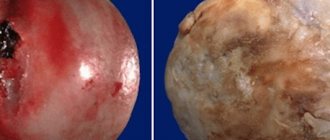
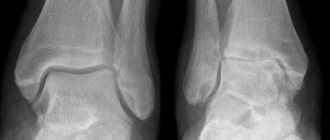
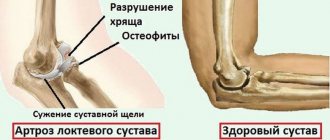
Arthrosis of the ankle joint or arthrosis of the tibiotalar joint is a fairly common pathology, although inferior in frequency to arthrosis of the knee and hip joints. The most common cause is previous trauma (in 60% of cases), another 10% is due to idiopathic arthrosis, the remaining 30% is divided between rheumatic diseases, osteonecrosis, septic arthritis, gout, etc.
Ankle fractures, one of the most common skeletal fractures, often result in a disruption of the relationship of the bones in the ankle joint. Changes in joint geometry and load distribution lead to rapid wear of cartilage, narrowing of the joint space, subchondral sclerosis and the growth of osteophytes. If untimely and inadequately treated, ankle fractures can lead to the formation of arthrosis of the ankle joint for several years after the injury.
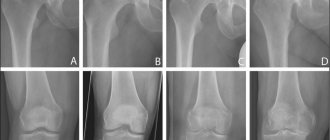
| Stage 1 | Subchondral sclerosis and the onset of osteophyte growth | |
| Stage 2 | Narrowing of the joint space in the medial region | |
| Stage 3A | Further narrowing of the joint space in the medial part of the joint until the contact of the subchondral bone | |
| Stage 3B | Narrowing of the joint space in the area of the roof of the dome of the talus to the contact of the subchondral bone | |
| Stage 4 | Complete obliteration of the joint |
-Pain with axial load (walking, running)
-Decreased range of motion (normally 20° dorsiflexion and 50° plantar flexion
flexion)
-Swelling in the ankle area
-Pain when checking range of motion during physical examination
-There may be visible deformation
For diagnosis, radiographs are taken in direct, lateral and oblique projections, with a load of body weight. X-rays reveal narrowing of the joint space, subchondral sclerosis, formation of cysts, deformation, and growth of osteophytes.
Conservative measures include reducing physical activity, using orthoses and braces, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
The use of orthopedic shoes with ankle relief can completely relieve pain in almost half of the cases.
If conservative measures are ineffective, surgical treatment is indicated.
Symptoms
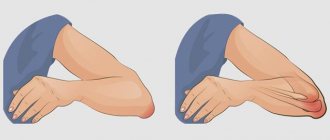
- Pain. At first, the pain appears after physical activity and disappears after rest. Over time, the pain becomes constant and limits the daily activity of patients.
- Impaired joint mobility. At the beginning, dorsiflexion is limited, then plantar flexion. As the disease progresses, the range of motion decreases. In the later stages of the disease, complete immobilization of the joint occurs (ankylosis).
- Swelling at the base of the first finger, redness.
- Lameness
Supramalleolar osteotomy.
At stages 2, 3A, with a relatively preserved range of motion and damage to the internal parts of the joint, a valgus supramalleolar osteotomy of the tibia is indicated.
This operation allows you to unload the medial parts of the joint and redistribute the axial load.
Stages of the disease
There are several classifications of arthrosis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint (Harttrup and Johnson, 1988; Barca, 1997; Easley, Davis et al., 1999, Coughlin MJ et al., 2003).
Depending on which of them is used, 3 or 4 stages of arthrosis are divided, not counting the pre-radiological stage (0).
First degree.
It manifests itself as periodic pain after excessive exertion, and rapid fatigue.
Second degree.
The pain syndrome is more pronounced. There is a limitation in dorsal flexion (extension) of the first finger. Radiographs reveal subchondral sclerosis, flattening of the articular surfaces, and narrowing of the joint space.
Third degree.
The pain becomes constant and bothers me even at rest. Dorsal flexion of the finger is absent, plantar flexion is limited. Joint deformity appears. Radiographs reveal bone growths and severe deformation of the articular surfaces.
Fourth degree.
All of the above symptoms become more pronounced, noticeable deformation appears, and the pain syndrome can become unbearable. In some cases, complete immobilization of the joint develops.
Causes of arthrosis of the talonavicular joint
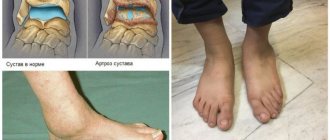
The susceptibility of the talonavicular joint to arthrosis is explained by the fact that due to the upright posture of a person, a significant load is placed on it. When a person stands or walks, the entire weight of his body is distributed over a relatively small plane of the foot, and the conditional line of gravity rests precisely on this joint. If articular dysplasia, flat feet, and poor posture lead to uneven distribution of the load, the risk of developing arthrosis increases. Provoking factors include hypothermia. Often arthrosis of the talonavicular joint is post-traumatic and develops as a consequence of an ankle injury.
