Knee pain when bending is a common ailment that many people experience. Prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position, excessive load or unsuccessful movement can lead to unpleasant sensations. However, much more dangerous is constant or regular pain caused by inflammation in the knee joint, ligaments, bones or adjacent soft tissues.
Pain in the knee area during flexion and extension occurs with varying intensities: from barely noticeable discomfort to acute and piercing pain. Sometimes it can reach the point that a person cannot freely perform an action with his foot.
Usually everything is accompanied by soft tissue swelling, clicking, local redness, soft tissue swelling and increased skin temperature in certain areas of the body.
Sometimes the pain is so severe that a person cannot fully bend or straighten the knee. If the illness bothers you for more than 1-2 days, then you should make an appointment with a traumatologist or orthopedist. The doctor will conduct an examination, identify the cause of pain and select a course of treatment.
The main causes of knee pain when bending:
The knee joint is one of the largest and most complex parts of the human body. It bears the main load while walking, running or dancing. Therefore, this part of the musculoskeletal system is constantly in action.
Painful sensations when bending and straightening a joint can significantly complicate future life. If suddenly severe pain appears in the knee when bending, and it does not go away, but continues for a long period, then first of all you need to determine its origin.
The occurrence of such pain in the knee is facilitated by:
- Overextension. In this case, muscles are affected, including ligaments and the bursa.
- A bruise caused by a fall or blow to the knee area. Usually the disease is accompanied by the accumulation of exudate in or outside the joint capsule and a characteristic reddish-blue tint of the skin.
- Arthrosis is a chronic disease of cartilage, which is accompanied by slow deformation of bone tissue.
- Bursitis of the knee joint, that is, inflammation of the synovial bursa in the knee area.
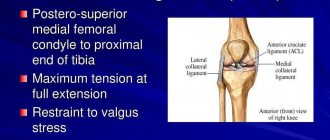
- Partial or complete rupture of the ligaments as a result of strong mechanical stress, for example, when the leg twists with prolonged loss of stability, severe pain in the knee when extending or flexing, or a complete inability to perform an extension movement.
- Rupture of the cruciate ligaments due to unsuccessful braking.
- Meniscus tear
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune systemic disease in which immune cells perceive the body's own tissues as foreign agents and attack them. Then the connective tissue and cartilage are gradually destroyed
- Patellofemoral pain syndrome is a consequence of mechanical stress, which manifests itself as pain in the anterior part of the knee.
Back side of the knee
All people know where this part of the body is located, but no one understands its correct name. Wikipedia says this: back of the knee. Doctors use the name “popliteal fossa”. People without medical education, communicating on forums, call this area of the lower limb differently: popliteal knees, leg armpits, popliteal cavities, popliteal cavities. Some argue that this place has no name.
Google provides links to “knee bend” and (less commonly) “popliteal bend.” People often use the expression “back of the knee.” Knee is the colloquial name for the knee joint. It has front, back and side surfaces.
There is no single term; everyone is right in their own way.
Russian poet Alexey Fedorovich Merzlyakov wrote that language is a reflection of what we see around us and what exists. And since this part of the body exists, it should have a name.
Types of knee pain when bending
Knee pain when bending is divided into several types according to the following criteria:
Because of
- physiological is meant as the body’s reaction to staying in one position for a long time or being in a standing position.
- traumatic, which occurs after an injury. Often the disease manifests itself over a period of time, when pain and swelling are less pronounced and persist only when trying to bend the injured leg.
- pathological - the result of an inflammatory process, infection, deposition of salt crystals or other pathology.
By frequency
- a one-time attack of pain occurs when movement is unsuccessful, most often it is physiological in nature and goes away on its own.
- periodic pain worsens after regularly repeated or prolonged exercise. For example, as a result of an intense workout or a working day spent in heels.
- chronic worries for a long time, can weaken and intensify, in most cases it is associated with diseases.
Description of the back of the knee
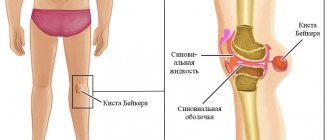
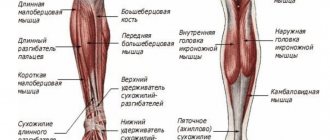
The popliteal fossa is a diamond-shaped depression located at the back of the knee. At the top of the right and left sides are the tendons of the biceps femoris muscle. At the bottom are the outer and inner heads of the gastrocnemius muscle.
The skin in this area is minimally thick. Veins and nerves run underneath it. The fatty tissue contains superficial, lymphatic and blood vessels. On the border of the popliteal cavity there are muscles in special capsules. They are located at a distance from each other, which is called the gill's fossa. The total length of the popliteal fossa is 12-14 centimeters.
All structures under the knee are covered with subcutaneous tissue. It protects joints from pathogenic bacteria. As a result, the risks of developing joint diseases and inflammatory processes are reduced.
If a person complains of pain under the knees during flexion and extension, it is recommended to pay attention to the condition of the popliteal fossa.
