One day hospital 3rd KO
Malykhin
Sergey Aleksandrovich
11 years of experience
First qualification category
Make an appointment
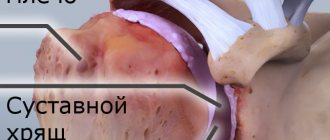
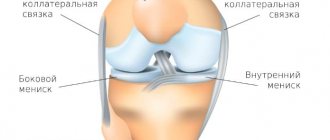
Gonarthrosis is arthrosis of the knee joint of a deforming type. The disease affects the hyaline cartilage in the surface of the joints of the tibia and femur. The pathology occurs in a chronic progressive form.
Clinical symptoms of joint gonarthrosis include the presence of pain that intensifies during movement, accumulation of fluid in the joint and limited movement. Late stages of gonarthosis are characterized by a lack of support on the leg. Diagnosis is based on the collection of complaints and anamnestic data, radiography and physical examination data. Treatment of knee joint gonarthrosis involves prosthetics if there is no effect from conservative treatment.
Gonarthrosis literally means knee joint. The pathology occurs in the form of deforming arthrosis. This means that the cartilage inside the joint is damaged in a physiologically dystrophic way, and not through an inflammatory process. The pathology occurs in a progressive form. This pathology is the most common type of arthrosis. The risk group most likely includes middle-aged and elderly women. At a young age, pathology occurs as a post-traumatic complication. Prevention is of great importance within the framework of preventive therapy.
Foci of deposited calcium salts in tendons and the apparatus of ligaments and tendons have a secondary role in the formation of gonarthrosis of the knee joint.
Symptoms and signs
Gonarthrosis of the joints develops gradually. The first stages of the disease practically do not bother patients, except for minor pain when going down or going up stairs. More sensitive patients report a feeling of stiffness in the joints or popliteal area.
A distinctive symptom of grade 1 gonarthrosis is the starting threshold of pain - this is the pain that accompanies the first steps after a sitting position. Further, in the process of walking, the pain disappears or is significantly dulled. Her reappearance will be marked by some kind of physical activity of significant severity.
External symptoms of gonarthrosis rarely appear. These mainly include swelling. Accompanying the pathology with fluid accumulation leads to synovitis. In this case, the joint swells to a spherical appearance and movements become constrained, and the patient feels heaviness.
Each degree of gonarthrosis has its own distinctive features. Grade 2 gonarthrosis is characterized by intense pain when walking and moderate physical activity. The progression of gonarthrosis leads to gradual immobilization of the joint. In this case, flexion and extension of the knee joint leads to crunching and sharp pain.
Grade 3 gonarthrosis is accompanied by constant pain. In this case, the movement of the joint is practically paralyzed and the patient cannot straighten his leg. The joint increases in size and becomes deformed. External signs of pathology appear - instability of gait, waddling nature of movements or inability to walk without additional support.
Do you have symptoms of gonarthrosis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Causes of occurrence and development
Almost always, pathology develops against the background of the complex influence of a number of factors:
- injuries - tibia fractures, damaged menisci, tears or ruptures of ligaments. The disease occurs between 2 months and 5 years after injury;
- physical activity – playing sports is useful if the set of exercises and their intensity correspond to the age of the patient;
- excess weight - obesity leads to excessive stress on the joints and their premature wear; patients with varicose veins are especially at risk.
Features of exercise therapy
Physical therapy for gonarthrosis is mandatory. Her goals:
- improving the motor capabilities of joints;
- improved blood circulation;
- prevention of muscle atrophy and complications;
- strengthening ligaments and muscles;
- reduction of pain.
It is prohibited to perform movements that provoke severe pain. You should not put excessive physical stress on the affected joints in the form of jumping, running, lifting heavy objects, etc.
The most effective exercises to strengthen the knee:
- Stand and relax your core muscles. Lower your arms down and perform shaking movements with your body, using your knees.
- Lean against the back of a chair, bend one leg at the knee. Pull the heel in the buttock, straighten the leg. Repeat the same with the other leg.
- Stand and rest your hands on your knees. Perform circular rotations with the joints in one direction, then in the other.
- Get on all fours and take a few steps.
- Sit down and bend your knees. Place your feet together. Slowly raise both legs one at a time.
- Lie on your side and lift your leg up. Bend your knee, straighten it and hold it for a few seconds. Then turn on the other side and repeat the same with the other leg.
- Lying on your back, perform the “bicycle” exercise.
- Sit down and place a weight on your feet. Slowly straighten your knees, tensing your muscles.
As an auxiliary treatment, massage can be practiced along with exercise therapy.
Routes of infection and risk factors
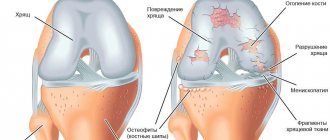
Gonarthrosis of the 1st degree - impaired blood circulation inside small bone vessels leads to the loss of the ability of cartilage to slide.
Grade 2 gonarthrosis – a change in the viscosity and thickness of the joint fluid, cartilage degeneration begins due to lack of nutrition, friction between the bones increases and the disease progresses.
Gonarthrosis of the 3rd degree - the bones are practically pressed into each other, the movement of the joint is limited, and the cartilage as such no longer exists.
Risk factors for developing the disease include:
- arthritis of any nature;
- hereditary ligament weakness;
- impaired metabolism;
- impaired innervation in a number of neurological diseases;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- spinal injuries.
Degrees
Doctors distinguish 4 degrees of gonarthrosis, which determine the stage of the disease and the extent of the lesion:
- 1st degree: the disease is detected only on x-ray, where single osteophytes are visible;
- Grade 2 is characterized by a noticeable narrowing of the joint space and pronounced degenerative foci in the cartilage tissue;
- 3rd degree: the joint is deformed, a large number of large osteophytes are found inside the cavity;
- 4th degree: cartilage tissue is completely destroyed, bones are deformed and often fused to each other.
Classification
Based on the ways the disease appears, there are:
- primary gonarthrosis - occurs on its own, often in the nature of bilateral gonarthrosis;
- secondary gonarthrosis of the knee - develops against the background of injuries or other pathologies of the knee joint, there are two types: right-sided gonarthrosis on the right leg and left-sided gonarthrosis on the left leg.
The severity of symptoms depends on the degree of gonarthrosis:
- Stage 1 – dull pain, slight swelling of the joint, no deformation;
- Stage 2 – increased symptoms and pain, the presence of a crunch, moderate limitation of movement and mild deformity;
- Stage 3 – maximum clinical symptoms, gait disturbance and severe constant pain, limited mobility and visible deformation of the joint.
Physiotherapy for gonarthrosis
All types of physiotherapy can be prescribed in the phase of remission or slight exacerbation of the disease, but not in the most acute phase with inflammation.
The most effective are:
- Electrophoresis with drugs such as bischofite or caripain. Deeper penetration of the drug in such cases is ensured with the help of dimexide;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Ultrasound;
- Microwave therapy;
- Paraffin treatment;
- Radon and hydrogen sulfide baths;
- Mud therapy.
To maintain and prolong the remission phase, it is necessary to undergo a course of physical therapy 2-4 times a year, depending on the degree of the disease.
Electrophoresis with caripain allows you to remove excess tone, promotes the resorption of contractures and adhesions. At least 20 procedures should be performed, since the drug is cumulative. It acts only when the maximum concentration is reached in the body. A course of 10 procedures will not justify the money spent.
A course of mud therapy for gonarthrosis must be completed 2 times a year, 10–15 procedures each. You can do it at home using mud purchased at the pharmacy. Before use, it must be heated to 38–40 °C.
Complications
Of course, the lack of competent and timely treatment of gonarthrosis leads to destruction and deformation of the knee joint, complete limitation of movement and disability. However, complications after neglected treatment of gonarthrosis can spread to other elements of the musculoskeletal system, the spinal column being considered the most significant.
Treatment of joint gonarthrosis is necessary to ensure adequate load on the spinal column, because restricting the movement of the knee joint increases the load on the spine by up to 75%. Therefore, among the consequences of pathology we will name the following:
- curvature of the spine;
- radiculitis;
- stenosis of the intervertebral canals;
- intervertebral hernias;
- osteochondrosis;
- vertebral instability.
Thus, the lack of relevant treatment for gonarthrosis of the joints leads to subsequent pathologies and their complications, growing like a snowball.
This development will lead to long-term treatment through a series of surgical operations not only on the knee joint. Other joints within the frame take on the load of the damaged knee joint, resulting in premature wear.
