Despite the fact that neck osteochondrosis is considered a common disease and today occurs even in adolescents, few people pay attention to it. A huge percentage of patients endure the pain, drowning it out with paracetamol or other NSAIDs, and only when more serious symptoms appear do they decide to visit a neurologist
. At this time, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can progress to stage 2, which complicates treatment, makes it longer, and provokes the risk of concomitant pathologies.
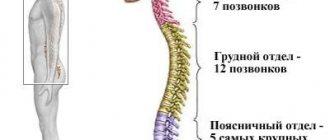
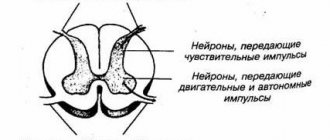
Structure of the cervical spine
The vertebrae of the cervical spine are the most mobile and least loaded part of the entire spinal column, therefore their sizes are much smaller than others. This is their anatomy. However, do not underestimate the importance of the cervical spine.
In the structure of each vertebra there are so-called “body” and “arch” that close the vertebral foramen. On the arch there are various vertebral processes, depending on their shape:
- paired joints (upper and lower)
- paired transverse
- spinous (it has no pair), protruding from the base
The arch at the very base is supplied with vertebral notches - upper and lower. And the intervertebral foramen, formed by the notches of two adjacent vertebrae, allows you to reach the spinal canal from all sides.
The cervical vertebrae differ from their counterparts from other sections in the following parameters:
- The presence of holes in the transverse processes.
- Enlarged triangular transverse hole.
- The shape and size of the body - at the cervical vertebrae it is smaller and has an oval shape, elongated transversely. The exception is Atlas, which does not have a body.
If you tilt your head forward, you can feel the spinous process of the 7th cervical vertebra.
The first cervical vertebra is called Atlas, the second is called Axis or Epistropheus. It is these two “brothers” that perform the function of connecting the skull and the spinal column, with the help of the atlantoaxial-occipital joint.
The anatomy and shape of the first and second vertebrae are different from the others. Between them there are three joints - two of them are paired, and one is located where the odontoid process, extending from the epistrophy, connects with the arch of the vertebra called the atlas.
If there is a violation of vertebra No. 1, then the consequences will not be long in coming and the atlas will fuse with the cranial base. This must not be allowed under any circumstances.
Although there is an opinion that the atlas is damaged from birth itself, that displacement supposedly occurs during the passage of the child through the birth canal, this should not be taken for granted. After all, in children who were born through a caesarean section, the atlas has a similar structure and location as in children born naturally.
From 3 to 7, the vertebrae, which have the same structure, perform the functions of support and mobility, as well as protection of the spinal cord. In each vertebra, in the transverse process, there is an opening through which the vertebral artery passes.
Such features make it possible to perform the following movements:
- flexion and extension
- lateral tilts
- rotational movements
- circular movements
- movements along the vertical axis
And the elastic cervical muscles and ligaments help in this, the anatomy of which allows you to harmoniously combine such features of the cervical spine as stability and mobility.
The sixth vertebra deserves special attention and is called the carotid tubercle. It is named so for a reason. The carotid tubercle is indeed the most prominent of all and it is against it that the carotid artery is pressed. Therefore, if this part of the neck is injured, an important artery can inadvertently be damaged.
In order to try to protect against such consequences, nature decreed that tubercle number six is better developed and mobile than the rest. Each vertebra, be it the atlas, thoracic or sixth carotid tubercle, carries a certain load and performs its function, and together they provide a whole microcosmic system of interaction and protection.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is clarified using the following research methods:
- A conversation with the patient, during which the doctor finds out the time of onset of symptoms by feeling the cervical spine, determines the location of the pathology.
- X-ray examination. In the picture you can see the general characteristics of osteochondrosis.
- CT. The study allows you to see the full picture of disorders in bone and cartilage tissue.
- MRI. The most effective research method. You can see not only damage to the intervertebral discs, but also to nearby tissues.
After clarifying the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes therapy.
Prognosis and prevention
Unfortunately, cervical osteochondrosis, like any other osteochondrosis, cannot be completely cured. With the help of well-chosen treatment, it is only possible to relieve acute symptoms, avoid progression of the disease, prevent complications and the transition of the disease to the next stage.
