Our voice is our main communication tool. Thanks to it, we convey the necessary information to others, we can express our own opinion on a particular issue. For some, the voice has become an integral part of the profession and a means of earning money (for example, for singers or announcers).
But our voice is not always resonant and loud. Like any other human organ or system, our vocal apparatus can malfunction.
The condition when the voice shrinks and becomes hoarse is called dysphonia in medicine. Temporary loss of voice is called aphonia.
A missing or dry voice becomes a real problem for a person, especially if he is a representative of the speech profession.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Why do such problems arise? What treatment will quickly and effectively eliminate them? What preventative measures will help avoid the occurrence of aphonia in the future? You will find answers to these and other questions in our new article.
How does a voice arise?
To understand why voice problems arise, you need to understand the mechanism of its formation. The vocal cords located in the larynx play a major role in the production of voice. They consist of muscle and connective tissue. There is a distance between the ligaments - the glottis. When a person is silent, this gap is wide open; when we speak or shout, it narrows. Sound is produced when air from the lungs passes through the glottis, causing vibrations and oscillations of the vocal cords. In this case, the ligaments must be stretched and closed when air passes through them.
It is logical that if a person’s voice shrinks or disappears, then for some reason the vocal cords are not adjacent to each other. At this moment, a person can only whisper: whispering occurs when the air flow rubs against the walls of the larynx.
Most often, problems with the vocal cords are associated with infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract, but you will be surprised that throat diseases are just the tip of the iceberg.
There are many more real causes of inflammation of the vocal cords, and they are not always associated with the ENT organs.
Secondary joint pain:
Tendinitis
inflammation of the ligaments and tendons of the legs. The joints of the legs are fixed by a large number of ligaments and tendons, so with tendinitis, both the ligaments and the joints themselves hurt. Typically, pain appears when moving and pressing on the tendon, accompanied by redness and increased temperature of the skin. With tendinitis, the strength of the tendons decreases, which causes the mobility of the legs to be impaired, and painful tendon ruptures and joint dislocations can occur.
Diseases of the lumbosacral spine
The sciatic nerve, which is responsible for the sensitivity of the legs, is attached to the sacral spine, so diseases of the sacrum and lower back cause pain in the legs. The appearance and mobility of the joints remain normal, but pain occurs simultaneously in all joints, more intense in the hip and weaker in the joints of the feet. Pain in diseases of the spine is constant, does not subside during rest and intensifies with prolonged sitting. In this case, there are sensations of numbness and “goosebumps” on the skin, coldness of the limb, a feeling of weakness and heaviness in the legs.
Causes of inflammation of the vocal cords
- Infectious diseases of the ENT organs. This is the most common cause of inflammation of the vocal cords. Pharyngitis, tonsillitis, flu, bronchitis, whooping cough, measles, etc. often complicated by damaged vocal cords. That is, in these cases, voice problems are more likely a consequence (symptom), rather than the main disease.
- Laryngitis. The disease is an inflammation of the larynx, affecting the vocal cords. With laryngitis, they noticeably thicken, become flabby, and cannot fully close. Acute laryngitis is most often caused by a viral infection, and less often by bacteria and fungi. In addition to dysphonia, the patient complains of symptoms such as attacks of dry cough, itching in the throat, and a feeling of a lump in the throat. If the inflammatory process in the larynx has become chronic, we talk about chronic laryngitis. This form of the disease can lead to pathological changes in the vocal cords. Chronic laryngitis can occur in three forms - catarrhal, hyperplastic and atrophic. With the catarrhal form, as a rule, symptoms such as dysphonia (hoarseness, hoarseness, change in voice timbre), dry cough during the day, and sputum production in the morning are observed. The hyperplastic form is most often diagnosed in representatives of speech professions, who, due to the nature of their activities, often overstrain their vocal cords. At the same time, they thicken, and small growths form on them - the so-called “singing nodules”. In the atrophic form, thinning of the mucous membranes occurs, which is manifested by persistent cough, discomfort in the throat and loss of voice.
- Hypothermia. Voice problems can occur when the throat is directly exposed to cold temperatures, such as breathing in freezing cold air or drinking ice-cold drinks.
- Overstrain of the vocal cords. Increased stress on the vocal apparatus is experienced by those people who have to speak or sing for a long time and a lot due to the nature of their work. These are singers, announcers, teachers, lecturers, guides, call center operators, etc. In this case, the voice is their working instrument, so quick and high-quality treatment of the vocal cords is a priority issue for them.
- Strong and loud scream. If you scream loudly and heart-rendingly, speak in a raised voice for some time, or sing along with a performer during a concert, you can “break” your voice. And you don’t need to be a professional singer to overstrain your ligaments. By the way, not only representatives of speech professions overexert their voices. If a person works in a factory where equipment is noisy all day long, he has to “shout over” the noise in order to talk to his co-worker. Spend a full working day like this, and hoarseness will certainly appear in the morning.
- Exposure to the mucous membranes of the larynx of chemicals, vapors and compounds. Workers in hazardous industries are susceptible to this impact. Therefore, it is imperative to wear personal protective equipment while working.
- Thermal burns. Sometimes hastily eaten hot food can lead to a burn of the larynx and, accordingly, the appearance of a hoarse voice.
- Chronic diseases of the ENT organs. The presence of a constant source of infection in the body can provoke the spread of infection to the mucous membrane of the larynx, thereby causing its inflammation.
- Allergic reactions. Upon contact with an allergen, the body responds, which is called an allergic reaction. It may manifest itself as swelling of the larynx and the appearance of hoarseness or hoarseness. In especially severe cases, Quincke's edema may occur - severe swelling of the larynx, when the lower respiratory tract is completely blocked, and in the absence of emergency help and treatment, a simple allergy can be fatal. The most common allergens are house dust, pet hair, pollen, medications, seafood, citrus fruits, chocolate and other foods. This item also includes prolonged stay in dusty rooms with polluted air. If you work in such unfavorable conditions, you need to take care of personal protective equipment, such as a respirator mask.
- Neoplasms of the larynx. These can be papillomas, cysts, granulomas, song nodules, cancer, etc. You can suspect the presence of neoplasms if suddenly, for no apparent reason or the presence of other symptoms, your voice begins to disappear or deepen.
- Neurological disorders. Problems with the nervous system can negatively affect any organ, including the larynx. Therefore, some neurological disorders, stress or nervous strain sometimes lead to temporary loss of voice.
- Smoking. Nicotine and other harmful substances contained in cigarettes negatively affect the mucous membrane of the larynx. With frequent and prolonged smoking, the voice acquires a characteristic hoarseness and becomes rough. Very often, such changes in voice become irreversible. The only remedy for treating voice in this case is to stop as early as possible and quit the bad habit.
The presence of so many causes of voice problems makes it very difficult to make an independent diagnosis. For example, it is impossible to determine whether you have tumors in the larynx. Therefore, if hoarseness, hoarseness or loss of voice occurs, it is imperative to consult with an otolaryngologist. Further tactics for treating the disease will be clear after a direct examination and the correct diagnosis.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Symptoms
Most often, pain in the vocal cords is detected in the morning. But it is extremely rare that hoarseness or loss of voice is asymptomatic. In addition to voice problems, depending on the final diagnosis or condition that caused the damage to the ligaments, a person may experience the following symptoms:
- sore and dry throat;
- a sore throat;
- cough;
- hoarseness;
- itching in the larynx;
- itching in the eyes;
- nasal discharge;
- elevated body temperature.
The appearance of at least one of these signs in combination with loss of voice or hoarseness is already enough to make an appointment with an ENT doctor to prescribe effective treatment. When treating a disease, the doctor relies primarily on the results of examining the patient and determining the cause of the pathology.
Once the cause of problems with the vocal apparatus has been established, treatment of the throat can begin.
Synonyms
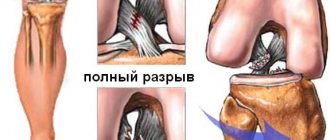
The following synonyms are used to refer to patellar tendinopathy:
- Patellar apex syndrome
- Runner's knee
- Jumper's knee
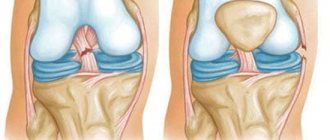
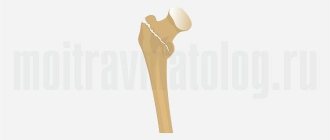
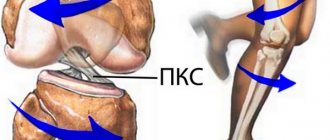
Anatomy of the knee joint
Knee-joint
is a movable connection of three bones: the femur (lat. femur), the tibia (lat. tibia) and the patella (lat. patella).
The powerful quadriceps tendon is attached to the patella from above, and from below it continues in the form of its own patellar ligament, which is attached to the tibia. The main function of the tendon is to transmit force from the extensor muscles to the lower leg, so it is subject to constant stress during sports.
Risk factors and causes
Anatomical factors
- The quality of tendon connective tissue gradually deteriorates with age
- Violation of the axis of the knee joint
- Foot deformities
- Shortening of tendons and muscles
- Structural anomalies, for example, varus/valgus of the knee joints
- Congenital weakness of the ligamentous apparatus
- Osgood-Schlatter disease
External factors
- Inappropriate shoes
- Violation of exercise technique when playing sports
- Walking on hard surfaces such as asphalt
- Excessive training duration
- Unusual stress, for example, starting to play sports too intensely
Sport
- Sports involving frequent jumping - volleyball, basketball, some athletics disciplines, such as long jump and high jump; hence the name "jumper's knee"
- Running – hence the name “runner's knee”1
- Sports involving frequent changes in direction of movement - football, handball
- Sports involving abrupt stops and starts – tennis, squash, badminton
Stages of apical patella syndrome
In a medical diagnosis, the stages of the disease are not usually indicated, but they help to better understand the clinical picture.2
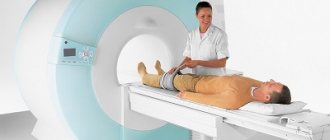
Initially, pain is felt only after playing sports. Subsequently, “starting” pain appears during sports or when performing normal movements, for example, climbing stairs or standing up after a long period of sitting. A long, wave-like presence of symptoms over many months or even years is typical. Periods of mild pain are followed by intense pain after exercise. Two knee joints are affected at once in 20-30% of patients. The examination uses ultrasound examination of blood vessels, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and radiography of the knee joint.
Treatment
Inflammation is usually treated conservatively, without resorting to surgery. