General description of the disease
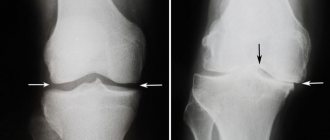
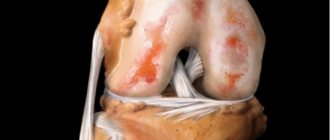
This is a disease that is associated with simultaneous or sequential inflammation of a group of joints. It is classified as a chronic disease. Polyarthritis also entails the destruction of the synoval membrane, which envelops the joint. This is accompanied by deformation and pain.
Causes of polyarthritis
There can be a huge number of reasons for the occurrence of polyarthritis. From infections to heredity. Let's look at the most common ones.
- hepatitis viruses (especially B);
- piggy;
- rubella;
- Epstein-Barr virus (a herpes virus associated with fever, swollen lymph nodes in the neck, sore throat, and sometimes swelling of the spleen);
- HIV (attacks the immune system and may increase the risk of developing polyarthritis);
- parvovirus infection;
- Wilson's disease (a rare inherited disease that prevents the liver from filtering excess copper from the body, resulting in copper buildup in the liver, eyes, brain and other organs);
- amyloidosis (a rare accumulation of a protein produced in the bone marrow that affects the heart, spleen, kidneys, liver, digestive and nervous systems);
- gout (high levels of uric acid in the blood);
- Lyme disease;
- tuberculosis;
- vasculitis (a disease in which the immune system attacks blood vessels);
- a thyroid disorder such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism;
- oncological diseases;
- ENT diseases, for example, such as chronic tonsillitis[4].
Symptoms of polyarthritis
Symptoms of the disease may develop slowly and not be felt for months. Or it may appear spontaneously and unexpectedly for the patient. As a rule, polyarthritis makes itself felt through pain in the joints, stiffness during movement, and swelling of the joints. Other symptoms often develop, for example, severe weakness, sweating, fever - within 38 degrees, lack of appetite, sudden weight loss, redness of the affected area, rash.
Types of polyarthritis
There are many types of arthritis. It is worth noting that there is monoarthritis, localized in one specific joint, as well as polyarthritis, which became the topic of this article, and is characterized by inflammatory foci simultaneously in several parts of the body. There are many types of polyarthritis, we will look at the most common of them.
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis is a type of disease that is common in children. It can develop from early childhood until late adolescence. Characteristic features include painful swelling in small and large joints from the ankles and wrists to the hips and knees. Doctors are not always able to determine what caused the development of this type of arthritis. However, with correct and timely treatment, the patient’s condition improves significantly.
- Lupus is an autoimmune disease caused by a person's own immune system attacking various organs and cells in the body. The result is damage and dysfunction of these cells and organs. In addition to directly affecting a person's joints, this type of arthritis can also affect the skin, connective tissues, nervous system, and kidneys. Most often it occurs in women aged 20 to 40 years. A characteristic feature is a red rash on the face, cheeks and nose.
- Psoriatic arthritis , as the name suggests, occurs in people suffering from psoriasis. However, in some cases, arthritis develops first, and then psoriasis. Characteristic symptoms include swollen fingers and toes, as well as the presence of a scaly red rash on the body[1].
- Fibromyalgia is a form of arthritis characterized by long-term and widespread pain in the ligaments, muscles and tendons. Fatigue and sleep disturbances are common symptoms of fibromyalgia. Typically, this form of arthritis is called a syndrome because it involves a collection of symptoms and signs that occur together without a known cause. Although classified under arthritis, fibromyalgia is not actually a form of arthritis in the classical sense due to the lack of inflammation or damage to joints, muscles, or other tissues.
- Infectious arthritis (septic) - provoked by bacteria, less often viruses or fungi. The infection can spread from nearby infected tissue through the bloodstream and eventually infect the joint[2].
- Allergic is a form of polyarthritis that develops as a result of an allergen entering the body (usually in the form of a vaccine). Has symptoms that are similar to an allergic reaction.
- Metabolic - appears due to a violation of metabolic processes, and as a result, salt crystals begin to be deposited on the joints. It can have acute and chronic forms.
