What is this?
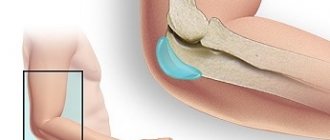
This is an inflammation of the periarticular bursae (from the Latin bursa - bag). Near some joints there are small cavities called bags that allow tissue to glide over the bones. Strictly speaking, the bursae are not directly related to the joints, are not connected to them, but are simply located nearby. From the inside, they are lined with a synovial membrane, which normally secretes a small amount of fluid, which is enough to lubricate and slide the tissues. When such a bursa becomes inflamed, the joint itself is not involved in the process.
Why is heel bursitis dangerous?
The disease causes pain and discomfort when walking
Heel bursitis, treatment of which is not started on time, becomes chronic. This may cause the bursa tissue to thicken, which interferes with the movement of synovial fluid. Chronic inflammation periodically worsens, causing discomfort when walking. Buying new shoes is a serious challenge, since any compression of the heel leads to swelling and pain.
Due to constant pain, a person’s gait changes. Bursitis can cause lameness. Due to disruption of the trophism of synovial fluid, inflammation can spread to small joints.
Purulent and infectious bursitis is especially dangerous. If left untreated, pathogenic microorganisms are carried through the bloodstream throughout the lower extremities, infecting the joints. If an abscess ruptures, the purulent contents enter the general bloodstream, which is potentially dangerous for sepsis.
What could be the reason?
Most often, damage or heavy load is necessary for the disease to develop. Less commonly, the disease is part of a symptom complex of another, more serious pathology. Therefore the main reasons are:
- Trauma (bruise, awkward movement)
- Physical overload
- Friction (for example, constant support on the elbow (with inflammation of the olecranon bursa) or moving on all fours with damage to the patella
- Some rheumatological diseases (gout, ankylosing spondylitis)
Sometimes the cause cannot be determined.
Pathologies
The accumulation of fluid in the joints is a health hazard and can lead to the development of the following pathologies:
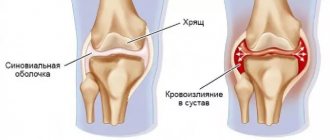
- Hemarthrosis is formed due to damage and blood flow into the joint.
- Arthrosis is the most common pathology and occurs as a result of mechanical damage or age-related changes.
- Arthritis can occur for a variety of reasons, including infections or allergic reactions.
- Synovitis is an inflammatory disease.
- Bursitis can develop due to injury or after an infectious disease.
Symptoms
Symptoms are caused by inflammation - the walls of the periarticular bursa thicken, discharge accumulates in it, sometimes a significant amount, up to 15 - 20 ml. The liquid is usually clear and yellowish in color. In case of injury, it may be stained with blood due to hemorrhage. When an infection occurs, pus accumulates in the cavity.
Complaints and other manifestations of pathology depend on the location of the lesion. The most common are pain, redness of the skin, and swelling.
There are serous and purulent bursitis. In the first case, the inflammation is aseptic (without the participation of microbes) in nature. In this case, the general condition suffers little, body temperature does not rise, local inflammatory phenomena are not pronounced. If the process is purulent, you can almost always find an entry point for infection (trauma, abrasions, microcracks). There is always hyperemia (redness of the skin), swelling, and an increase in body temperature, sometimes to high levels. When diagnosing, it can be difficult to distinguish these two varieties; if there are difficulties, a diagnostic puncture is required.
In this article we will consider serous bursitis as the most common one.
Physiotherapy
Timely treatment will prevent the disease from becoming chronic.
If you notice signs of calcaneal bursitis, the symptoms and treatment of which depend on the form of inflammation, you should begin treatment as soon as possible. In addition to drug therapy, physical therapy plays an important role in treatment, aimed at restoring metabolic processes in the feet. This helps prevent possible complications.
Electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, and UHF are usually prescribed. To restore normal movement of synovial fluid, therapeutic massage is indicated. Such methods can both cure acute calcaneal bursitis and prevent it from becoming chronic.
Bursitis of the knee joint
In the projection of the patella (kneecap), swelling, moderate pain, and less commonly, redness appear. There are several bursae - prepatellar, infrapatellar, etc. Depending on which of them is inflamed, the symptoms may differ in location and severity. With prepatellar bursitis, there is swelling immediately above the patella (photo below), there is practically no swelling, pain, or redness of the skin. In the case of infrapatellar inflammation, on the contrary, pain predominates.
