Joint pain in the hand not only interferes with normal life, reduces motor activity, leads to impaired performance, but also worsens the emotional state due to constantly occurring painful discomfort.
That is why, when a person has pain in the joints of his fingers, the first thing that interests him is the causes of this phenomenon and possible treatment.
Carpal tunnel syndrome: causes, symptoms, prevention and treatment
- Cause of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Examination and diagnosis for carpal tunnel syndrome
- Treatment for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Prevention of carpal tunnel syndrome
From the previous article you learned - Why computers hurt your eyes, and what rules you need to follow in order to avoid vision deterioration when working at a computer for a long time. In this article, we will look at another very common problem that arises when working with a computer for a long time and often leads to serious negative consequences - this is the so-called “carpal tunnel syndrome”.
Treatment of pain in the hands
Regardless of the cause, treatment of diseases of the wrist joint should be comprehensive and aimed at solving three problems at once:
- elimination of pain symptoms;
- therapy of the causative disease;
- restoration of functional mobility.
Pain syndrome is relieved with anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers (analgesics). They should be prescribed by a doctor at our clinic, taking into account your illness and related problems.
The doctor also prescribes treatment for the underlying cause. If it is a dislocation or fracture, it is necessary to immobilize the joint, fixing it in a stationary position. Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome and other nerve-related diseases should be carried out by a neurologist. Osteoarthritis and arthritis should also be coordinated with other specialists. Physiotherapy plays a huge role in facilitating treatment and restoring the joint.
An integrated approach to treatment gives the most effective results. This is exactly the approach we offer to patients at the KANO clinic.
Therapeutic massage normalizes local blood circulation, improves tissue nutrition and oxygen saturation, and increases muscle tone. Massage is a preparatory measure for physical therapy itself, aimed at mobilizing the joint and improving its mobility.
In addition to massage, other physiotherapeutic procedures will help restore blood flow and metabolism - paraffin therapy, therapeutic mud, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis.
Shock wave therapy shows good results. In some cases, its timely use allows one to avoid surgical treatment and prevent exacerbations of the disease.
To restore a joint after a dislocation or fracture, physical therapy, gymnastics and mechanotherapy are recommended.
By adhering to an integrated approach and responsibly following doctors’ recommendations, you can achieve excellent results and get rid of pain in your hands.
Treatment of pain in the hands in Minsk
Prevention of pain in the hands
- If uncomfortable movements occur in the hand, it is necessary to change the type of load or give the joint a rest and stretch it.
- When gripping, distribute the load on your hand evenly: don’t grab with just your fingers, use your palm too.
- When working at a computer, position your hands comfortably, choose a comfortable sitting position, and use an ergonomic keyboard and mouse.
- Do not lift heavy objects; it is better for your health to carry a large load in parts.
- During tennis training, golf and other sporting events, it is a good idea to protect the wrist joint from damage (bandages, calipers, gloves with wrist protection).
Cause of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The cause of pain in carpal tunnel syndrome is a pinched nerve in the carpal tunnel. Pinching can be caused by swelling of the tendons that run close to the nerve, as well as swelling of the nerve itself.
The cause of pinched nerves in carpal tunnel syndrome is a constant static load on the same muscles, which can be caused by a large number of monotonous movements (when working with a computer mouse) or an uncomfortable position of the hands while working with the keyboard, in which the wrist is in constant tension.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The initial stage of the disease is characterized by trembling, itching and tingling in the fingers. Most often, such symptoms occur a few hours after finishing work, so people do not associate their manifestation with working on a computer. Later, numbness, loss of sensitivity in the hand area, pain and heaviness in the hands, irritation and swelling of tissues, tingling in the wrist, palm and fingers may appear. An indirect manifestation may be insomnia caused by pain and cramps. You may feel stiffness in your fingers in the morning.
Advanced syndrome leads to atrophy of the thumb muscle. The ability to bend the thumb and tightly clench your hand into a fist is lost. Sometimes the hand, palms and fingers become unruly. When trying to lift a heavy object, pain may occur, and the hands may also switch off - objects fall out of them against their will. Other symptoms may include the inability to talk on the phone for a long time, hold the steering wheel of a car for more than 10 minutes, or read a book while holding it in front of you.
It should be noted that pain in the hands can be caused not only by pinching of the carpal nerve, but also by damage to the spine (osteochondrosis, herniated intervertebral discs) in which the nerve coming from the spinal cord is damaged.
Examination and diagnosis for carpal tunnel syndrome
The diagnosis is made when the patient is examined by a neurologist. Of the instrumental methods, electromyography is used, with which you can determine the degree of damage to the muscles of the forearm.
You can determine the presence of this disease yourself. You need to connect the backs of your hands and lower your arms down. The elbows should be directed in different directions, and the wrists should be bent at right angles. If you feel pain or discomfort within a minute, this means the onset of the disease.
Treatment for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
In case of acute pain, severe inflammation and severe tunnel syndrome, you should contact a clinic where you will be prescribed medication. It includes the injection of corticosteroids (prednisolone, dexamethasone) into the wrist area, the use of drugs that improve blood circulation (vasoactive) (trental, nicotinic acid), and anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen).
Against the background of proper nutrition and providing the body with all vital vitamins, microelements and biologically active substances, treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome becomes more effective, recovery is accelerated, and the time for rehabilitation and restoration of working capacity is reduced.
