the nature of the dosage is as follows:
- The first two weeks it is administered intravenously as a dropper, 200-500 ml one-time, at least 2 and no more than 4 times a day;
- Then, for 14 days, 250 mg intramuscularly through a syringe 2-3 times a day.
Therapy with this solution is carried out in a hospital setting.
Dosage regimen
The dosage of the drug is determined not only by the degree of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs and associated complications, but also by the characteristics of the pathological process (stage of subcompensation or decompensation). The scheme for using Mexidol in the stage of decompensation (when positive dynamics cannot be achieved despite competent and timely drug correction) is shown in the table below.
Table. Dosage of Mexidol for acute osteochondrosis
| Form of application | Dosage |
| Intramuscular injections | 1 ampoule per day for 7-10 days. |
| Intravenous injections | 1-2 ampoules per day. When using a jet infusion, the infusion time should be at least 5-7 minutes. The course of treatment is 3-10 days. |
| Infusion drip (droppers) | 2 ampoules (diluted with 200 ml of isotonic saline solution with a salt concentration of 0.9%). The recommended duration of treatment is 3-5 days. The infusion rate is 60 drops per minute. After this period, the patient should be transferred to oral dosage forms or intramuscular injections. |
| Pills | 150-450 mg per day. The minimum duration of therapy is 2 weeks. |
For complex treatment of subcompensated pain syndrome, Mexidol is used in the form of injections 2 times a day, 1-2 mg ampoules. The drug in tablet form is usually prescribed in a dosage of 125-250 mg 2-3 times a day. The duration of therapy depends on the degree of hypoxia and existing complications and is determined individually.
Side effects
Mexidol is a fairly strong drug that has a pronounced effect on the body. It has a number of side effects, if detected, the patient should immediately consult a doctor.
- Drowsiness with prolonged use in large dosages;
- Allergic reaction or individual intolerance;
- Nausea;
- Dryness of the mucous membranes in the mouth.
The presence of side effects is not always a reason to discontinue the drug - the question of the advisability of continuing treatment with it is decided by the doctor individually in each specific case. If withdrawal does not occur, then side effects are eliminated symptomatically.
In case of overdose, increased drowsiness may develop. The consequences are eliminated by gastric lavage.
This effect of the drug is especially relevant for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar region, where inflammatory, dystrophic and degenerative processes are most severe. In the case of treating the cervical spine, the drug is useful because it has an antihypoxic effect.
Simply put, it increases tissue resistance to oxygen deficiency. This is especially true, since such a deficiency often occurs against the background of cervical osteochondrosis. In this case, the posterior parts of the brain are affected, which manifests itself as dizziness and impaired coordination of movements.
Mexidol has a certain effectiveness in terms of improving cognitive functions (memory, attentiveness, speed of decision-making). This is also useful for osteochondrosis, since these functions are affected in most patients (if the cervical spine is affected).
Mexidol tablets
Mexidol can be used in the treatment of osteochondrosis of any location. In particular, it can be used for combined diseases (for example, cervicothoracic) and generalized (when all segments of the spine are affected at once).
It should be used if you have the following symptoms:
- Frequent dizziness.
- Chronic cervicogenic headaches or tension headaches.
- The presence of visual artifacts due to neck disease (floaters, lightning, and blurred vision).
- Presence of tinnitus (low-frequency constant squeaking in the ears).
- Severe painful syndrome (in this case, Mexidol is used infrequently, and as an auxiliary therapy, since in itself it gives little analgesic effect).
- Severe inflammatory, degenerative or dystrophic processes in the tissues of the spine.
- Oxygen starvation of the brain (hypoxia), due to persistent spasm of the neck muscles or due to compression (squeezing) of the vertebral arteries by the vertebrae.
- Disorders of trophism and metabolic processes (metabolism) in the tissues of the spinal column.
- The patient has cognitive and mnestic disorders (attacks of depersonalization, memory impairment, impaired coordination of movements, unsteadiness of gait).
- Frequent paresthesia (feeling of numbness).
When else is the product used?
Thoracic osteochondrosis is the rarest form of the disease. However, Mexidol is also prescribed for its treatment. Only the attending physician can prescribe the drug, as well as prescribe the recommended dosage. "Mexidol" for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region has been taken for a long time and is effective.
The medicine will also help in the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis. In this case, both tablets and injections may be prescribed.
You can inject if you do not have:
- severe deformation of the spine, which immediately excludes any possibility of a blockade;
- skin diseases at the site of exposure;
- allergy to active components.
