So-called rheumatism or acute rheumatic fever (according to new terminology) is a systemic inflammatory disease of connective tissue, in which the pathological process has an affinity for the membranes of the heart and joints.
Even at the beginning of the 20th century, the concept of “rheumatism” meant almost any disease of the joints - doctors did not have the need or opportunity to differentiate these ailments, especially since the range of healing procedures was not diverse. Today, a rheumatologist has a wide range of diagnostic methods in his arsenal, allowing him to distinguish rheumatism from many other rheumatological diseases, each of which has its own treatment strategy.
Rheumatism is a disease predominantly of children aged 6 to 15 years, and only 1 child in 1000 suffers in this age group.
Primary rheumatism in adult patients is observed less frequently. According to statistics, women are 2-3 times more likely to suffer from this disease than men.
Rheumatism usually begins some time after a streptococcal infection of the nasopharynx, and after a few years it can turn into a chronic, incurable disease. Fortunately, only 1-3% of patients who have an infection become victims of rheumatic fever.
1
Consultation with a rheumatologist
2 Consultation with a rheumatologist
3 Consultation with a rheumatologist
Causes of rheumatism
Why do some people get rheumatism, while others under the same conditions do not? People who often suffer from ENT diseases are more likely to get rheumatism. Those at risk are those whose relatives have this disease and those who have the B-cell marker D8/17 in their blood.
So, the risk factors:
- streptococcal infection (angina, scarlet fever, pharyngitis);
- defects of the immune system, the presence of autoimmunity;
- genetic predisposition to the disease.
1-2-3 stages
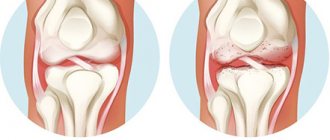
The severity of the disease is characterized by 3 stages. The first is the stage of synovitis, the second is productive-destructive, the third is deforming and ankylosing.
- The first stage is initial and low active in relation to the structures of the articular apparatus. Its characteristic signs are inflammation and thickening of the synovial membrane of the hip joint, accumulation of inflammatory exudate in the cavity. Vital movements may be slightly difficult due to pain and swelling due to synovitis. In general, the integrity and shape of the structures are preserved.
- The second stage is arthritis with moderate activity and severity. At this stage, destruction processes begin to progress. That is, there is ulceration and loss of the hyaline cartilage that covers the surfaces of the femoral head and acetabulum. X-rays reveal a narrowing of the joint space, and periarticular osteoporosis may be detected. The range of motion is noticeably reduced, and stiffness is pronounced. By the middle of this stage, articular cartilage has been massively lost, and the ends of the articular bones are practically exposed.
- In the third phase - highly active and severe - deformation of the bone elements occurs at a rapid pace, their partial or absolute fusion in an intact position. Ankylosis is a “classic” of late rheumatoid arthritis. The joint space is critically narrowed or completely blocked. The patient is unable to move normally and independently perform even basic daily tasks. At this stage, surgery is recommended.
Disease in dynamics.
Clinical picture of rheumatism
The trigger for the development of rheumatism is the entry of streptococcus into the body, as a result of which the immune system begins to produce antibodies to fight the infection. However, in the body itself, namely in connective tissues and heart muscle, there are molecules of the same structure. Due to the presence of this factor, the immune system begins to “fight” its cells. As a result, connective tissue is damaged, and this is fraught with heart defects and joint deformation.
Forms of rheumatism
- cardiac form (cardiac rheumatism), when all the membranes of the heart are affected (pancarditis), myocardium (myocarditis), endocardium (endocarditis);
- articular form (rheumatism of the joints);
- cutaneous form;
- pulmonary form (pleurisy);
- rheumatic chorea (St. Vitus' dance).
What diseases does a rheumatologist treat?
A specialist in rheumatology treats many diseases. Among them:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- psoriatic arthritis;
- rheumatic fever;
- vasculitis;
- gout;
- ankylosing spondylitis;
- osteoarthritis;
- chronic inflammation of connective tissue: systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, Sjogren's syndrome;
- osteoporosis;
- sarcoidosis;
- fibromyalgia, etc.
Many joint problems are temporary, but when rheumatic disease sets in, it makes sense to act early before permanent changes occur. Modern rheumatology is moving in such a direction that images of joints deformed by the inflammatory process can only be found in archival photographs in textbooks.
