Mechanism of injury
Mechanism of Injury
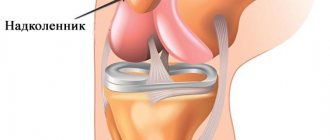
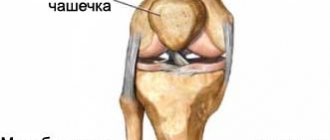
The kneecap is a bony structure that takes part in the formation of the knee joint. It is located anterior to the articular surfaces of the thigh and lower leg and is held in place by a ligamentous apparatus formed by strong connective tissue cords.
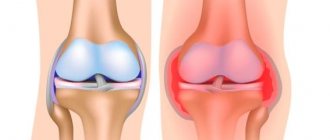
If there is excessive impact on the joint in the area of the kneecap (excessive flexion or extension of the knee, rotation of the hip with a fixed shin, direct mechanical shock), a mechanical violation of the anatomical integrity of the bone, cartilaginous base of the patella or ligamentous structures occurs. This leads to a significant disruption of the functional activity of the structures, as well as the development of an inflammatory reaction in the tissues, aggravating the clinical symptoms of the injury.
Patella
The condyles of the femur, the upper articular side of the tibia, as well as the patella act as different parts, which combine to form the knee joint. The patella, or, as it is also called, the patella, is an almost flat, rounded bone. It is the largest sesamoid bone in the human skeleton. You can find it deep within the quadriceps tendon. The patella, even without additional equipment, can be felt with fingers. And if you straighten your knee, you can even move it a little to the sides, as well as up and down. And all because this bone is the most mobile in our skeleton. During knee straightening, the bone is placed on the articular side of the femoral condyles. During flexion, the patella goes down and moves slightly back, thereby falling into the space in front of the intercondylar fossa. The tendon of this bone connects a large muscle called the quadriceps and the tibial tuberosity. At the moment of contraction of the quadriceps, the lower limb extends in the area of the knee joint. The patella becomes a support for the tendon, which gives power to the quadriceps.
The patella belongs to the group of short bones; like them, in its center there is spongy bone, which is closed at the edges by compact bone. It is somewhat thicker on its frontal zone than on the back. The patella is formed through several areas of ossification. In the period from three to five years, they unite into a single new formation. It also happens that the bone does not heal. In this case, the patella remains divided into several parts. Its complete transformation into bone ends around the age of twenty.
The patella can be divided into several parts. It has an upper and lower end. The upper end is the base, while the lower end has a certain point called the apex. The base has a slight bevel, directed from top to bottom and from back to front. A tendon that is part of the quadriceps femoris muscle is attached to this part of the patella. The apex is divided into two zones - lateral and medial. Each of them is slightly pointed. In this part of the patella, the lower bundles from the wide femoral muscles dock. The posterior articular side is divided into two zones by means of a comb placed vertically. These are the smaller, that is, medial, and the larger, that is, lateral zones. The back side of the patella, or rather most of it, is covered with hyaline cartilage. This area connects the patella to the femur. Hyaline cartilage has a perfectly smooth surface. This makes it possible to reduce friction during movement along the surface of the thigh bone. The front surface, on the contrary, is somewhat rough. In addition, it also has a convexity, inside which hides a large number of holes intended for vessels. Well, it’s all covered with periosteum.
The second place in the number of knee joint injuries was given to dislocations. This injury occurs most often in athletes and even dancers. In general, it can be obtained by turning sharply right on the spot or during a jump.
Causes
Violation of the anatomical integrity of the cartilaginous and bone parts of the cup, as well as the ligamentous apparatus, occurs due to the influence of various causative factors. Of these, the most common are:
- Road traffic accidents.
- Domestic injuries.
- Industrial injuries.
- Sports injuries.
The mechanism of development of a violation of the anatomical integrity of the knee has certain similarities, regardless of the reason that led to its implementation.
Patella deformity
High kneecap is a rare occurrence and is associated with abnormal development of the rectus femoris muscle. Generally, children's joints have good mobility after birth. But after a few years it gets worse, resulting in a complete inability to bend the knee.
In such cases, the doctor makes a small incision and lengthens the fibrous elements to restore the joint's ability to bend. This is followed by a rehabilitation period, which includes exercise therapy to strengthen the lower leg muscles.
It is also recommended to read another article about the symptoms of arthrosis.
Classification
Depending on the nature and location of injuries to the patella and its structures, they are divided into several main types. Depending on the nature of the injury, there are:
- A fracture of the bone base, which can be with or without displacement of bone fragments. A comminuted fracture with the formation of several bone fragments is distinguished separately.
- A dislocation of the kneecap, which is usually accompanied by a torn ligament.
- Sprain and damage to the patellar ligament.
A common injury is injury to the patellar retinaculum (the main ligament that stabilizes the bony base of the kneecap). In this case, the medial suspensory ligament of the patella is predominantly injured. Damage to the structures of the ligamentous apparatus can be isolated or combined with other injuries (fracture or dislocation).