Pay attention to the main ways to prevent cervical osteochondrosis. In order to prolong the period of remission, you must follow the following recommendations:
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Eat well.
- Treat infectious and inflammatory diseases in a timely manner.
- Avoid increased stress on the spine.
- Do not overcool, avoid drafts.
- Increase immunity.
- At the first sign of exacerbation, consult a doctor.
These recommendations will help not only prevent the exacerbation of existing osteochondrosis, but also prevent its occurrence in general.
Characteristic symptoms
The severity of the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis depends on the degree of destruction of the vertebral structures. Symptoms are aggravated by the growth of bone tissue with the formation of osteophytes, radicular syndrome (radicular pain due to a pinched nerve), intervertebral hernia (protrusion of the disc into the spinal canal).
The first signs of the disease are periodic headaches in the back of the head, pain in the neck, crunching and clicking in the vertebrae when turning the head, and sometimes a slight tingling of the shoulders. Over time, symptoms increase and the intensity of pain intensifies.
Pain syndrome is the main manifestation of osteochondrosis. Pain in the neck can be dull, constant or sharp with shooting below the back of the head when turning the head. The entire cervical spine or the projection area of the modified vertebra may hurt, as well as the collarbone, shoulder, scapula, and heart area.
It is possible that pain may radiate to the lower jaw, teeth, arm, ear, and eye area. The muscles of the neck and shoulders are tense and painful on palpation. It is difficult to raise the arm on the affected side - a lumbago immediately occurs in the shoulder or neck. Limitation of head movements due to pain often occurs in the morning after sleeping in an uncomfortable position.
The disease leads to compression of the roots of peripheral nerves (radicular syndrome) and causes pain along these nerves. There may be numbness of the hands or fingers, impaired sensitivity of certain skin areas innervated by the pinched nerve.
Some characteristic symptoms can suggest which vertebrae are affected:
- The narrowing of the lumen between the C4 and C5 vertebrae leads to pain in the collarbone, heart, decreased tone of the neck muscles, and breathing problems.
- If C6, C7 are affected, cervicobrachial radiculitis may develop: weakness in the arms appears, the patient is not able to squeeze the doctor’s hand as much as possible.
- Destruction of C3 is accompanied by impaired sensitivity of the tongue, and in severe cases, loss of control over it.
Cervical vertebrae (C1-C7). Click on photo to enlarge
Cervical osteochondrosis is always accompanied by headache. Severe, persistent pain increases with turning the neck or sudden movements. Some patients complain of heaviness in the head. Compression of the vertebral artery leads to attacks of dizziness and nausea. There is noise, ringing in the ears, flashing black dots before the eyes. Deterioration of cerebral circulation provokes a progressive decrease in hearing and visual acuity, numbness of the tongue, and changes in taste sensations.
Clicking or crunching when moving the neck almost always accompanies cervical osteochondrosis and is observed in every patient. A crunch appears when you sharply turn your head or throw it back.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of the second stage of cervical osteochondrosis is cervicalgia , that is, pain accompanied by muscle tension, limited neck mobility, dizziness, blurred vision and autonomic dysfunction. The pain can be localized in one place or spread throughout the entire back.
The most common manifestations of the pathology are:
With cervical osteochondrosis, the muscles of the neck and back are always tense; tension in the neck muscles;- cervical pain syndrome;
- headache, mainly in the back of the head and temples;
- ringing in the ears, ripples in the eyes;
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- hearing loss, memory loss;
- imbalance;
- nausea;
- pressure surges.
Due to a weakened muscular frame, vertebral subluxation and disc displacement occur. In this case, a sharp burning pain appears, especially when turning the head. If the vertebrae are displaced to the side, pain and tension are one-sided and lead to the development of asymmetry of tension in the spinal muscles.
