Your orthopedist
Everything about the musculoskeletal system on one site: Back, Joints, Bones and more
Home › Injuries › Sprain of the hip joint: causes, symptoms and main methods of treatment
When a ligament is sprained, severe pain occurs in any joint. Later, other signs of injury appear. In this article we will answer the question of what is treatment for a hip sprain.
Sprain is caused by a strong load on the ligamentous apparatus
- Causes of injury Risk group
- First aid
Causes of injury
The sprain is caused by a strong load on the ligamentous apparatus. The main sources of injury should be considered:
- a fall;
- involuntary sliding;
- movement on uneven surfaces;
- an incompletely cured injury that has contributed to weakening of the ligaments;
- sudden change in body position;
- a disease that adversely affects muscle tissue and nerve conduction;
- genetic predisposition;
- impaired technique of performing exercises during sports training;
- monotonous movements with load.
Risk group
Children, the elderly and athletes are more susceptible to injury
In children, the bone structure is rather poorly developed; many people who have crossed the sixty-year threshold have a history of osteoporosis. Sports sprains are caused by too much stress on the joint tissues.
Note! Sprains sustained by adults are fraught with complications.
Treatment and rehabilitation period require more time.
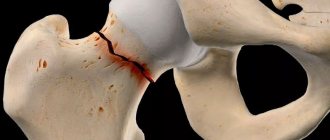
Causes of hip sprain
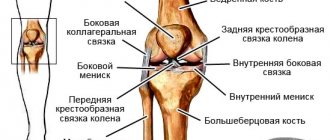
In order to understand the causes of sprains and sprains of the hip joint, you need to understand its anatomy, physiology and structure. So, this is the articulation of two bones: the head of the femur, located on the short neck, and the acetabulum of the pelvic bone. This is a joint in which rotational movements, abduction, adduction, flexion and extension of the lower limb are possible. The joint is located inside the joint capsule filled with synovial fluid. All bone surfaces are lined with cartilage tissue.
The hip joint is surrounded by numerous muscles of the gluteal and femoral region. All muscles have their own attachment points using tendons and fascia. The stability of the bones is ensured by the ligamentous apparatus. Excessive abduction of the leg, sudden flexion or extension, may place excessive physical stress on the muscles, tendons and ligaments. microscopic ruptures occur.
Thus, potential causes of hip sprain include:
- domestic and sports injuries;
- excessive physical activity;
- weightlifting and athletics without preliminary warm-up aimed at warming up and increasing the elasticity of the ligamentous and muscular apparatus in this area;
- passion for sports and outdoor games;
- wearing high-heeled shoes;
- incorrect foot placement when walking;
- valgus and varus deformity of the leg and thigh.
People who are overweight, avoid regular physical activity, and have untrained muscles of the lower extremities are more susceptible to this injury. Deformed posture and bad habits can play a role.
Severity
Tension refers to the destruction of the small fibers that make up the ligamentous tissue.
It can be either partial or complete. The severity of the injury is presented in the table.
Table 1. Main degrees of severity:
| Degree | Description |
| Lightweight | A certain number of individual threads of tissue are destroyed. |
| Average | All tissue connections are severed. Over time, the fibers break and separate from each other. |
| Heavy | The ligament is completely torn and separated from the bone. |
| Particularly heavy | A ligament rupture is accompanied by a piece of bone breaking off. This injury is very rare and is called an avulsion fracture. |
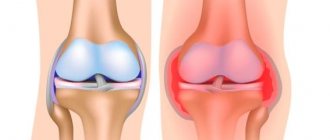
Main signs of injury
The main symptoms are swelling and pain
The following symptoms of hip sprain are identified:
- swelling of the damaged area;
- slight redness;
- painful sensations that are present even when the joint is at rest;
- pain that occurs during movement;
- When the ligaments are torn, deformation of the joint is observed.
Note! The pain syndrome can radiate to the knee and ankle areas.
At the moment of injury, a specific click appears. Severe pain immediately comes. The sensitivity of the tissues at the site of the lesion is impaired.
Severe injury is characterized by disruption of the integrity of blood vessels. Bruising occurs in the femoral area.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment for a hip sprain depends on the extent of the injury. The affected joint is ensured complete immobility. At the second stage of treatment, the patient is prescribed painkillers.
The rehabilitation period involves taking a course of hip joint massage.
First aid
Timely measures taken will help avoid the development of serious complications
The instructions will tell you how to proceed:
- In order to relieve swelling and inflammation, you need to apply an ice compress to the affected area for 10 minutes. After this time, take a break for 30 minutes.
- Secure the joint with an elastic bandage. The bandage should not be very tight.
- Provide complete rest to the hip joint, eliminating any stress.
If severe pain is present, it is allowed to take a medicine that has an analgesic effect.
Painkillers
The table presents the most effective means of relieving pain.
Table 2. Best painkillers:
| A drug | Description |
| NSAIDs. It has a strong analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effect. |
| A combined medicine with analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effects. Helps suppress prostaglandin synthesis. |
| Helps relieve arthralgia at rest and during movement, reduces morning stiffness and swelling of joints, and increases range of motion. |
Ointments for athletes
For people professionally involved in sports, local preparations with analgesic, warming, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects are recommended. The table lists the best joint ointments for athletes.
Table 3. Effective sports ointments:
| A drug | Description |
| A combined product based on bee venom. It has a local irritating effect and helps stimulate peripheral nerve endings. |
| It helps well with post-traumatic inflammatory process that has developed in soft tissues and joints. |
| Has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. |
| Helps reduce pain and inflammation, is effective for painful joint syndrome during movement and at rest, and relieves morning stiffness. |
Medicines for children
In the acute stage, ointments are prescribed that have a strong analgesic effect. The best drugs are listed in the table.
Table 4. Recommended medications for children:
| Medicine | Description |
| An anti-inflammatory pain reliever that helps improve tissue regeneration. |
| A herbal remedy that promotes rapid healing. |
| Dietary supplement based on Siberian larch. It has a vasoregulatory, antioxidant and tonic effect. |
Note! If the injury is severe, the child must be urgently admitted to a hospital.
Complex ointments
Such funds help to increase the effectiveness of complex treatment. The table presents the best ointments.
Table 5. Recommended complex ointments:
| Means | Description |
| A combined medicine that has a local irritant, analgesic and absorbable effect. |
| A powerful analgesic with a local irritant effect. |
| A combined product containing locally irritating components capsacin and camphor. |
Diagnostics
In case of injuries, diagnostic measures are carried out by traumatologists. Degenerative and inflammatory diseases are managed by orthopedists and rheumatologists. In case of purulent processes, the participation of surgeons is necessary. The examination includes collecting complaints, studying the medical history, physical examination, and additional studies. Taking into account the characteristics of the pathological process, the following methods can be used:
- Radiography.
It is a basic technique for most joint diseases. Detects fractures, dislocations, changes in the contours of the acetabulum and femoral head, marginal and intraosseous defects, bone growths, and narrowing of the joint space. - Ultrasound.
Most informative when studying soft tissues. Reveals signs of inflammatory and degenerative processes, areas of calcification. Used to diagnose effusion, articular mice. - MRI and .
Clarifying techniques are used when the data from basic studies are ambiguous, to clarify the nature, prevalence and location of the pathological focus. Can be performed with contrast. - Joint puncture.
Has a diagnostic or therapeutic-diagnostic character. Allows you to remove effusion, study the composition of intra-articular fluid, and determine the causative agent of infection using laboratory tests. - Arthroscopy.
During a visual examination of the joint, the doctor assesses the condition of the bone and soft tissue structures,, if necessary, takes a biopsy for subsequent histological examination, and carries out therapeutic measures. - Lab tests
. Prescribed to determine signs of inflammation and markers of rheumatological diseases, assess the general condition of the body, the activity of various organs in severe infectious or systemic pathologies.
X-ray of the hip joint. Fracture osteosynthesis with internal fixation devices
Folk remedies
Depending on the degree of injury, the use of folk remedies is permitted. The best recipes are presented in the table.
Table 6. Effective recipes:
| Means | How to cook | How to use |
| Mix a small amount with yogurt to achieve a sour cream consistency. Grate 1/2 onion, the same amount of raw potatoes and 100 grams of white cabbage. | Before going off, apply to the affected area and secure. |
| Combine 100 ml of freshly squeezed juice with the same amount of garlic and soak cheesecloth. | The lotion is done during the day. When the pain subsides, the procedure should be stopped. The main contraindication is an allergic reaction to citrus fruits. |
| Mix 30 grams with 1 egg yolk, add 150 ml of warm water, soak gauze with the resulting solution. | The lotion should be applied throughout the day. |
Physiotherapy
Recommended exercises are presented in the table.
Table 7. Exercises for hip joints:
| Exercise | Description | How to perform |
| Stretching the hip joints helps relax the muscles. They become more flexible. | Place your upper limbs on your hips, tense your abdominal muscles and, without bending your back, lean forward. The duration of the pose is 20 seconds, the number of repetitions is 3. |
| Strengthening the anterior hip flexor muscles. | Stand next to a support and raise one of your lower limbs as high as possible. Hold for 2 seconds, then “hit” at a slow pace on an imaginary ball. The number of swings for one leg is 10. |
| Increased flexibility in the hip joint | Sit on the floor, bring your soles together. The feet are pulled closer to the groin. You need to hold this pose for 15 seconds. Number of repetitions - 3. |
If your hip joint hurts after stretching, then the load needs to be reduced. If the pain does not subside, you must notify your doctor. The cost of deviating from this recommendation can be very high.
How to find the cause
Since pain in this joint can have a variety of origins, the doctor will recommend undergoing a diagnosis in several stages:
- Examination by a specialist. The doctor will determine the acute or chronic condition, the presence or absence of inflammation, joint deformation, assess the level of pain and how limited mobility is.
- Plain X-ray of the pelvis. X-ray covers the sacral spine and hip joints at the same time. Using special quantitative criteria, already at this stage it is possible to calculate whether the patient has arthrosis of the hip joint.
- Blood tests for markers of inflammation. Indicated if the doctor suspects the patient has an autoimmune nature of arthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis or other diseases. As a rule, they are prescribed for minimal changes on the radiograph, as well as for people with coxarthrosis under 50 years of age.
- MRI. Using magnetic resonance therapy, it is determined whether the patient has an intervertebral hernia, which can also cause joint pain. This examination is also indicated when other methods have not made it possible to establish the original source of pain.
The younger the patient, the more tests may be needed to find the cause of the pain.