Thus, damage to the medial retinaculum of the patella is accompanied by dislocation and damage to the cartilaginous structures, the internal meniscus of the knee, collateral ligament and tendons of the femoral muscles are injured. Injury to cartilage structures is called osteochondral damage to the patella and is usually a consequence of degenerative pathological processes in cartilage tissue (osteoarthrosis).
Patella injuries
It is worth considering several cases presented above. One of them is a broken kneecap . This injury most often occurs as a result of direct trauma, i.e., a strong blow or fall to the kneecap. There may also be an overuse fracture (usually seen in young children) and a traumatic dislocation of the kneecap. Fractures are located at the top or bottom of the patella, or at the lateral or medial border of the patella. Such damage to the patella can be identified by compression pain, as well as by swelling located above the knee, sometimes also by intra-articular hematoma. The patient often cannot straighten his leg at the knee. Sometimes the patella in the knee becomes displaced .
If such displacement occurs without destruction, then the so-called lateralization of the patella . This knee injury usually affects active people. It manifests itself as pain in the kneecap in the front, difficulty moving the kneecap inward, problems with climbing stairs, doing squats, crunching of the patella when moving, and a feeling of the kneecap slipping.
About
Symptoms
Clinical symptoms of patella injury include several characteristic manifestations, which include:
- Pain in the anterior surface of the knee in the area of the patella, which is usually of high intensity and intensifies when attempting to move.
- The appearance of clicks and crunching, which accompanies damage to the cartilage of the patella, in particular against the background of chondromalacia (destruction of cartilage tissue against the background of a degenerative-dystrophic process).
- Pathological mobility of the kneecap, which indicates that the medial patellar ligament is injured. Damage to the lateral (side) ligament of the knee can cause the lower leg to deviate to the side.
- Restricted knee mobility.
- Swelling of soft tissues, redness (hyperemia) of the skin, which are a sign of the development of an inflammatory reaction.
Symptoms are accompanied by impaired functional activity of the knee with limitation of active and passive movements in it.
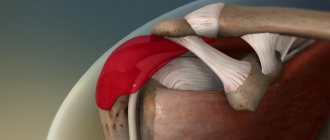
Symptoms of a torn patellar ligament
Typical mechanism of injury to the intrinsic ligament:
- powerful contraction of the quadriceps muscle when pushing, lifting,
- sometimes you can hear a crunching, crackling sound,
- there is a sharp pain,
- movement in the knee joint becomes impossible.
With these complaints, you should urgently consult a doctor.
The traumatologist will look at the knee joints, palpate the knee joint, and can determine hemarthrosis, that is, blood in the knee joint. When the ligament is completely ruptured, the patella moves upward due to the traction of the thigh muscles, and extension in the knee joint becomes impossible. In some cases, you can palpate the hole in the place where the patellar ligament should be.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound
Damage to the patella of the knee joint is diagnosed using techniques for visualizing its structures. These include:
- radiography;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging;
- Ultrasound;
- arthroscopy.
The most informative, but invasive procedure is arthroscopy. It involves inserting a tube with lighting and a camera into the cavity of the knee joint. This technique is often performed for therapeutic purposes.
Treatment of patellar ligament rupture
To fully restore your own ligaments, surgery is necessary.
Conservative treatment of patellar ligaments does not bring results. Moreover, it is advisable to perform the operation as early as possible, this will lead to a better result. During operations, the traumatologist finds the ends of the torn patellar ligament and stitches them together. Sometimes the ligament is additionally strengthened with absorbable or synthetic materials. There are a huge number of techniques, but their point is to stitch the ligament, restore its length and strengthen it.
After kneecap surgery, the leg is immobilized in a straight position with a cast or orthosis. An orthosis is preferred because it is possible to adjust the angle of flexion in the knee joint and to carry out early development of movement in the knee joint, since active development has been proven to accelerate the fusion of the ligament.
The prognosis is usually favorable. The main thing is to perform surgery as early as possible.
| Arthroscopic meniscal resection | To the list of articles | Patella fractures |
Patella dislocation
Most often in medical practice, patients are diagnosed with patellar dislocation. Reasons for this problem:
- amyotrophy;
- sprain of the external ligament;
- defect in the shape of the legs;
- injuries of various types.
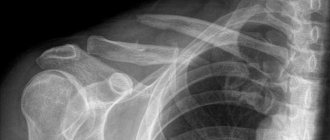
If a specialist has diagnosed a dislocation of the patella, then it is necessary to first reduce the dislocation using local anesthesia, after which the sore spot is fixed with a plaster cast. After reduction, the patient must undergo a control x-ray, which will show the presence of osteochondral bodies, which can sometimes appear as a result of the injury.
Important! In case of acute dislocation, it will be necessary to ensure the immobile position of the limb for 1 - 1.5 months. The doctor also prescribes physiotherapeutic procedures and massage courses. All of them are performed without removing the splint.
