- What are the types of ligament ruptures?
- Collateral ligaments
- Cruciate ligaments
- Patellar ligament
- Arthrotherapy for ligament restoration
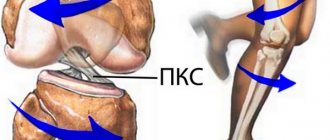
Ligament ruptures are among the most common types of traumatic injuries to the knee joint. In terms of frequency, this injury is in second place, after meniscus tears. Approximately 45% of patients who see an orthopedist or traumatologist for a knee injury are diagnosed with a knee ligament rupture. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is much more commonly injured. Much less often - rear or lateral. While ACL disruption can occur in isolation, rupture of other ligaments is usually associated with other knee injuries.
Clinic of Dr. Glazkov. Treatment of the knee and shoulder joint.
Clinic of Dr. Glazkov.
Treatment of the knee and shoulder joint. Knee ligaments are connective tissue bands whose main function is to strengthen the joint. They are quite strong formations, they have little elasticity.
When exposed to excessive mechanical force aimed at increasing their length, the fibers of the connective tissue cord are stretched. With further exposure to force, micro-tears of the fibers or a violation of the integrity of the entire ligament appear.
This condition is accompanied by a violation of the functional state of the knee joint, as well as an inflammatory reaction. The possibility of restoring damaged anatomical structures of the knee depends on the degree of integrity damage. If the ligaments are torn, their independent restoration without adequate treatment is impossible.
Diagnosis of rupture/damage to the ligamentous apparatus of the fingers in the clinic
Diagnosis of injuries to the ligamentous apparatus of the fingers begins with a simple examination and questioning of the patient. The doctor performs a visual inspection. He determines the type of damage by palpation (palpation of the hand). Additionally, instrumental examination methods are prescribed.
Our doctors have the necessary skills and knowledge for quick and high-quality diagnosis and diagnosis. We can conduct examinations using modern, high-precision, expert-class equipment from the world's leading brands. Diagnosis will take a minimum of time, and the doctor will be able to begin treatment immediately.
Localization of injury
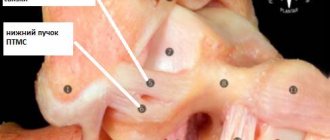
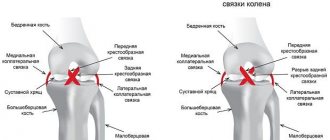
More often, the external or internal lateral (lateral), anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments of the knee are subject to ruptures.
The location of the injury depends on the strength and direction of the excessive mechanical force applied to the knee:
- in a side impact, the lateral ligaments are more often damaged;
- with excessive knee flexion - anterior cruciate;
- with excessive extension - posterior lateral.
The doctor makes the initial conclusion about the extent of the injury and the location of the injury based on questioning the patient about the circumstances of the injury.
What are ligaments
Ligaments are many collagen and elastic fibers of connective tissue. Strength depends on the former, and elasticity and elasticity on the latter. In appearance, the ligament resembles a strong tourniquet or belt. The functions of the ligaments include:
- strengthening bone joints;
- inhibition and direction of movements in the joint;
- support of internal organs in a stable stationary state.
When ligaments are damaged, disturbances of varying degrees and nature are observed. For example, even a minor rupture of the tibiofibular ligaments causes difficulty walking. With more serious injuries, displacement of those internal organs that were held by this ligament is possible.
Causes
The main cause of corresponding knee injury is excessive flexion or extension of the joint, as well as lateral mechanical forces. This injury may more often occur in athletes, especially those involved in contact (wrestling) or active (running, football, hockey) sports.
In everyday life, such a knee injury occurs in the winter season when there is ice, as well as when walking or running on an uneven surface with a sharp turn of the body. This injury also occurs in cases of direct impact with a blunt object to the knee area.
Causes of ligament damage
The most common injuries to the shoulder ligaments occur in athletes. Due to excessive stress on the joints, the strength of the tendons is reduced, which leads to stretching or rupture.
But shoulder ligaments can be damaged not only by playing sports. Injuries also occur in everyday life, in accidents. For example, tears and sprains occur with sudden movements, twisting the arm outward, falling on the upper part of the shoulder or outstretched arm, hitting the front of the shoulder, etc.