Osteochondrosis also causes neurological symptoms, which Mexidol will help to cope with. The product is used for the following problems:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- epilepsy attacks;
- autonomic disorders;
- atherosclerosis in the vessels of the head;
- peripheral neuropathy.
Attention! Despite the positive effect of Mexidol on the human body, mandatory consultation with a specialist is necessary before using it. An excellent way to get rid of pain and maintain muscle tone will be tips from Alexandra Bonina
An excellent way to get rid of pain and maintain muscle tone will be advice from Alexandra Bonina.
By the way, if you want to get a step-by-step plan for eliminating pain and pinching in the cervical spine, then go to this page right now.
There you will find a free training course that will help you get rid of these problems once and for all at home.
Denial of responsibility
The information in the articles is for general information purposes only and should not be used for self-diagnosis of health problems or for therapeutic purposes. This article is not a substitute for medical advice from a doctor (neurologist, therapist). Please consult your doctor first to know the exact cause of your health problem.
To study Lordosis of the cervical spine - treatment
I will be very grateful to you if you click on one of the buttons and share this material with your friends
By the way, if you want to get a step-by-step plan for eliminating pain and pinching in the cervical spine, then go to this page right now.
There you will find a free training course that will help you get rid of these problems once and for all at home.
Pharmacological action of the drug
- Reduces the viscosity of the membrane shell.
- Normalizes protein-lipid bonds.
- Increases enzyme activity.
- Increases the concentration of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the brain.
- Stimulates blood circulation.
- Restores contractility of the middle layer of the heart.
- Has a reducing effect on platelet fusion.
The retention period of Mexidol in the human body is 5 hours from the moment of ingestion. The medicine quickly penetrates the tissues due to the high absorption of the active substance.
Release forms
Mexidol is available in the form of tablets and injection solutions.
- Tablet form - 1 piece contains 125 mg of the active ingredient. The package contains 50 tablets.
- Ampoules 5% - in packages of 5, 10, 20, 50 pieces, volume - 2 ml, 5 ml. One ampoule contains 50 mg of active substance.
What is more effective?
In cases of timely detection of pathologies in the neck area, injections are not required. Taking Mexidol tablets is enough.
How to use
The instructions indicate recommended dosages. The doctor draws up a course of treatment based on the stage of cervical osteochondrosis. It is advisable to use injection forms due to high bioavailability.
We advise you to study - “Nimesil”: reviews for osteochondrosis
Chronic course. Injections for 10 days (1 r./day, 200 mg), tablets – 5 days (3 r./day). Prescribed in droppers for acute hypoxia.
Important information
Mexidol is not recommended for use in pregnant women, during lactation and in childhood.
An absolute contraindication is the presence of intolerance to the components of the drug, liver and kidney pathologies.
Nausea, vomiting, skin rash, and dizziness are rarely observed.
Mexidol affects brain function by increasing dopamine levels. By supplying blood to cells, anxiety, depression, and fears that accompany osteochondrosis are eliminated.
Indicated use for restoring sleep and increasing performance. Mexidol increases stress resistance and calms.
The drug is often prescribed for encephalopathy, vascular atherosclerosis, VSD, intoxication with alcohol, psychotropics, and after a head injury.
Analogs
There are many analogs of Mexidol that cost less.
Structural: Mexifin, Neurox, Mexiprim.
Mexidol is most often prescribed for advanced stages of osteochondrosis, when metabolic and blood flow disorders are most pronounced. In addition, Mexidol has a strong antioxidant effect, so its use is justified in cases of degenerative processes in the vertebrae for the export of half-life products.
A certain effectiveness of Mexidol is observed in terms of improving attentiveness, memory and reaction speed in patients undergoing treatment with this drug.
It is important to consider that Mexidol is most effective in complex treatment, which is especially important for cervical osteochondrosis.
Mexidol for osteochondrosis. What should you know about this drug?
Osteochondrosis and its complications require an integrated approach to treatment. Often, drugs that were developed for completely different diseases are effective. An example of such drugs is Mexidol.
Brief description of Mexidol
Mexidol is a drug with a diverse mechanism of action. Its main effect is considered to be the fight against free radicals - reactive oxygen species that destroy body cells. Other mechanisms of the therapeutic effect of the drug are:
- increasing energy production;
- stimulation of blood flow;
- increasing the survival of nerve cells under conditions of oxygen starvation;
- acceleration of impulse transmission through nerve cells;
- normalization of metabolism.
The medicine is available in tablet form of 125 mg and in the form of a solution of 2 and 5 ml, which is administered intravenously or into the muscle.
Mexidol is widely used for diseases of the cardiovascular and nervous systems. It has few contraindications: kidney and liver dysfunction, childhood, pregnancy, lactation, individual intolerance.
