28.06.2017
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system | Osteoarticular system
Life and movement are inseparable! The human body is provided with everything necessary to perform a wide variety of movements. In fact, all organs and systems are involved in this. But the most obvious representatives of internal and external “movers” are muscles, bones, ligaments and joints.
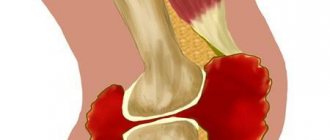
The main characters of today's story are the synovial bursae (“bursae” in Latin) - representatives of the auxiliary apparatus for ensuring movement. Anatomically, these are cavities (in the form of a slit), they are lined with a special membrane, rich in blood vessels and nerves, and filled with the fluid it produces. Both are called “synovial”. They are located in the space between protruding areas of bone and soft tissue, be it muscles, skin or tendons. Hence the principle of their classification: axillary, subcutaneous, subtendinous, subfascial. What are they doing:
- are in charge of metabolic processes in the articular cavity;
- nourish cartilage tissue;
- protect joint tissues from inflammatory damage that begins in neighboring tissues;
- absorb movement in the joints, reducing the impact of its constant companions - pressure and friction, etc.
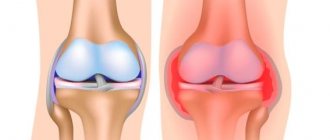
It is not surprising that the maximum number of such “bursae” is located near the most mobile joints - the elbows, shoulders, knees and hips.
Defenders are also vulnerable. Too much physical and/or infectious stress on the bursa can cause damage to it - the so-called. bursitis. In this case, too much liquid is formed inside the bag and its composition changes significantly. This inflammatory fluid is called exudate. Its name and composition vary depending on the nature of the inflammation (serous, purulent, hemorrhagic, etc.).
1.What is bursitis and its causes?
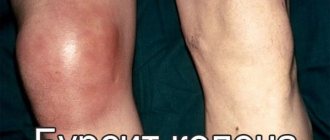
Bursitis is inflammation or irritation of the bursa, a special periarticular “bag” filled with fluid. The bursa is located between the bones, muscles, tendons and skin in the joint area, and its main function is to reduce the friction that occurs during movement.
Causes of bursitis
Bursitis most often occurs due to minor but repeated exposure
to a particular area and as a result of more serious and sudden
injury
. Age also affects the appearance of bursitis. Older people are at higher risk of developing bursitis than younger people. Bursitis most often occurs in adults over 40 years of age.
Overuse, strain and joint injury
During various activities can also increase the risk of developing bursitis. Examples include gardening, shoveling, furniture assembly, painting, and various sports such as tennis, golf, skiing. Incorrect posture, as well as insufficient warm-up before training, are another cause of bursitis.
Additional stress on the bursa occurs due to abnormal position of bones and joints
(for example, with arthritis or due to different lengths of a person's legs), which also increases the likelihood of developing bursitis.
The risk group includes people with inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, psoriatic arthritis, and people with thyroid diseases
.
Inflammation of the bursa sometimes occurs due to infection
.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Causes of bursitis
Damage! Character:
- traumatic;
- infectious.
The first, caused by overload, can be acute and lead to the development of acute inflammation. Or become a consequence of prolonged traumatic exposure and develop into chronic inflammation. Athletes are the first at risk of developing severe or chronic bursitis. It is not for nothing that this nosological form belongs to the so-called. occupational illnesses. Chronic bursitis is often the fate of people with large weights due to the constant increased load on the joints.
Infectious lesions of the bursa are usually secondary to the development of an inflammatory process in nearby or distant tissues. The primary source of infection is often:
- boils and carbuncles;
- felon;
- erysipelas of soft tissues;
- osteomyelitis;
- bedsores.
Pathogens enter the bursa through the blood or lymph flow.
Primary infection of the bursa is possible in the event of direct entry of the pathogen into the cavity of the bursa, for example, due to injury.
Other factors of damage to the joint capsule may include:
- autoimmune processes;
- allergies;
- intoxication;
- endocrine pathologies.
2.What parts of the body does bursitis affect?
Bursitis can develop in different joints. And depending on the location, there are different types of bursitis
:
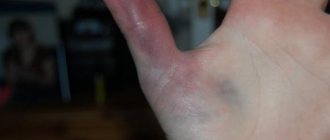
- Elbow bursitis, or bursitis of the elbow joint;
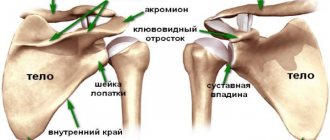
- Shoulder bursitis, or bursitis of the shoulder joint;
- Bursitis of the hip, or bursitis of the hip joint;
- Bursitis of the knee, or knee bursitis, bursitis of the knee joint;
- Bursitis of the calcaneal tendon, or calcaneal bursitis, subcalcaneal bursitis.
Visit our Traumatology and Orthopedics page
Symptoms of synovitis of the wrist joint
Specialists from the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences remind that earlier contact with a medical institution will ensure complete restoration of joint functionality without complex surgical intervention. You can suspect the presence of synovitis based on the following signs:
- Joint mobility is limited and accompanied by pain;
- Signs of inflammation are visible on the projection of the skin - swelling, redness, increased local temperature;
- Malaise;
- Feeling of weakness in the body.
Based on the differential symptoms, the doctor will determine the form and degree of development of the disease. Thus, infectious synovitis is characterized by a sharp and significant increase in body temperature. As the disease becomes chronic, symptoms become less pronounced
4. Treatment of the disease
Elbow bursitis, shoulder bursitis, knee bursitis and other types of bursitis can be treated in different ways:
- First of all, you should avoid those actions that caused bursitis;
- The affected area should be given maximum rest, without stress;
- At the time of injury, you can apply cold to the painful area;
- Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications can be used.