Main components of the knees:
- the bottom of the fossa is the posterior surface of the knee capsule;
- in the popliteal fossa there are lymph nodes;
- veins and arteries responsible for blood supply run through the center;
- accumulation of nerve endings (neurovascular bundle).
The functional load of the knee sockets contributes to the manifestation of undesirable symptoms.
What to do if your knees hurt when bending?
If you feel pain in your knee, first of all, you need to consult a doctor.
However, everyone should be able to react competently and provide first aid in case of pain in the knee area. First, you need to immobilize your leg and apply a cold compress to the affected area, then seek help from a medical facility by calling an ambulance. At the clinic, the first thing a specialist will do is conduct an examination, examine your knee and check for mobility, bruising and swelling. Then the doctor will prescribe the necessary medications to relieve pain. For this, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are usually prescribed.
When diagnosing arthritis, your doctor will prescribe medications that relieve inflammation and kill germs. The specialist prescribes warming herbal compresses and ointments that increase the protective properties of cartilage. If necessary, you need to undergo additional examinations - MRI, ultrasound, CT or X-ray.
In addition, after consulting with your doctor, you can protect and rest your injured knee at home by applying ice, applying a compression bandage, and keeping your knee above the level of your heart. To relieve short-term, mild pain and reduce inflammation, you can take over-the-counter painkillers for internal and external use.
Diseases that cause pain in the popliteal fossa
The back of the knee hurts with the following diseases:
- Baker's cyst. The pathology is manifested by swelling in the middle of the popliteal fossa, which is more noticeable when the knee is extended. A characteristic sign is that upon palpation, the fluid moves back into the joint, so the size of the cyst decreases. Usually the cyst appears on both legs at once. Treatment is carried out in a conservative form: tablets, injections, physiotherapy. If these methods are ineffective, surgery is performed.
- Meniscus cysts. They are located in the posterior horns, located behind the lateral ligaments. Causes pain in the knee socket. Sometimes cysts are small and not visible, but they lead to pronounced pain. To determine your health status, it is recommended to undergo a comprehensive examination and clarify the diagnosis. Meniscus cysts occur due to joint injuries during physical activity and sports training, and a lack of nutrients in the cartilage tissue.
- Meniscal tears. Pain in the area under the knee occurs when the posterior horn of the meniscus is torn off. More often this occurs on the inner meniscus with strong rotation of the lower leg. A tear of the posterior horn of the meniscus blocks the knee joint and impairs the function of the legs. Meniscus tears occur due to injury, disease, nutritional disorders and destruction of cartilage tissue. Initially, anti-inflammatory treatment and restriction of movements are provided.
- Inflammation of the tendon bursae of the semimembranosus muscle and the 2nd head muscle. In case of pathology, a compaction located near the inner or outer edge of the popliteal fossa is palpated.
- Infected wounds, abscess of the popliteal fossa. There are lymph nodes in the back of the knee, so infection from wounds, cracks and other minor injuries to the skin of the foot and leg is possible. The active development of the inflammatory process leads to lymphadenitis with the formation of pus. Lack of timely treatment threatens with an abscess of the popliteal fossa. Initially, the symptoms appear weakly, since the lymph nodes are located deep in the subcutaneous fat. There is no swelling or redness, there is only slight swelling and pain when moving the leg.
- Tibial nerve tumor. Together with the artery and vein, the nerve passes through the popliteal fossa. When it becomes inflamed and tumors, a pronounced pain syndrome occurs. Uncomfortable sensations spread to the foot. Upon examination, changes in skin sensitivity, impaired muscle tone and problems with reflexes are revealed. Surgical treatment is performed to remove the tumor. If necessary, treatment includes taking medications.
- Aneurysm of the popliteal artery. The walls of the artery become stratified and form a sac-like protrusion. The main symptom is nagging and throbbing pain at the back of the knee joints. Externally, the aneurysm is similar to a Baker's cyst, but upon palpation, pulsation is clearly visible. The pathology is dangerous due to massive bleeding, so the use of a special bandage is required to protect the arteries of the legs. Subsequently, an operation is performed.
If the area behind the knee hurts, swells, or interferes with movement, you should consult a doctor. The main task is to conduct an examination to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Consequences
For minor injuries, recovery will last up to 1-2 weeks. However, if you ignore treatment of the injury, the consequences of the disease may worsen and provoke habitual dislocations and chronic pain.
Inflammatory and degenerative diseases without timely treatment are fraught with gradual destruction of the joint, loss of elasticity, and in some cases, ossification. Patients with advanced pathological processes lose the ability to move normally and often become disabled.
Damage and illness
Joints are an important component of the musculoskeletal system. Every day they are exposed to heavy loads. This is why injuries to the kneecap and popliteal region often occur. This part is complex, and if a person experiences pain there, it is always difficult to determine its cause. The following diseases are associated with the area of the back of the knee joint:
- Baker's cyst (popliteal hernia);
- nerve damage;
- inflammation of soft tissues;
- muscle strain or damage;
- neoplasms (lipomas, fibromas, sarcomas);
- bursitis that developed due to infectious or aseptic inflammation;
- injuries of intra-articular ligaments;
- phlebeurysm;
- damage to fatty tissue.