Due to muscle tension, patients experience weakness, increased fatigue, and sleep disturbances. During an exacerbation of the disease, there may be sensations of suffocation, numbness of the tongue, increased sweating, and toothache. At this stage, damage to the vertebral artery is not yet observed, but the nutrition of the discs and vertebrae is disrupted, which provokes the progression of the disease.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease begins with asking the patient about the symptoms and visual examination. The doctor asks the patient about existing chronic diseases, profession, and lifestyle. It also collects information about the duration and nature of symptoms, treatment methods, including self-help. Then the doctor evaluates the patient’s posture, the symmetry of the location of the shoulders, shoulder blades, and the degree of freedom of rotation and tilt of the head.
The key diagnostic methods are:
- X-ray of the spine . It should cover the base of the skull and the upper thoracic vertebrae. The images clearly show the narrowing of the intervertebral spaces, hardening of the surface of the vertebrae, and the presence of osteophytes (bone growths).
- MRI . This is a layer-by-layer image of the spine, which shows all the processes occurring in the spine, hernias and protrusions.
- CT . Computed tomography, which differs from MRI in the presence of radiation exposure.
The patient is also prescribed a blood test to exclude or confirm the inflammatory process. With inflammation in the blood, an increase in ESR is detected.
Video: “Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine: symptoms, treatment”
Symptoms of grade 2 cervical osteochondrosis
One of the main symptoms of this disease is severe pain in the back of the cervical spine. Pinching of nerve endings and roots leads to the localization of pain spreading to the shoulder blades, forearms and cervical-collar region.
Osteochondrosis of the 2nd degree is usually accompanied by muscle weakness in the problem area, numbness of the upper extremities and spasms of the neck muscles, which limit mobility.
Other symptoms include:
- periodic discomfort and pain in the cervical region;
- constant tension in the muscles of the neck, back or upper shoulder girdle;
- headache in the temporal and occipital region;
- loss of coordination, ripples in the eyes, noises in the head and fainting;
- sudden jumps in blood pressure;
- frequent dizziness, deterioration of hearing, memory and decreased mental abilities.
Such osteochondrosis provokes displacement of the vertebrae, which leads to a noticeable curvature of posture. The second stage of the disease is characterized by high sweating, trembling of the head, compression of the arteries, toothache, numbness of the tongue, as well as unpleasant sensations in the throat, reminiscent of choking or a lump.
To study Displacement of the cervical vertebrae treatment
The essence of the pathology, risk factors
Osteochondrosis is degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs caused by pressure on them from the vertebrae.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is very common , since the neck has good mobility and bears most of the load. In addition, the anatomically the cervical vertebrae have a different structure, which makes this section very vulnerable.
The disease has four stages.
The first is asymptomatic, only occasionally pain appears in the neck area, which is not taken seriously by the patient. Therefore, most people consult a doctor with a history of stage 2 of the disease.
At stage 2, degeneration of the fibrous ring appears , weakening of the posterior longitudinal ligament, and sometimes disc cracks are observed. Due to degenerative changes in the fibrous capsule of the disc, the distance between the vertebrae decreases. This leads to pinched nerve roots. Subsequently, the vertebrae become displaced, protrusions and hernias appear. The second stage of the disease can last 4-5 years, periodically exacerbating and subside. Then the disease enters the third stage.
With cervical osteochondrosis of the 2nd degree, degeneration of the fibrous ring occurs
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis of the II degree
Since at the 2nd stage of the disease there are no serious changes in the tissues of the spine, but the manifestations of the pathology are quite pronounced, so therapy is mainly aimed at eliminating the symptoms. For this purpose, medications, manual and physical therapy methods, and therapeutic exercises are used. If a person feels severe pain and stiffness in movements, you need to stay in bed or wear a special corset around your neck, avoid sudden movements and hypothermia.
Drug treatment
Medicines that are used for the treatment of second-degree cervical osteochondrosis,
- Analgesics and NSAIDs. Painkillers (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Ketanov, Ketorol) are used for cervical osteochondrosis in the form of tablets, capsules, ointments and gels, and the specific option must be chosen by the doctor taking into account the patient’s concomitant diseases. In severe cases, novocaine blockades are used - the affected area is injected with injections of a solution, due to which even the most severe pain syndrome disappears.