Another common cause of arthrosis of this joint is flat feet. A change in the shape of the foot occurs due to weakness of connective tissue, muscles and ligaments, due to wearing uncomfortable shoes, and excessive stress. The load on our legs is created not only by the weights we carry, but also by our own excess weight. Inflammation of the joints, vascular and endocrine diseases, metabolic disorders can also cause degenerative changes characteristic of arthrosis. Primary arthrosis often develops in individuals with a genetic predisposition (impaired collagen synthesis, cartilage defects) and older people.
It is interesting that doctors often diagnose “arthrosis of the talonavicular joint,” although anatomists do not consider this joint to be an independent articulation, but consider it in conjunction with the calcaneocuboid. Together they form the transverse tarsal joint.
How to treat arthrosis conservatively?
Treatment of the disease can be based not only on medications, but also on physical exercise and adherence to a regimen for unloading the affected joint.
Read also: Who treats gonarthrosis of the knee joint
Treatment with medications consists of taking non-steroidal drugs that are effective in relieving inflammation in the affected area. If the situation requires it, the use of hormonal drugs is prescribed. To reduce the intensity of pain, you can take painkillers.
Only a doctor should select medications strictly on an individual basis, taking into account all contraindications and side effects. Self-prescription of treatment is prohibited, especially taking corticosteroids, since these drugs can have a detrimental effect on overall health if used incorrectly.
Chondroprotectors are also prescribed, which protect against damage and regenerate cartilage. But it is worth noting that the effectiveness of such funds has not been sufficiently proven by research. Their effectiveness can be determined only 6 months after the start of their use. If there is no improvement in health, the doctor stops using them.
In addition to medications, it is necessary to systematically unload the joint, using specialized orthopedic devices that help temporarily fix it at rest. To improve the condition of cartilage, you must follow a diet. So, it is necessary to consume more products that contain collagen, sulfur and selenium - the main “building materials” for cartilage. Consumption of jellied meat, eggs, milk, garlic, beef, apples, cabbage will help restore cartilage tissue.
No less useful is physical education, which is also prescribed on a strictly individual basis. Its implementation should be supervised by the attending physician, because excessive intensity of movements can harm an already damaged joint.
It is worth noting that young men with pathology of the 1st and 2nd degrees are exempt from conscription into such a place of stay as the army. Running and other stress on the musculoskeletal system, which is prescribed by the army, is contraindicated for arthrosis of degrees 1 and 2.
Treatment options
Patients with arthrosis of the subtalar ankle joint can be restored only through complex therapy, which involves physical therapy, taking properly selected medications, wearing orthopedic shoes, physical therapy and diet. Various traditional medicine recipes also show effectiveness, which should be considered as a supplement to basic health improvement.
Today, effective drugs have been developed that stop the destruction of joints, restoring damaged cartilage, allowing patients to completely recover in the initial stages of the disease. All drugs must be prescribed exclusively by a doctor, taking into account diagnostic data, existing contraindications and the stage of the disease.
To eliminate grade 1 osteoarthritis of the talonavicular joints, non-steroidal drugs Meloxicam and Diclofenac are prescribed. The course of treatment is up to 10 days. Hormonal glucocorticoid drugs, which are prescribed in the form of intra-articular and periarticular injections, are effective.
Chondroprotectors restore damaged tissue, while at the same time being an excellent prevention of bone diseases. Such medications are prescribed in courses lasting up to six months. Patients are advised to take multivitamins and medications that stimulate regional blood flow.
In addition to taking tablets and injections, local therapy using various ointments and creams shows effectiveness. All medications and duration of courses should be chosen exclusively by the doctor. Self-medication in the presence of arthrosis will only worsen the pathology.
Therapeutic exercise is carried out under the supervision of a rehabilitation physician, who develops a set of exercises taking into account the stage of joint damage. The main goal of gymnastics is to maintain limb mobility.
Recommendations for exercise therapy:
- Yoga and swimming show excellent results.
- At the first stage, healthy joints are worked on.
- All exercises are divided into passive and active.
- As you practice, the range of movements increases.
- Exercises are performed systematically.
In the presence of severe inflammation, physical therapy exercises are not recommended. Such recovery should be performed only after the main symptoms of joint arthrosis have been relieved. It is not recommended to choose exercises on your own and do them at home without first consulting a rehabilitation specialist.