If treating bursitis at home within a week does not produce noticeable results, you need to consult a good doctor.
The doctor may recommend medications
to reduce inflammation. Corticosteroid anti-inflammatory drugs are often used to treat bursitis because they quickly help reduce inflammation and pain. Steroids can be given directly to the injured area as an injection. Often, although not always, this method of treating bursitis is very effective. Sometimes a repeat injection is required. However, multiple injections of steroid medications are generally not used because they may cause side effects. In addition, if such treatment does not work, there may be another problem that frequent injections will not reveal.
Treatment of bursitis with physiotherapy
is another common method. When combined with splinting the thumb, forearm and other areas, it can be very effective. In rare cases, when other treatments for bursitis do not help, surgery may be performed.
Treatment of bursitis of the shoulder, elbow, knee joints
Main vectors of therapy:
- Reducing the load on the joint (immobilization, pain relief).
- Reducing pain.
- Relief of inflammation (compresses, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy; physiotherapeutic procedures).
- Creating conditions for the restoration of affected tissues (nutrition, water regime, physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises).
Surgical intervention (puncture, cryotherapy, laser therapy, bursectomy, etc.) may be required in case of significant damage, prolonged course, or development of complications.
Treatment of synovitis of the wrist joint
If the pathology has a traumatic etiology, the patient is given local therapeutic treatment. The acute form requires observation and treatment in a hospital setting. Purulent synovitis is treated through surgery, including partial or complete excision of the synovial bursa.
Physiotherapy has proven itself well in the treatment of synovitis of the left or right wrist joint. At the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences, as part of physiotherapeutic treatment, patients are prescribed magnetic therapy, laser or ultrasound exposure.
Treatment methods
The exact treatment for bunions depends on several factors:
- severity of symptoms;
- the nature of the inflammatory process;
- the presence of calcifications;
- accompanying illnesses.
If the disease is associated with injuries and is an uncomplicated aseptic inflammation, conservative treatment is used. In the presence of calcifications and other salt deposits, surgical intervention is necessary. Additionally, traditional medicine is used as symptomatic therapy.
The basis of treatment is anti-inflammatory drugs
Conservative treatment
Treatment of any joint diseases begins with symptomatic therapy, which includes the use of drugs of three groups:
- analgesics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- corticosteroids.
Analgesics help relieve pain and improve overall well-being. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to reduce pain and inflammation. They are prescribed both in tablets and in forms for external use.
Corticosteroids are powerful drugs that can quickly stop inflammation. They are injected using a syringe directly into the joint capsule.
During treatment, it is necessary to ensure complete rest of the diseased limb. To do this, you can use special clamps.
For infectious bursitis, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. Usually tablets are used, but in severe forms antibacterial injections may be prescribed.
When the inflammatory process is stopped, the doctor may prescribe physical therapy. Treatment of bursitis of the finger is supplemented with shock wave therapy, laser method and heat. All these methods improve local metabolic processes and accelerate the restoration of joint mobility.
Surgery
Surgeries for bursitis are prescribed only if conservative therapy is ineffective. This is usually practiced in the presence of calcifications or deposits of uric acid salts in the joint capsule. During the operation, all these growths are removed. The joint is then covered with a bandage and a brace is used to limit movement.
When salts are deposited in the joint, conservative therapy helps only temporarily
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine for bursitis is used only as an auxiliary method. The main means of combating inflammation are medications.
In folk medicine, it is proposed to treat bursitis with lotions, compresses and rubbing.
- Apply a little vodka to the sore finger and rub it in with massage movements. Vodka can be used as a compress by soaking gauze in it and fixing it with cling film on your finger. The compress should be left overnight.
- Cabbage leaf with honey will help relieve swelling and inflammation. To do this, you need to stretch the leaf with your fingers until the juice comes out, grease it with honey and fix it on the sore joint, leaving it overnight.
- Another effective remedy is rubbing with vinegar and honey. To prepare the mixture, you need to take 3 parts of honey and 1 part of the bite, apply to the joint, and gently rub in with massage movements. The same mixture can be used as a compress.
- For bursitis, dry heating can be used. To do this, you need to heat salt in a frying pan, pour it into a tight bag and apply it to the sore limb for 10 minutes.
Compresses and heating are used only if there is no purulent inflammation. Before using traditional medicine, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
How to eat with bursitis?
Proper nutrition for bursitis will help get rid of the disease faster. To do this, you need to exclude any fatty foods, milk, and pork from your diet.
For joint inflammation, any spicy foods, spices, or alcohol are prohibited.
The basis of the diet should be fruits and vegetables, dairy products, fish, chicken and veal. Porridge must be limited. It is useful to eat legumes, zucchini, and bell peppers.
If you are prone to the formation of calcifications, you should consult your doctor about which products help remove salts.
Diagnostics
For diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a series of tests and examinations. First, the doctor examines the patient and collects anamnesis. Despite the fact that bursitis is diagnosed by visual examination, additional examinations are necessary to clarify its nature.
The patient will have to take a blood test, which can accurately determine the presence of an inflammatory process. The next step is an X-ray, ultrasound or MRI of the affected joint, which are necessary to clearly visualize the localization of inflammation.
The doctor also performs a puncture to collect synovial fluid. This is done by puncturing the joint capsule with a needle. The liquid is sent for analysis. Studying its composition is necessary to exclude the bacterial nature of inflammation.