- Muscle relaxants. “Mydocalm”, “Mefedol”, “Sibazon”, “Myocain” and their analogues relieve muscle spasms, due to which pain and other unpleasant symptoms, including headaches and dizziness, disappear.
- Steroid anti-inflammatory drugs. Medicines based on glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone) quickly relieve swelling and inflammation in the affected areas, but have a fairly large number of contraindications.
- Chondroprotectors. The chondroprotectors “Arthra”, “Teraflex”, “Chondroxid”, “Condronova” and other drugs include chondroitin and hyaluronic acid, which promote the restoration and regeneration of cartilage tissue.
- Vitamins. Most often, for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, B vitamins are used, which improve blood circulation, the functioning of the nervous system and nourish the tissues, due to which unpleasant symptoms disappear.
Prices for vitamins and minerals
Other treatment methods
To improve the therapeutic effect of drug treatment, physiotherapy procedures are used, including electrophoresis with the use of painkillers and restorative drugs, magnetic therapy, ultrasound and other techniques. They are used after relief of acute symptoms of the disease, improve blood circulation, relieve muscle spasms and promote tissue regeneration.
Ultrasound therapy. Ultrasound treatment
Manual therapy involves influencing the affected areas to restore the functions of the spine, improve blood circulation and alleviate the patient’s condition. The procedure may consist of acupressure and segmental massage, as well as traction of the spinal column using special devices or manually. It should be noted that a chiropractor must be fluent in treatment techniques, since even the slightest mistake can lead to serious consequences, including disability.
Manual therapy
Massage is a more gentle procedure than manual therapy, which also effectively eliminates the symptoms of the disease. A light massage can be performed independently at home - for this you need to do stroking, rubbing and vibrating movements in the area of the affected segment of the spine.
Massotherapy
One of the most effective procedures for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is acupuncture, or acupuncture. It acts directly on nerve endings, thereby relieving muscle spasms and activating blood circulation and metabolic processes in tissues. To alleviate the patient's condition, as a rule, 2 to 7 sessions are required.
AcupunctureTherapeutic exercise is used during the recovery period to strengthen the muscle corset and prevent relapses of the disease
Exercises should be performed carefully and slowly, without causing pain or other discomfort, preferably under the supervision of an experienced specialist. The complex, as a rule, consists of warming up, bending and turning the head to the sides, moving the shoulders and arms
Yoga, swimming, Pilates and other sports that are aimed at increasing muscle elasticity and strengthening the muscle corset have a good effect.
Yoga for neck pain
Non-drug treatment
Non-drug treatment is prescribed for any stage of cervical osteochondrosis and may consist of:
- Wearing a Shants collar.
- Exercise therapy. The set of classes is selected depending on the patient’s condition, as well as the stage of development of the disease.
- Spinal traction (hardware traction). Performed to increase the space between the vertebrae and relieve pain.
- Manual therapy. Correction of spinal diseases manually.
- Massage. Impact on the diseased area using pressure, stroking, pressure, as a result of which local blood circulation improves.
- Acupuncture. Relieving inflammation and reducing pain with needle injections.
- Physiotherapeutic methods – magnetic and laser therapy, UHF. They are used additionally with medicinal methods.
By prescribing procedures from the physiotherapy room, doctors achieve relief of pain and ongoing inflammation by improving blood circulation. Typically, phonophoresis and ultrasound are used for these purposes.
But, it must be remembered that such procedures can harm the patient during periods of exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis, so their use is permissible only during periods of recession. Therapeutic massage can only be performed during periods of absence of symptoms.
But patients sometimes engage in dangerous self-massage, intensively kneading the sore areas, resulting in injury to the neck. It is best to visit a massage room, where the procedure is performed according to all the rules.
Physical therapy helps to cope with the causes of osteochondrosis very well. The degree of load and increase in dosage should occur under the supervision of an experienced physician.
Manual therapy procedures are considered the most risky method of treatment.
Particular care should be taken, since osteochondrosis causes a risk of injury, jeopardizing the health and sometimes life of a person
Massage and self-massage go well with physical therapy and physiotherapy. You can take a massage course either in any medical institution or by contacting private practices. Massage is necessary for cervical osteochondrosis to strengthen muscles and relieve tension in the neck.
