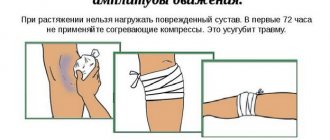
Understanding the anatomical structure of the ankle ligaments is critical for proper diagnosis and treatment. Damage to the ligamentous apparatus of the ankle joint is one of the most common traumatic reasons for visiting a doctor. Chronic pain in the ankle area is most often a consequence of failure of any of the ligaments.
Ankle ligaments can be divided into 3 main groups: lateral (outer) group, deltoid ligament (inner group), tibiofibular ligament group.
Anterior talofibular ligament.
It is the most commonly injured ligament of the ankle joint. Plays an important role in limiting anterior displacement of the talus and plantar flexion of the foot. The ligament is located in close proximity to the articular capsule and is often represented by two bundles. The bundles are separated by vascular branches from the peroneal artery.
The anterior talofibular ligament originates from the anterior edge of the fibula 10 mm from its apex. In the neutral position of the foot, it is directed strictly horizontally and is attached to the body of the talus in its proximal part, immediately at the border with the articular surface. The width of the attachment to the talus is 6-10 mm.
With plantar flexion of the foot, the upper bundle of the tendon is loaded; with dorsiflexion, on the contrary, only the lower bundle is loaded.
Ligaments: structure and functions
Ligaments are special formations of dense connective tissue that play an important role in the human musculoskeletal system.
They are located throughout the body, performing a variety of functions and having different tissue structures. So, the ligaments that are located around the joint hold it in place, preventing the bones from moving in the wrong direction and preventing injury. Many ligaments are located in the abdominal cavity, where they intertwine the internal organs, giving them the correct position. They have the ability to slightly stretch, but at the same time retain their rigidity, otherwise the fixation of organs and joints would be too strong.
The tissue of the ligaments is poorly innervated, so a person does not feel them until he receives an injury - a sprain or rupture. The pain is so strong and intense that it is compared to a broken bone. Such injuries are fraught not only with painful sensations: dysfunction of the ligaments leads to instability of the joint, which can easily cause further injury.
The structure of ligaments is very similar to the structure of cartilage: collagen fibers, which are penetrated by a network of elastin. Thus, they combine the characteristics of both types of proteins, they are both strong and elastic. The ligaments that are located in the joints are not monolithic; they are usually divided into bundles. The bundles, depending on the specific purpose, are intertwined into ribbons or braided around the joints from the outside.
Such tapes are located, for example, on the sides of the knee joint; they prevent the lower leg from moving sideways relative to the thigh. The components of the elbow joint are braided with ligaments in a circle; they prevent stretching in length. The skeleton of the hands is almost completely covered with them, because such a multitude of small bones would be difficult to hold with muscle strength and skin alone.
Ligaments do not consist entirely of protein fibers: between the latter there is spongy tissue that provides blood supply, nutrition and innervation. It also contains cells called fibroblasts. Their task is to form new fibers during growth or to replace damaged ones. After injuries, only collagen fibers are formed, so with age, the stiffness of the ligaments increases to the detriment of elasticity.
The attachment of ligaments to the bones is provided by collagen fibers, which fuse with the periosteum, mutually penetrating each other. The periosteum, also called the periosteum, is penetrated by blood vessels and nerves, which makes it possible for additional nutrition. The intergrowth is so strong that damage to the ligament will inevitably cause damage to the periosteum.
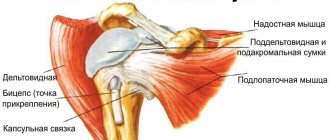
Each joint has its own unique ligament structure. Around large joints that are subject to heavy loads, thickenings are formed, giving strength and rigidity. These formations are called periarticular, although they are also referred to as bursa or capsular ligaments. The load does not fall only on them; each joint is additionally braided with many fibers that are aimed at inhibiting specific movements. They are called external, although they can also pass inside the capsule.
In addition to joints, they are formed in the peritoneum and in other places of the human body: female mammary glands are penetrated by thin threads of collagen fibers that maintain their shape. The ligaments that support internal organs have more elastin than others: during physiological processes, organs can change size and shape, so they need additional elasticity.
Calcaneofibular ligament.
It originates directly below the anterior talofibular ligament. Fibers connecting these ligaments are often found. In neutral, the foot extends downward and slightly posteriorly toward its insertion on the outer surface of the heel bone. The ligament has a circular cross-section, 6-8 mm in diameter, and 20 mm in length. In this case, almost along its entire length, the calcaneofibular ligament is covered by the tendons of the peroneal muscles.
The calcaneofibular ligament is separated from the joint capsule, but has the posterior wall of the synovial sheath of the peroneal muscles covering it almost along its entire length.
In 1/3 of cases, the calcaneofibular ligament is connected to the talocalcaneal ligament. Isolated ruptures of the calcaneofibular ligament are extremely rare. Most often, simultaneous damage to the anterior talofibular and calcaneofibular ligaments occurs.
The calcaneofibular ligament remains tense during both dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot; it relaxes in the valgus position of the foot and is most severely tense in the varus position.
The calcaneofibular ligament assumes an almost vertical position when the foot is dorsiflexed and horizontal when the foot is plantar flexed.
