Many patients wonder why the face goes numb, what causes this unpleasant sensation, and what can be done to get rid of this symptom. It’s worth immediately dispelling all intrigues - no other processes other than disruption of innervation can cause this sensation. Numbness is the lack of normal conduction of nerve impulses along certain axon bundles. The wider the zone of insensibility, the closer to the spinal cord the source of compression or nerve damage is located.
The face often goes numb with cervical osteochondrosis of the spinal column. This degenerative disease leads to complete or partial destruction of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs. As a result of the decrease in disc height, pressure begins to be exerted on the radicular nerves extending from the spinal cord. If the posterior pairs are damaged, a feeling of numbness in the face, scalp, tongue, lips, and ears may occur. When the posterior root nerve is damaged on the left side, numbness occurs in the left half of the head and face. And in the same way - on the right side.
Reasons why part or half of the face goes numb
The reasons why part of the face goes numb are listed above. These are the consequences of long-term developing osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. If only one posterior root nerve is damaged, then a sensitivity disorder occurs and half of the face and scalp go numb. Accordingly, the ho on this side is captured.
But another localization of the process of compression of the facial nerve is also possible. In this case, the reasons why the face goes numb may be hidden behind the following factors:
- tissue deformation in the area of the maxillary canal;
- osteoarthritis of the jaw joint;
- incorrect position of the lower jaw in the absence of a number of teeth, changes in the bite;
- changes in posture in the cervical spine;
- inflammation of the submandibular and lymph nodes located behind the ears;
- inflammation and degeneration of the facial or trigeminal nerve.
If part of the face becomes numb, an urgent consultation with a neurologist is necessary. Do not forget that such a symptom may manifest itself as an acute or transient disorder of cerebral circulation. This condition is fraught with paralysis and permanent disability. Therefore, if you have even the slightest suspicion of a stroke, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Note! With long-term developing cervical osteochondrosis, the patient may develop vertebral artery syndrome. This condition provokes cerebrovascular accident and the onset of spinal stroke.
Therefore, if you have pain in the neck, accompanied by a feeling of numbness in half or part of the face, you should immediately consult a doctor. This can be done at our manual therapy clinic. We see a neurologist, a doctor of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences. The initial consultation is provided to each patient completely free of charge. You can make an appointment at any convenient time. All you need to do is call us at the number provided.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is manifested by several syndromes:
1. Reflex-irritative syndrome
Burning pain in the cervical-occipital region that occurs after sneezing, sudden movements of the head or a prolonged static state, for example, after sleep or an immobile state and subsequent movement of the head or neck, are common complaints with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The pain may radiate to the shoulder or chest.
2. Spinal canal narrowing syndrome (spinal canal stenosis)
This syndrome develops as a result of compression (squeezing) of the spinal cord and its vessels, which leads to impaired circulation in the affected area and the development of myelopathy - a rare but most dangerous complication of osteochondrosis. Vertebrogenic cervical myelopathy occurs mainly in middle-aged and elderly people as a result of compression of the spinal cord or its vessels by posterior osteophytes, thickened ligamentum flavum, and herniated intervertebral discs. The disease develops gradually, at first there is often pain and limitation of movements in the cervical spine. In the future, cervical osteochondrosis can cause dysfunction of the upper and/or lower extremities, manifested by numbness, tingling sensation in the fingers, a feeling of cottony legs or arms, up to the development of paresis and paralysis
3. Radicular syndrome
Manifestations of radicular syndrome in osteochondrosis of the cervical spine will depend on which nerve root is compressed as a result of structural changes in the disc. However, in any case, cervical osteochondrosis will occur with headaches that have an aching, pulsating or burning character, sometimes occurring as hypertension. Back pain is rarely local and usually radiates to the shoulder blades, forearm, shoulder and/or arm, down to the fingers.
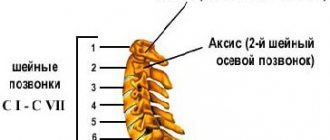
Depending on the affected spinal segment, the following symptoms may occur:
- C1-C2: lesions in this segment, as a rule, occur as a result of automobile injuries and are manifested by impaired sense of smell and speech, wasting of the facial and hypoglossal muscles and decreased sensitivity in the occipital-parietal region.
- C2-C3: also rarely affected and is accompanied by impairment of hearing, vision and control of the movement and sensitivity of the tongue muscles, which leads to speech and taste disorders, a feeling of inflammation, soreness or a lump in the throat.
- C3-C4: since the phrenic nerve departs in this segment, in addition to pain in the clavicle and shoulder girdle, spam of the splenius and trapezius muscles, pain also develops in the right hypochondrium and heart, and respiratory movements are disturbed. In addition, gondus, a feeling of nasal congestion, snoring, decreased sense of smell, sagging facial muscles, and deterioration of the teeth may develop.
- C4-C5: damage in this segment is accompanied by pain in the shoulder girdle, hypotrophy of the deltoid muscle, decreased sensitivity of the outer surface of the shoulder, glenohumeral periarthritis and inflammation of the skeletal muscles in this area. Other symptoms may include changes in voice, a feeling of inflammation in the larynx, and snoring.
- C5-C6: the segment is most often susceptible to degenerative lesions and has extensive symptoms. First of all, pain and impaired sensitivity of the skin develop from the scapula, the outer surface of the shoulder to the radial surface of the forearm and the thumb. Subsequently, somatic symptoms develop, including frequent and difficult to treat diseases of the lungs and bronchi, including asthma, rheumatic and allergic manifestations, and symptoms of angina pectoris.
- C6-C7: damage to the nerve root in this segment leads to pain in the scapula, posterior surface of the shoulder, along the dorsal surface of the forearm to the dorsum of the hands. In addition, damage to this segment may be accompanied by symptoms corresponding to diseases of the thyroid gland, mediastinal organs and the cardiovascular system.
- C7-T1: damage to the C8 spinal root is accompanied by hypertrophy of the triceps muscle and the abductor of the little finger, which leads to a weakening of the flexion reflex and pain with impaired sensitivity of the skin from the neck, shoulder, shoulder blades, to the elbow joint and little finger. In severe cases, symptoms similar to angina pectoris, arrhythmia and asthma may develop.
4. Cardiac syndrome with cervical osteochondrosis
Cardiac syndrome develops when the nerve roots innervated by the diaphragm (phrenic nerve) or the pectoralis major muscle are irritated. The symptoms are exactly identical to an attack of angina, but the attack lasts unnaturally long, the pain intensifies with a sudden movement of the head or neck, with a sharp sneeze or cough. Standard coronary drugs do not bring relief, and the ECG at the time of the attack does not show a violation of the coronary circulation. At the same time, cardiac syndrome may be accompanied by tachycardia, arrhythmia and high blood pressure.
5. Vertebral artery syndrome
This syndrome is one of the most common and dangerous manifestations of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. This syndrome develops against the background of compression of the vertebral artery and circulatory disturbances in the corresponding parts of the brain (cerebellum, brain stem and posterior lobes), which determines the clinical picture.
One of the main manifestations of vertebral artery syndrome is a severe pulsating and/or burning headache, constant or paroxysmal, involving the crown of the head, the superciliary part, the temples and the back of the head. Usually the pain is one-sided. In the first stages of development, headaches arise or intensify after a long stay in an uncomfortable position with the head thrown back, after physical exertion or after sudden movements. As the lumen of the artery narrows, the pain becomes more pronounced and frequent, sometimes permanent. In severe cases or at the peak of the headache, vomiting may occur, and fainting is possible.
Visual disturbances in cervical osteochondrosis can occur either separately or against the background of headaches and can be expressed by pain in the eyeball, impaired visual acuity, a feeling of veil before the eyes, dryness or heat in the eyes. One of the characteristic symptoms of narrowing of the vertebral artery is sudden short-term attacks of dizziness or loss of orientation in space. Such attacks occur for a few seconds and pass quickly. There may be sudden noise in the ears or pulsation in the scalp. Also, damage to the vertebral artery can lead to the development of cardiac syndrome.
In severe cases, an attack of “ischemic attack” may develop, manifested by severe headaches, vomiting, loss of coordination, changes in handwriting, unsteadiness of gait, double vision, impaired speech and balance.
Why do my face and ears, lips and tongue go numb?
A situation where the face and lips go numb can be associated not only with cerebral circulation disorders. The face and tongue often go numb with the development of cervical osteochondrosis. But you need to understand that such a symptom may indicate a serious pathology in the intervertebral disc area. This may be an intervertebral hernia or severe protrusion.
A fairly serious pathology is manifested by numbness of the ears and face, and this may be a signal that the posterior structures of the brain are suffering from a total deficiency of arterial blood. And this is associated with vertebral artery syndrome.
In any case, the patient requires immediate medical attention. It is important to eliminate the cause of impaired blood flow to the posterior cerebral structures or compression of the radicular nerve as quickly as possible. This can be done using manual therapy methods. Osteopathy and traction traction of the column make it possible to quickly and safely relieve pinching of the radicular nerve responsible for the innervation of the facial zone. Manual therapy and massage can restore impaired cerebral circulation and prevent the risk of developing a spinal stroke. But in order for this to happen, you need to seek medical help immediately.
