Dislocation is an unnatural condition in which a complete displacement of the articular surfaces relative to each other occurs. Bone dislocations in the wrist joint account for less than 5% of the total number of dislocations. These injuries occur in the wrist joint. The wrist joint consists of: on the upper side - the radius and ulna bones, and on the lower side - eight small bones of the hand. Eight of these bones, arranged in two rows, create the wrist. To a greater extent, wrist injuries occur with the lunate and scaphoid bones; dislocations of other bones of the hand are less common.
Treatment
Treatment of wrist injury involves a set of measures to restore the natural position of the bones.
Treatment steps include:
- Reduction of hand bones using local anesthesia or general anesthesia
- Immobilization with application of a plaster cast to ensure immobility and rest of the injured arm (applied for 2-3 weeks)
- If the median nerve is pinched, surgical intervention is possible
- If necessary, the patient is prescribed painkillers
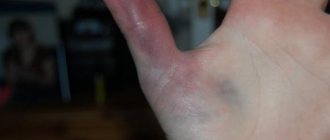
Symptoms of a dislocated finger
A dislocated finger on the hand has characteristic signs:
- sharp pain;
- swelling swelling;
- change in joint shape;
- limitation of movements in the sore finger;
- hyperemia of the skin in the area of the injured joint.
After receiving a dislocation, the patient cannot move his finger, since any movement causes severe pain and increased swelling. The injured area takes on a red tint, while the skin of other parts of the hand may turn pale due to impaired blood flow. Palpation of the hand is sharply painful. The skin of the finger is hot to the touch and quickly turns purple.
Dislocation of the thumb joint can be complete or incomplete, as well as dorsal and palmar. During an injury, severe pain occurs, the finger becomes swollen and deformed at the metacarpophalangeal joint. If a dorsal dislocation occurs, the finger shortens, bends at the metacarpophalangeal joint and extends at the interphalangeal joint. When a palmar dislocation occurs, the finger moves toward the palm.
Both with a dislocation of the thumb and with dislocation of other fingers, the patient requires the help of a traumatologist. At home it is impossible to carry out treatment corresponding to the severity of the damage. The only thing you can do to feel better is to apply dry ice, which will help reduce swelling and dull the pain. All other treatment measures should be carried out by qualified specialists. The first minutes after a dislocation, swelling begins to increase. Therefore, if possible, try to remove all jewelry from the fingers of the damaged hand. Do not hesitate to contact a traumatologist: if the patient is not given first aid, the reduction of the joint will be difficult and may require surgical intervention.
Rehabilitation after dislocations
Immediately after the reduction of any dislocation in the wrist joint, it is necessary to develop the fingers of the hand, and after removing the plaster cast, the entire hand;
Restoring the functionality of the hands includes:
- Physiotherapy (magnetic therapy, ultrasound treatment, inductotherapy, mud therapy, UHF)
- Therapeutic gymnastics (with a recommended set of exercises to develop an injured joint)
- Massage of the fingers; after removing the cast, lymphatic drainage massage is prescribed
- Hydrotherapy
- Vitamin therapy
- The use of wound healing and restorative ointments
Causes of a dislocated finger
The main reason for a dislocated finger is a force that exceeds the ability of the ligaments to stretch. Such injuries are often caused by sudden bending or straightening of the fingers. Damage can occur when falling on an outstretched arm or hitting something hard.
Finger injuries are common among professional athletes who suffer sprains during active training. The joint of the little finger is considered the weakest, which is often damaged even from light blows and falls. Some patients are predisposed to finger dislocations. At risk are elderly people suffering from joint pathologies, as well as patients with a history of repeated limb injuries.
If obvious signs of a dislocated finger appear, you should immediately visit a traumatologist. Only a doctor can assess the extent of damage to the phalanx and promptly realign the joint. In our Clinic, patients can undergo a high-quality examination and, based on its results, receive an individual treatment plan.
What is a sprained ankle
A fairly common injury to the lower extremity is a sprained ankle. The likelihood increases among pensioners, athletes and women who prefer high heels. In most cases, this problem occurs in people in winter, during icy conditions. A telltale sign of a sprained ankle is when the ligaments are damaged and the bone is pushed out of the joint.
The symptoms are as follows:
- the appearance of pain that is localized in the ankle. The pain is constant. Its strengthening occurs with additional loads.
- Swelling appears. It can be noticed immediately after the injury has occurred.
- A hematoma or subcutaneous hemorrhage appears.
- The joint shape is disrupted.
- The presence of a characteristic click that a person hears when a dislocation occurs.
- Mobility of the foot is impaired.
- Local temperatures rise.
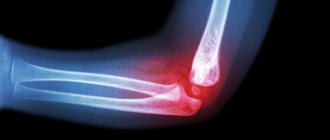
Fresh hand dislocations
For fresh wrist dislocation, anesthesia is used. The reduction is carried out by a surgeon and an assistant, since only two people can correct the hand. An assistant is needed to keep the shoulder immobilized, while the surgeon stretches the wrist joint by stretching along the axis of the forearm. One hand of the specialist should pull one finger of the hand, and the other hand should pull the others.
