Gonarthrosis of the knee, a disease that brings a person daily pain and limits normal activity. If quality therapy is not provided, the disease will progress. Treatment of gonarthrosis with folk remedies will reduce the symptoms of the pathology, slow down its development and return the person to the opportunity to lead a normal life.
Content
- How does the disease develop?
- Causes and risk factors
- Symptoms of the disease
- Signs of disease progression
- Types and forms of the disease
- Stages of the disease
- Expert opinion
- Diagnostic methods
- Which doctor should I contact?
- Conservative (non-surgical) methods
- Drug therapy
- Orthobiology methods
- Physiotherapeutic treatment
- Prevention
- Surgical tactics
- Bibliography
- Our treatment methods
- Treatment prices
- Why do they contact us?
- Patient reviews
- Make an appointment
- Questions for the doctor
The disease has several names: gonarthrosis (from the Greek gona - knee), deforming osteoarthritis (deficient arthrosis or DOA) - implies damage not only to cartilage tissue, but also bone deformation, and osteoarthritis - the term reflects the modern understanding of the pathogenesis and course of the disease. Arthrosis is characterized by a long chronic course, with periods of remission and exacerbation. Seasonality of incidence is characteristic: spring-autumn. The majority of patients are over 50 years of age. More often (2/3 cases) women suffer.
Infusions and decoctions
Other folk remedies can be used for treatment: water and alcohol extracts. They are most often used for compresses, because they contain burning or irritating substances.
Ficus tincture
The product is prepared with alcohol or vodka. To prepare, take 1 medium leaf of indoor ficus, chop it and pour alcohol. Leave for 2 weeks and filter. The tincture can be used for rubbing and compresses. You can't drink it.
Maclura (Adam's apple) tincture
Grind the maclura fruit on a grater and pour in an equal volume of alcohol. Place the mixture in a dark, warm place and leave the jar there for 2 weeks. The container must be shaken daily. When the tincture is ready, strain and use for rubbing. The medicine cannot be taken orally.
How does the disease develop?
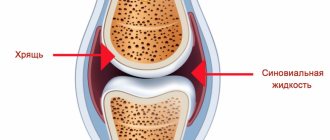
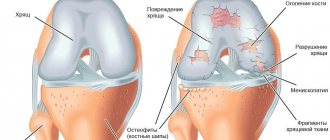
Under the influence of external and internal factors, the blood supply and nutrition of joint tissues is disrupted, degenerative dystrophic damage to articular cartilage develops, with subsequent participation in the inflammatory process of the underlying bone structures of the femur, tibia and patella. The gradual destruction of cartilaginous surfaces leads to loss of function of the knee joint, limits movement and disrupts the patient’s quality of life.
Forecast of the incidence of gonarthrosis among the population for the next 20 years, according to the World Health Organization (WHO)
Causes and risk factors
The main reasons for the development of osteoarthritis of the knee joint:
- Constant excessive physical stress on the joints leads to microtrauma of cartilage tissue and the development of the inflammatory process. At risk are loaders, installers, miners, and quarry workers. Professional athletes (weightlifters, cyclists, tennis players, football players, basketball players, hockey players, etc.) often suffer from arthrosis of large joints.
- Knee injuries. Damage to ligaments, tendons, menisci, and bruises lead to severe disturbances in the biomechanics of the joint. Fractures and dislocations of bones with a violation of the structure of cartilage, after 5-10 years, lead to the development of a pathological process and a deterioration in the health of patients. If treated incorrectly, this leads to the development of post-traumatic arthrosis.
- Surgical operations on the knee joint can lead to damage to the articular cartilage, ligaments and capsule. For example, removal of the meniscus, plastic surgery of the ligamentous apparatus;
- Excess body weight increases mechanical stress on the joints of the lower extremities. Up to 80-90% of the progression of all osteoarthritis is associated precisely with overload of the joints against the background of obesity and excess weight.
- Elderly age. In people over 50-60 years old, regenerative processes slow down, collagen production decreases, and hormonal levels suffer. Which leads to the development of degenerative changes in the knee joints.
- Hormonal disorders in women. During menopause, the production of estrogen decreases, which disrupts the absorption of calcium, leads to weakening of the musculoskeletal system, and makes bones fragile. The risk of developing osteoporosis, especially in the area of the epiphyses of the femur and tibia, increases.
- Problems with the thyroid gland. Thyroid hormones are involved in the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body. Their deficiency leads to weakening of bone tissue, the development of bone deformation, osteoporosis, and can provoke the development of gonarthrosis.
- Genetic predisposition. Collagen mutation can cause disturbances in connective tissue elements, which leads to a deterioration in the shock-absorbing function of articular cartilage.