Why does my head hurt and feel dizzy and my face goes numb?
The reasons for the numbness of the face and head (its hairy part) may be hidden in the cervical spine or in the structures of the brain. You can distinguish the first from the second by a number of indirect signs:
- if the face becomes numb and dizzy, then this is most likely vertebral artery syndrome with insufficient blood supply to the posterior cerebral structures;
- if your head hurts and your face goes numb, then this may be a symptom of an essential form of migraine attack and this has nothing to do with cervical osteochondrosis, although it can also be quickly treated using manual therapy methods;
- if the head and face go numb due to severe muscle strain in the neck, then you can safely make a diagnosis of osteochondrosis and begin appropriate treatment.
But only an examination by a specialist will help make a more detailed diagnosis. When palpating the spinous processes, the doctor will be able not only to detect characteristic signs of destruction of the intervertebral discs, but also to relieve muscle spasms that cause pain.
If you want to know why your head and face are numb, make an appointment with a doctor at our chiropractic clinic. Do not self-diagnose or treat. This way you lose the time needed to quickly begin treatment for the disease at an early stage.
Diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis
The doctor can make the primary diagnosis of “cervical osteochondrosis” already during the first examination of the patient, and also determine the level of the affected spine, anatomical features, including posture, physique, body structure, line of the spinous processes, lateral contours of the neck, lower angle of the shoulder blades; localization, nature and degree of pain; range of motion of the spine, relief and muscle tone.
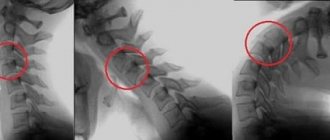
The diagnosis is clarified using visual diagnostic methods (x-rays, CT, MRI), which makes it possible to determine the stage of the disease, the level of damage to the spine, and the exact location of the deformed disc. And based on these data, the most optimal treatment for cervical osteochondrosis is selected.
Muscles or skin on the face go numb – how do you know?
Numbness of muscle groups and the feeling of tingling on the upper layer of the epidermis are completely different conditions. And you need to be able to distinguish and diagnose them. If the facial muscles become numb, then when you try to smile or express any other emotion, nothing comes out. Moreover, a serious distortion appears - paresis is visible only on one side. This is a serious pathology associated with a violation of deep innervation. May be a consequence of nerve fiber necrosis due to facial or trigeminal neuritis.
If an attempt to smile is successful, this indicates that the skin on the face is numb, and this is due to damage to the surfaces of the nerve endings located in the middle layer of the epidermis. This may be facilitated by exposure to unfavorable environmental factors.
Self-diagnosis is rarely correct. There is only one reliable way to find out whether the skin or muscles on the face are numb. This is a visit to the doctor. Only a doctor can adequately assess the patient’s condition, conduct a full examination and make an accurate diagnosis.
If the face and neck become numb due to cervical osteochondrosis
Complaints that the face and neck are numb often come from patients suffering from degeneration of the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc. The cause of this pathology can be prolonged static tension in the muscles of the shoulder girdle and collar area. It appears in people engaged in mental sedentary work.
This is a very unfavorable sign. Therefore, if the face becomes numb due to osteochondrosis, it is recommended to take at least an x-ray to identify destruction of the intervertebral disc and exclude hernial protrusion of the nucleus pulposus. If a hernia does form, treatment should be started immediately. If this is not done in a timely manner, a problem may arise with the innervation of the cardiovascular system.
With cervical osteochondrosis, the face becomes numb only in one case - if there is compression of the radicular nerve. This condition occurs when there is severe protrusion of the annulus fibrosus. Even if there is no hernia yet, it may appear in the very near future. Therefore, it is necessary to begin adequate and effective treatment as soon as possible.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis with NANOPLAST forte therapeutic plaster
In the therapeutic treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, various agents are used, such as NSAIDs, analgesics, and antispasmodics. All these remedies are effective, but if used for a long time they can cause harm to the body. Therefore, it is very important to minimize side effects and increase the effectiveness of treatment. A new generation product can help with this - the pain-relieving anti-inflammatory medical patch NANOPLAST forte.
The NANOPLAST forte therapeutic patch relieves pain and inflammation, improves blood circulation in the affected area, and allows you to reduce the dose of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
When treating osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the NANOPLAST forte therapeutic plaster is applied to the disturbing area of the neck, avoiding the anterior surface, especially the area of the carotid arteries and lymph nodes. A course of treatment of 9 days or more is recommended. It is usually recommended to use the patch in the morning for 12 hours, but it can also be used at night.
High efficiency, unique composition, long-term (up to 12 hours!) therapeutic effects, ease of use and affordable price make NANOPLAST forte the drug of choice in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis.