If there is no effect from drug therapy for carpal tunnel syndrome, there are indications for surgical treatment (open or endoscopic).
Prevention of carpal tunnel syndrome
To prevent carpal tunnel syndrome, you should take care of the convenience of your workplace:
- When working with the keyboard, the bend angle of the arm at the elbow should be straight (90°).
- When working with a mouse, the hand should be straight and lie on the table as far from the edge as possible. The elbow should be on the table.
- It is advisable to have a special wrist support (mouse pad, specially shaped keyboard or computer desk with special silicone pads, etc.)
- A chair or armchair must have armrests.
A set of exercises to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome
1. Slowly clench your hands into fists, and then slowly unclench them. Repeat this exercise five to six times. 2. Place your palms on the table and press them onto its surface. Bend your fingers one at a time. 3. Raise and lower your arms several times. Draw a few circles with your brushes and then with each finger. 4. Perform rotational movements with your hands, then move your fingers. Clench your hands into fists and rotate them around your axis. 5. Shake your hands. 6. Clasp your hands together and press one hand onto the fingers of the other.
Complex No. 2 (designed to relax hands)
1. Raise and lower your arms several times, shake your hands. 2. Clench your fists tightly for a few seconds, then unclench them and relax your hands. Repeat the exercise five to seven times. 3. Perform rotational movements with your hands - 10-12 times in each direction. 4. Extend your arms in front of you and actively move your fingers for one minute. 5. Place your palms together and turn your fingers towards you, with your wrists facing away from you. Slowly press with one hand on the fingers of the other hand from the side of the palm, as if turning the palm and wrist outward. Repeat five to seven times.
1. Rub the outer and inner surfaces of your palms until you feel warm. 2. Using the thumb of your left hand, bend each finger of your right hand back. Perform four presses on each finger, then repeat for the right hand. 3. Connect your fingers together, palms should be turned towards each other with their inner sides and slightly apart. Press your fingers into each other, then relax your hands and shake them. 4. Slowly clench your hands into fists. Shake your brushes and relax them. 5. Slowly clench your fingers into a fist, then sharply unclench them, throwing your fingers away. Lower your arms, shake your hands.
During breaks from working at the computer, if it is not possible to perform a full set of exercises, from time to time raise your arms up and rotate your hands. If you notice signs of carpal tunnel syndrome, such rotations should be very slow and careful. Shake your hands periodically to relax your muscles.
I can't clench my hand into a fist
Everything begins someday. This is such an incomprehensible illness, when you cannot clench your hand into a fist, it seems to come out of nowhere and suddenly. What reasons could there be for this phenomenon? As usual, there are many reasons. Let's name a few of the most important ones.
Spinal problems
Sometimes a person cannot clench his hand into a fist if he has problems with the cervical and thoracic spine, more precisely with the fifth, sixth and seventh cervical and first, second and third thoracic vertebrae. A computed tomography scan should be done; the pictures usually show everything at once.
Sore stomach or intestines
Yes, a diseased gastrointestinal tract can be the source of many health problems. For example, an infection that has entered the intestines and caused inflammation can cause complications in the joints and cause inflammation. It is possible that in this case, a diseased stomach or intestines gives such a side effect. It doesn't hurt to check.
Arthritis
This reason is perhaps the most serious. A person wakes up at night due to aching in the elbow or shoulder, or a twisted knee. After the massage he feels better. But over time, the pain not only does not disappear, but also intensifies, the fingers become unruly, the hand does not clench into a fist, the legs do not bend at the knees. The joints are gradually destroyed due to the onset of inflammation. It is important here not to bring the matter to surgical intervention. If pain, swelling, or redness of the skin appears in the joint area, you should contact a rheumatologist as soon as possible.
It is especially important to start treatment on time for reactive arthritis . This type of arthritis appears after a sore throat, after an intestinal or sexually transmitted infection, as well as when an infection gets inside a joint during surgery. With reactive arthritis, large joints on the legs are affected, the treatment is asymmetrical.
Cartilage, ligaments and joints are also destroyed in rheumatoid arthritis. The inflammatory process usually occurs due to a malfunction of the immune system - the so-called. autoimmune disease. With this disease, the human immune system begins to actively protect the body from an imaginary enemy and attack its own cells inside the joint. Left untreated, it can lead to wheelchair use. You can name the signs of rheumatoid arthritis. The wrist and fingers suffer, and they hurt on both hands at the same time. In the morning, a person cannot clench his hand into a fist; his fingers have to be stretched for a long time. A person “paces” for a long time, getting rid of stiffness of movements.
Gout, or microcrystalline arthritis (salt deposition) is caused by metabolic disorders, dietary errors, kidney disease, and stress. With gout, there is an increased level of uric acid in the blood. Sodium crystals begin to deposit in the joints, the joint swells and gives severe, sometimes unbearable pain.
Hernia on the spine
This cause can be easily tracked by taking an x-ray or MRI.
Heart diseases
In these cases, side sensations occur in the area of the left shoulder blade and chest. You can try taking Corvalol and artificially inducing a cough - this should help.
Source: nmedicine.net
Stages of disease development
Depending on many factors, there are three degrees of progression of the pathology:
1. Initial stage. The disease at the start of its development does not bring significant discomfort. At most, the victim feels minor pain in the finger area, which quickly subside. At the same time, he begins to be alarmed by the characteristic weak click heard after moving his finger.