- Heredity. There is a high probability of developing the disease if the patient’s family has relatives who suffered from diseases of the musculoskeletal system, mainly in the female line.
- Inflammatory diseases. Infectious arthritis, bursitis, synovitis caused by bacterial or viral infection are accompanied by degenerative changes in articular cartilage.
- Vascular diseases. The tissues do not receive proper nutrition, the blood supply is impaired, which leads to the development of ischemia and dystorophic changes.
- Poor nutrition and metabolic disorders. Eating foods high in purines (proteins) contributes to the deposition of salts in the knee, for example, gouty arthritis is considered one of the causes of arthrosis.
- Specific diseases - gonorrhea, tuberculosis, syphilis, chlamydia, influenza - can cause exacerbation of joint syndrome.
- Intoxication of the body with various chemicals, including some medications, for example the blood pressure drug atenolol, can cause arthralgia.
- Autoimmune disorders are associated with a violation of the body's immune defense when antibodies are produced against its own cells, for example rheumatoid arthritis of small joints.
- Weakness of the hip muscles and ligaments leads to instability and the development of degenerative joint diseases (chondromalacia, osteoarthritis).
Main risk factors for osteoarthritis
Rubs and baths
For rubbing, alcohol extracts from plant materials are used. Their action is based on the irritating and vasodilating effect of alcohol. In this case, the beneficial substances of the plants penetrate into the capillaries through the skin and have a local analgesic effect. Tinctures for rubbing can be prepared from cinquefoil herb, red elderberries, horse chestnut fruits or red pepper. You cannot drink such tinctures.
Healers especially recommend dandelion tincture. To prepare it you need a bottle of any capacity and triple cologne. The flower baskets of dandelions are poured into the bottle, filling it to ½ volume or a little more. Then the container is filled to the top with cologne, closed with a tight stopper and the liquid is infused for 1 month. After this, it is ready to use; the flowers can be strained or left in the bottle.
Dandelion tincture should be stored in a dark place at room temperature and used by rubbing it into the area of the sore joint 2 times a day for 1 month.
A good rub can be made from mumiyo (3 g) and honey (100 g). You need to mix the ingredients until smooth and rub the mixture with massage movements into the sore joint at night. Relief occurs after 1 week of treatment. The product is contraindicated for allergies.
Recipes for medicinal baths involve the use of decoctions of medicinal plants, salt or other components:
- Place 1 kg of salt, 2-3 handfuls of pine needles, 2-3 chopped Jerusalem artichoke tubers, 2 tbsp. l. honey and 1 tsp. turpentine. Pour hot water, let it brew for about 20 minutes and pour the infusion into a bath of hot water (+ 37°C). Take the procedure for 15–20 minutes, daily or every other day. The course of treatment is 10–12 baths.
- A bath infusion can be prepared from St. John's wort, oregano, calendula, nettle and burdock root. Each herb needs to be collected when it blooms, cut and take 3 tbsp. l. masses. Steam the collection with boiling water for 1 hour. Pour 500 g of clay and strain the liquid into a bath of hot water. Take a bath for 20 minutes, every 1 day. A total of 8 procedures are required.
- A decoction of Jerusalem artichoke leaves is prepared from the aerial part of the earthen pear. Place leaves and stems (2 kg) in a bucket. Pour boiling water over the herb and leave until it cools. Local baths are made with this decoction, immersing the joint in warm liquid until the pain goes away.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of gonarthrosis | Description |
| Knee pain | Painful sensations of an aching nature are disturbing at rest, intensify during exercise, and can occur at night. In case of exacerbation, the pain becomes severe stabbing, piercing, localized along the inner surface of the joint, in the projection of the narrowest part of the joint space, below or behind the knee. |
| Crunching and clicking | Pathological sounds arise as a result of friction of the articular surfaces, during movement, during flexion and extension, caused by a violation of the congruence of the articular surfaces, the growth of bone spines (osteophytes), and are associated with the appearance of areas of degeneration and cartilage defects. |
| Edema and swelling | Caused by the development of an inflammatory process in the knee or surrounding soft tissues. Inflammation of the synovium leads to increased production of synovial fluid and the occurrence of synovitis. |
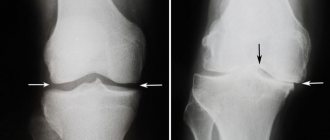
| Narrowing of the joint space | In the early stages of the disease, the width of the interosseous space does not change, however, with the development of the pathological process, thinning and a decrease in the height of the articular cartilage occurs, which indicates the progression of osteoarthritis (hence the name of the disease deforming arthrosis); |
| Joint deformity | Caused by the appearance of bone growths, growths, osteophytes, which can be felt under the skin, the development of local inflammation of the bone tissue of the femur and tibia. |
| Curvature of the limb axis | Loss of calcium and vitamin D deficiency lead to the development of local osteoporosis of the cancellous bone of the articular surfaces, which leads to varus deformation of the limb axis (O-shaped), this symptom is characteristic of stage 3 arthrosis of the knee joint. |
| Atrophy and weakness of the thigh muscles | They develop against the background of physical inactivity caused by pain, the volume of the quadriceps and biceps muscles decreases. |
| Limitation of movements | Caused by pain, the development of an inflammatory process, the growth of osteophytes (bone spines), scar tissue, and adhesions. Morning stiffness in the knee is typical, when it is not possible (due to pain) to immediately get up and walk after sleep or a long rest, but you have to walk around, the so-called starting pain. As a result, physical inactivity further reduces the physical activity of patients, closing a vicious circle. |
| Increase in local temperature | Speaks of an acute inflammatory process in tissues. Indeed, diseased joints have a higher local temperature, and some patients complain that their knees are burning. |
The first signs of osteoarthritis that you should pay attention to are pain that occurs during or after exercise. The pain goes away with rest and does not require medication.
