Osteoarthritis is the most common joint disease associated with the destruction (degeneration) of cartilage tissue. The disease is manifested by pain and restriction of movement in the diseased joint, which sharply worsens the quality of life of patients and is a common cause of temporary or permanent disability.1 Clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis are observed in more than 20% of the population.2 More often, osteoarthritis develops in joints that experience heavy loads, in particularly in the knees. According to WHO forecasts, osteoarthritis of the knee joints (gonarthrosis) will become one of the main causes of disability among the population in the next few decades.3
Main characteristics
Most often, this disease appears in people after the age of 45, since it is during this period that age-related changes occur in the body. The tissues begin to thin out and become vulnerable to injury and damage. In younger people, such negative changes occur as a result of active participation in professional sports.
Treatment of the disease in the initial stages of development involves the use of conservative methods. Men over 45 years of age, as well as women over 55 years of age are at risk. Also, the risk of developing gonarthrosis is present in people who have a genetic predisposition to diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a non-inflammatory disease; it progresses slowly. As it develops, the quality and quantity of cartilage tissue changes. The main symptoms include pain. Most often they appear in the following cases:
- during joint flexion;
- when climbing stairs;
- after prolonged sitting.
In the initial stages of development, stiffness and pain occur in the morning after waking up. After some time, these symptoms go away on their own. As the disease progresses, the duration of unpleasant symptoms increases.
If irreversible changes occur in the cartilage tissue, inflammatory processes may develop in the joint. In this case, the disease, which is initially non-inflammatory in nature, is complemented by an inflammatory process. The main goal of therapy is to reduce the frequency and duration of the period of inflammation.
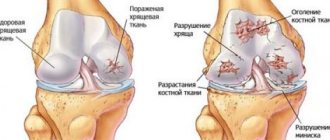
Articular cartilage gradually wears out, and its amount between the rubbing surfaces of the bones decreases. Gonarthrosis is one of the most common diseases in the world among older people. Age is considered a significant risk factor.
Types and causes of gonarthrosis
There are two types of gonarthrosis of the knee joint: primary and secondary.
Primary gonarthrosis most often occurs due to metabolic disorders in the tissues of the joint, intense stress on the knees and natural aging of the body. The disease usually develops after 40 years of age. It appears due to curvature of the legs, hormonal disorders.
Secondary gonarthrosis appears due to injury or fracture of the knee, infectious disease, metabolic disorder, or development of the knee. Secondary gonarthrosis can occur at any age.
There is unilateral and bilateral gonarthrosis. The latter affects the knee joints of both legs. Left-sided gonarthrosis causes pain in the left knee, and right-sided gonarthrosis causes pain in the right.
Disability
In order to determine whether a person needs to be given a disability, one must first diagnose what stage the disease is at.
A person is recognized as able to work in the following cases:
- if the changes are minor or moderate;
- the disease is accompanied by various disorders of static-dynamic functions, but the course of gonarthrosis is slowly progressive.
Disability of the third group is given to people in the following cases:
- if a moderate impairment of motor function is diagnosed;
- if a person performs work that involves significant physical activity;
- if a person is forced to constantly be on his feet;
- if there is a pronounced violation of the static-dynamic function.
There are certain situations in which patients with gonarthrosis will be sent to undergo a disability commission:
- if the progression of the disease lasts for three years or longer, with exacerbations occurring at least three times during the year;
- if the patient underwent surgery to treat arthrosis of the knee joint, as a result this significantly affected his ability to work;
- in case of violation of the musculoskeletal function of a limb, if this process is pronounced.
During the commission, the patient's medical history is studied. The person’s complaints must be taken into account and the clinical picture is assessed. The patient must show how able he is to work. Disability of the second and third groups is confirmed once a year, and the first group must be confirmed once every two years.
Who is at risk
Most often people suffer from gonarthrosis:
- aged people;
- men and women with leg injury or surgery;
- overweight people - they suffer from gonarthrosis 3 times more often than others;
- professional athletes;
- women during menopause;
- men who work physically hard;
- relatives of patients with gonarthrosis.
Factors that increase the likelihood of this problem also include:
- genetic predisposition, such as Marfan syndrome, in which the joints become “loose”;
- varicose veins, interfering with normal nutrition of the joint;
- various types of arthritis;
- problems with vascular innervation;
- metabolic disorder.