2. Middle stage. With further tightening of the tendons, unpleasant symptoms cannot be avoided. A phase has arrived when the affected finger has difficulty changing its position, and the tubercle that appears in the problem area hurts when pressed.
3. Late stage. If you ignore the alarming symptoms of the first two stages of development of stenosing ligamentitis, the finger cannot return to its original position without additional help. The only way out of the situation is surgical intervention.
Why does pain occur in the elbow when clenching a fist?
The elbow joint is one of the most complex and mobile elements of the musculoskeletal system. It contains many small and large muscles that are important in the functioning of the fingers. Almost every second person experiences pain in the elbow joint when clenching a fist. But the obsessive nature of the pain can limit movement and bring suffering if treatment is not applied in time.
Possible causes of pain
When a person lifts weights with his hands or performs physical work, he may feel pain in the elbow joint after the load. But this is not the main and only cause of pain. Pain can be caused by pathological processes in the elbow, including injury, inflammation, tumor, and degenerative changes in the joint.
During flexion and extension
If your elbow hurts when bending, this indicates arthrosis, bursitis, arthritis or osteoarthritis. In such diseases, the movement of the hands is characterized by pain and crunching. The acute form of the disease is accompanied by increased temperature, swelling, and redness of the skin of the elbow joint.
Pain during extension, rotation, and flexion can occur due to epicondylitis. Epicondylitis of the elbow joint is an inflammatory disease that forms in the connecting place of the muscles and bones of the forearm. Pain, difficulty moving the upper limb, swelling - indicates a rupture of the tendons of the forearms and the elbow area. Individuals suffering from this disease cannot bear weight on an outstretched arm and feel discomfort when clenching their fist.
During physical activity
After physical activity, severe pain occurs, which is considered the main symptom of the pathology. Inflammation of the shoulder develops, discomfort appears when bending or straightening the arm. Mostly the painful sensation occurs on the back of the elbow. Also, increased load on the joint stimulates pinching of the spinal cord nerves, which can result in pain in the elbow and shoulder.
In addition, the load in the form of pulling up on the horizontal bar contributes to the appearance of pain in the joint. If the pain is constant and not associated with sports training, then it characterizes the presence of a joint disease (arthritis, malignant tumors, neuritis). If there is no load, the pain may be reflected from the internal organs.
Injury after tennis
Elbow pain may indicate an injury, sprain, dislocation, or subluxation. The phenomenon can be provoked by incorrect exercise technique, sudden movement, or overstrain of the musculoskeletal system. But if a pain threshold occurs after every tennis workout, then this most likely indicates the presence of epicondylitis.
Why does stenosing ligamentitis form?
The reasons that the finger begins to click may vary in its pathogenesis:
1. Selected area of professional activity. This disease is often a consequence of frequently repeated movements of the fingers in one direction. As a result, a kind of tendon blocking effect occurs. People who fall into the “risk group” for the occurrence of this disease are milkmaids (with the exception of machine milking operators), hairdressers, manicurists and pedicurists, masons, musicians, seamstresses, etc.).
2. Hereditary factor. It cannot be called the main cause of the development of stenosing ligamentitis. However, isolated cases of inherited predisposition to the disease have been recorded.
3. Congenital defect. We are talking about an abnormal structure of the tendon-ligamentous apparatus of the hand, which can only be corrected by surgical intervention.
4. Injury. After a bruise or sprain in the arm without further examination by a doctor, stenosing ligamentitis may develop.
5. Chronic diseases. Symptoms of the disease are sometimes difficult to recognize in time against the background of existing pathologies such as arthritis or rheumatism. The disease can also develop due to diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis and thyroid dysfunction.
6. Physiological and age-related changes. This factor especially concerns pregnant women and women at the onset of menopause, in whom, due to hormonal changes, water is retained in the synovial membrane.
7. Systemic autoimmune changes. Stenosing ligamentitis can be triggered by scleroderma, lupus erythematosus, polymyositis, Sharp, Weber-Christian and Sjögren's syndromes.
Treatment methods
The disease is not considered severe and does not lead to loss of performance, but people still need to know how to treat pathology of the elbow joint. After all, untimely therapy leads to exacerbation and deterioration of the victim’s health, the development of acute and chronic forms of the disease. The main goal of treatment is not only to relieve pain, but also to eliminate inflammation, improve metabolism and blood circulation. But the most important thing is to restore mobility and joint function and prevent muscle atrophy.
The following methods are used to treat the elbow joint:
- Medications.
- Physiotherapy.
- Exercise therapy.
- Ethnoscience.
Drug therapy
To cope with pain, painkillers will help when squeezing your hand. They are prescribed by the doctor after examining the limb and interviewing the patient. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs relieve pain and inflammation. These include: Nimesil, Nise, Naproxen, Ibuprofen.
Therapeutic physical training and massage
To improve the condition of your joints, you can do regular exercise after consulting your doctor. If the pain during exercise is too strong, then various ointments and balms are used. Massage improves blood flow to the affected joint, which helps relieve swelling faster.
The same banned issue for which Ernst fired Malakhov!
Joints and cartilage will be cured in 14 days with the help of ordinary...