Mexidol for osteochondrosis
It should be noted that you will not find such an indication as “osteochondrosis” in the instructions for use of the drug. The fact is that Mexidol does not directly affect the musculoskeletal system. Its action in cases of spinal pathology is realized in three directions:
- Improving the nutrition of spinal cartilage tissue. This allows the cartilage to recover faster and also improves the delivery of other medications to it.
- Restoration of peripheral nerves. A common complication of osteochondrosis is radiculopathy - disruption of the nerve roots extending from the spinal cord. This occurs against the background of their compression by the vertebrae or a herniated disc. Mexidol stimulates the conduction of nerve impulses, so even a pinched nerve retains its function for a long time. The same mechanism is triggered during the development of myelopathy – compression of the spinal cord by intervertebral hernias.
- Normalization of cerebral circulation. This mechanism is relevant in the case of compression of the vertebral arteries by bone or cartilage structures. Against this background, it is even possible to develop a stroke - the death of some brain cells with reduced blood supply. Mexidol improves blood flow and makes cells more resistant to adverse factors, preventing the dangerous consequences of cervical osteochondrosis.
Treatment regimens for osteochondrosis with Mexidol vary greatly: it all depends on the stage of the disease, the severity of symptoms, and the general condition of the body.
In acute conditions, the course begins with droppers or intravenous injections - 5 ml of solution is administered. For less severe symptoms, use intramuscular injections.
The course of injections is 5-15 days, then switch to tablets of 125 mg 2-3 times a day for 1-3 months.
Mexidol is usually combined with other drugs: milgamma, neuromidin, actovegin and painkillers.
Mexidol for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
For pathology of the cervical spine, the medicine is prescribed if there are signs of cervical radiculopathy:
- numbness, tingling, burning in the fingers;
- weakness in the arms;
- atrophy of the muscles of the upper limbs.
Another indication for prescribing the drug is signs of cerebrovascular accident due to compression of the vertebral arteries:
- dizziness, nausea, lack of coordination, which intensifies when turning or tilting the head;
- headache;
- blurred vision with certain neck movements.
For radiculopathy, treatment can begin with intramuscular injections; if blood flow in the brain decreases, intravenous administration of the drug is optimal.
Mexidol for lumbar osteochondrosis
Indications for prescribing medication for lumbar osteochondrosis are the phenomena of lumbar radiculopathy and myelopathy:
- numbness, burning, discomfort in the legs;
- weakness and atrophy of the muscles of the lower extremities;
- disturbance of the passage of urine and feces.
In such a situation, treatment usually begins with intravenous injections.
Feedback from patients mostly boils down to the fact that Mexidol helps better with cervical osteochondrosis than with lumbar osteochondrosis. This is due to two factors.
Firstly, the drug has a good effect on cerebral blood flow, which is only relevant for pathology of the cervical spine.
Secondly, the nerve roots at the cervical level are much thinner than the lumbar ones, and it is easier to restore their function than to improve the functioning of the more massive nerve fibers of the lumbar region.
Research results
The diagnosis of RCC was made in both groups based on a detailed history and thorough neurological examination. It should be noted that in the OG in 19 (17.3%) patients the disease was detected for the first time, in the remaining 91 (82.7%) - again, in the GS - 14 (14.7%) and 81 (85.3%) respectively. Almost all those who applied for inpatient care underwent a course of outpatient treatment, which either did not give a positive result, or the expected effect was incomplete. Since all patients in the compared groups experienced pain to one degree or another, much attention was paid to assessing the regression of pain. The simplest and most informative test for quantitative assessment of pain perception, according to a number of researchers [4], is the visual analogue scale (VAS), which is a straight line segment 10 cm long, where the starting point (zero) corresponds to the absence of pain, and the ending point ( ten) – unbearable pain. The patient was asked to depict the intensity of the pain experienced daily during the entire examination period, which made it possible to assess the dynamics of the patient’s perception of his pain and the effectiveness of the therapy. In the GS, severe pain syndrome (7–10 points) was observed in 29.4% of patients, moderate intensity (4–6 points) – in 53.6%, moderate intensity (1–3 points) – in 16.8% of cases (28 , 51 and 16 people respectively). In the OG the same indicators were distributed as follows: 7–10 points – 26.4% (29), 4–6 points – 51.8% (57) and 1–3 points – 21.8% (24). After completing the course of treatment, when assessing the pain syndrome in the MG, a decrease in pain by 5 or more points was noted in 48 (43.6%) patients, a decrease by 1–4 points – in 62 (56.4%). In the GS, a decrease of 5 points or more was observed in 8 (8.4%) patients, by 1–4 points – in 48 (50.5%), without dynamics – in 38 (40%), increased pain was noted in 1 ( 1.05%) case. Thus, when carrying out complex therapy using Mexidol, the results in reducing the intensity of pain in the MG are much more optimistic than in the GS.