But sudden movements of the hands or strong blows do not always lead to damage to the ligaments. In many cases, additional factors that contribute to the weakening of the tendon-muscular system play an important role, for example:
- age - over time, ligaments lose their properties, the likelihood of damage increases;
- osteophytes - growths that affect bone tissue;
- metabolic disorder;
- poor nutrition – due to a lack of vitamins and other nutrients, the condition of the ligaments may worsen;
- excess weight – increases the load on the joints;
- lifestyle - smoking or drinking alcohol can affect the elasticity and firmness of the ligaments;
- the presence of a disease that requires hormonal therapy;
- birth defects, joint abnormalities, etc.
Injuries associated with sprained or torn ligaments of the shoulder joint are a fairly common type of injury, regardless of the patient’s age.
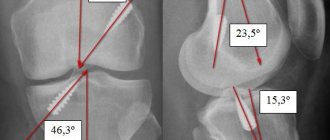
x-ray examination
x-ray examination
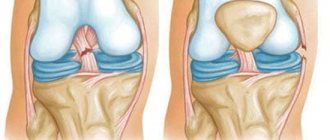
- 1st degree – the integrity of the structures is preserved. Partial rupture of several fibers occurs (this degree of rupture is also called stretching).
- Grade 2 – a more severe rupture with a significant amount of damaged connective tissue fibers. In general, the anatomical relationship of the ligaments and their integrity are preserved.
- Grade 3 – severe injury with complete rupture of one or more ligaments. This severe injury is usually accompanied by damage to the meniscus of the knee or the articular processes of the femur, tibia or fibula.
Dividing the injury into severity levels is possible after an objective diagnosis with visualization of the tissues and structures of the joint.
Degrees of sprain
Typically, the more severe the pain, the more serious the injury. Sprains range from minor to severe.
- Minor - A minor sprain causes the ligament fibers to stretch too far or tear slightly. You may feel tenderness and pain when you touch or move the affected limb. The swelling is minor. Repeated minor sprains can weaken the joint. In most cases, with a minor sprain, the limb can withstand the load and fully recovers within 2 weeks.
- Moderate - When the fibers tear, it means you have a moderate injury. Sensitivity and pain are average. Swelling and bruising may appear on the injured limb.
- Severe - If one or more ligaments are completely torn, the injury is severe. The affected limb is very painful, swollen and bruised. You cannot move or put pressure on the injured joint. When you try to move the joint, you feel it become unstable.
Signs
Symptoms of a knee joint injury with stretching depend on the location and severity of the injury:
- Rupture of the lateral collateral ligament - develops when a person twists his leg and is characterized by severe pain and swelling of the tissues on the outside of the knee.
- Rupture of the internal collateral ligament - severe pain appears on the inner surface of the leg, which intensifies when attempting movements in the knee joint, as well as when palpating (feeling) the area of damage.
- Anterior cruciate ligament rupture occurs when there is a direct mechanical impact (impact) on the front surface of the knee. It is accompanied by instability and pathological joint mobility, tissue swelling, as well as intense pain.
- A posterior cruciate ligament rupture is a rare injury, usually combined with other injuries. It is characterized by pathological mobility of the knee joint, its instability, swelling and pain.
The lack of adequate treatment for such a knee injury leads to the development of complications in the form of arthritis (inflammation) and arthrosis (degenerative changes) of the knee joint.
Diagnosis of sprains
Ligament rupture is characterized by a sharp limitation of joint function and pain on palpation. Upon examination, the doctor detects hemorrhage at the site of injury, swelling and smoothness of the silhouette of the damaged joint. Unlike a fracture, when a ligament is sprained or torn, there is no deformation of the limb. A fracture or serious damage to the ligaments may be suspected if pain and difficulty moving the joint does not go away within 2 to 3 days. The doctor may take an X-ray to rule out a fracture.
If a sprain occurs in a large joint, then damage to the internal ligamentous apparatus may occur, which is expressed in sharp pain, inability to straighten the joint, clicking or crunching in the joint.
Treatment
Once a knee ligament rupture has been diagnosed, comprehensive treatment is prescribed. It includes conservative and surgical approaches.
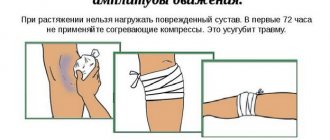
Conservative therapy is carried out using:
- medications (anti-inflammatory drugs, diuretics to reduce swelling, chondroprotectors);
- immobilization (immobilization of the joint);
- mandatory reduction in the functional load on the leg.
For grade 1 damage, only conservative therapy is usually used.
In case of a complete rupture, surgical intervention is prescribed. It is aimed at restoring the anatomical integrity of the joint structures, as well as the subsequent restoration of its functional activity. Surgical treatment is carried out using several techniques:
- Microsurgical reconstruction with suturing of injuries using microinstruments and an endoscope.
- Plastic surgery using autografts - the damaged ligament is replaced with connective tissue fibers taken from other areas of the human body.
- Plastic surgery using an allograft - a synthetic durable material is used for replacement, which has low reactogenicity and does not cause a reaction from the immune system.
The choice of surgical intervention technique depends on the nature and severity of the knee injury or ligament rupture. Treatment must be selected individually for each patient.
Diagnosis of ligament rupture
Although the symptoms of the problem are pronounced, only a doctor can determine the extent of the damage. Treatment directly depends on the severity of the rupture. And successful recovery is only possible in the case of a professionally established diagnosis. In many cases, inspection and palpation are sufficient for this.
In difficult situations, additional examinations are prescribed:
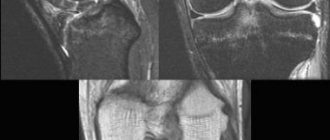
- MRI;
- x-ray of the area;
- Ultrasound.
It is strongly recommended not to self-medicate and not to delay visiting a doctor. If the ligaments, the rupture of which has not been fully healed, are subjected to stress or, even worse, injured again, there is a huge risk of being left with a completely immobilized limb. There are cases where, due to incorrect diagnosis and poor-quality treatment, it was not possible to restore the elasticity and strength of the joint due to a ruptured ligament, which over time brought the patient under the surgeon’s knife. To avoid the need for surgical intervention, you should visit the emergency room or the OSTEO POLY CLINIC as soon as possible, where you will be seen at any convenient time.
Our medical center employs highly qualified practitioners with many years of experience and successful experience in restoring patients after ligament rupture. Call and make an appointment or leave applications on the website.
We have the most modern treatment methods, competent doctors and reasonable prices for services. In addition, our medical center cooperates with many high-tech medical institutions, where you can undergo not only a full examination, but also receive prompt surgical care.
Examination methods
The main examination methods include:
- Ultrasound. An ultrasound examination allows you to assess the condition of the hand and determine the functionality of tendons and ligaments. Examining the hand, the doctor determines damage to the nerve threads, pinching, and small bone fractures that are not visualized on x-rays.
- X-ray examination in frontal and lateral projection. This examination is aimed at clarifying the type of injury. It also allows you to confirm or refute a bone fracture. Also, an x-ray can reveal the degree of injury to hard tissues that are located next to the ligamentous apparatus.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). This survey is accurate and informative. It may be prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
Examination methods are chosen by the doctor.
Injuries and classification
Trauma is the action of a mechanical force that has a different direction. The tissues of the joint, ligaments, and surrounding muscles counteract this force. Depending on the mechanism and force of impact, the following types of injuries are distinguished:
- Open. The skin is damaged.
- Closed. The skin survived, but other structures were damaged.
By type of damage:
- Injury. Soft tissues are damaged.
- Incomplete and complete ligament ruptures, more often called sprains in everyday life.
- Intra-articular fracture. Depending on the fracture line, it may pass through contacting surfaces, be located outside the bone contact areas, or be comminuted.
- Periarticular fracture.
- Dislocation. Often accompanied by damage or stretching of the capsule.
- Fracture-dislocation.
- Meniscus tear. Such an injury occurs only in the knee joint, where there is a special cartilage layer.
Ankle joint
Ankle joint injury is the most common, especially in winter when there is ice, as well as among athletes, skiers and lovers of high-heeled shoes.
Most often, ligaments are torn, followed by fractures. The vulnerable spot is the ankles or lateral processes of the tibia, forming the “fork” of the joint. This joint transfers the full weight of the human body to the foot. Based on the number of broken processes, one-, two- and three-malleolar fractures are distinguished, when the edge of the tibia is also broken.
A fracture may be accompanied by dislocation, subluxation and displacement of fragments. Such fractures are often treated conservatively, but there is a pattern: it takes at least four weeks for one ankle to heal.
You should consult a doctor immediately after a fall, jerk, or joint pain. It is impossible to determine “by eye” what exactly happened in the joint. If a fracture occurs, the strong leg muscles literally “pull” the fragments in different directions, and over time it is very difficult, and sometimes impossible, to reconcile them. What could have been corrected yesterday by applying a splint, today has to be treated surgically.
Traumatologists at the CELT clinic are always ready to quickly come to the rescue. The clinic has unique medical equipment for monitoring the geometry of joints and the position of limbs. You need to understand that a tiny shift in one place inevitably entails changes throughout the entire body. The bones, muscles and ligaments adjacent to the damaged joint adapt to what is there and change too. If you put off visiting a doctor for too long, you can develop arthrosis and many other troubles.