Another type of complication of the disease is the presence of an inflammatory process and large amounts of fluid that can leak outside the knee joint, causing new destruction and deformation, as well as the formation of a hernia or tumor.
When to see a doctor
If you have the slightest discomfort when moving or pain in the knee joint, you should contact a traumatologist or orthopedist; you can also seek an initial consultation with a surgeon.
JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) employs doctors from 66 medical specialties who have extensive work experience and are constantly improving their qualifications. You can make an appointment and choose a doctor on the website, by calling +7 (495) 775-73-60 or from the administrators at the clinic: Moscow 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskoy Lane, 10.
Advantages of the clinic
“Health Energy” is a multidisciplinary medical center engaged in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases. Each client is expected to:
- doctors with extensive experience who regularly update and confirm their knowledge;
- modern diagnostic and treatment equipment;
- maximum comfort from the first minutes of your stay in the clinic;
- own day hospital;
- affordable prices for all services.
Gonarthrosis is an insidious disease that can completely change your life. Don’t let pain deprive you of the ability to move, contact an orthopedist at the Health Energy clinic. Get treatment in a timely manner!
Diagnostics
Gonarthrosis is diagnosed by a traumatologist-orthopedist or surgeon. Initially, a detailed medical examination and x-ray are performed.
During the initial examination, signs can be detected only at stages 2 and 3 of the pathology due to deformation of bones and joints, curvature of the limbs of the bone and roughness of its contours. Palpation allows us to understand the presence and nature of pain.
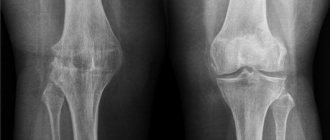
Radiography is one of the classical examination methods. It makes it possible to clarify the diagnosis and differentiate it from other pathologies, gives an idea of the depth of the lesions and the dynamics of the development of the process. In this case, the initial stage is usually difficult to see. In older people, changes are present due to age and, in the absence of clinical symptoms, do not lead to a diagnosis of gonarthrosis.
Modern research methods are CT and MRI, which are used extremely rarely.
Disease detection
To diagnose gonarthrosis, the most effective way is to conduct several types of studies in a comprehensive manner.
Most often, a simple x-ray is sufficient.
List of diagnostic measures to identify the disease:
- palpation of diseased joints;
- blood test for erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR);
- general blood analysis;
- blood test for rheumatoid factor;
- tests to detect urea levels;
- radiography of the affected joints;
- Ultrasound examination;
- MRI;
- advanced biochemical blood test.
The patient may need to consult an orthopedist, rheumatologist, surgeon, endocrinologist and traumatologist.
Treatment
How to treat gonarthrosis? There are two groups of treatment methods: conservative and surgical.
Conservative methods are used by traumatologists and orthopedists. Their success depends on the timely start of treatment - the earlier, the more successful. Periods of exacerbation must be spent in a state of complete rest. This therapy includes:
- gymnastics for gonarthrosis and physical therapy, which involves performing exercises for gonarthrosis;
- mud therapy;
- physiotherapy – electrophoresis with novocaine, magnetic and laser currents, diadynamic currents, UHF;
- medications – the following groups of drugs are administered through injections for gonarthrosis: chondoprotectors, steroid hormones;
- Spa treatment.
It is important to follow some rules - relieve the knee joint with a cane or orthoses, select comfortable shoes and insoles, control weight, and have a proper daily routine.
Surgical methods are used at the third stage of the disease, when standard therapy has not brought any visible effect or improvement. Surgical treatment is based on knee replacement. Prescribed to young and middle-aged people to compensate for limited physical activity. The period of rehabilitation and full recovery lasts from three months to six months.
Diet
Diet for gonarthrosis of the knee joint
- Efficacy: healing effect
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1700-1800 rubles. in Week
One of the most important factors slowing down the development of degenerative-dystrophic processes in the cartilaginous tissue of the joints is therapeutic nutrition, which, in combination with drug treatment, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, orthopedic regimen, therapeutic massage and spa treatment, can improve the patient’s quality of life. The diet for gonarthrosis is aimed primarily at correcting metabolic processes, regulating body weight/fighting obesity , preventing pathological changes in the hyaline cartilage of the knee joints, stopping the inflammatory process and normalizing articular connective tissue structures. Medical nutrition is based on the following principles:
- Physiological completeness and balance of the diet with a high content of minerals/vitamins. For patients with normal body weight, the energy value of the diet should not exceed the average daily energy expenditure.