Complications of polyarthritis
If polyarthritis is not promptly controlled and treated, it can negatively affect the functioning of other organs and systems of the body.
- Lungs : A scar in the lungs can cause complications such as shortness of breath and chronic cough.
- Skin : Rash or scars developing under the skin.
- Heart : The lining around the heart can become inflamed, causing chest pain. The risk of heart attack or stroke also increases.
- Eyes : With polyarthritis, the thin membrane covering the whites of the eyes or the entire eyeball may become inflamed. Sometimes this leads to loss of vision.
Prevention of polyarthritis
There are more than 100 types of arthritis, and, unfortunately, the disease is not always preventable. But there are a number of healthy habits that you can develop to significantly reduce your risk of developing this disease.
- 1 Eat fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines, trout) regularly. It contains polyunsaturated fatty acids, which help reduce inflammation in the body. Research shows that women who regularly eat fish are less likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis.
- 2 Control your weight. Excess weight puts more stress on your joints, especially your knees. People who are overweight are almost four times more likely to develop knee osteoarthritis.
- 3 Play sports. Moderate physical activity not only helps you lose weight, but also strengthens the muscles around your joints. This stabilizes them and protects them from additional wear. Swimming, walking, aerobics, and stretching are excellent types of exercise for preventing polyarthritis.
- 4 Avoid injury. Joints wear out over time; this is a natural process in the body. But additional injuries cause faster wear and tear and make joints more vulnerable. When playing sports, use high-quality shoes, uniforms, and special equipment, if provided.
- 5 Get regular check-ups with your doctor. Do not delay your visit if you have signs of illness. Remember that it progresses quite quickly, so it is important to keep your health under control[6].
Risk factors
Risk factors for polyarthritis are of two types: those that a person can influence and those that are irreversible. The first category includes the following:
- Lifestyle : Smoking, drinking alcohol and caffeine can make a person more vulnerable to factors that trigger the development of polyarthritis.
- Childhood experiences , for example, if a child grows up in an environment with smoking parents or in unfavorable conditions, this can also make him vulnerable later in life.
Factors that cannot be influenced:
- Age : People become more likely to develop polyarthritis as they age.
- Gender : the frequency of diagnosis of cases of polyarthritis in women is higher than in men.
- Heredity : Specific genes can make a person more likely to develop polyarthritis[1].
Treatment of polyarthritis in official medicine
Polyarthritis is a disease that is difficult to diagnose due to the fact that it can be caused by a large number of factors and have a number of other symptoms in addition to joint pain. Here are a number of alarming signs, if you notice them you should definitely consult a doctor:
- Joint pain that makes daily activities difficult.
- Redness in the joint area, as well as an increase in body temperature in a certain part of the body. For example, if you notice that your knee is reddish and warmer than the rest of your body, you should definitely consult a doctor.
- Swelling in the joints, stiffness.
The doctor will do a variety of tests, including blood tests that may look for evidence of viral infections, or for a marker called rheumatoid factor (RF). RF is a protein that can attack healthy tissue in the body[1].
There are a number of criteria that help determine which type of treatment is advisable to choose.
- number of affected joints;
- the presence of inflammation in the joints;
- main symptoms other than joint pain.
Medical treatment may include drugs that will prevent further damage to the joints and help keep them active. Analgesics and anti-inflammatory steroid drugs are also often prescribed, which have a quick effect and relieve pain. Here are the groups of drugs that are prescribed for polyarthritis:
- 1 Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - reduce inflammation, help cope with moderate pain, but have a number of side effects and negatively affect the gastric mucosa. Therefore, along with them, protective drugs are also prescribed that will prevent damage to the stomach.
- 2 Corticosteroids – reduce inflammation. Because many of the diseases that cause polyarthritis are associated with autoimmune diseases, corticosteroids also suppress the immune response that accompanies autoimmune diseases.
- 3 Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs are a broad group of drugs that are designed not only to relieve inflammation and reduce pain, but also to slow down and modify the progression of the disease, softening the lesions that it can provoke[5].
It is also suggested that the symptoms of polyarthritis can be minimized by making lifestyle changes. If the patient is also overweight, losing weight will help reduce pressure on the joints, and thereby reduce pain. It is also important to switch to a healthy diet and enrich your diet with healthy foods, a list of which is given in the corresponding section of the article.