Treating heel bursitis at home
Here are a few folk recipes that will help alleviate the symptoms of the disease:
- Wrapping with raw potatoes, cabbage leaves and beets. For the desired effect, you need to alternate the ingredients, applying them in turn every night for two weeks. Potatoes and beets need to be cut into thin slices, and the cabbage leaf should be mashed a little.
- Dilute one part of finely grated laundry soap and one part of honey in a water bath. Place the mixture on a clean cloth, and add a grated medium onion on top. Apply the compress to the sore area, covering the top with plastic. You need to keep this compress for two hours. The course consists of 10-14 procedures.
- Take about 250 grams of pine cones or twigs. Boil for 30 minutes in three liters of water, then leave for 12 hours. Take foot baths in this decoction for 20-30 minutes for two weeks.
Diagnostics
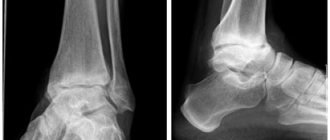
In simple cases, the diagnosis is made on the basis of symptoms; a simple examination by a doctor is sufficient. The easiest way to diagnose the disease is in the area of the elbow and patella. With the shoulder and hip, the situation is more complicated; here, as a rule, additional research methods are needed - ultrasound, X-ray, MRI. Most often, one or less often two of these methods are sufficient to make a correct diagnosis. If it is impossible to differentiate between serous and purulent bursitis, a diagnostic puncture is performed - the cavity is pierced with a needle and syringe. With serous inflammation, a clear yellowish or reddish liquid is obtained, with purulent inflammation, pus is obtained.
Laboratory tests are of little value. If no obvious causative factor is identified (trauma, etc.), then rheumatological tests are prescribed to exclude systemic diseases.
Folk remedies
Compresses and lotions will help relieve swelling
Traditional medicine knows how to treat heel bursitis. Treatment of heel bursitis with folk remedies is carried out using compresses and lotions.
- Regular ice will help relieve swelling and reduce pain during non-infectious inflammation. It should be applied for 5-15 minutes up to four times a day.
- At night it is recommended to apply a compress with propolis ointment. To prepare it, you need to melt 100 g of butter or any other fatty base and slowly dissolve 10 g of fresh propolis in it.
- To reduce inflammation, you can make applications with pine oil. To do this, take 3 tablespoons of olive oil and add 3 drops of pine essential oil to it. Soak a cotton pad in the product and apply it to the heel for half an hour.
Having figured out how to treat heel bursitis at home, you should understand that folk remedies will only be effective in combination with drug therapy. The listed folk methods cannot be used for purulent or infectious bursitis.
Treatment
In most cases it is conservative. Restriction of physical activity is recommended, sometimes immobilization bandages are applied for this purpose. A quick and good result is obtained by puncture of the bursa with evacuation of the contents and administration of a powerful anti-inflammatory drug (see video below). In complex therapy, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Voltaren, Nimesil, etc.), physiotherapy, and kinesiotaping are used. If fluid accumulates again, repeat punctures are performed.
If the disease persists and repeated punctures are ineffective, surgical treatment is indicated - excision of the affected bursa. The intervention is performed under anesthesia in orthopedic hospitals.
With the development of purulent bursitis, surgery is also necessary - the abscess is opened from a small incision under local anesthesia and sanitized with antiseptics. Antibiotics are indicated. Hospitalization is not required; the procedure is performed on an outpatient basis.
Advantages of Dr. Elshansky I.V.
Our clinic, located in the center of Moscow, traditionally deals with bursitis of various types and locations.
Main competitive advantages:
- Doctor with extensive (over 25 years) experience, Ph.D.
- The ability to perform all necessary manipulations immediately, on the day of treatment, incl. ultrasound guided punctures
- If necessary, an ultrasound scan is performed immediately during the appointment and is included in the cost.
- We do not prescribe unnecessary tests and examinations, and if there is still a need for them, we do not require them to be done exclusively in our clinic
- Qualified, polite staff
- No queues - we plan the time and accept appointments strictly by appointment
- Convenient transport accessibility - 5 minutes walk from Turgenevskaya metro station, Chisty Prudy, Sretensky Boulevard
Achilles bursitis
Experts' opinions:
Treatment of bursitis
Video on the topic:
all videos on the topic
What is the disease
The pathology is an inflammatory process involving the synovial bursa in the area of attachment of the calcaneus to the Achilles tendon.