- Any fish/meat broths containing extractives, refractory fats, fatty meats, smoked meats (ham/bacon), semi-finished meat/fish products or canned food containing various kinds of food additives in the form of preservatives, flavor enhancers and dyes should be excluded from the diet. , salo.
- Limit to 5-8 g/day salt and salty foods.
- Introduction of 1-2 fasting days/week in the form of a curd fasting day (350-400 g of cottage cheese and 500 grams of milk for 3-4 doses); fruit and vegetable fasting day (1.5 kg of fruits/vegetables with rosehip decoction); kefir fasting day (1.5-2 liters of kefir).
The basis of nutrition for gonarthrosis should be a diet enriched with vitamins/microelements - low-fat varieties of sea/river fish, seafood, dietary meat, low-fat cottage cheese, offal, chicken eggs, butter, cereals, vegetables/fruits, unsalted cheese, whole grain varieties bread, nuts, low-fat dairy products, virgin vegetable oils.
To maintain the cartilage tissue of the joints, it is necessary to include in the diet foods containing mucopolysaccharides, which are by their nature natural chondroprotectors (red fish, cartilage, chicken/pork legs, chicken meat, hard cheeses, gelatin) from which it is recommended to prepare jellied fish, jellies, fruit jellies/jelly. These products, when taken frequently/long-term, normalize the structure of cartilage tissue, help accelerate the processes of its synthesis, slow down degenerative processes and normalize joint function.
In case of obesity/body weight exceeding the norm, the calorie content of the diet should be reduced within 500-600 kcal and not exceed an average of 1800-2000 kcal/day, which allows for a gradual reduction in body weight. First of all, simple carbohydrates up to 250-300 g and refractory animal fats up to 60 g are subject to restrictions, and the protein content must correspond to the physiological norm.
Limit the consumption of white bread, pastries, sugar, confectionery, sweets, cream-containing products, honey, chocolate, fast food, fatty meats, mayonnaise, high-fat dairy products (cream/sour cream), duck/goose meat, smoked meats, animals/ cooking fats. It is prohibited to consume salty foods (canned food, pickles, preserves), starchy foods, cocoa, strong black tea, coffee, seasonings/spices that increase appetite - ketchup, vinegar, garlic, ground black pepper, horseradish, mustard, onions. All fried foods are also excluded. Meals are fractional. Sweet carbonated/alcohol-containing drinks are subject to restrictions.
Prevention
Preventive measures for gonarthrosis are of great importance as part of preventive therapy. Such events include:
- maintaining body weight at an average level;
- training the muscles of the lower extremities;
- avoiding joint injury;
- timely treatment of inflammation in the joints;
- moderation and strength of physical activity;
- compliance with the rules of a healthy lifestyle - proper nutrition, activity in accordance with the age limit, adherence to sleep and rest patterns;
- strengthening the immune system.
Surgical measures
When traditional drug treatment does not provide improvement, the affected joints lose their function, become deformed, and the patient may require surgical intervention.
Types of operations performed:
- Osteotomy . A complex procedure, the essence of which is to secure the articular bones at a different angle. This helps redistribute the physical load on the leg. Osteotomy is used in the initial stages of the disease. The disadvantage is that rehabilitation takes a very long time.
- Arthrodesis . Provides for the removal of affected cartilage tissue. Due to the fact that this method does not preserve natural mobility in the diseased joint, it is rarely practiced.
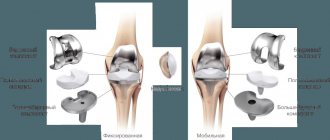
- Endoprosthetics. The most effective and common operation for gonarthrosis. The affected joint is completely removed and an artificial analogue is installed in its place.
After endoprosthetics, the pain goes away and normal mobility in the joint returns. The effect of the procedure can last up to twenty years.
Often surgery is the only way to help the patient.
Despite all the advantages of endoprosthetics, dangerous complications can also develop (necrosis, infection, thrombosis, etc.). The procedure has a number of contraindications.