Injuries very often result in sprains, especially in the shoulder and forearm area. The causes of shoulder sprains are trauma. Muscle injuries often occur not only in the shoulder joint, but also in the forearm. The symptoms have their own specificity and it is important to differentiate them from a dislocation or fracture. Afterwards, a full-fledged treatment is prescribed, which returns the person to duty. The diagnosis of sprain has its own code in ICD-10, but it is better to understand everything gradually.
Symptoms
A shoulder sprain can manifest itself in different ways, however, there are symptoms that help determine the truth, not only in the shoulder area, but also in the forearm. At first there is pain, so severe that you cannot touch the joint, it becomes swollen.
Symptoms may include fever, the joint area turns red, and subcutaneous hemorrhages are often observed. How pronounced they are depends on the intensity of the injury. Movements and rotations bring sharp pain, these symptoms are so strong that a fracture or dislocation can be suspected. But simply relying on the symptoms is not enough: both in case of damage to the forearm and the shoulder joint, diagnosis using instrumental methods is important.
Causes of glenohumeral periarthritis
Humeroscapular periarthritis can develop after a shoulder injury, sudden and excessive physical exertion, or forced long-term immobility. Typically, several days pass from the moment of injury or overload before pain and inflammation occur. An acute attack of pain lasts several weeks.
The following diseases can contribute to the development of the pathological process:
- Diabetes;
- Obesity,
- Pathology of internal organs.
In some diseases of the cardiovascular system (myocardial infarction, coronary heart disease, peripheral vascular pathology), blood circulation deteriorates, especially in the left shoulder area, and glenohumeral periarthritis occurs. A common cause of the disease is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, intervertebral hernia. Damaged vertebral discs wear out over time and lose their elastic properties. The distance between them decreases, the vertebrae come closer and pinch the nerve endings. When nerves are pinched, a reflex spasm of blood vessels occurs and blood circulation is disrupted. Inflammation of the shoulder tendons causes pain.
There are several theories that explain the mechanism of development of glenohumeral periarthritis. Muscle overstrain, professional overload, macrotrauma and microtrauma cause reactive inflammation in the tissues located around the joint, and reflex muscle-tonic reactions in the muscles that fix it contribute to the development of the degenerative process. In tissues with poor blood supply, as a result of constant tension and microtrauma, ruptures of individual fibrils are observed, foci of necrosis, hyalinization and calcification of collagen fibers are formed. Local damage to the periarticular tissues in the shoulder area is caused by the fact that the short rotators of the shoulder and the biceps tendon are constantly exposed to high functional load, often under conditions of compression, since the tendons are located in a narrow space.
Diagnostics
After receiving an injury, you need to consult a doctor and tell him not only about all the symptoms, but also about how the injury occurred, because this is important. For a more accurate diagnosis of damage to the shoulder joint or forearm, x-rays are used. This method puts everything in its place, while eliminating damage to the bones. But the technique does not affect soft tissues; they allow the rays to pass through freely.
To determine the condition of the ligamentous apparatus and muscles in the shoulder joint, it is recommended to conduct an MRI. If it is not possible to perform this research method, you can resort to arthroscopy, which, in addition to diagnosis, is also a treatment method. It cannot be done on the joints of the forearm. If complete or partial damage to the ligaments of the joint is established, then surgery simply cannot be avoided; it will be necessary to restore the anatomical integrity of the damaged anatomical formation.
Diagnosis of shoulder ligament lesions
To properly diagnose an injury, a doctor needs to know the symptoms, timing, and circumstances of the injury. For an accurate examination, it is important to establish the nature of the pain in order to determine the extent of ligament damage. The specialist may also ask about past injuries, if any, and methods of treating them.
When examining the patient, the specialist determines:
- presence and degree of edema;
- degree of shoulder mobility;
- intensity of pain.
In order to exclude the presence of dislocations, cracks, fractures and other mechanical damage, the patient may be prescribed an X-ray examination. It is done when the doctor suspects that the shoulder ligaments are injured.