All about joints
Human hands are significantly different from animal limbs. Since the hands have a complex structure and a large number of flexible joints, a person can perform many movements that are distinguished by jewelry precision.
Unfortunately, many people do not pay attention to how important it is to monitor the functionality and condition of their fingers and hands. In most cases, due to such irresponsible behavior, the finger or hand becomes deformed and pain appears.
Many reasons have been identified to explain why the joint of the fingers hurts. You should know the main ones that cause pain in the fingers.
Diagnostics
Since pain in the joints of the hands can be caused by a very wide range of disorders, it is necessary to determine the exact reason why the fingers are stiff, swollen and/or painful. The diagnosis is made using the following studies:
- radiography;
- scintography;
- ultrasound examination;
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography;
- immunological tests;
- laboratory testing of blood and urine.
If necessary, to accurately diagnose the causes of joint pain in the fingers, a tissue biopsy and synovial fluid analysis are performed.
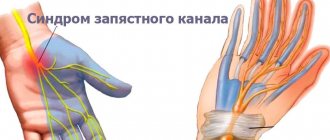
Carpal tunnel syndrome
The pathology is a neurological disease, which is expressed in compression of the median nerve inside the carpal tunnel. This refers to the space between the tendons and bones of the wrist.
The median nerve is involved in the innervation of the skin of the palmar surfaces of the index, thumb and middle fingers of the left and right hands. In addition, the nerve works when flexing the hand and abducting the radius to the side.
When carpal tunnel syndrome occurs, the following symptoms are typical:
- the thumb hurts (inner surface),
- discomfort in the index finger,
- numbness in the area of innervation of the median nerve,
- decreased accuracy of fine motor skills of the hand,
- thinness of the muscles in the area of the eminence of the first finger.
If there is prolonged compression, and treatment is not started in a timely manner, the functionality of the nerve may disappear forever, which threatens the inability to carry out small movements of the fingers of the left or right hand. Thus, disability is very likely.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is formed due to prolonged overload of the ligaments and joints of the hand. As a rule, the condition appears in those people who, due to the nature of their work, constantly perform flexion-extension movements with their hands.
We are talking about artists, pianists, sign language interpreters, people who constantly work with a computer.
Causes of pain in the hands
There are many ways to damage your hand joint in everyday life. First of all, long-term monotonous work has an extremely negative impact on the condition of this joint, so programmers, testers and other IT workers are at risk.
Such pains often plague athletes: tennis players, golfers and people who are professional rowers. When making sudden movements in the hand - such as gripping or bending the wrists - the load on the ligamentous apparatus can become excessive and lead to injury to the ligaments. From such regular microdamages, a disease called “tendonitis” develops - inflammation of the tendons.
No less important in the etiology of hand diseases is that when a person falls, they reflexively put their arms forward, which means they unconsciously put their hand and wrist at risk. Injury to the wrist joint is accompanied by a characteristic symptom: sharp severe pain, swelling, redness and impaired joint mobility. If, after an injury, a deformity of the hand in the wrist area is visually noticeable, then an X-ray examination is required to exclude a fracture of the scaphoid and lunate bones. This is important because an undiagnosed wrist fracture can lead to complete loss of mobility in the hand.
Wrist pain may be symptoms of the following diseases:
- Dislocation, sprain,
- Fracture of the bones of the hand or wrist,
- Arthritis or arthrosis,
- Tunnel syndrome (carpal tunnel syndrome),
- Deforming osteoarthritis of the hand joints,
- Neurological reasons.
Which doctors should you consult if your wrist hurts?
The examination should begin with a visit to an orthopedist-traumatologist. As a rule, his area of expertise includes most possible causes of pain in the hands. And if necessary, the doctor will give you a referral to a doctor of another specialty.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
Diagnostic and treatment methods
At the initial visit, the doctor needs to find out your life history, find out your concomitant chronic diseases (diseases of the cardiovascular system, arthritis and arthrosis of other joints, osteochondrosis). The doctor will ask when the problem started, what you attribute it to, and whether there were any blows or falls.
Afterwards, the doctor will conduct an external examination of the joint and diagnostic tests, for example, a test for passive flexion and extension of the joint, palpation and tapping along the nerve.
An important research method is radiography. It allows you to judge the integrity of the bones, helps to identify their displacement and deformation. According to indications, an analysis of synovial (articular) fluid obtained through joint puncture can be performed.
CBCT visualizes the condition of bone structures in detail - at a higher level, allows you to determine bone density and its defects. And MRI visualizes soft tissues - ligaments, tendons, joint capsule. A competent specialist will prescribe the necessary types of diagnostic measures and recommend a consultation with a doctor of another specialty, if necessary.
Syndrome and Raynaud's disease. Polyosteoarthrosis
Raynaud's syndrome is a pathology associated with impaired tone of the capillaries of the fingers and small arteries. In the vessels, either for no reason or in response to irritation, blood flow decreases, they spasm, which manifests itself as follows:
- The blood vessels first sharply narrow, causing the finger or hand to turn pale. One finger or several may be affected. At this time, a characteristic numbness appears, which people often mistake for pain. In most cases, the nail phalanges are affected, but the entire finger can be involved in the pathology.
- At the next stage, paralytic vasodilation begins, the finger becomes red, may be dark or even bluish. At this time, the pain becomes very acute and the fingers swell.