To correct a dorsal dislocation, the surgeon must apply pressure to the bulging area at the wrist joint using his or her thumbs. Next, fixation at an angle of 40 degrees relative to the neutral position of 90 degrees is relevant. The area from the elbow to the metacarpophalangeal joint is fixed. At the final stage, a control x-ray is performed.
After a couple of weeks, the hand must be removed from the specified position and fixed again with a plaster splint for 2 weeks.
First aid to the victim
Every person should be able to provide assistance to a patient whose arm has been dislocated. The first thing to do is apply a cold compress to the area where the upper limb is injured (this can be a heating pad with ice or cold water) and give a painkiller from the analgesic class.
You should not adjust the arm yourself, as this can cause even more harm to the patient. It is advisable to fix the person’s injured arm in a forced position. To do this, you can use any available means (board, rags, etc.). In this situation, the victim should be taken to the nearest medical facility.
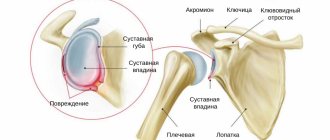
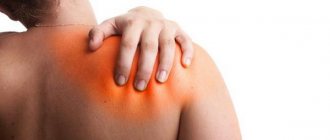
About the symptoms of shoulder dislocation
If this problem happens, and it always happens at the wrong time, the person will feel a sharp pain. The fact is that at this moment the joint capsule ruptures/tears. Nerve endings located inside signal this. In addition to this part, tendons and muscle fibers are also affected.
Interesting fact! According to medical observations, a person who has been injured for the first time feels pain most acutely. Repeated dislocations may be completely asymptomatic.
When a shoulder joint is dislocated, a person cannot move his arm. In this case, all attempts to move the hand will return it to its place. Doctors call this feature “springy resistance syndrome.” In addition, what other signs make it possible to recognize the presence of complexity.
- Among the obvious symptoms is a visual deformation of the shoulders: they look asymmetrical. A protrusion is visible on the dislocated shoulder.
- Swelling appears around the shoulder.
- The hand may become numb, the arm may feel tingling and turn blue.
Now we need to verify the presence of injury at the medical level.
Why does dislocation occur?
The cause of dislocation is indirect trauma, when the injured area is distant from the affected joint. In addition, the appearance of traumatic dislocation is associated with sudden movements that exceed the norm of joint mobility. More rarely, you can find a dislocation that is the result of direct injury to the joint.
It often happens that a person is diagnosed with a dislocation due to a previous illness. This includes the appearance of tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, arthrosis, arthritis, etc. Such joint damage can be either acquired or congenital. The appearance of congenital dislocation is due to the fact that the child’s musculoskeletal system, which develops in the womb, is not formed correctly.
How to recognize a dislocation
Symptoms depend on the type of dislocation a person has. For example, with congenital dislocation of the hip joint, a person’s gait is disrupted, asymmetry of the gluteal folds is observed, and over time, one leg will be shorter compared to the other, resulting in lameness. With bilateral hip dislocation, a duck's gait appears.
With congenital dislocation of the knee joint, a person notices the appearance of severe pain and gait disturbance. In addition, the joint becomes inflamed and immobilized. Traumatic dislocation is characterized by swelling, immobility and pain in the joint.
There are also general signs of dislocation:
- The appearance of redness in the place where the joint is damaged.
- The appearance of severe pain, which intensifies during any movement of the affected limb.
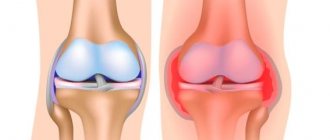
- Visual determination of joint deformity. Dislocation provokes a change in both the size and shape of the joint.
- The appearance of severe swelling in the place where the dislocation occurred.
- If the nerves are damaged, the person will no longer feel the affected limb.
- Motor function is impaired.
- Body temperature rises (changes in heat and chills occur).
Diagnostics
A patient who has sustained a hand injury must be urgently taken to a medical facility, where specialists will diagnose and provide emergency care. The doctor at the trauma center will carefully examine the injured arm, perform palpation, and interview the patient. While palpating the damaged area, the specialist determines not only the sensitivity of the skin, but also the motor function of the upper limb. Careful palpation will reveal any abnormalities in the neurovascular bundle, as well as check the rhythm of the artery pulsating.
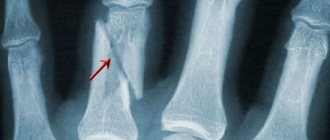
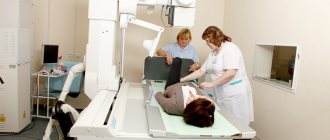
After a personal examination, the patient will be sent for an x-ray, thanks to which it will be possible to determine whether, in addition to the dislocation, there are any other injuries (fracture, bone crack, etc.) of the upper limb. Typically, x-rays are taken in two or three projections, and the results are stored in a medical institution (they must be given to patients upon request).
If, during diagnostic measures, serious injuries to the limbs were identified, the patient is sent to the surgical department, where he will undergo emergency surgery. Sometimes there are cases when patients were diagnosed with dislocation of the same joint more than 3 times. This category of patients requires surgical treatment, after which they will be assigned a disability group. The male half of the population with such a diagnosis will automatically be exempt from the obligation to serve in the Army.
When diagnosing a traumatic dislocation, a specialist during palpation determines how much the shape of the joint has changed. It is equally important to identify whether retraction has occurred at the locations of the articular endings. During palpation, the traumatologist may feel springy resistance in the damaged area.
With traumatic dislocation of the upper limbs, patients may experience:
- tear or complete rupture of tendons;
- extensive capsule rupture;
- compression of nerves;
- rupture of blood vessels, etc.
Causes of injury
The cause of dislocated arms is most often a fall, that is, displacement of the bones in the joint occurs due to the distribution of body weight on them when the limb is bent or straightened.
Other factors can also trigger the occurrence of such an injury:
- improper grip and sudden lifting of large objects;
- incorrect self-massage technique or seeking help from an inexperienced massage therapist.
Very often, the cause of dislocation of the upper limb can be the progression of various pathologies:
- bone tuberculosis;
- arthrosis and arthritis;
- arthropathy and other diseases that change the structure of the joint capsule.
What happens if you don't get treatment?
Fresh, uncomplicated dislocations respond well to treatment. Doctors can easily adjust them. A person wears a cast for several weeks, and after it is removed, he “develops” the affected hand. At the end of the rehabilitation period, the functions of the injured limb are completely restored. Most patients return to their normal lifestyle, including playing sports and performing precise manual work.
If left untreated, displaced bones begin to “overgrow” with connective tissue. After this, it is impossible to return them to their place. Dislocations that previously could be easily reduced using a closed method become irreducible. In this case, the functions of the hand can only be restored through surgery.
Contracture is one of the complications in the absence of correct treatment.
All complicated dislocations require immediate treatment. If left untreated, they can lead to permanent loss of hand function.
Definition and classification
“An effective and affordable remedy for joint pain exists...” ...
In medicine, a dislocation is a violation of the congruence of the articular surfaces of bones due to their displacement. This leads to dysfunction of the joint and a decrease in the range of movements in it. The reason for this phenomenon is incongruence, that is, the shape of the articular surfaces does not correspond to each other.
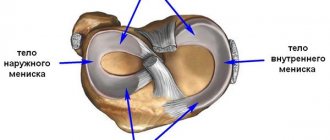
The hand consists of the carpal, metacarpal and phalangeal bones. Any of them can be displaced under the influence of a traumatic factor. Traumatologists distinguish dislocations of the carpal, metacarpal bones and phalanges of the fingers. This article will discuss the displacement of the wrist bones.
Table 1. Types of hand dislocations
| By the nature of the displacement | |
| True | Characterized by complete displacement of the carpal bones relative to the articular surface of the radius |
| Perilunar | It is manifested by a dorso-central displacement of all bones of the wrist, with the exception of the lunate. Often accompanied by various fractures |
| Other dislocations | The wrist consists of 8 small bones. Any of them can be displaced under the influence of traumatic factors. Due to the anatomical features of the structure, dislocation of the bones of the upper row of the wrist (scaphoid, lunate) most often occurs. |
| By prescription | |
| Fresh | We are talking about fresh dislocations if less than 3 days have passed since the injury |
| Stale | Stale displacements are those that occurred a maximum of 2 weeks before going to the hospital. |
| Obsolete | More than two weeks have passed since the injury. Such dislocations are difficult to treat |
| According to the presence of complications | |
| Uncomplicated | Characterized by displacement of the articular surfaces of bones without fractures, rupture of ligaments, tendons, etc. |
| Complicated | Accompanied by damage to nerves, blood vessels, and soft tissues. In some cases, patients are diagnosed with intra-articular fractures of the wrist bones |
| Closed reduction if possible | |
| Reducible | Bone reduction can be successfully accomplished without surgery. All fresh, uncomplicated dislocations are considered reducible. |
| Irreversible | It is impossible to restore the congruence of the articular surfaces using the closed method. In this case, doctors perform surgery. The majority of chronic and complicated dislocations are considered irreducible. |
Consequences of a shoulder dislocation
Some of the main injuries resulting from shoulder dislocation are:
- fracture or Hill-Sachs defect, i.e. a change in the shape of the outer part of the head of the humerus (described by American doctors in 1940: Harold Arthur Hill (1901-1973) and Maurice David Sachs (1909-1987)).
- Bankart injury, i.e. a fracture of the anterior edge of the articular process of the scapula along with damage to the articular labrum.