The dynamics of pain intensity reduction during treatment are shown in Fig. 1a, b, which shows that in the MG the greatest rate of pain reduction occurs from the 10th to the 20th day of treatment, and by the day of discharge (25–30th day) in more than 50% of patients the pain syndrome is completely relieved, in others it becomes moderate, requiring the use of painkillers only periodically. In the GS (Fig. 1b) a regression of the pain syndrome is also observed, but less significant than in the OG. By the time the course of treatment is completed, patients (51.6%) with moderate pain syndrome predominate in the GS, but the number of people with pain of moderate intensity, requiring constant use of painkillers, remains significant (25.3%).
In patients with RCC in the compared groups, before treatment, various neurological symptoms were revealed in the form of anisoreflexia, tension symptoms (Lasega, Nery, Dejerine, Bonnet, Wasserman, Sicard), changes in the statics and dynamics of the spine, muscular-tonic syndrome, loss of sensitivity in the corresponding dermatomes, vegetative - trophic disorders (dry skin, thinning hair on the lower extremities, hyperkeratosis of the feet); in some cases, a decrease in strength in certain muscle groups was noted.
The vast majority of patients: 92 (83.6%) in the OG and 88 (92.6%) in the GS had unilateral lesions, 18 (16.4%) and 7 (7.4%) people, respectively, had bilateral lesions. Assessing the dynamics of clinical symptoms in both groups, it should be noted that in the OG, all patients, except one, underwent a reverse development of muscular-tonic syndrome, while in the GS - only 6 (33.3%) out of 18; In 72 (69.2%) patients with OG, tension symptoms were relieved, in GS - only in 11 (11.6%). Dynamics were observed in the reflex sphere: recovery (complete or partial) was registered in the OG in 40 (42.6%) patients, in the GS – in 14 (16.3%). No dynamics were noted in the remaining patients. Positive dynamics in the restoration of sensitivity took place in the OG in 36 (36.7%) patients, in the GS – in 13 (14.6%); muscle strength in the OG in 5 (21.7%) patients, in the GS – in 1 (6.3%). No negative dynamics were noted. Thus, the most significant regression of neurological deficit was achieved in the MG, especially in relation to muscular-tonic syndrome and tension symptoms, which, together with pain, cause the greatest suffering to patients.
In addition, it should be noted that the restoration of reflexes and sensitivity is faster than in GS, which may indicate a decrease in inflammatory and hypoxic disorders in the root and peripheral nerves, a decrease in edema, as well as the beginning of remyelination processes. In the OG, a positive trend was noted in the restoration of motor activity in patients with distal paresis: in 5 (21.7%) - complete recovery, in the remaining 18 (78.3%) - positive dynamics; in GS – complete recovery in 1 (6.2%) patient, positive dynamics – in 4 (25%) patients, without dynamics – in 11 (68.8%). It should be noted that complete recovery was recorded among patients with initially mild paresis (3.5–4.5 points) and a relatively short duration of the disease (up to 6 months). When subjectively assessing the effectiveness of treatment in the OG, 108 (98.2%) patients noted “improvement”, in the GS – 37 (38.9%).
Data from the Roland-Morris questionnaire “Pain in the lower back and impairment of life activity” before treatment revealed a pronounced disturbance in all aspects of the patients’ life activity, especially active movement outside the home and the emotional and mental sphere, sleep. The total number of points in patients was 11.6 ± 0.4 in POG-1; in PGS-1 – 11.3 ± 0.6; in POG-2 – 13.2 ± 0.9 and in PGS-2 – 14.2 ± 0.8. The presence of distal paresis significantly worsened many aspects of daily life of patients (p < 0.05). After treatment, the average values of the total number of points in patients were in POG-1 – 6.8 ± 0.3; in PGS-1 – 9.6 ± 0.8; in POG-2 – 8.1 ± 0.5 and in PGS-2 – 11.9 ± 0.6. In the MG subgroups, the differences between the indicators before and after treatment were significant (p < 0.001). In GS, improvement (p < 0.05) was achieved after treatment only in PGS-2. Complex treatment including Mexidol had a positive effect on restoring sleep and reducing emotional experiences; the refusal of external support was especially convincing in 13 (56.5%) POG-2 patients, which indicated a significant improvement in motor function.