Rhizarthrosis and polyosteoarthrosis
When the joints of the thumbs hurt, then first of all you need to consider the presence of a disease such as rhizarthrosis, that is, osteoarthritis of the first finger.
Rhizarthrosis affects the joint located at the base of the first finger; it connects the wrist joint to the metacarpal bone (first). About 5% of cases when the left or right hand hurts is the formation of rhizarthrosis.
This pathology, as a rule, goes away together with polyosteoarthrosis, but in 20-30% the disease proceeds independently, which seriously complicates diagnosis.
The main symptoms of rhizarthrosis are:
- the base of the first finger of the right or left hand hurts, the pain becomes stronger during movements,
- the joint crunches,
- the thumb bone is deformed,
- range of motion is limited.
When rhizarthrosis occurs as an independent disease, it is important to carry out a differential diagnosis with a disease that manifests itself with similar symptoms, for example, de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
With osteoarthritis, an x-ray reveals a pathological change in the bones of the left or right hand; this never happens with tenosynovitis.
First aid
If you notice swelling on your fingers, then prepare a solution of dimexide or other anti-inflammatory gel and apply a gauze bandage with it to the affected area. Follow the instructions carefully to avoid getting burned.
Our hands are significantly different from the limbs of all other living organisms. Thanks to its complex structure and large number of flexible joints, we can perform any movements at a jewelry level. Unfortunately, many people do not realize how important the function of the hands and fingers is until these movements become impossible due to pain or deformity.
There are many reasons why your finger joints hurt. Some of them are frivolous, and some are very dangerous. Let's look at the main reasons why pain in the fingers of the upper limb may occur.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
This is a neurological disease that is caused by compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel (the space between the bones and tendons of the wrist). The median nerve provides innervation to the skin of the palmar surface of the thumb, index and middle finger, and is also involved in flexion of the hand and its abduction towards the radius.
With the development of carpal tunnel syndrome, patients complain of:
- pain in the thumb along the inner surface;
- painful sensations in the index fingers;
- numbness of the skin in the area of innervation of the median nerve;
- decreased accuracy of small hand movements;
- muscle loss in the area of the eminence of the first finger.
With prolonged compression, if treatment is not prescribed on time, the function of the nerve may be lost forever, and this can lead to the inability to perform small movements of the fingers, which can even cause disability.
The cause of the development of this tunnel syndrome is prolonged overload of the joints and ligaments of the hand. Most often, the pathology develops in people who, on duty, perform monotonous flexion-extension movements with the hand. For example, sign language interpreters, pianists, artists, people who work with computers, etc.
Raynaud's disease and syndrome
This is a pathological condition that is associated with impaired tone of small arteries and capillaries of the fingers. In response to any irritants or for no reason, the vessels spasm for a certain time, blood flow in the tissues of the fingers is disrupted, which is manifested by the corresponding symptoms:
- First, the blood vessels narrow sharply, which causes the skin of the fingers to become pale. One finger on the hand or several at once may be affected. At this stage, a characteristic numbness develops, which patients often perceive as pain. Most often only the nail phalanges are affected, but the entire finger can be retracted.
- At the next stage, paralytic vasodilation occurs, the skin turns red and becomes dark, sometimes bluish. At this stage, the pain becomes burning. Fingers swell.
A distinction is made between Raynaud's disease, when the cause of such symptoms cannot be determined, and the syndrome, when the patient has an underlying disease. For example, Raynaud's syndrome is a frequent companion to systemic connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, dermatomyositis).
The danger of Raynaud's syndrome or disease is the high risk of developing gangrene of the hand. If the spasm does not go away in time, the soft tissue may die. Also, such patients have an increased risk of developing felons (purulent inflammation of the finger), trophic ulcers, fungal infections of the skin and nails.
Polyosteoarthrosis
One of the main reasons why the joints of the fingers hurt is deforming polyosteoarthrosis (about 40% of all cases). Mostly women fall ill after 45-50 years of age.
This disease, in addition to chronic pain in the affected small joints, is characterized by the development of nodular formations in the area of the joints of the hand (Bouchard and Heberden nodes). The former are localized in the area of the proximal interphalangeal joints, the latter - distal. They develop symmetrically on both hands and are accompanied by pain and deformation of the hands, which often leads to inferior function.
From time to time, these nodules, like the affected joints themselves, can become inflamed, swollen and red. During this period, the pain intensifies, anti-inflammatory treatment is necessary. Outside of exacerbation, painful sensations usually appear after overstraining the joints of the fingers.
Rhizarthrosis
If the joints of the thumbs hurt, then you must first rule out a disease such as rhizarthrosis. Essentially, this is osteoarthritis of the first finger. The pathology affects the joint, which is located at the base of the first finger, and connects the wrist joint to the first metacarpal bone. Rhizarthrosis accounts for up to 5% of cases of all pain in the hands.
Most often, this pathology is observed together with polyosteoarthrosis, but in 20-30% of cases it has an independent course, which significantly complicates diagnosis. The main symptoms of rhizarthrosis: pain at the base of the first finger of the left or right hand, which intensifies during movements, a characteristic crunch in the joint, deformation of the thumb bone, limited range of motion in the diseased joint.