Moderate physical activity, such as swimming, will also be beneficial. It does not greatly deplete the body, but at the same time helps to use all major muscle groups at the same time[4].
General rules
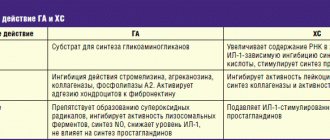
Rheumatoid arthritis ( polyarthritis ) is a disease with an unclear etiology, the leading role in the development of which is played by autoimmune reactions with the formation of circulating immune complexes deposited in the articular synovium, promoting increased activity of inflammatory mediators, impaired microcirculation and activation of chemotaxis .
In the clinical picture of rheumatoid polyarthritis, the leading one is articular syndrome. The disease is usually provoked by cold, acute/exacerbation of chronic infection, stressful situation, trauma. The diet for rheumatoid polyarthritis is included in the complex of mandatory therapeutic measures and is aimed at relieving the inflammatory process and pain syndrome, tissue allergies , correcting metabolism and strengthening connective tissue structures. The diet is based on the phase of the disease (active/inactive), manifestations of the disease and the degree of joint damage, the patient’s condition, the presence of complications ( amyloidosis , circulatory failure) and medications taken. It is generally accepted that rheumatoid polyarthritis is more severe in patients with excess body weight, so weight correction is of extreme importance.
The basic principles of dietary nutrition for patients with rheumatoid arthritis are:
- balancing the daily diet with all food macro/micronutrients and ensuring adequate energy needs of the body;
- restriction in the diet of fats (due to animal fats) and easily digestible carbohydrates;
- exclusion/limitation of products with high allergenic activity;
- reducing the consumption of table salt to 3-5 g/day;
- fractional meals (5-6 times/day).
The diet for polyarthritis is based on the classic therapeutic Diet No. 10R . With normal weight, the energy value of the daily diet is 2400-2500 kcal (90 g protein, 70 g fat and 350 g carbohydrates); with increased body weight, the calorie content of the diet should be reduced by 20-25%. The total amount of free liquid is 1.0 l.
Features of diet in the acute stage (exacerbation) of rheumatoid arthritis
This stage of the disease is characterized by a pronounced metabolic disorder, mainly water-salt and carbohydrate metabolism, which, in combination with a violation of the permeability of the walls of blood vessels, leads to the retention of fluid and sodium in the tissues of the body. During this period, the patient is prescribed a diet with a decrease in energy value (1700–1800 kcal) by reducing easily digestible carbohydrates in the diet to 250–300 g (sugar, jam, honey, preserves). Sugar consumption should not exceed 20–30 g/day. By reducing the consumption of easily digestible carbohydrates, it is possible to reduce the severity of the inflammatory process and hyperallergic reactions.
In the acute period, protein intake is also limited to 70-75 g/day, since protein promotes the development of autoimmune reactions. However, when prescribing corticosteroid hormones to patients during this period, due to the catabolic effect of hormones, the protein content in the diet should remain at the physiological norm. The fat content in the diet is reduced to 70 g/day. At the same time, about 25% should be vegetable fats. Limiting salt to 2-3 g/day, which helps reduce swelling and reduce effusion into the joint capsule.
Food is prepared without adding salt, and ready-made dishes are added with salt at the table within the daily allowance. It is also necessary to exclude from the diet foods high in salt - canned food, marinades, pickles, sausages. Alcoholic and carbonated drinks are strictly prohibited.
The diet in the acute period should be enriched with vitamins , bioflavonoids ( vitamin P ), potassium, which is achieved by including fresh fruits/vegetables, juices, dried fruits, rosehip decoction, wheat bran, baked potatoes, bananas, and green tea in the diet. Cooking is gentle on the gastrointestinal mucosa. This is extremely important when prescribing glucocorticoids, salicylates, and indomethacin , which cause irritation of the gastrointestinal mucosa. Food is prepared by steaming or boiling.
Broths and broths based on meat, fish, mushrooms, fatty meat and fish, spicy snacks, beef fat, lard, smoked meats, pastry, ice cream, strong tea/coffee are excluded from the diet. Meals are fractional (up to 6 times a day). It is useful to practice fasting diets once a week containing an increased amount of potassium or calcium (apple diet, cottage cheese-kefir diet, dried fruit diet, vegetable diet).