To objectively assess the rate of loss of self-care ability using the Scale for Assessing the Adaptive Status of Patients with Spinal Pathology, the degree of maladaptation (DM) was calculated, which before treatment in POG-2 was 37.6 ± 2.2%, in PGS-2 – 36.8 ± 1 .8%, in POG-1 – 22.4 ± 1.2%, in PGS-1 – 24.2 ± 1.4%. Differences between subgroups within groups were significant (p < 0.001). After treatment, a more significant decrease in DM was found among patients in the OG: in POG-1 – by 80.4%, in PGS-1 – by 47.1%; in patients with paresis: in POG-2 – by 37.8%, in PGS-2 – only by 15.2%. DM decreased significantly (p < 0.001) among patients POG-1, POG-2 and PGS-1; in PGS-2 it was not possible to achieve a significant reduction (p > 0.05). The results of therapy were assessed by the effectiveness coefficient of the treatment performed. Excellent results were observed only in POG-1. In general, patients in the groups had good and satisfactory treatment results, with a clear predominance of good scores in the OG (Fig. 2). Unsatisfactory results in PGS-2 exceeded 30%.
According to X-ray examination and MRI, all patients in both groups showed signs of spinal osteochondrosis, spondylosis and spondyloarthrosis (from 1-2 vertebrae to complete damage to the lumbosacral region). Schmorl's hernias were diagnosed in 9 (4.4%) cases, in 1 patient multiple; In 100% of cases, intervertebral posterior protrusions and (or) hernias were detected: in 28 (13.7%) - median, in 147 (71.7%) - paramedian, in 30 (14.6%) - lateral, incl. including multiple in 25 (12.2%) patients. The localization of protrusions and hernias was as follows: in 128 (62.4%) patients at the levels L5–S1, in 71 (34.6%) – L4–L5, in 4 (1.95%) – L3–L4, one each (0.5%) – at the levels L2–L3 and L1–L2. In 133 (64.8%) cases, protrusion and hernia compressed the anterior wall of the dural sac, and in 20 (9.8%) cases, a violation of liquor dynamics was noted. Lumbar stenosis was detected in 47 (22.9%) cases.
When comparing the clinical picture with MRI results, in 181 (88.3%) cases, the level of localization and direction of the protrusion corresponded to the level of detected radiculopathy, which indicates the high sensitivity of this examination method. In other cases, the localization of the protrusion or hernia did not correspond to the side and level of radiculopathy. For example, in patient Z., posterior median protrusions of the L1–L2 and L2–L3 discs measuring 3.0 and 3.5 mm were detected without signs of compression of the dural sac, and clinically and according to the results of ENMG, bilateral radiculopathy L5, S1 with secondary axonal - demyelinating lesions of both tibial nerves.
The results of ENMG are presented in the table.
* Statistically significant differences between indicators in patients before and after treatment (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.001); # statistically significant differences between the indicators of patients after treatment and the indicators of the control group (# p < 0.05; ## p < 0.001).
According to ENMG, before treatment in both groups, even in the clinical absence of motor deficits, in patients with reflex and sensory disorders signs of demyelination were revealed not only of the spinal roots, but also of the peripheral nerves (see table). At the same time, the formation of peripheral distal paresis of the muscles of the lower extremities occurred with axonal demyelinating damage to the peripheral nerves, as evidenced by a decrease in the amplitude of the M-response (in the second subgroups p < 0.05 compared with GC) and even more pronounced (p < 0.05 ) than in the first subgroups, a decrease in SPI in motor fibers (MF). The damage to the tibial nerves in patients with paresis was more pronounced, since a statistically significant (p < 0.05) increase in terminal latency was also detected compared with HC. The study of the H-reflex showed that the processes of demyelination affected both the sensory and DV roots of S1–S2, and the tibial nerve. There were no significant differences in the latency of the H-reflex between the subgroups in the OG and GS (p > 0.05), the indicators in the subgroups (POG-1 – 33.2 ± 1.6 ms, POG-2 – 35.6 ± 1, 8, PGS-1 – 32.9 ± 1.3, PGS-2 – 36.1 ± 1.7 ms) were increased and significantly different from the GC (p < 0.05). As a result of the treatment (see table), the amplitude of the M-response in POG-2 increased significantly (p < 0.05); there were no statistically significant differences with HA (p > 0.05); in GS, the results obtained were significantly different from GC (p < 0.05). Positive dynamics in the second subgroups in the form of a decrease in terminal latency upon stimulation of the tibial nerve prevailed in POG-2 (p < 0.05). In the MG subgroups, the SPI for the DV of the tibial (p < 0.001) and peroneal (p < 0.05) nerves significantly increased, but in the second subgroups the GC result could not be achieved; the differences were significant (p < 0.05). In the GS, there was no significant increase in SPI after treatment (p > 0.05); the results obtained (except for the SPI for the peroneal nerve in PGS-1) were significantly different from those in the GC (p < 0.001). In the OG, restoration of conduction in the roots (decrease in F-wave latency) was noted in both subgroups, especially in POG-1. In the GS, the positive dynamics were insignificant in both subgroups; the results after treatment were significantly different from those in the GC (p < 0.05). Restoration of nerve impulse conduction (decrease in H-reflex latency) was detected in POG-1 (29.1 ± 1.3 ms, p < 0.05). In PGS-1 (32.1 ± 1.5 ms) and POG-2 (31.2 ± 1.4 ms) the effect was incomplete; the obtained values did not differ significantly from those in the GC (p > 0.05). Only in PGS-2 the positive effect was insignificant (34.3 ± 1.6 ms).