If rhizarthrosis is observed as an independent pathology, then it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with a disease that manifests itself with similar symptoms, with de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. In contrast to the latter, pathological changes in the bones can be detected on an x-ray with osteoarthritis, which is not the case with tenosynovitis.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis accounts for 5-7% of all cases. People of any age and even children get sick. Women get sick 5 times more often than men. As a rule, pathology develops after 30 years.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory systemic disease that mainly affects small joints of the body, but large joints and internal organs may also be involved in the pathological process.
The disease, as a rule, begins acutely after an acute respiratory viral infection, a stressful situation, or hypothermia. The metacarpophalangeal joints of the index and middle fingers become inflamed. The joints swell, turn red, and the skin over them becomes hot to the touch. The joints hurt a lot, the person cannot even clench his hand into a fist. The lesion is often symmetrical on both hands. A characteristic feature is that the inflamed joints hurt in the morning or in the second half of the night, this is accompanied by stiffness of movements in the hands. By evening the pain goes away.
At the same time, other joints can become inflamed, for example, wrists, knees, ankles, and elbows. Often an exacerbation of the disease is accompanied by fever and general malaise.
Over time, if the patient has not received adequate treatment, the hand becomes deformed and its function is completely lost. Moreover, the curvature of the hand is so characteristic and typical that they are called the “calling card” of rheumatoid arthritis.
Gouty arthritis
Gout is a metabolic disease that is accompanied by excessive formation of uric acid in the body and its deposition in the form of salts in peripheral tissues. Most often, gout affects the joint of the first toe, but sometimes (especially in women) psoriatic arthritis affects the upper extremities with the development of arthritis, which is very similar in appearance to rheumatoid arthritis.
Signs of psoriatic arthritis of the fingers:
- Inflammation manifests itself in the form of unexpected attacks.
- The pain is very acute, it is impossible to touch the finger.
- The joint turns red, swells, the skin over it shines and has a bluish tint.
- With a long course of the disease, gout-specific tophi nodules appear under the skin, which are an accumulation of urate salts.
- The attack lasts 3-10 days and goes away on its own or under the influence of treatment (injections, tablets, ointments).
If you do not resort to therapy and secondary prevention (diet, medications), then over time the affected joints are destroyed, the hand becomes deformed and loses its function.
Psoriatic arthropathy
In 7% of cases, the skin disease psoriasis is complicated by the development of chronic inflammation of the joints (psoriatic arthropathy). The causes of this, like psoriasis itself, are unknown.
This arthritis is characterized by a so-called axial lesion, when all joints of one or more fingers become inflamed at the same time. This makes it look like a sausage (sausage-shaped fingers).
The pain is very severe, observed both at rest and with movement. The finger is enlarged, red, the skin over it is hot. The defeat is asymmetrical. Diagnosis is aided by the patient's indication of a history of psoriatic skin rash or its current presence.
Vibration disease
Occurs in people who work with hand-held power tools that produce vibration. With prolonged exposure, a local vibration disease can develop, which has several stages.
At the beginning, patients complain of transient pain, numbness, and a feeling of pins and needles in the fingers. Further, the pain becomes more pronounced, the sensitivity of the skin of the fingers is gradually lost, and other types of sensitivity, for example, temperature and vibration, also disappear. Vascular tone is impaired and Raynaud's syndrome may additionally occur. At the last stage, trophic complications develop (ulcers, gangrene), which threatens the loss of individual fingers or the entire hand.
Felon
This is a purulent inflammation of all tissues of the finger. The nail phalanx is usually affected. The cause of felon is the penetration of infection into soft tissues, for example, a cut, puncture of a finger, pulling out hangnails, unsuccessful manicure, etc.
The first sign of panaritium is pain, which has a twitching or pulsating character, intensifies at night. Then redness and swelling occur, the skin becomes hot to the touch, and a wound with pus may be detected. The general condition of a person also suffers: the temperature rises to high values, and general malaise develops.
Panaritium is a dangerous disease not only for one finger, but also for a person’s life, because the infection can enter the bloodstream with the development of sepsis and death. Therefore, purulent inflammation is an emergency condition that requires urgent surgical care and adequate antibiotic therapy.
These are just the main reasons why your finger joints hurt. In fact, there are a lot of them. If the pain does not leave you for a long time, is not associated with a bruise, or is accompanied by other pathological signs, then you should definitely be examined by a doctor. After all, such a seemingly trivial symptom can cost not only your arm, but also your life.
Comments
Sveta – 03.12.2016 – 02:07
- answer
Add a comment
- My spina.ru © 2012—2019. Copying of materials is possible only with a link to this site. ATTENTION! All information on this site is for reference or popular information only. Diagnosis and prescription of medications require knowledge of the medical history and examination by a physician. Therefore, we strongly recommend that you consult a doctor regarding treatment and diagnosis, and not self-medicate. User AgreementAdvertisers
Rheumatoid and gouty arthritis
When a joint hurts due to rheumatoid arthritis, this happens in 5-7% of cases. People are susceptible to the disease at any age, even children get sick. However, women get sick more often, about 5 times. Pathology often develops after 30 years.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease. Basically, the pathology is characteristic of small joints of the body; it is also possible that internal organs and large joints are involved in the process.
The disease, as a rule, begins in the acute phase, against the background of:
- stressful situation,
- ARVI,
- prolonged hypothermia.