Diet in the subacute stage of the disease
When inflammatory manifestations subside and the patient’s condition is satisfactory, the protein content in the diet increases (up to 90 g), with a normal fat content (80 g). The trend towards limiting carbohydrates continues and their amount should not exceed 300 g (no more than 40 g of sugar). Salt intake is limited, although slightly increased (4-6 g). Free fluid at the level of 1-1.2 liters per day. The requirement for increased vitaminization of the diet remains, for which the diet includes rose hips, sweet peppers, wheat bran, black currants, gooseberries, lemons, oranges, apples, tangerines, green tea, buckwheat, and lean meats/fish.
Diet during remission
During the period of remission, patients are recommended to be prescribed a physiologically complete diet of protein and fats, but with a limitation of easily digestible carbohydrates (up to 350 g/day). Salt intake is at the level of 9-10 g/day. It is recommended to exclude from the diet strong tea and coffee, products of the nightshade family (tomatoes, eggplants, potatoes), fatty meats, animal and cooking fat, canned food, smoked meats, strong broths, savory snacks, butter dough, legumes (peas, beans), spinach, vegetables with coarse fiber (radish/radish), sorrel, chicken eggs, nuts, chocolate, pickles, marinades, ice cream, alcoholic drinks, foods with food additives. It is useful to include in the diet for rheumatoid arthritis foods high in ω-3 fatty acids - fish oil, fatty varieties of sea fish.
How to eat with arthrosis
- Remember that any alcoholic beverage increases your appetite.
- Serve food in small portions.
- Serve food in small plates - portions will appear larger.
- Eat slowly, chewing each bite as thoroughly as possible.
- Take short breaks while eating.
- Never eat if you don't want to, and don't force others to.
- When you feel full, stop eating immediately. Don't overeat!
- After each meal, rinse your mouth thoroughly.
- After every meal, take 100 steps.
- If possible, do not eat after 7 pm.
- Watch your weight!
- Watch the chair. There should be a bowel movement every day.
arthrosis with diet alone , however, following basic nutritional recommendations and losing excess weight in combination with other therapeutic measures contributes to the overall health of the body and the improvement of the condition of the joints.
Read more about NANOPLAST forte
Authorized Products
The diet for rheumatoid polyarthritis includes the inclusion of vegetarian soups with the addition of cereals and vegetables. For second courses, dietary poultry (turkey, chicken) and rabbit meat, lean varieties of red meat boiled or baked in the oven are used.
Both sea and river fish are allowed, mostly lean ones. Eating porridge is permitted both as a side dish and as an independent dish. Fats are introduced into the diet in the form of unsalted butter and various vegetable oils (linseed, olive, sunflower). Dried white bread and crackers are allowed. Chicken eggs can be used in the form of a steamed protein omelet. The diet should include low-fat fermented milk products, cottage cheese and dishes made from it, skim milk, unsalted/mild varieties of cheese.
The volume and range of vegetables/fruits should be increased. They can be consumed raw (vinaigrette/salads), seasoned with vegetable oil, or boiled/stewed. As a dessert, you can use marshmallows, marshmallows, jam, marmalade. Drinks include freshly prepared vegetable/fruit juices, weak green tea, compotes, fruit drinks, decoctions of bran, rose hips, chicory, slightly mineralized non-carbonated alkaline waters.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| squash | 0,6 | 0,1 | 4,3 | 19 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| plums | 0,8 | 0,3 | 9,6 | 42 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| pumpkin seeds | 24,5 | 45,8 | 4,7 | 556 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Bakery products | ||||
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
| bran bread | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 | 227 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| kefir 2.5% | 2,8 | 2,5 | 3,9 | 50 |
| Ryazhenka 2.5% | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,2 | 54 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
| yogurt | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| sulguni cheese | 20,0 | 24,0 | 0,0 | 290 |
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
Meat products | ||||
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken | 16,0 | 14,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| sturgeon | 16,4 | 10,9 | 0,0 | 163 |
| herring | 16,3 | 10,7 | — | 161 |
| tuna | 23,0 | 1,0 | — | 101 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| corn oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| cucumber juice | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,5 | 14 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| Apple juice | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 42 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Fully or partially limited products
The diet for rheumatoid polyarthritis excludes fatty concentrated meat/fish broths, fatty red meats (pork) and waterfowl poultry (goose, duck), various types of offal (tongue, liver, brains), as well as meat products - sausages , semi-finished meat products, ham, ham. Animal fats, hydrogenated foods (mayonnaise, margarine), cooking oil, smoked, pickled, salted and canned foods are excluded from the diet. The consumption of confectionery products, chocolate, cocoa, products made from premium flour, starch and yeast-containing products, strong coffee, and black tea is not allowed.