Performing physical procedures allows you to stimulate regeneration processes, improve blood flow, prevent muscle contracture and reduce pain. Treatment should be performed by a specialized specialist who can determine the degree of joint damage to ensure maximum effectiveness of the therapy.
For arthrosis, the following procedures are performed:
- Thermal therapy involves water heating pads, ozokerite and paraffin applications, and mud therapy in a hospital setting.
- Infrared radiation stimulates regeneration processes. It is recommended to perform such procedures twice a day.
- Ultraphoresis involves exposing the affected joint to ultrasonic pulses. This method is used in parallel with the use of medicinal ointments.
- During magnetic therapy, a weak magnetic field is applied to the affected cartilage and joints to resolve hematomas and reduce pain.
- Electrophoresis has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating effects.
As changes in the joints progress, complete death of the cartilage is observed. It reduces the patient's motor function. Immobility, foot deformity and constant pain are indications for surgical intervention. Modern technologies and endoprosthetics make it possible to completely restore the patient, returning him to his former healthy life.
In endoprosthetics, damaged joints are replaced with artificial ones. After such operations, recovery takes two to three months, and upon completion of the rehabilitation period, the patient’s motor function is completely restored.
Arthroscopy is a low-impact surgical procedure in which an astroscope is inserted into a small incision in the joint. The surgeon uses such a device to remove damaged areas of cartilage. The effect of such an operation is short-lived, so it is recommended only for young patients with the first and second degrees of arthrosis.
In the past, orthopedists used arthrodesis surgery to treat this disease. Modern medicine has almost completely abandoned this method of surgical intervention, since after completion of the operation the joint is fixed in one position, bones fuse, and the movement of the limbs is severely limited.
What to do if you are still called up?
The decision of the military registration and enlistment office can be appealed, according to the Constitution of the Russian Federation, Article 46. An appeal in court is possible. In order to appeal the commission’s decision, it is necessary to prepare a complete list of documents confirming the groundlessness of assigning the “fit” category.
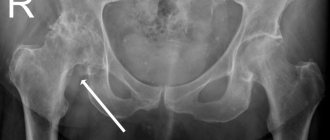
To do this, it is necessary to collect doctors’ opinions, x-rays, and also draw up an application for appeal. It is important to remember that if a person entered the service and was given the rank of “private”, then he will no longer be able to appeal the conscription. If the complaint is filed only for the purpose of deferring conscription, and the young man has no medical grounds for this, then the situation may worsen. You can appeal the decision of the draft commission within 3 months from the date of the decision by the military registration and enlistment office.
Arthrosis of the 2nd degree and higher in some cases limits the suitability of a conscript for serving in the army. To verify the presence of pathology, it is necessary to undergo a full examination and receive a diagnosis at a public clinic.
How to treat arthrosis surgically?
Arthrodesis of the talonavicular joint is carried out when conservative treatment methods are ineffective, and diagnostics show that their ineffectiveness can cause disability. As a rule, this operation is a decisive step, which a doctor can prescribe only after applying all other treatment methods.
Arthrodesis is performed when persistent pain syndrome persists, as well as when there is a complete loss of support function. Thanks to an operation such as arthrodesis, all defects and pain can be eliminated.
During the operation, the cartilage tissue is completely removed, after which the surfaces of the two articulating bones are firmly fixed. Once these bones have fused, they will no longer rub against each other, thereby causing pain.
On an x-ray they will look like one solid bone. To speed up fusion, a method such as artificial compression of the articular ends using a special apparatus is used.
We can talk about a positive result after arthrodesis surgery only if there is no pain syndrome when walking a distance of about 4 km, and also if there is no difference in the length of the healthy and operated limb. You can also talk about a favorable outcome of arthrodesis surgery if you can wear regular shoes that do not cause discomfort and pain.
Compliance with the following simple requirements will help prevent the development of any type of arthrosis, including arthrosis of the talonavicular joint:
- Moderate exercise is a prerequisite for prevention. Maintaining a balanced motor regime contributes to the proper functioning of the joint without the possibility of further deformation. At the same time, the muscle corset is strengthened and blood circulation is increased.
- Hypothermia is an enemy to health in general, including joints.
- Maintaining a proper diet. It is not recommended to abuse meat products that contain excess fat. You can strengthen your joints with sufficient consumption of seafood, fish, fresh vegetables and fruits, lean meat, porridge, and dairy products.
- Elimination of excess weight, which increases the load on the joint.
- Joint injuries should be avoided.
- Wearing the right shoes with low heels and wide toes.
And, the most important rule of prevention is timely consultation with a doctor if you suspect a disease. After all, with timely initiation of treatment, it is possible to slow down and stop the further development of arthrosis.