The massage therapist’s task is to remove harmful metabolic products by increasing the outflow and inflow of blood in the diseased area, as well as relieve spasm from the pathological area.
The main techniques used by specialists in neck massage are: stroking; squeezing; trituration; vibration; kneading.
The self-massage technique can be performed using the following techniques:
- stroking (movements should be soft, without much effort forming folds)
- kneading (deep impact on muscles by gripping, pressing and pushing up)
- vibration (oscillatory effect by tapping, shaking, patting).
Self-massage should always end with stroking. During vibration, you can use a massager.
Acupressure relieves headaches during exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis, helps with pressure surges, normalizing it. Scheme of acupressure:
- Impact on the feng fu point, which is located under the occipital protuberance, for 1 minute.
- Impact on the Feng Chi point, located two fingers' width from the mastoid processes of the skull.
- Exposure for 1-1.5 minutes to the ya-men point (located at a distance of three fingers’ width from the feng fu point).
- Sedative effect for 1-1.5 minutes on the Da Zhui point (7th cervical vertebra).
After acupressure, you need to lie down for a few minutes, as you may feel slightly dizzy.
Manual therapy helps cope with both acute and chronic pain, also increases range of motion and improves posture.
Basic techniques of manual therapy for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine:
- Relaxing and segmental massage. Used to warm up muscles and relieve tension.
- Mobilization - effects aimed at restoring joint function. by traction method.
- Manipulation is a sharp push aimed at the patient’s pathological areas. The procedure is accompanied by a characteristic crunch (the joint returns to its normal position).
A specialist practicing manual therapy must master these techniques perfectly. Otherwise, any mistake can lead to injury.
Acupuncture promotes the release of cortisol into the blood. This hormone has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. acupuncture Acupuncture is performed by applying pressure to points near the inner edge of the shoulder blade.
The needles are inserted to a depth of 1–2 cm and left to act for 10–30 minutes.
Treatment
Fortunately, grade 2 osteochondrosis does not imply severe damage to the vertebral artery. Therefore, it does not require surgical intervention. Treatment is carried out using conservative methods: drug therapy, physiotherapy, physical therapy.
Drug therapy
Did you know that...
Next fact
The goal of therapy is to relieve pain, relieve muscle tension, and restore mobility of the cervical spine. For this, the following types of drugs are prescribed:
Group Description Drugs Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs This is a group of drugs that have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic effects. The disadvantage of these drugs is their negative impact on the human heart and kidneys. For mild symptoms of osteochondrosis, preference is given to gels, creams, and patches.
Declofenac Ibuprofen Nise
Painkillers They are used in combination with NSAIDs to relieve severe pain. Ketanol injections have a good effect. Hormonal Quickly relieve inflammation in the nerve roots. Ointments based on prednisolone and hydrocortisone. Chondroprotectors are used to restore damaged spinal cartilage. Glucosamine and chondroitin have a good therapeutic effect. The drug Teraflex is widely used. Muscle relaxants Used to relieve muscle tension
It is important to choose the right drug so that it reduces, but does not suppress, muscle tone.
Mydocalm Sibazon
Vitamins Prescribed to improve nutrition of the spine and restore cartilage tissue. These are complexes with vitamins B, C, E, calcium and zinc. Neuroprotectors Prescribed in the presence of dizziness and surges in blood pressure.
Actovegin Thiocetam
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy in combination with medications speeds up the healing process.
They relieve inflammation, pain and muscle spasms. Electrophoresis, amplipulse, and ultrasound are widely used.
Such procedures are allowed only during the period of remission.
Manual therapy and massage complement the treatment. They relax muscles and improve blood circulation.
It is important that the procedures are carried out by qualified specialists; you cannot do massage yourself, as this can aggravate the situation. Massage is carried out after the exacerbation is relieved
Massage is carried out after the exacerbation is relieved.
Physiotherapy
Therapeutic exercise is aimed at strengthening the muscle corset and relaxing tension. A set of exercises should be developed by a specialist, taking into account the individual characteristics of the course of the disease. You can perform the exercises at home.
The success of therapy is achieved by an integrated approach to treating the disease.