A patient with an old dislocation requires surgical treatment, which includes surgery. Then it will take at least 2 months to restore the knee joint.
Functional load
Since the patella is a sesamoid bone, it acts as a trochlea (like all the other bones in this group). Due to them, a person controls muscle efforts, as well as the direction of the limb in the desired direction during movement. This bone belongs to the group responsible for the functioning of the flexion and extension apparatus of the lower leg. The main functions of the cup are in the following aspects:
- With its help, the strength of the quadriceps femoris increases (works as a block);
- Allows you to stabilize the knee joint. Thanks to the concave structure of the cup, the edges of the bones are held, eliminating displacement to the sides;
- Performs a protective function of the knee from mechanical injuries. From early childhood, the child falls to his knees, receiving abrasions and wounds. It is the patella that prevents serious damage to the knee itself from fractures and ruptures.
Thanks to the tendon bags, the friction of the tendons themselves on the surface of the bones is reduced, they provide optimal gliding. The structural feature of the knee includes a different number of bones of the femoral-patellar joint. Thus, each person has his own number from two to four. In medical practice, there are also cases when the cup on the inside does not have a concave shape, but an irregular flat one. The condyles may be too small, and in some cases the ligaments may be longer or shorter than normal. Such individual deviations are pathological, which lead to displacement of the patella. This provokes you to work incorrectly, and, accordingly, perform functions not as needed. Knee problems develop.
interesting fact! When the knee is bent to a right angle, the load on the femoral-patellar joint exceeds 500 kg. At an angle of 130 degrees, the load exceeds one ton.
Treatment and rehabilitation after a patellar fracture
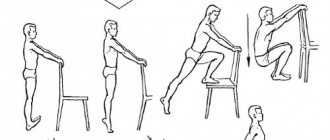
Treatment of a patellar fracture can be conservative or surgical. If the injury occurred without displacement and the fracture is closed, the doctor will apply a posterior plaster splint for 15-20 days. In this case, the patient is allowed to walk, but only with crutches. Rehabilitation after a fracture of the patella should begin immediately after applying a cast - this includes laser exposure, physical therapy and massage. As a rule, the patient’s full working capacity is restored after 2 months.
If a displaced fracture occurs and the fragments have moved from the site of injury by 0.5 cm or more, then this is a direct indication for surgery. The Berger-Schultze method is most often used: after matching all the fragments, muscle-tendon plasty is performed. The operation for a fractured patella ends with the application of a plaster cast and immobilization of the injured limb for at least 30 days. If the fracture is multi-fragmented, then in some cases doctors have to remove the fragments during surgery - in this case, it will not be possible to maintain the integrity and functionality of the kneecap.
Recovery after a patellar fracture lasts at least 3 months. For the first 30 days, the patient is in a supine position, he is extremely rarely allowed to get up, and can only move around on crutches. After removing the plaster cast, the patient will have to undergo rehabilitation, which involves:
- physical therapy and massage aimed at restoring the function of the knee joint;
- physiotherapeutic procedures - exposure to weak currents, etc.
The results of rehabilitation after a patellar fracture depend on the regularity and correctness of all procedures. Doctors do not recommend completely avoiding putting stress on the injured leg - as the limb recovers, the patient should perform physical exercises and develop the knee joint.
More detailed information about a fracture of the patella can be obtained on our website dobrobut.com.
What is tendonitis?
One of the common diseases of the patellar ligament is tendonitis. It is an inflammation of tendon tissue that often occurs at the point of attachment to the bone. The pathology occurs in middle-aged people, as well as in athletes and those who spend a lot of time in the same position.
Disease Prevention
To avoid the occurrence of patellar pathologies, simple preventive measures should be taken:
- Do not load the popliteal and patella surfaces. When working sedentarily, you should periodically take short breaks and perform a few simple exercises.
- Adequate rest and sleep is necessary.
- Those who are prone to knee diseases should not engage in strength sports. It is better for such people to sign up for swimming or play volleyball.
Regular and gentle exercise will help maintain healthy legs.
Pathologies
Among the main diseases are:
- patellar instability. Typically occurs due to injury. In this case, a lateral, that is, external, dislocation is observed. It often resolves on its own, but recurrent cases occur as a result of ligament damage. A person feels pain in the knee, as well as instability on the leg while moving. Patients cannot fully bend their leg;
- patellar balloting. Determined by the presence of fluid in the joint cavity. When you press on the cup, it moves lower. When the pressure disappears it returns to its place.
To treat chronic instability, surgery is performed - lateral release. The lobed structure of the patella is in most cases diagnosed in men (90%). This pathology implies a calyx consisting of several fragments. Most often, two lobes are identified, in rare cases - three. There is no special treatment, but the anomaly leads to the development of gonarthrosis. Patients are advised to maintain a level of physical activity intensity. In most cases, people do not even suspect the presence of such abnormalities until they receive an injury and undergo an x-ray.
If you experience problems with your knees, you must begin treatment immediately. Delaying pathological processes can deprive the main function of movement.