Additional diagnostic methods are usually used:
- arthroscopy – minimal surgical manipulation using special equipment;
- Ultrasound – examination using ultrasonic waves;
- MRI – visualization of a joint using a magnetic field.
Only a specialist can correctly determine the nature and extent of damage to the shoulder ligaments. In addition, the symptoms of their sprains are similar to other possible shoulder injuries, so it can sometimes be difficult to determine what kind of injury the victim suffered.
Treatment
To reduce pain, apply cold immediately after injury. Additionally, it is recommended to take an analgesic tablet and go to see a doctor at an emergency room or hospital. Once a shoulder sprain has been documented, the injury can be treated. This condition does not require surgery, even though the sprain involves a partial rupture of the ligamentous apparatus.
Everything heals relatively quickly, it is important to follow only the doctor’s recommendations.
A traumatologist deals with this problem in the clinic; first it is recommended to give the hand complete rest. This is done using a scarf bandage; it is advisable to apply a plaster cast for such damage in case of severe pain. Additionally, the damage must be treated using physiotherapy. The following procedures are effective in combating the disease:
- UHF;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound with Novocaine or anti-inflammatory ointments;
- diodespeaker.
An anti-inflammatory ointment is prescribed locally, which is chosen at the discretion of the doctor. The choice of ointment in the pharmacy is very large, often you have to select it over a certain period of time. The choice should fall on those ointments that, along with warming, have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
The ointment is complemented by the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Along with the use of ointments, these products can relieve pain in the muscle area and reduce the manifestation of the inflammatory process. Along with NSAIDs, decongestants are prescribed, however, if an ointment copes with the task, then they do not need to be prescribed. NSAIDs should be taken with caution; they are not recommended for people with stomach problems. And the doctor prescribes them for no more than a week, then you need to cancel them.
There should be rest in the muscle area for several days. They complement the treatment of shoulder joint ligaments with folk remedies. Just be sure to take into account that damage can be treated at home with folk remedies, but it is recommended to do this only with the permission of a doctor. Otherwise, a passion for folk remedies can have dire consequences for the body.
To strengthen muscle strength, vitamins are prescribed, especially B vitamins, which are good for nerves. Also antioxidants in the form of vitamins A, E, C, they are found in large quantities in vegetables and fruits. By creating complete rest for the muscles, you will have to forget about sports for a while, especially if the person led an active lifestyle before the injury. The doctor decides how much the patient will have to limit himself based on the dynamics of treatment.
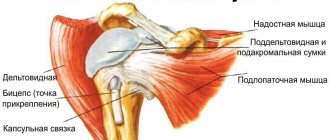
Anatomical structure of a normal shoulder joint.
The shoulder joint is formed by three bones: the head of the humerus, the glenoid cavity of the scapula and the clavicle, which is not anatomically connected to the joint, but significantly influences its function. The head of the humerus corresponds in shape to the glenoid cavity of the scapula, also called the glenoid cavity (from the Latin term cavitas glenoidalis - glenoid cavity). Along the edge of the glenoid cavity of the scapula there is an articular lip - a cartilaginous roller that holds the head of the humerus in the joint.
The strong connective tissue that makes up the shoulder capsule is essentially a system of glenohumeral ligaments that helps the head of the humerus stay in the correct position relative to the glenoid cavity of the scapula. The ligaments are firmly fused with the thin joint capsule. These include the coracobrachial and articular-brachial ligaments (has three bundles: upper, middle and lower). The shoulder joint is also surrounded by powerful muscles and tendons that actively provide stability through their efforts. These include the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis muscles, which form the rotator cuff. Each of these muscles performs its own function: the subscapularis rotates the arm inward, the supraspinatus raises the shoulder and “anchors” it, i.e. presses the head of the humerus into the glenoid cavity of the scapula when the shoulder is abducted to the side. In this case, the main force of abduction is determined by the deltoid muscle, and the supraspinatus muscle works as a commander, directing the efforts of the deltoid muscle. The infraspinatus muscle rotates the shoulder outward, and the teres minor also rotates outward and brings the arm to the body.