Symptoms of rheumatism
Rheumatism has a wide variety of manifestations: damage to the heart, joints, nervous and respiratory systems. 2-3 weeks after contracting a sore throat or pharyngitis, the first signs of rheumatism appear: fever, weakness, fatigue, headache. In some people, acute rheumatism begins 1-2 days after hypothermia, even without connection with infection.
Rheumatism of the heart
Already at the beginning of the disease, pain in the heart begins, increased heartbeat, shortness of breath even at rest.
Rheumatic arthritis
With articular rheumatism of the legs and arms, pain appears in the knee, elbow, wrist, and shoulder joints. The joints swell, active movements in them are limited. As a rule, after taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, pain from rheumatism quickly disappears.
Skin rheumatism
With cutaneous rheumatism, vascular permeability increases. Therefore, skin rashes appear on the lower extremities.
Rheumatic pleurisy
A fairly rare manifestation of the disease. Main symptoms: body temperature remains above 38 degrees, severe pain in the chest, dry cough, shortness of breath, pleural noise can be heard on auscultation. More often the disease is limited to a fairly mild form of pleurisy.
1 ECG
2 Echocardiography with Doppler analysis
3 X-ray examination
Rheumatic manifestations of damage to the nervous system
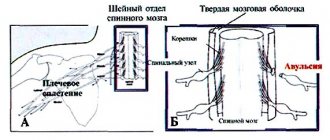
Sometimes rheumatism can provoke damage to the meninges, subcortex and medulla. One of the manifestations of the disease is the dance of St. Vitus. With this complication, convulsive, involuntary contraction of the muscles of the face, torso of the arms and legs occurs. With a sharp contraction of the glottis, suffocation can occur, which is very dangerous for human life.
Abdominal syndrome
This type of complication is typical for children and adolescents. Accompanied by elevated body temperature, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain in the form of contractions.
Rheumatism should not be left to chance or treated by relying on the advice of friends and relatives, even those familiar with this disease. Loss of time leads to progression of the disease and dangerous complications in rheumatism. There is a threat of developing atrial fibrillation and myocardiosclerosis. Possible damage to the lungs and kidneys. And the most dangerous thing is thromboembolism (blockage of the pulmonary artery by a blood clot), which can suddenly end the patient’s life.
Forms
Signs of rheumatism may differ slightly depending on what part of the person’s body is affected. There is a classification of the disease, which is based on where exactly the stalemate is concentrated. process. Based on this, the following forms are distinguished:
- rheumopolyarthritis;
- rheumatic heart disease;
- skin rheumatism;
- rheumochorea;
- rheumopleuritis;
- rheumatism of the eyes;
- rheumatism of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnosis of rheumatism
When diagnosing the disease, the following methods are used:
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- X-ray examination (helps to see changes in the size and shape of the heart);
- general blood test (can show ESR level, anemia, etc.);
- immunological blood test (appearance of C-reactive protein, presence of streptococcal infection).
1 General blood test
2 Immunological blood test
3 Diagnostics of rheumatism in MedicCity
Prices
| Initial consultation on the prevention of rheumatism | From 500 rub. |
| First treatment cycle (12 sessions) | From 6,500 rub. |
| One lesson | From 700 rub. |
| Zonal taping | From 500 rub. |
| General massage | From 1,000 rub. |
| Aerogymnastics (1 lesson) | From 400 rub. |
Based on the results of the consultation, diagnosis and/or treatment will be prescribed.
*Prices in different regions may vary; current information on the cost of services can be obtained from the center manager.
Surgery for hip arthritis
Minimally invasive endoprosthetics in the Czech Republic: doctors, rehabilitation, terms and prices.
Find out more
Among the surgical treatment technologies today, endoprosthetics and arthroscopic synovectomy predominate. Hip replacement is primarily indicated for people with rheumatoid arthritis, preferably in the phase before the joint “locks up.” And this is stage 2 of RA. If bone ankylosis has occurred, endoprosthesis replacement surgery is also possible, although it will involve the greatest technical difficulties (separation of ankylosis and determination of the direction of femoral neck osteotomy), but quite surmountable for experienced specialists. Installation of an endoprosthesis in place of a native joint affected by severe arthritic arthrosis is the only way to return the patient’s quality of life with good functional results. Various conservative methods are ineffective for severely advanced forms of coxitis.