Possible complications
All degenerative changes in the spine pose a danger to the patient’s health, as they limit his movements, cause pain and worsen the person’s quality of life.
Even more dangerous are the complications of grade 2 osteochondrosis. The most common complications :
- instability of the cervical vertebrae:
- protrusion and hernia;
- vertebral artery syndrome;
- spinal canal stenosis.
If left untreated , compression of the nerve endings occurs and blood supply is disrupted . The result is vertebral artery syndrome. Due to impaired cerebral circulation, the patient begins not only functional, but also organic changes. First, the patient experiences throbbing headaches, disturbances in speech, hearing, and balance. Ischemic attacks may begin - sudden dizziness and falls with preservation of consciousness.
sharp jumps in blood pressure begin . When nerves are pinched, numbness in the shoulder and arm down to the fingers can occur. Stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal provokes paralysis of the limbs.
Therapy
Osteochondrosis of the 2nd degree of the cervical spine requires immediate consultation with a doctor, otherwise, as the disease progresses, a pathological change in the internal organs will occur, leading to irreversible consequences in their work. Osteochondrosis also leads to pinched nerve endings and the development of intervertebral hernia.
The second degree of the disease is characterized by radicular compression, a reduction in the distance between the vertebrae, destructive processes in the fibrous ring and nearby tissues. Capsular ruptures and tears continue, leading to frequent and periodic exacerbations.
During severe pain, when nerve roots are pinched, under no circumstances should you treat yourself; you should immediately consult a specialist. Before receiving medical attention, apply an ice pack to the sore area and drink a pain reliever. You should immediately call a doctor at home, especially if the diseased vertebra has protruded. You cannot adjust it yourself, otherwise this can lead to compression of the nerve roots, instability of the spinal column and other dangerous consequences for health.
Treatment for grade 2 osteochondrosis includes:
- Medicines to relieve pain and relieve inflammation. Diclofenac is suitable for these purposes.
- Epidural injections into the spine. They are prescribed when there is severe pain. They use steroids and narcotics that are injected into the site of the spinal lesion.
- Physiotherapy. If a diagnosis of “2nd degree osteochondrosis of the lumbar region” is made, then to alleviate the condition of the sick person, phonophoresis, electrical stimulation, exposure to high-frequency currents, and vacuum therapy are prescribed. The same procedures are used for cervical osteochondrosis. Hirudotherapy produces a good effect, which ensures the normalization of blood composition and restores blood circulation in the affected areas of the spine. Acupuncture is also used. The duration of sessions is determined by the doctor depending on the person’s condition.
- Manual influence. It helps well with osteochondrosis of any part of the spine of the 2nd degree using hands. You can use a relaxing massage, work with an osteopath, or a chiropractor. During manual exposure, muscle tension is eliminated and blood supply to tissues is stimulated.
- Exercise therapy. Physical therapy, which is a mandatory component of the complex treatment of osteochondrosis, also helps in restoring the spine. Exercise therapy exercises are selected individually for each patient based on health status, age and stage of development of osteochondrosis. A set of physical therapeutic exercises, which is agreed upon with the physical therapy instructor and the attending physician for each patient with osteochondrosis, should be performed daily. But you don’t need to overexert yourself or lift weights. The load is increased gradually. Basically, therapeutic and gymnastic exercises are prescribed, aimed at gently stretching the cervical or lumbar vertebrae. After just a few sessions, patients note a significant improvement in their general condition.
Osteochondrosis is a disease that requires complex therapeutic intervention. Timely diagnosis allows you to quickly and efficiently treat the disease at any stage.
For grade 2 osteochondrosis, all treatment methods are aimed at restoring blood supply to tissues. Thanks to them, swelling is relieved, muscle spasms are eliminated, and metabolic processes in tissues are restored. In addition to drug treatment, the patient is recommended to switch to proper nutrition.
But most often, when the disease worsens, it is necessary to use medications that can relieve pain. Patients are prescribed injections of various painkillers that relieve pain and inflammation in tissues and muscles. Even when using strong remedies, you should not expect quick relief. Sometimes the discomfort disappears only after three sessions.