Speech apparatus and defects
The degree of development of the speech apparatus determines the quality of pronunciation of sounds. Diseases of any of the departments are manifested by a deterioration in sound pronunciation and change the characteristics of a person’s voice. The task of speech therapists and doctors when identifying phoniatric symptoms is to identify the causes of their occurrence and select methods to eliminate the defects.
Due to the complexity of the structure of the speech apparatus, there are many possible causes of impaired sound pronunciation. Diagnostic measures should always be comprehensive and selected individually for each person. There are several reasons for the development of speech defects, which occur most often:
- organic disturbances in the structure of individual structures;
- their functional immaturity, which causes incorrect movements during the conversation;
- neurological disorders in those parts of the central and peripheral nervous system that are involved in the formation and formation of sounds.
With these defects, a person often notices problems with breathing, swallowing food and liquids. Such symptoms gradually lead to a decrease in the level of quality of life and can cause impaired adaptation in society, depression and other negative consequences. If you have delayed speech development or other defects, you should always seek professional help from doctors or a speech therapist. Specialists will conduct the necessary examinations and select corrective measures to eliminate the organic or functional defect.
The human vocal apparatus has a complex structure and consists of three main parts: respiratory, vocal and articulatory, or sound-pronouncing. All structural departments act in concert, determining not only a person’s voice, but also the formation and pronunciation of all sounds and words. The regulation of the speech process is carried out by the central nervous system, namely the cerebral cortex, subcortical extrapyramidal systems and the nuclei of the cranial nerves. Knowledge of anatomy allows you to promptly identify changes in the speech organs, primarily located in the oral cavity.
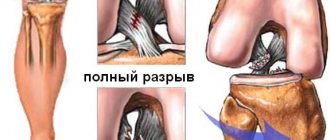
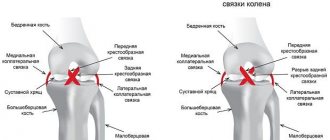
Anatomy of the posterior cruciate ligament.
The PCL is stretched between the medial medial condyle of the femur and the posterior region of the tibia. It is protected by a synovial membrane and, although further from the center, is located inside the knee joint. The main function of the PCL is to stabilize the articular part and prevent displacement of the femur backward relative to the tibia. Damage and rupture of the PCL is a rare but extremely serious injury. It is difficult to damage this element of the joint - as a rule, this happens with a powerful impact - in a traffic accident, during skiing (due to a collision with an obstacle at high speed), as well as in high-speed sports.
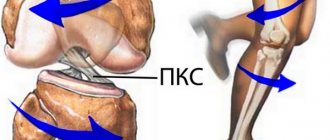
The structure of the ACL.
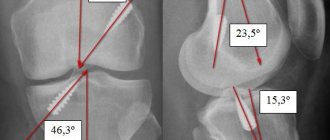
The anterior cruciate ligament starts from the outer edge of the femur, and then extends through the entire knee joint, ending with an attachment to the tibia. It is located in the central part of the knee. With normal development and no abnormalities, it has an anatomical rotation of 110 degrees, and the angle of twist of collagen fibers is about 25 degrees. When a person begins to move and, in particular, extends the joint, the ligament takes on a more vertical position. When the joint bends to an angle of 90 degrees, the position becomes closer to horizontal. The fundamental function of the ACL is to limit the movement of the femur relative to the tibia. Being an important part of the knee joint, it is constantly exposed to serious stress and is one of the elements of the body that is often injured.
The peculiarity of the injury is related precisely to the specific functions of the ligament - due to the prevention of displacement of the tibia during a strong blow/push, damage or rupture of the cruciate ligament may occur. There are cases when an injury occurs when the hip rotates while the foot is in a fixed position. Sometimes such an injury is accompanied by other injuries - for example, a meniscus tear or a PCL injury. If this happens, the dysfunction affects the entire limb, and the lower leg is also injured.
You can read about the features of treatment of anterior cruciate ligament ruptures here - Diagnosis and treatment of anterior cruciate ligament ruptures.
Features of the clinical picture
Experts distinguish three main degrees of severity of joint ligament damage, the type of which determines the characteristics of the clinical picture of the pathological condition:
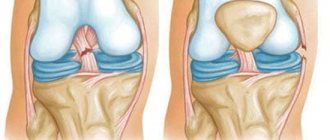
- I degree or mild damage is the occurrence of minimal ruptures of individual fibers with the formation of a small zone of tissue damage. This condition is characterized by pain of moderate intensity and preservation of the ability to move the joint. With a mild degree of ligament rupture, there is no hematoma.
- II degree (medium) or so-called incomplete ligament rupture. In practice, the injury is manifested by the development of severe pain in the area of the affected joint, pronounced swelling of the soft tissues, and a sharp limitation of movements.
- III degree or severe rupture - complete separation of the fibrous elements, which is characterized by sharp, intense pain, severe swelling in the area of the injured joint, hemorrhage with the formation of a hematoma and impaired motor function. In such a joint, when performing movements, a specific click and pain occurs, as well as pathological mobility or instability.
Symptoms of these injuries may vary from patient to patient depending on the characteristics of their body. When a sprain is severe or completely torn, some people have severely limited mobility, while others can move around despite pain. This depends on the pain threshold of a particular person, his hardening and sports training.