Read more about NANOPLAST forte
Treatment for a feeling of numbness in the face
If the face is numb, treatment for such a sensation may consist of symptomatic and etiological effects. In the first case, various pharmacological drugs are used to improve the conduction of nerve impulses. Complex vitamin preparations are prescribed that restore trophism and the condition of the neural structure of axons. Symptomatic treatment alleviates the patient’s condition, but, unfortunately, leads to the fact that all the symptoms soon return again.
Etiological treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of the numbness of the face, and this leads to complete recovery. In most cases, after a course of manual therapy, patients completely get rid of the feeling that the face and scalp are numb.
Our manual therapy clinic uses only safe and effective methods without the use of pharmacological drugs. First, the doctor finds the potential cause of the numbness. Then he develops an individual course to eliminate this factor. Thus, for cervical osteochondrosis, a course is carried out that restores the normal structure of the intervertebral disc. This could be osteopathy, massage, kinesitherapy, reflexology, therapeutic exercises, etc.
If you are interested in therapy, schedule a free consultation and find out all the information you need. During the initial appointment, the doctor will give you the correct diagnosis and tell you about all the prospects for future treatment.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
In the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, surgical and conservative methods are used. But surgical treatment is prescribed only in the presence of severe complications that occur in the later stages of osteochondrosis if:
- stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal has formed;
- the vertebral artery is compressed;
- a significant hernia or protrusion has formed, compressing the nerve roots;
- excessive spinal instability developed.
In other cases, the standard treatment for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is conservative therapy. This is due to the fact that with all the achievements of modern medicine, the consequences of surgical intervention are not always expected.
Conservative treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
The best results in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, as well as other types of osteochondrosis, are achieved with early consultation with a doctor. Unfortunately, many patients often do not pay attention to minor back discomfort or occasional headaches. On the other hand, there are many cases of incorrect diagnosis and long-term useless treatment, since osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can simulate other diseases, such as arthritis, myalgia or angina. That is why vertebrologists recommend checking the spine if there are symptoms of any disease, especially those accompanied by headaches or back pain.
In the effective treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, an integrated approach is of great importance, including the following areas:
- drug therapy - aimed at improving the trophism of the intervertebral disc and relieving pain, relieving muscle spasm and inflammation during an exacerbation. For these purposes, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors are prescribed to stimulate the restoration of joint cartilage tissue, multivitamins and B vitamins;
- physiotherapy - prescribed to reduce pain, improve nutrition of the cartilage tissue of the disc, stimulate cartilage regeneration processes, relieve muscle spasms, inflammatory processes in the postoperative period for a speedy recovery;
- manual therapy - used to eliminate muscle spasms, reduce pain, improve blood and lymphatic metabolism, correct posture and improve the range of motion of joints. The manual intervention scheme is selected individually for each patient;
- massage is a long-used and well-proven method of treating diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Has the same effect as manual therapy;
- Physical therapy is one of the most important methods of treating all types of osteochondrosis, including osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The purpose of exercise therapy is to relieve muscle spasm and compression of nerve roots, improve blood and lymph flow in the spine, strengthen the muscle frame and increase the flexibility of the ligamentous apparatus. A set of exercises is selected for each patient, the correct implementation of which is monitored by a specialist;
- Reflexology is an alternative type of treatment that is widely used today and gives very good results when combined with other treatment methods. The essence of the method is the impact on acupuncture points and/or reflexogenic zones in order to achieve the same results as with other therapeutic methods (reduction of pain and muscle spasm, decompression of the spinal roots, improvement of tissue trophism in the vertebrae), as well as to improve sleep , relieving psycho-emotional stress, normalizing weight, and so on.
For the treatment of chronic osteochondrosis, chondroprotectors, B vitamins (B6, B12), preparations for external use - ointments, creams, gels that contain NSAIDs, local irritants and tissue regeneration stimulants are also used.
In addition to the main methods of treatment, for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, patients are recommended to change their usual lifestyle, since in most cases the disease occurs against the background of low mobility, poor or unhealthy diet, obesity or, conversely, excessively low weight and the presence of bad habits. In most cases, in the early stages of cervical osteochondrosis, it is enough to lead a healthy lifestyle, prevent the occurrence of muscle spasms and overload of the muscles of the cervical-shoulder region, provide comfortable sleeping conditions, normalize nutrition and follow the doctor’s recommendations for exercise therapy in order to stop the further development of the pathological process, and at the first stage even achieve recovery.
In the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis , especially in its initial stages, as well as for the prevention of this disease with constant static or dynamic stress in the cervical-brachial region, an effective remedy of a new generation - the therapeutic pain-relieving anti-inflammatory patch NANOPLAST forte - can provide effective assistance.