Mexidol and osteochondrosis
Degenerative diseases of the spine provoke compression of blood vessels and nerve endings, which leads to a deficiency of brain nutrition. "Mexidol" for osteochondrosis allows you to restore normal cerebral blood flow, remove toxins from damaged vertebrae and improve the general well-being of the patient. Used in complex and monotherapy.
Active component and its properties
The main active ingredient of the drug is the antioxidant "Emoxipin". In terms of therapeutic properties and mechanism of action, Mexidol is superior to many psychotropic drugs. The product helps to neutralize the destructive effects of free radicals and eliminate the symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain, which often manifests itself due to pinching of blood vessels by deformed vertebrae in cervical osteochondrosis.
When taken together with Mexidol, the effect of sedatives, anticonvulsants, psychotropic drugs, and antidepressants is enhanced, so it is recommended to reduce the dosage of the drugs.
The drug improves blood circulation.
The medication has membrane protective and anticonvulsant activity, normalizes blood properties, reducing the amount of cholesterol and reducing platelet aggregation. It has a positive effect on the brain, activates its activity, improves cognitive functions and increases dopamine levels. By normalizing blood supply and nutrition to brain cells, the drug eliminates increased anxiety, fear or depression, which often accompanies osteochondrosis. Mexidol removes harmful substances from damaged vertebrae, thereby promoting their recovery. The medicine is sold in the following forms:
- coated tablets of 125 mg of active ingredient;
- injection solution in ampoules of 2 ml or 5 ml.
Diseases for which the drug is indicated
The antioxidant drug Mexidol is used in cases where it is necessary to stabilize cerebral circulation and eliminate the consequences of oxygen deficiency in tissues. A good therapeutic effect is obtained by using the drug for osteochondrosis of any part of the spine. It is often included in a treatment complex regimen, for example, it is used with the vitamin preparation “Combilipen” with a similar effect on cerebral blood flow. The drug will also help with the following conditions and ailments:
- consequences of cerebral circulation disorders and brain injuries;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- cardiac ischemia;
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- withdrawal syndrome in alcoholism;
- anxiety disorders and neuroses;
- encephalopathy of various nature;
- seizures;
- acute intoxication with alcohol or psychotropic drugs.
We advise you to study - Injections for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
How to treat spinal osteochondrosis with Mexidol?
In case of pathology, the drug is prescribed by a doctor in combination with other drugs, both in tablets and in the form of injections. If the vertebrae of the cervical spine or chest are affected, it is recommended to take 1-2 tablets 3 times a day for 2-6 weeks. Lumbar osteochondrosis requires intramuscular administration of 125-200 mg, 2-3 injections per day for 10 days. Advanced forms of the pathology are treated with intravenous administration of Mexidol 150-400 mg, in combination with saline, 2 times a day. The course of therapy is up to 2 weeks. A jet injection or dropper is used. The daily dose of the drug should not exceed 800 mg.
The dosage of tableted Mexidol should be gradually reduced over 2-3 days.
Contraindications and side effects of the drug
In addition to its beneficial effects, the medication can also harm certain categories of patients. You cannot treat with Mexidol tablets or injections to people with hypersensitivity to any component of the drug, acute kidney and liver dysfunction. The drug is not recommended for pregnant, lactating women and children. The medicine is well tolerated when taken in doses prescribed by a doctor. Sometimes treatment with Mexidol may be accompanied by allergic reactions and unpleasant symptoms from the digestive system. Drowsiness, impaired coordination of movements, and depression may occur. Due to the intense effect of the drug on the brain, it can only be dispensed from the pharmacy with a prescription.