Diagram of a healthy joint and one affected by osteoarthritis
Diagnosis of gonarthrosis
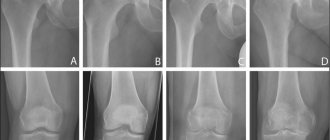
To diagnose a patient with gonarthrosis, a combination of collecting complaints, examination, and X-ray examinations is necessary.
An X-ray image of a joint today is the simplest and most easily accessible research method, with the help of which it is possible to diagnose the patient with a sufficient degree of accuracy, observe the development of the process over time, and determine the tactics of further treatment. Among other things, an x-ray allows you to make a differentiated diagnosis, for example, to exclude a tumor process in the bone tissue of the thigh or lower leg or an inflammatory one. Also, to diagnose gonarthrosis, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are used, which can show changes not only in bone structures, but also in soft tissues.
In old age, everyone has certain signs of gonarthrosis, so a diagnosis can be made only after a complete collection of anamnestic data, complaints and visual examination, as well as instrumental research methods.
Signs of disease progression
With the development of symptoms of gonarthrosis, the clinical picture becomes brighter: the knees begin to bother at rest and even at night, during movements associated with flexion or extension. Lameness appears, stiffness of movement increases, swelling of the soft tissues, inflammation of the synovial membrane occurs, effusion can accumulate in the joint cavity, externally the knee increases in volume, the contours are smoothed out.
The progression of DOA and a further increase in the degree of destruction are evidenced by the following changes:
- Curvature of the limb axis in the form of O-shaped legs (usually indicates the transition of the disease to stage 3);
- Constant nature of pain, night pain and the manifestation of pain when the weather changes (meteosensitivity);
- Deterioration of motor functions, with the development of flexion contracture;
- Weakness and atrophy of the thigh muscles progresses.
Read more about what to do in case of exacerbation of arthrosis here>
Types and forms of the disease
There are:
- Primary arthrosis develops as an independent disease and is associated with age-related changes and heredity.
- Secondary gonarthrosis occurs against the background of various diseases or injuries, for example post-traumatic osteoarthritis.
Depending on the main causes and pathogenesis, the following types of osteoarthritis are distinguished:
- Ischemic, associated with problems with blood supply to tissues and vascular disorders;
- Post-infectious, caused by infections, viruses, autoimmune processes that cause damage to the articular surfaces;
- Idiopathic, the causes of the occurrence and development of the pathology remain unclear;
- Metabolic is associated with metabolic disorders - gout, hemochromatosis, chondrocalcinosis;
- Involutionary, as a result of age-related processes of destruction of the body;
- Post-traumatic arthrosis and previous injuries cause the development of degenerative changes in the joint;
- Dishormonal - due to hormonal imbalances, changes occur in the musculoskeletal system, primarily in the skeletal system of the body.
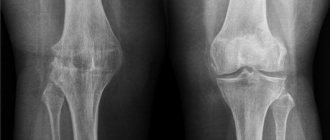
Degrees and stages of development of gonarthrosis
The division of the disease into stages is arbitrary, since the disease progresses over time. Depending on the symptoms and data from instrumental examination methods, four stages of osteoarthritis are distinguished.