All together they function as the rotator cuff of the shoulder.
Recovery
It is impossible to properly treat a sprain without an adequate period of rehabilitation. Physical therapy is used, which is prescribed until the joint moves normally. Swimming and exercises in water are excellent for rehabilitation. Movements should be smooth, pain-free and help strengthen the ligamentous apparatus of the joint.
You need to follow your doctor's recommendations exactly as prescribed. You cannot adopt the experience of neighbors or friends: each person is individual. And a treatment that suits one person will cause a lot of complications for another. In general, the pathology is not that complicated; with normal and timely treatment, everything will go away in about 10 days, leaving no trace behind.
Shoulder ligament rupture in Israel: prices
In the treatment of such a pathology as a ruptured shoulder ligament in Israel, the cost will depend both on the severity of the injury and on the treatment methods adopted.
As you understand, conservative treatment for shoulder ligament rupture is much cheaper than surgical treatment. Arthroscopic joint surgery in Israel costs approximately 8-12 thousand US dollars. This is 20-30% cheaper than in European countries, while the quality of the operation in Top Ichilov is no worse than in the best clinics in Germany or the USA.
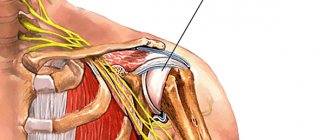
Rotator cuff
The supraspinatus muscle is located highest in the rotator cuff, while its tendon passes in a narrow space between the acromion process of the scapula and the head of the humerus, which determines the tendency for the tendon to be injured.
Rotator cuff: general appearance, tenopathy and entrapment of the rotator cuff tendons in the subacromial space (impingement syndrome)
You can learn more about the anatomy of the rotator cuff and the anatomy of the shoulder joint on our website (click to go to articles about anatomy).
Causes of diseases and injuries of the rotator cuff
The rotator cuff tendons, like all tendons, have a relatively poor blood supply. Insufficient blood supply to the rotator cuff tendons leads to the frequent development of degenerative changes: so-called tenopathy occurs. It is worth noting that the development of tenopathy is promoted not only by insufficient blood supply (a number of scientists generally deny the role of blood supply in the development of tenopathy). Another reason for the development of tenopathy is hereditary pathology of connective tissue. Tendons are mainly composed of a special protein - collagen, which comes in 4 types. With an abnormally high percentage of collagen types 3 and 4, tenopathy develops more often. In general, tenopathy can develop in any of the rotator cuff tendons (and in several tendons at the same time), which can lead to pain in the shoulder joint during movements in which the corresponding muscle is involved. For example, with tenopathy of the supraspinatus tendon, the pain intensifies when moving the arm to the side, with tenopathy of the subscapularis muscle - when bringing a spoon or fork to the mouth, when combing one's hair, or when placing one's hand behind the back. Often these tenopathies are called glenohumeral periarthritis , but this is an absolutely illiterate diagnosis, which was already abandoned throughout the world several decades ago. “Humeral periarthritis,” manifested by pain in the shoulder, may in fact be not only tenopathy of a particular rotator cuff tendon, but also a number of other diseases, which deserves consideration in a separate article. In addition, the development of tenopathy is facilitated by the use of certain antibiotics (fluoroquinolones).
The most common reason contributing to the development of tenopathy is chronic tendon injury, which is possible in two fundamental scenarios:
|
|
Three types of anatomical shape of the acromion process (lateral view). The hook-shaped shape of the acromion process contributes to traumatization of the rotator cuff tendons
With age, degenerative changes in the tendon progress, tenopathy becomes more pronounced, the tendon weakens and rupture may occur. Tendon rupture most often occurs between the ages of 35 and 55 years. However, with a sufficiently severe injury (fractures of the greater tubercle of the humerus, other fractures of the proximal part of the humerus, dislocations in the shoulder joint, etc.), a rupture can occur without previous tenopathy, i.e. in relatively young people.
Complete rupture of the supraspinatus tendon and partial rupture of the subscapularis tendon
Symptoms
As we have already noted, most often rupture of the rotator cuff tendons due to injury occurs against the background of previous degenerative changes (tenopathy). The rupture is characterized by a sharp increase in pain and weakening of the arm, up to the complete inability to move the arm. Ruptures can be partial or complete when the tendon of a particular muscle is completely torn from its attachment to the humerus. The intensity of the pain depends on the size of the tear - as a rule, the larger the tear, the greater the pain, and the greater the limitation of movement. With partial ruptures, the ability to move the arm is preserved.
The location of the pain depends on which rotator cuff tendon is damaged. Most often, the supraspinatus tendon is damaged, which usually manifests itself as a complete inability to abduct the arm to the side (with a complete rupture) or increased pain when abducting the arm to the side in an amplitude of 30 to 60 degrees. Many patients note that they cannot sleep on the side of the sore shoulder joint.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, the doctor will ask you about the mechanism of the injury, how long ago the injury was, the nature of the pain in the shoulder, whether and how long the shoulder hurt before the injury. Let us remind you once again that with significant tenopathy, tendon rupture can occur without any injury at all.
Next, the doctor conducts an examination, during which he performs special tests (moves your arm or asks the patient to make a special movement), during which it is highly likely to find out which tendon is damaged.
As a rule, when a tendon is completely ruptured (or separated from its attachment to the bone), the movement for which this muscle is responsible is impossible.
With partial ruptures, the ability to move the arm is preserved, but movement is painful.
It is necessary to perform an x-ray, in which, in case of ruptures of the rotator cuff tendons, characteristic signs can be detected on the lower surface of the acromion process - the so-called subchondral sclerosis. It is formed as a protective reaction of the bone from repeated impingement of the head of the humerus and the lower surface of the acromion (impingement syndrome), and these impingements lead to damage to the rotator cuff tendons, causing their tenopathy, and ultimately rupture. Of course, the absence of these signs on the x-ray does not mean that the rotator cuff tendons are not damaged, but the presence of these x-ray signs most likely indicates problems with the rotator cuff tendons. It is important to evaluate the acromioclavicular joint on the radiograph: arthritis of this joint can cause similar pain.
X-ray: Impaction of the humeral head (blue arrows) and the inferior surface of the acromion process (red arrows) leads to damage to the supraspinatus tendon running between them.
In case of an unclear diagnosis and in order to clarify the extent of the damage, an ultrasound examination or magnetic resonance imaging is performed, which allows using magnetic waves to see and capture soft tissues and bones in the form of layer-by-layer sections.
Magnetic resonance imaging showing a complete rupture of the supraspinatus tendon
Treatment
Initial treatment
Initial treatment for an acute, recent rotator cuff tear is to relieve pain. As a rule, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used, such as aspirin, Voltaren, Xefocam, etc. Also in the acute period, it is necessary to keep the sore arm at rest - the arm is immobilized in a scarf or on a special abductor splint. Applying ice packs wrapped in a towel to the shoulder is effective in reducing pain and swelling.
Rules for applying a scarf bandage
A special abduction splint used to treat rotator cuff tendon tears. Most often, the supraspinatus tendon is torn from its attachment to the humerus. Immobilizing the arm in abduction position brings the end of the severed tendon closer to its attachment to the humerus. The same abduction splint is also used after operations for rotator cuff tendon ruptures.
Complete rupture of the supraspinatus tendon and partial rupture of the subscapularis tendon. When the arm is moved to the side, the torn ends of the tendon come closer together. The red arrow shows the axis of the humerus. On the left - the shoulder is brought to the body, on the right - the shoulder is abducted to the side.
Conservative therapy
For tenopathies and minor, small tears, when movements in the shoulder joint are preserved, conservative therapy is prescribed. After reducing the pain, light physical exercises are prescribed to develop the joint. In a later period, strength exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles of the upper limb are added to these exercises. This will allow the sore arm to gradually return to its previous range of movements. Typically, the duration of conservative therapy is from 6 to 8 weeks. During this time, pain in the shoulder completely stops, and strength in the arm muscles is partially restored.