Most often, the problem affects people over 40 years of age, but in young people it can also occur, primarily due to traumatic causes (such as playing sports).
If you are at risk, pay attention to the prevention of gonarthrosis. We will talk about it at the end of the article.
Causes of pathology
Experts identify certain provoking factors for gonarthrosis:
- previous injuries and injuries to the knee joints;
- if there is instability of the joint due to damage to the ligamentous apparatus;
- if you have previously suffered a meniscus tear;
- in the presence of direct injuries to cartilage tissue;
- if the person is over 45 years old;
- if a person systematically experiences high physical activity, with regular lifting and carrying heavy objects;
- if you are overweight;
- with frequent emotional stress;
- if there is a genetic predisposition to diseases of the joint and musculoskeletal system;
- if there is a lack of physical activity;
- in the presence of disturbances in metabolic processes.
It is impossible to determine the reliable cause of the development of the pathological process. Gonarthrosis in most cases is primary; changes in the joint are caused by wear and tear of the cartilage tissue. Secondary gonarthrosis is also diagnosed, which develops against the background of other degenerative changes in the body. For example, secondary gonarthrosis is often present in people suffering from clubfoot.
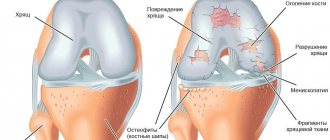
The key clinical manifestations of the disease are:
- painful sensations in the joint, which manifest themselves when going up or down stairs, when bending or straightening the joint;
- pain syndrome, a feeling of stiffness in the joint after a long rest. As the person moves, the pain decreases;
- the pain syndrome becomes intense after undergoing heavy stress - physical or sports;
- swelling in the joint, knee deformity;
- crunching in the joint when moving, flexing or extending;
- increased pain due to rainy or cold weather.
As the disease progresses, symptoms become more pronounced. The pain does not disappear even with rest. In this case, the pathological process is complemented by a decrease in the range of motion in the joint. Most often, such changes are present at the third stage of development of gonarthrosis. If unpleasant symptoms appear, it is important to visit a traumatologist, orthopedist or rheumatologist as soon as possible. After a while, the pain syndrome can no longer be relieved with painkillers. The person will develop lameness and will be forced to walk with the help of a cane.
Symptoms
Osteoarthritis of the 3rd degree of the knee joint is manifested by two main symptoms: pain and dysfunction. Pain at this stage is constant or periodic and intensifies with movement. With rest, the pain usually decreases or subsides completely. The movements may also be accompanied by a crunching sound in the affected knee. This sound is caused by the friction of collapsing articular surfaces.
Dysfunction of the joint is manifested by a feeling of stiffness and a sharp limitation in the range of movements. This leads to changes in daily activities and limitation of the patient's ability to work. At the third and fourth stages of gonarthrosis, curvature of the limb may also be observed due to changes in the configuration of the joint.4
Diagnostic methods
The key methods for diagnosing diseases of the articular apparatus are:
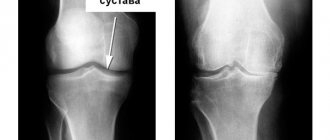
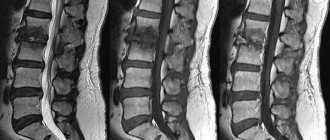
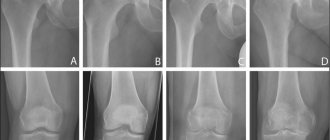
- radiography of the knee joints. In this case, it is necessary to determine at what stage the disease is. X-rays of both extremities usually need to be taken;
- computed tomography - allows you to determine how worn out the cartilage tissue is, how pronounced the changes in the joint structures are. The diagnosis also determines whether there are ligament injuries and whether there are other pathologies, for example, a Baker’s cyst;
- magnetic resonance imaging of the knee joints - with this procedure you can determine the severity of changes in the tissues. MRI helps to assess the condition of vascular structures and determine how much blood circulation has worsened;
- sometimes doctors prescribe a procedure such as a topogram;
- The collection of anamnestic data is mandatory. The doctor evaluates the patient’s complaints, clinical manifestations of the disease;
- Using ultrasound examination of joint tissues, you can determine how worn out the cartilage tissue is. You can find out whether pathological processes are present in the ligamentous, muscular apparatus, in the periarticular space, whether there are changes in the meniscus;
- Joint arthroscopy is a diagnostic puncture. After the procedure, the resulting material is sent to the laboratory for further research.
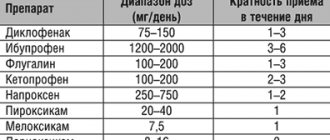
Drug therapy
Conservative therapy is effective if gonarthrosis is in the early stages of development. If the disease is detected at the second or third stage, with the help of medications it is possible to only slightly relieve the inflammatory process and pain.
With the help of drugs you can achieve the following results:
- stop the inflammatory process;
- pain syndrome, a feeling of stiffness in the joint after a long rest. As the person moves, the pain decreases;
- accelerate the regeneration of cartilage tissue;
- get rid of severe painful sensations;
- restore joint function.
In parallel with the use of medications, it is important to limit the load on the affected limb during treatment. As part of conservative therapy, the following drugs are prescribed:
- analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotectors;
- local application of ointments, gels, creams;
- Intra-articular injections of drugs are administered. Most often these are hormonal drugs that help get rid of the inflammatory syndrome within a short period of time. They also replenish synovial fluid and promote the restoration of cartilage tissue;
- intra-articular injections of the patient's processed plasma are administered;
- Regenerative medicine is used - this is the introduction of intra-articular injections of autologous cartilage tissue cells, which are obtained from the lipid structures of the patient’s body.
Auxiliary treatment
- Physiotherapy. Special therapeutic exercises are mandatory for those people who strive to maintain motor function of the joints for as long as possible. With the help of therapeutic exercises, muscle strength and endurance increase, and coordination improves. With regular exercise, synovial fluid is actively produced, which is a natural lubricant between the joint. Thanks to it, joint friction is reduced.
- Special food. This is a must for those people who are obese. If you are overweight, your knee joints experience regular heavy loads. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend monitoring your diet in order to reduce body weight and reduce stress.
Additional methods also include physiotherapeutic procedures:
- UHF;
- magnetic therapy;
- massage
- balneotherapy
- cryotherapy
- electrophoresis
- current therapy;
- manual therapy;
- acupuncture
- hirudotherapy
- mud baths;
- ozone therapy
- galvanotherapy
If the listed methods for treating grade 3 gonarthrosis are ineffective, the doctor prescribes the following procedures:
- Arthroscopy is not only a diagnostic procedure. With the help of arthroscopy, surgery is performed on the meniscus, cartilage tissue, joint effusions and fluid accumulation in the joint are removed;;
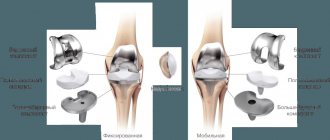
- endoprosthetics - this procedure is prescribed for complete destruction of cartilaginous structures. It involves replacing a joint or one of its parts with an implant that is not rejected by the body;;
- osteotomy – involves surgery on the bone. The main task is to restore the integrity of bones, as a result of which the destruction of cartilage tissue slows down.
Doctors also recommend wearing special orthoses. With their help you can reduce the load on the joint. Orthoses and bandages will be especially useful for those people who play professional sports or for patients who regularly exercise their joints.
Treatment of gonarthrosis of the knee joint
When the first signs of a knee joint disease appear, you should consult an orthopedic doctor as soon as possible. At the initial stage of the process, the doctor prescribes drug therapy and complete rest of the affected limb.
After the acute period has subsided, it is possible to prescribe:
- exercise therapy course,
- massage,
- as well as physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis with analgesics, UHF therapy, magnetic or laser therapy, phonophoresis with steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, mud treatment, etc.)
At the next stage of treatment, the doctor may prescribe drug therapy, which involves taking chondroprotectors that stimulate metabolic processes in the joint. Sometimes intra-articular injections with hormone-containing drugs are required. If the patient has the opportunity to receive sanatorium-resort treatment, it is recommended to him. Often, the patient is recommended to use a cane when walking to unload the joint. You can use special orthopedic insoles or orthoses for prevention.
If the patient is diagnosed with the third stage of gonarthrosis, in which its manifestations are most pronounced (pain, impairment or complete lack of functioning of the joint), surgical treatment may be required, consisting of knee replacement. Rehabilitation measures until the joint function is completely restored usually take from 3 to 6 months, after which the patient can return to a full life.