Arthrosis stage 1
The initial stage is associated with a deterioration in the quality and decrease in the quantity of biologically active substances in the synovial fluid (articular fluid, provides nutrition to cartilage, has shock-absorbing properties, and promotes the sliding of articular surfaces). Malnutrition leads to wear and degradation of cartilage tissue, pain and inflammation. At the initial stage, movements are not impaired, in full. Patients experience slight pain, discomfort, tingling, and crunching in the joints when moving. Pain occurs during physical activity, long walking or after it. At the initial stages of gonarthrosis, external changes in the knee joint are not noticeable, there are no differences from a healthy one. More details>>
Osteoarthritis stage 2
It is characterized by the following symptoms: thinning of the cartilage up to 1.5-2.0 mm (normal 2.5-3.0 mm), slight narrowing of the joint space (no more than 10-20% of the norm), small single bone growths (osteophytes) appear. up to 5mm, the articular surfaces begin to deform. The inflammatory process is wavy in nature, with periods of emission and exacerbation. Grade 1-2 gonarthrosis is characterized by: pain with minor exertion, when the weather changes, after walking you feel tired, moderate swelling, and weakness of the thigh muscles. Limitations of mobility are insignificant, morning stiffness and sometimes crunching or clicking are disturbing. It is at this stage that patients most often consult a doctor. More details>>
Stages of development of osteoarthritis (see text for description)
Gonarthrosis stage 3
Pathological changes are caused by further progression of the disease, external deformation of the joint and surrounding tissues becomes noticeable, the axis of the limb is curved (varus or O-shaped deformity). At the third stage, the cartilage tissue is severely damaged, thinned to 1-1.5 mm, and exposed bone is visible in places. Bone growths and bone deformities can be easily felt under the skin, and the range of motion of the affected joint is significantly reduced. At 2-3 degrees of osteoarthritis, an even greater narrowing of the joint space occurs, movements are limited, accompanied by pain, crunching, morning stiffness and lameness are characteristic, and contracture develops in the joint. I am bothered by aching and sometimes sharp pain in the knee, even at rest. Due to severe pain, patients often suffer from insomnia due to the fact that they cannot take a comfortable position and react to weather changes. More details>>
Stage 4 gonarthrosis
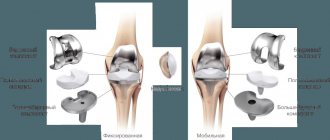
This is the last stage of the disease, characterized by clinical signs: complete destruction of the articular surfaces, exposed bone is visible, the cartilage is represented by rare “islands”. There is a noticeable significant narrowing of the joint space throughout, a pronounced O-shaped deformity of the lower extremities, and swelling. Mobility is almost completely lost. Treatment with non-surgical methods at this stage is ineffective, and recovery is not possible; help is of a multilateral nature. At this stage, it is recommended to replace the joint with an endoprosthesis. More details>>
Commented by orthopedic doctor Ph.D. Litvinenko Andrey Sergeevich:
To accurately determine the stage of osteoarthritis, in addition to examining the patient, it is extremely important to conduct an instrumental examination: ultrasound, radiography, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Bilateral gonarthrosis is common, so before treatment it is recommended to examine the left and right joints simultaneously. This will help you choose the optimal tactics, and therefore prevent further progression of the disease.
Features of folk remedies
If grade 2 gonarthrosis of the knee joint has developed, treatment with folk remedies will not bring complete relief. It is impossible to be completely cured, but everyone can improve their condition in simple ways.
Sometimes, after diagnosis, medical professionals recommend surgery, as this is the most effective treatment method. But, although surgery solves the problem in many cases, this method is not suitable for everyone. There is no point in agreeing to a major surgical intervention without trying to improve the condition with the help of traditional joint treatment.
There are many methods for treating gonarthrosis at home. With the help of traditional therapy, you can improve the condition, and for this you do not need to take expensive chemicals.
To treat gonarthrosis of the knee joint at home, available products, compresses, lotions, decoctions and infusions are used.
Although most methods are harmless, before starting therapy you should consult with your doctor, because there is always the possibility of an allergic reaction, individual intolerance or contraindications.
It is important to correctly assess what results can be achieved using this method of therapy. If grade 1 gonarthrosis of the knee joint is diagnosed, complete healing is possible. When the pathology is at stage 2 or 3, in addition to traditional treatment, it is worth using medicinal methods.
To see improvements, it is not enough to use the recipe only once. It is important to carry out the procedures regularly, in courses, strictly observing the order of the event and the recommended dosage.
To prepare all formulations, it is necessary to use environmentally friendly and fresh raw materials. The dose and frequency of use should not be exceeded. If you are allergic to any ingredient, the therapy method should be completely abandoned. If adverse symptoms appear after starting treatment, the drug should be discontinued.