Clinical and neurological monitoring of long-term treatment results in subgroups of patients
To check the durability of the achieved treatment results and evaluate them in the longer term, we examined 38 patients with RCC 6 months after completion of treatment. 21 people from the OG (11 from PGS-1 and 10 from PGS-2) and 17 from the GS (8 from PGS-1 and 9 from PGS-2) came for the return visit. Maintaining or even improving the clinical effect over six months was recorded in 17 (81.0%) of 21 patients in the group: 8 (72.7%) patients from POG-1 and 9 (90.0%) from POG- 2 and only 3 (17.6%) of 17 patients had HS (all from PGS-1). There was no deterioration of the condition in the form of increased pain in the MG; in the GS, pain resumed or intensified in 14 (82.4%) patients, and 6 (35.3%) patients were re-treated during this period of time. When studying the dynamics of pain intensity in the MG subgroups, a significant (p < 0.05) decrease was noted: from 2.78 ± 0.25 to 1.34 ± 0.18 points; on the contrary, in the GS the pain intensity increased from 3.56 ± 0.79 to 4.86 ± 0.52 points. In the MG subgroups, further regression of neurological symptoms and improvement in life activity were also observed (according to the Roland-Morris scale). In the GS, a deterioration in these indicators was noted, especially in the second subgroup. In the OG subgroups, there was a steady decrease in DM (in POG-1, DM decreased from 6.4 to 3.8%, in POG-2 - from 12.8 to 8.4%), in PGS-1 the positive result was insignificant ( from 23.4 to 22.6%), in PGS-2 maladjustment increased from 31.2 to 32.4%.
Thus, further regression of neurological symptoms, associated improvement in social adaptation and basic aspects of life in patients of the main group indicated the prolonged action of Mexidol, its positive effect on the frequency of exacerbations and the duration of remission of patients with RCC, regardless of the presence of motor deficit.
general characteristics
Mexidol is a medicine from a domestic manufacturer. It belongs to the category of antioxidants and is often prescribed for osteochondrosis. Recommended for use in complex treatment of complications. The medication is significantly different from its analogues and other neuropsychotropic drugs, significantly surpassing them in effectiveness.
Among the main properties are the following:
- Ability to neutralize the effects of free radicals
- Provides protection to cell membranes from damage
- Prevents tissue hypoxia
- Blocks stress and reduces excitability
- Helps restore immune and metabolic processes
- Prevents cramps in muscle tissue
- Activates brain activity by increasing dopamine
- Reduces cholesterol and improves blood circulation
Can enhance the effect of antidepressants. With dysfunction of the vertebrae of this department, the blood supply and nutrition of the brain cells are primarily disrupted, which causes headaches, ear congestion and nervousness: together, all these symptoms form a depressive state. This will reduce your intake of antidepressants, which means reducing their side effects.
Comparison with analogues by price and effect
The price of the drug depends on the dosage:
- ampoules of 2 ml (pack of 10 pcs.) - about 560 rubles;
- 5 ml (5 ampoules) – 420 rubles;
- 50 ampoules of 2 ml - on average 2200 rubles;
- tablets (30 pcs.) – 270 rubles;
- tablets (50 pcs.) – 450 rubles.
It should be borne in mind that Mexidol is only available with a doctor's prescription, which is due to a number of contraindications and a direct effect on brain function.
| Firm | Form, dosage, quantity per package | Price in rubles |
| "ZiO-Zdorovye" (Russia, Podolsk) | Tablets, 125 mg, 30 pcs. | 250 |
| Tablets, 125 mg, 50 pcs. | 405 | |
| Ampoules with solution 2 ml, 10 pcs. | 445 | |
| "Alsi Pharma" (Russia, Kirov) | Tablets, 125 mg, 30 pcs. | 220 |
| Tablets, 125 mg, 50 pcs. | 390 | |
| Ampoules with solution 2 ml, 10 pcs. | 420 | |
| "Armavir biofactory" | Ampoules with solution 2 ml, 10 pcs. | 475 |
| Ampoules with solution 5 ml, 10 pcs. | 480 | |
| MEZ (Russia, Moscow) | Tablets, 125 mg, 30 pcs. | 256 |
| Tablets, 125 mg, 50 pcs. | 430 | |
| Ampoules with solution 2 ml, 10 pcs. | 430 | |
| Ampoules with solution 5 ml, 10 pcs. | 550 |
Synonymous products (that is, direct analogues in composition, but produced by other companies) are: Mexiprim, Mexicor, Medomexi and Mexifin. In terms of quality and price, they are exactly the same as Mexidol, so if desired, you can treat with them. But you should understand that the listed drugs cannot be taken together with Mexidol: since they are absolute analogues, an overdose will occur if taken at the same time.