Causes
The main reason is load. It is more common in people who are obese or in physically demanding jobs. There may be a hereditary predisposition to the development of a disease such as osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, in the presence of factors influencing the development of the pathological process.
Stress, a sedentary lifestyle (hypodynamia), sedentary work and grade 2 injuries to any part of the spine - all this can be considered the main reasons for the development of grade 2 osteochondrosis. Most often, people get injured during active sports. And this is one of the reasons for the appearance in the patient’s chart of such a conclusion as osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine.
Also, a poor and unvaried diet, food not rich in vitamins and minerals can indirectly affect the development of the disease. An uncomfortable sleeping place can aggravate the situation, so it is better to sleep on a quality mattress than on a sofa.
Beauty is beauty, but girls who abuse frequent and prolonged wearing of uncomfortable shoes and high-heeled shoes, which change the physiological position of posture, coupled with flat feet, are also at risk.
Any hormonal changes in a woman’s body require attention to health and timely adjustments. This means that pregnant women should think about their health. Pregnancy is not a disease, it is a physiological and at the same time an “emergency” state of women, when the body works for two. Therefore, a balanced diet and additional intake of vitamin and mineral complexes are extremely important during pregnancy. In addition, due to a shift in the center of gravity, pregnant women's posture and gait change. Which indirectly also speeds up the development of osteochondrosis.
Women during menopause should also follow a balanced diet, wear comfortable shoes, take vitamins as recommended by a doctor, and support their body in every possible way.
Causes and risk factors
The exact cause of osteochondrosis has not yet been determined . There is an opinion that the disease is acquired by a person during natural childbirth. As the baby’s spine passes through the birth canal, it experiences a tremendous load and compression of the vertebrae occurs.
This explains the appearance of the disease in childhood. Up to a certain point, the pathology does not manifest itself in any way, but when exposed to provoking factors, it enters the active stage.
Provoking factors include:
- A sedentary lifestyle combined with prolonged exposure to one position, lying or sitting.
- Poor nutrition with lack of vitamins and minerals.
- Hereditary factor.
- Poor posture, scoliosis.
- Frequent hypothermia.
- Infectious diseases.
- Spinal injuries.
- Reduced immunity.
- Disturbances of the endocrine system.
People in certain professions that involve staying in one position for a long time are at risk: salespeople, hairdressers, surgeons, drivers. Also teenagers who spend a lot of time on the computer.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis plays an important role, because all therapeutic therapy depends on it. The disease is diagnosed by its symptomatic manifestations. The main stages of diagnosis are:
- Anamnesis collection. The doctor gets acquainted with the patient's medical history. During the conversation, he learns how the disease progresses and its symptoms. The doctor must find out whether any treatment was carried out and how effective it was. The specialist must know about hereditary factors, the patient’s bad habits, as well as the conditions of the place of work.
- Examination of the patient. The doctor examines the patient and finds out how the disease manifests itself. Examines the neck, its position relative to the body, difficulty of movement. Be sure to examine the skin to see if any changes have occurred. Feels the neck area and determines whether there are any lumps. Using a needle (tingling) the presence of sensitivity is checked.
- Radiography. This study is carried out to provide accurate information about the condition of the spine and cervical spine. Pictures are taken so that they can be seen directly and from the side. Sometimes the patient is asked to rotate the neck to obtain a functional radiograph. Thanks to X-rays, you can find out how mobile the damaged vertebrae are, their displacement, salt deposits and the presence of compactions.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. MRI is one of the most effective methods for diagnosing neck osteochondrosis. This procedure is painless and quite accurate. As a result of creating a magnetic field, it is possible to identify not only the disease itself, but also determine the severity. This makes it possible to find an effective treatment method.
- CT scan. Diagnosis is carried out using x-ray irradiation. The patient is placed in a tomograph, which can be closed or open. Next, scanning occurs, and the information enters the computer, after which it is processed. These images make it possible to determine the exact picture of the disease.
How to treat arthrosis of the interphalangeal joints of both hands, stage 2, can be found by clicking on this link.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The reasons for the development of cervical osteochondrosis are varied. First of all, the disease appears due to an incorrect lifestyle - physical inactivity, sedentary work, excess body weight.