The inflammatory process of the metacarpophalangeal joints of the middle and index fingers begins. The joints become red, swollen, and the skin above them increases in temperature. The joints also begin to hurt greatly; in most cases, a person cannot clench his hand into a fist. Often the lesion occurs symmetrically on both arms.
A characteristic feature is that the inflamed joint hurts in the morning or in the second half of the night. The pain is associated with stiffness of joint movements. Until the evening the pain syndrome does not bother me.
Often another joint, such as the knee, wrist, ankle or elbow, can become inflamed at the same time. As a rule, an exacerbation of the disease is accompanied by a general loss of strength and an increase in temperature.
If a person has not received qualified treatment, then over time the hand begins to deform, losing its function. Hand distortions can be very noticeable. The joint is deformed so typically that such curvatures are usually called the “calling card” of rheumatoid arthritis.
Gout is a metabolic disease accompanied by excessive formation of uric acid in the human body. The acid is deposited in the form of salt crystals in peripheral tissues.
As a rule, with gout, the joint of the first toe is susceptible to changes. In some cases, and especially in women, psoriatic arthritis affects the hands. The disease is similar in appearance to rheumatoid arthritis.
Psoriatic arthritis of the fingers is expressed by the following symptoms:
- Inflammation is characterized by sudden attacks,
- The pain in the finger is very sharp, it is impossible to touch it,
- The joint begins to swell, turn red, the skin above it shines, having a bluish tint,
- With prolonged treatment of the pathology, tophi nodules, characteristic of gout, begin to form under the skin. This is, in fact, an accumulation of urates, that is, salts,
- The duration of the attack is from 3 to 10 days, it goes away on its own or after treatment with ointments, injections or tablets.
If therapy and secondary prevention (supportive medications, diet) are not carried out, then in the future the affected joint will collapse, the hand will become deformed, and will lose its function.
Causes of pain
Painful sensations in the hand can be caused by a variety of diseases, many of which have fairly similar symptoms. Most diseases are chronic, and the prerequisites for their development often go unnoticed. Let's find out why the joints on the fingers of one or both hands hurt.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a constantly progressive connective tissue disease that affects joints (mainly peripheral ones). Due to chronic inflammation of the synovial membrane, cartilage destruction occurs. Periarticular tissues are affected. The pathology develops as a result of immune autoaggression. The clinical picture is characterized by:
- destruction of cartilage tissue;
- osteoporosis;
- pain, joint deformities (primarily the hands), subluxations, contractures;
- deterioration of the condition of blood vessels, damage to the lymph nodes;
- changes in the skin, nails, increased pigmentation;
- the formation of specific rheumatoid nodules;
- disorders of the heart (rheumatoid carditis);
- dystrophic changes in muscles;
- various pathologies of the kidneys (most often amyloidosis), liver;
- functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- neurological disorders, rheumatoid neuropathy.
The disease can be caused by infections, hypothermia, injury, physical or nervous stress. There is a genetic predisposition to the disease. Women suffer from arthritis approximately 3 times more often.
The earliest manifesting and most important symptom is a feeling of morning stiffness throughout the body, especially noticeable in the joints of the hands, which disappears after physical activity. At the initial stage, there may be a temporary deterioration in the general condition, when the joints of the fingers and toes periodically ache, appetite decreases, heartbeat increases, sweating, and a low temperature appears.
Later, the pain - primarily in the small joints of the hands and feet - intensifies, especially in the morning, after sleep and when performing movements. The period of morning stiffness lengthens and becomes painful. Joint mobility is increasingly limited. Severe inflammatory edema and hyperemia appear, the temperature of the skin above the site of inflammation rises, and fever begins.
Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbations and remissions, sometimes long - for months and even years. With each exacerbation, the process covers new joints.
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the spine leads to lumbago in the back, neck, neurovascular disorders, the formation of herniated intervertebral discs, deterioration of blood flow in the vertebral arteries, pinched nerve roots and signs of other neurological symptoms. Most often, the disease is accompanied by a feeling of numbness in the fingers, but there may be pain that is mistaken for pain in the joints.
Osteochondropathy. Kienböck's disease
Pain in the fingers can be caused by osteochondropathy - necrosis of bone tissue caused by increased mechanical load, mainly in childhood and adolescence. In adults, the disease is diagnosed less frequently. The development of pathology is provoked by injuries, functional overload, infections, rapid growth in children, constitutional features, and sometimes vitamin imbalance.
One such disease is Kienböck's disease, which affects the wrist joint. This type of osteochondropathy is characteristic mainly of men aged 18 to 30 years with chronic microtrauma or overstrain of the hand (mechanics, turners, carpenters, joiners). The symptomatic complex includes:
- persistent pain covering the fingers, wrist area;
- persistent swelling;
- increased pain when pressing the wrist joint;
- bone destruction, subluxation of the intercarpal joints at the final stage of the disease.
The process, as a rule, affects only one side.
Reactive arthritis
A recent infection (1-1.5 months ago) and the development of joint inflammation after it can explain why the fingers hurt, especially when bent. Reactive arthritis is presumably a consequence of an immune response to microbial antigens located outside the joint, which causes the development of immune complex synovitis in the synovium.
Symptoms of the disease are expressed:
- pain in the affected joints, tendons;
- deterioration of skin condition, changes in nails;
- diseases of the genitourinary, cardiovascular, lymphatic systems.
The clinical picture of reactive arthritis is varied and depends on the causative agent of the infection: streptococcus, salmonella, meningococcus, shigella and many others.
Gout
Gout belongs to the group of metabolic arthritis - diseases of the musculoskeletal system caused by metabolic disorders, in this case uric acid. The disease mainly affects men over 40, but gout can develop in young people 20-30 years old and in menopausal women.
Violation of purine metabolism can be caused by:
- increased synthesis due to genetically inherited characteristics;
- renal failure;
- some blood diseases;
- taking medications;
- significant consumption of foods high in purines and fat (meat, fish), alcohol;
- infections;
- a combination of various factors affecting uric acid metabolism.
The disease is accompanied by the development of hyperuricemia - an excess content of uric acid in the blood serum, resulting in the deposition of urate in the tissues of the joints.
Gout is characterized by an attack-like course with the involvement of an increasing number of joints and tendons, the gradual occurrence of persistent visible deformations, stiffness, osteoarthrosis, and the formation of tophi (gouty nodes).
Symptomatic exacerbation of inflammation manifests itself:
- sharp pain, usually at night;
- swelling of the joint area, hyperemia;
- weakness, fever, chills;
- increased nervousness;
- stool disorders.
The localization of gouty arthritis in the small joints of the hands is atypical. However, gout may be a very possible explanation for why your finger joints hurt.
Psoriatic arthritis
Patients with psoriasis quite often develop chronic inflammation - psoriatic arthritis, the classic form of which is considered to be damage to the joints of the hands and feet. The disease usually develops unnoticed, with a gradual increase in symptoms, although sometimes an acute onset is possible. You can suspect developing arthritis based on the following signs:
- the joints of the fingers and toes hurt in the morning or throughout the day;
- there is painful swelling;
- the skin over the joint becomes bluish;
- trophic changes occur in the nails.
Damage to the joints subsequently causes deformation of the fingers, contractures, and leads to the development of chronic synovitis and arthrosis.
Extra-articular rheumatism
Extra-articular rheumatism in the form of diseases of soft periarticular tissues often leads to pain in the fingers. The main development factors are injuries, prolonged stereotypy of movements, hypothermia, dampness, infections, and insufficient nutrition and blood supply are often observed. Pain may occur due to:
- tendinitis - degenerative tendon damage;
- tenosynovitis (otherwise known as tenosynovitis, ligamentitis) – inflammation of the middle part of the tendons, the inner lining of the vagina, extra-articular ligaments;
- bursitis is an inflammatory process in the serous bursa, usually resulting from tendovaginitis.
In the hands, the tendons of the wrist and hand are most often affected, due to their almost constant functional tension. Most often, the reasons why a finger hurts over the entire surface or in the joint are syndromes caused by:
- de Quervain's disease - tenosynovitis of the tendons of the muscles responsible for abduction and extension of the thumb;
- carpal tunnel syndrome - tenosynovitis of the flexor fingers, often combined with Guyon's tunnel syndrome - compression in the palmar ligament of the ulnar nerve and ulnar artery;
- ligamentitis of the wrist tendon;
- Knott's disease (“snapping” finger), affecting the tendons of the superficial flexor muscles of the fingers and their sheaths;
- bursitis (tendobursitis).
Pain usually occurs or increases with movement, and bothers you at night. Swelling, stiffness, and sensory disturbances may occur.
Osteoarthritis
Degenerative-dystrophic processes in articular cartilage with the formation of osteophytes - osteoporosis - are the most common type of articular pathology, the frequency of which increases with age. It occurs due to two reasons: increased mechanical impact on the joint and deterioration of the cartilage.
Damage to the joints of the hands leads to pain in the finger or the entire palm, at first only when bending, significant physical activity, and then even at rest, in the morning, sometimes at night. In addition, the disease is accompanied by:
- stiffness, contractures;
- joint deformities;
- sometimes hot swelling.
Osteoarthritis is characterized by a long-term course with a gradual increase in symptoms, usually without sharp exacerbations. The main types of disease affecting the hands are osteoarthritis of the interphalangeal joints and the metacarpal joint.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
It is an autoimmune polysyndromic disease with a chronic course, generalized vascular damage and changes in connective tissue. It mainly affects teenage girls and young women 20-30 years old.
The development of the disease can be either invisible or acute and sudden. A gradual onset occurs against a background of weakness, weight loss, low-grade fever, signs of arthritis (synovitis), and minor skin manifestations. Acute – characterized by severe pain in the joints, fever and bright rashes on the skin. The disease may also be accompanied by:
- hair loss, nail changes;
- sensitivity disorders;
- stomatitis;
- damage to the cardiovascular system, most often pericarditis;
- sometimes muscle atrophy (primarily of the hands), deformation of the joints of the fingers, wrist, ankle;
- pulmonary pathologies (pneumonitis, candidiasis, tuberculosis, etc.);
- kidney damage (lupus glomerulonephritis);
- vegetative and emotional disorders;
- decreased intelligence, hallucinations, convulsions.
Arthritis is the most common symptom of systemic lupus erythematosus.
That is why the appearance of skin erythema and discomfort caused by pain in the joints of the fingers ( especially if the causes of the pain lie in the force created when squeezing the hand) is the basis for conducting an examination for this disease.