Instead of Mexidol for osteochondrosis, the doctor may prescribe other antioxidants and antihypoxants. These may be the following drugs: Cortexin, Cavinton, Gipoxen, Actovigen. They are also taken to improve blood supply, increase resistance to hypoxia, and stimulate metabolic processes. In addition to antioxidants, products with pentoxifylline (Trental, Euphellin) can be prescribed, which normalize blood flow and relax blood vessels, thus improving oxygen supply to the intervertebral disc and brain.
Let's summarize: Mexidol is a high-quality remedy to help with impaired blood supply caused by cervical osteochondrosis. If there are no contraindications for taking Mexidol, then you should choose it, since it is considered the most effective medicine in the antioxidant category.
Why do you need Mexidol for cervical osteochondrosis?
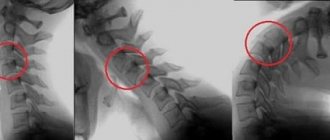
Osteochondrosis is, first of all, a degenerative pathology in which deformation of the intervertebral discs occurs (the vertebrae are compressed and crush the disc located between them). An intervertebral disc is a formation of fibrocartilaginous annular plates filled with a gelatinous jelly-like core and surrounded by a connective tissue membrane. With osteochondrosis, compression of two adjacent vertebrae occurs, which puts pressure on the disc and causes displacement of the pulp, which begins to bulge and protrude through the fibrous membrane. Such displacements are called hernias and protrusions.
One of the characteristic symptoms of osteochondrosis is the formation of protrusions and hernias in the spine
Hernias and protrusions can cause not only compression of the spinal endings, but also compression of the blood vessels through which blood enriched with minerals and oxygen enters the brain cells. Muscle spasms and swelling of paravertebral soft tissues can also interfere with the flow of lymph and blood. Clinically, circulatory disorders in cervical osteochondrosis of the 3rd degree are manifested by chronic headaches, instability of blood pressure, visual and auditory dysfunction.
Circulatory disorders caused by osteochondrosis are manifested by painful headaches
Mexidol allows not only to establish microcirculation of fluids in blood and lymphatic vessels, but also to improve the neurotrophic parameters of tissues, as well as reduce the degree of endogenous intoxication caused by the destruction of intervertebral disc components.
The clinically significant effect of treatment with the drug is manifested by the following result:
- relief or significant reduction in the intensity of cervicogenic headaches and dizziness;
- elimination of noise and squeaking in the ears;
- restoration of impaired visual function (disappearance of spots, flickering, ripples before the eyes);
- the severity of neurological disorders (paresis and paresthesia) decreases.
After taking the drug, limbs become less numb and the severity of neurological disorders decreases
Support of the body
It is known from a school article that the spinal column is a chain of vertebrae. To fix them, special cartilaginous connections are used - intervertebral discs. To better understand the specifics of osteochondrosis, you need to remember how the spinal column is structured - in general, and the cervical region in particular.
- To prevent individual vertebrae from rubbing against each other and compressing the passing capillaries and nerves, there is an intervertebral disc between them, which is a kind of layer of cartilage tissue.
- The structure of the intervertebral disc provides for the presence of a thick jelly-like fluid (nucleus pulposus), which is kept from leaking by a protective membrane - the fibrous ring. During the aging process (usually after 50 years), the main parameters of the nucleus pulposus deteriorate against the backdrop of a slowdown in metabolic processes, but the degree of approximation of individual vertebrae depends on how elastic the intervertebral disc remains.
- The intervertebral discs of an adult receive the nutrition they need through diffusion - absorbing everything they need from the environment. This happens due to the work of the vertebrae, when physical activity creates pressure drops required for diffuse nutrition. Accordingly, a decrease in physical activity leads to disruption of metabolic processes.
Contraindications for use
The drug has a pronounced effect on the body, therefore not all patients can use Mexidol for cervical osteochondrosis. The following contraindications for use are identified:
- Individual high sensitivity or individual intolerance, allergy to the components of the composition;
- Renal dysfunction, renal failure;
- Impaired liver function, liver failure.
There is no reliable data on the use of the composition during pregnancy and lactation, since such studies with careful control have not been conducted.
Therefore, the drug is not recommended to be used in these cases, or it should be done with great caution. A similar situation is observed with pediatric patients, therefore the use of the drug in patients under 18 years of age is not recommended.
Severe hypersensitivity is likely to develop in patients with bronchial asthma. But for this there must be an initial predisposition and high sensitivity of the body to sulfites.