During inflammation, more synovial fluid is released than usual, so a lump forms just above the heel. This lump causes sharp pain when moving, and as the lump grows larger, motor activity decreases.
Types and causes of occurrence
Pathology is diagnosed quite often. Among the possible causes of inflammation, the following should be noted:
- irritation due to mechanical damage,
- wearing narrow shoes that don't fit,
- wearing shoes with hard backs,
- wearing high heels,
- bone deformation,
- high degree of flat feet,
- long-term immobilization of the ankle,
- overweight.
Heel bursitis is often diagnosed in athletes. Due to overstrain of the tendon, the integrity of the synovial bursa is disrupted and the tendons are injured. Achilles bursitis is mainly detected in football or hockey players.
Achilles bursitis can be of several types - serous, purulent, hemorrhagic and fibronous. Heel bursitis progresses faster when infected after mechanical damage. If a pathogen penetrates the synovial bursa, the heel bone becomes inflamed in just a few hours. Basically, this clinical picture is observed in patients with syphilis, gonorrhea and other specific infections.
Symptoms
At first, the patient may not pay attention to the discomfort around the heel, but as the disease progresses, the pain intensifies, which affects the normal rhythm of life.
Achilles bursitis can be suspected based on the following signs:
- motor dysfunction. It is painful to step on the injured leg, sometimes the patient limps,
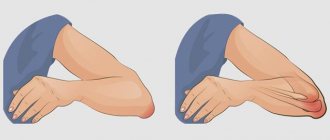
- swelling and redness of the heel. When compared with a healthy limb, the back limb of the lower leg, closer to the heel, swells and thickens. The skin is hyperemic and the soft tissue around the tendon is very swollen,
- throbbing pain below the knees, which is present even at rest and does not decrease after walking. The pain intensifies when you try to stand on your toes or put on high-heeled shoes,
- crunching and clicking noises when moving,
- lameness,
- heat when touching the heel.
Separately, it is worth noting the painful protrusion of an oblong shape. Due to the accumulation of exudate in the bursa, a lump appears from the heel bone to the Achilles tendon. As a result, the patient cannot put on shoes or walk in shoes with backs.
With chronic Achilles bursitis, there are no other signs of the disease other than pain and thickening of the tendon.
Which doctor should I contact for achillobursitis?
Inflammation of the Achilles tendon is treated by an orthopedist. He conducts an examination and examination, establishes the form of the disease, and then selects treatment therapy individually for each patient.
Treatment methods
First of all, all efforts are devoted to stopping inflammation. To do this, the limb is immobilized with a pressure bandage or orthopedic bandage, and the patient is kept in bed, otherwise the symptoms will only increase. As a rule, the swelling decreases and the pain stops after a few days.
Among the medications, the doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers. If the cause of the disease lies in infection, then a puncture of the synovial bursa is performed. The cavity is washed with an antiseptic, filled with a corticosteroid, and then the patient takes antibiotics. At home, the orthopedist recommends making compresses with Dimexide, applying ointments and creams with an anti-inflammatory effect.
When the pain has subsided, inflammation has decreased, and bone and cartilage structures are restored. For this purpose, physiotherapy is prescribed - UVT, paraffin baths, magnetic therapy, ultrasonic waves. It should be noted that the only acceptable procedure at the beginning of the disease is electrophoresis. It is allowed in the acute period. At the discretion of the doctor, procedures are combined or carried out in a course.
Surgery is rarely resorted to. Surgery for Achilles bursitis involves suturing the damaged tendons, removing the contents of the bursa and excision of the bursa itself if necessary.
results
Achilles bursitis responds well to treatment at the initial stage of the disease. It is worth noting that the positive dynamics of treatment increases faster if you follow bed rest and do not wear high-heeled shoes.
Rehabilitation and lifestyle restoration
During the recovery phase, you need to wear comfortable shoes without heels, use heel pads and shock-absorbing orthopedic insoles.
Restorative procedures begin as soon as the pain subsides. They perform passive movements of the limb to strengthen the tendon, and also undergo a course of physical therapy.
Return to list