It is prohibited to consume seafood (mussels, squid, crabs, oysters, shrimp), crustacean seasonings based on them, anchovies, red fish caviar, products of the nightshade family - eggplant, tomatoes/tomato products, potatoes, sweet peppers, paprika, seasonings/spices. Citrus fruits, grapes, avocados, raspberries, pomegranates, strawberries, wild strawberries, and currants are subject to restrictions. It is prohibited to include in the diet full-fat whole milk, legumes, fatty dairy products, vinegar, honey, snacks, jam, jam, alcohol and drinks containing carbon dioxide.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| beans | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,5 | 57 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| chickpeas | 19,0 | 6,0 | 61,0 | 364 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| soybeans | 34,9 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 381 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| lentils | 24,0 | 1,5 | 42,7 | 284 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| figs | 0,7 | 0,2 | 13,7 | 49 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
| cranberry | 0,5 | 0,0 | 6,8 | 26 |
| raspberries | 0,8 | 0,5 | 8,3 | 46 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| baked milk | 3,0 | 6,0 | 4,7 | 84 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream 25% (classic) | 2,6 | 25,0 | 2,5 | 248 |
| sour cream 30% | 2,4 | 30,0 | 3,1 | 294 |
| Ryazhenka 6% | 5,0 | 6,0 | 4,1 | 84 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| pork kidneys | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
| mutton | 15,6 | 16,3 | 0,0 | 209 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 28,2 | 27,5 | 0,0 | 360 |
Bird | ||||
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| fried fish | 19,5 | 11,7 | 6,2 | 206 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| squid | 21,2 | 2,8 | 2,0 | 122 |
| shrimps | 22,0 | 1,0 | 0,0 | 97 |
| mussels | 9,1 | 1,5 | 0,0 | 50 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| sardine in oil | 24,1 | 13,9 | — | 221 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| mackerel | 18,0 | 13,2 | 0,0 | 191 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| white dessert wine 16% | 0,5 | 0,0 | 16,0 | 153 |
| red dessert wine | 0,5 | 0,0 | 20,0 | 172 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| cognac | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 239 |
| liquor | 0,3 | 1,1 | 17,2 | 242 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| coffee | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 2 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Reviews and results
Reviews from most patients with rheumatoid polyarthritis indicate that diet is the most important component of the treatment process and can reduce the clinical manifestations of the disease and accelerate the attenuation of the acute process.
- “... I recently went to the hospital about joint pain. After the examination, a diagnosis was made: rheumatoid seronegative arthritis, early stage, activity II, non-erosive (X-ray stage I), ACCP (+), FC I. They prescribed many medications and dietary Table No. 10. I had to completely change my approach to nutrition and introduce many restrictions. Fortunately, I can cook myself, so my food’s taste hasn’t suffered much. The only drawback is the limitation of salt, but I try to use garden greens, which conceals the lack of salt. In general, I started to feel better”;
- “... I have been suffering from rheumatoid arthritis for more than 12 years. Every time during an exacerbation I go on a strict diet. I think that the diet helps me a lot, in addition, I practice traditional methods of treatment.”
Etiology
The causes of polyarthritis of the shoulder and other joints can be very different, from viral diseases to metabolic disorders. They include the following:
- colds, ARVI;
- tuberculosis;
- brucellosis;
- viral hepatitis;
- gonorrhea and other sexually transmitted infections;
- a variety of injuries;
- hereditary predisposition;
- metabolic disease;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- intense physical activity;
- allergic reactions;
- being overweight.