In this case, the main cause of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is poor circulation in this area. As a result, the nutrition of the tissues of the intervertebral discs deteriorates, which entails a change in their structure.
There are several factors contributing to the development of this disease:
- physical inactivity;
- weak muscle corset of the back;
- excess weight;
- neck injuries;
- stress;
- hypothermia;
- systemic connective tissue diseases (lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis).
Physical inactivity is one of the most important factors in the development of spinal column diseases. People who spend a lot of time in a sitting position experience osteochondrosis due to lack of physical activity. A lot here also depends on posture and back muscles. Incorrect position of the neck during long-term work at a desk leads to disruption of the nutrition of the intervertebral discs, which over time results in degeneration of cartilage tissue and the development of osteochondrosis. For this reason, the disease is often diagnosed in schoolchildren and students, since their daily activities involve sitting at a table or desk for many hours. Also, osteochondrosis is often diagnosed in office workers and all people who spend a lot of time at the computer.
Weak back muscles are another factor that provokes the development of this disease. To maintain posture and correct head position, developed muscles in the back of the neck and thoracic region are necessary. If a person slouches, does not play sports, and has never strengthened the muscle corset with special exercises, there is a high chance of developing osteochondrosis.
Excess weight is one of the main factors in the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Due to the large body weight, the load on the spine and legs is distributed unevenly, as a result, some parts of the back are more strained. Most often it is the neck that suffers.
Osteochondrosis can be a consequence of muscle spasm. This is often associated with frequent stress. Many people feel how, during psycho-emotional stress, the muscles of the neck literally “stiffen” - this is both the cause of the development of osteochondrosis and one of the first symptoms of this disease.
Note! Stress is a dangerous condition that negatively affects the entire body, including the musculoskeletal system. You need to be able to deal with stress
If you cannot cope on your own, it is recommended to consult a doctor - a neurologist, psychologist or psychotherapist. Avoiding stress will help you maintain good health for many years.
As a rule, the development of osteochondrosis occurs under the influence of several provoking factors. Many doctors consider osteochondrosis not an independent disease, but a natural consequence of an unhealthy lifestyle. Constant fatigue, stress, incorrect body position while sleeping or working at the computer, excess weight and bad habits - all this harms the health of the spinal column. As you know, a strong back is the key to good health and longevity.
Despite the fact that osteochondrosis is not life-threatening, this disorder can significantly worsen overall health and cause the development of other diseases, so it is important to promptly identify the disease and undergo comprehensive treatment
Clinical picture
Symptoms of grade 2 cervical osteochondrosis are the most pronounced. At the initial stage, the pathology manifests itself only as discomfort, and with stage 3 disease, the pain syndrome weakens due to the stabilization of the spinal segments by bone growths. The pathology is characterized by increased muscle tone. A person constantly feels strong tension in the back of the neck and shoulders. The pain is no longer localized in areas with affected discs. It radiates to nearby areas of the body - shoulders, forearms, shoulder blades, upper chest.
Since the ligamentous-muscular corset has weakened, subluxations of the cervical structures become more frequent. The resulting pain is so acute that the person avoids turning or tilting his head for some time. Pathology of the 2nd degree manifests itself as follows:
- performance decreases, weakness, apathy, and weakness often occur;
- blood pressure increases or decreases;
- headaches and dizziness become more frequent;
- developing hypoxia provokes a temporary decrease in visual and hearing acuity;
- when turning or tilting the head, clicks, crunching, crackling sounds are heard;
- The sensitivity of the back of the neck and sometimes the shoulders decreases.
At this stage of development of osteochondrosis, pain may be felt at night. It usually occurs when changing body position. Sleep disorders further aggravate neurogenic symptoms and negatively affect memory and concentration.
The pathology is characterized by frequent alternation between remissions and relapses. Exacerbations occur after hypothermia, excessive physical exertion, and even with sudden head movements.
Symptoms of grade 2 cervical osteochondrosis during relapses appear comprehensively and most clearly. At the remission stage, pain subsides, range of motion is slightly limited, but increased muscle tone remains.