As for synovectomy, it is performed when the inflammatory process with the accumulation of pathological fluid persists for a long time and is not amenable to drug treatment. Chronic synovitis is treated using an arthroscopic technique, which is minimally invasive (the procedure is done through small punctures). The essence of this operation is partial or complete excision of the synovial membrane of the hip joint. Along with the removal of this tissue, the pathological cells located on it, which produced a large amount of complement and immunoglobulins responsible for tissue inflammation, are also removed.
Note that with the help of arthroscopy, in case of acute purulent pathogenesis, a puncture and washing of the articular cavity can be performed, followed by the introduction of antibiotics or antiseptics into it
Frequently asked questions about the disease
Which doctor should I contact?
It’s better to start with a therapist, he will advise who to contact. A surgeon treats purulent processes, a rheumatologist - everything else, except for tuberculosis, you need to contact a phthisiatrician.
Can juvenile arthritis be cured without surgery?
With adequate treatment, you can get rid of relapses of the disease and its progression. Modern methods of conservative treatment allow patients to forget about exacerbations forever during maintenance treatment. Surgery is a last resort, but sometimes it is still necessary.
Literature:
- Yablokova E. A. Clinical features and impaired mineralization of bone tissue in children with inflammatory bowel diseases. Diss. Ph.D. honey. Sci. M., 2006. 185.
- Dzyuba G.G., Reznik L.B., Erofeev S.A., Stasenko I.V. Modern methods of treating surgical infection of the hip joint // Modern problems of science and education. – 2021. – No. 5.
- D'Incà R., Podswiadek M., Ferronato A., Punzi L., Salvagnini M., Sturniolo GC Articular manifestation in inflammatory bowel disease patients. A prospective study // Dig Liver Dis. 2009, Mar 9.
- Rodriguez VE, Costas PJ, Vazquez M., Alvarez G., Perez-Kraft G., Climent C., Nazario CM Prevalence of spondyloarthropathy in Puerto Rican patients with inflammatory bowel disease/Ethn Dis. 2008, Spring; 18(2 Suppl 2):S2–225–9.
Themes
Arthritis, Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 12/09/2020 Date of update: 03/12/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (2)
Anti-arthritic prevention measures
To avoid the recurrence of arthritis after successful therapy, as well as to prevent the disease if a person has not yet encountered it, please familiarize yourself with the general principles of prevention and adhere to them. Recommended rules for carrying out preventive control are as follows:
- avoid hypothermia of the body and joints in particular, dress appropriately in cold weather;
- maintain the correct daily routine - balanced and normal frequency of meals, reasonable hours for rest and work, daily exercise and healthy physical activity;
- adding foods containing B vitamins to your diet if there are not enough of them on your table;
- wash vegetables and fruits before eating, and cook foods that require mandatory heat treatment until fully cooked;
- drink enough clean water daily (2-2.5 liters);
- avoid stress and nervous situations;
- watch your weight, high body weight is an enemy for bones and joints;
- promptly and efficiently treat any bacterial, infectious and viral diseases, including even common colds and caries;
- completely give up smoking, eliminate alcohol or minimize its consumption as much as possible (a little bit and only on holidays);
- do not sit for a long time in a monotonous position, eradicate habits such as crossing “legs over legs” and tucking your limbs in a bent position under you;
- maintain general and intimate hygiene;
- be vigilant about casual sex (increased risk of catching an STI), so if you are not sure about your partner, use a condom for the entire session, and then be examined for sexually transmitted infections;
- at the first unpleasant sensation localized in the joint, immediately go to the doctor (self-medication will not be without consequences);
- carry out all treatment measures and prevention of all existing chronic diseases in a timely manner, according to the instructions of a specialized doctor.
Approach to treating the disease at the Paramita clinic, Moscow
Patients with suspected hip arthritis are always carefully examined by specialists at our clinic using modern laboratory and instrumental methods, including MRI. During the examination, the main and concomitant diseases are identified and only after that individually selected treatment is prescribed.
Our doctors are trained in all existing methods of treating this disease. The Western techniques they use allow them to act directly on the source of inflammation, while the Eastern ones – on the body as a whole, restoring the proper functioning of all organs and systems, including the hip joint.
This approach to treatment allows you to quickly eliminate the pain syndrome and stimulate the patient’s desire for recovery. Then the main course of treatment is carried out, aimed at suppressing inflammation and progression of the disease. The final stage is the restoration of lost joint function. Treatment allows patients to forget about pain and lead a normal life. More information about treatment methods for hip arthritis can be found on our website.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis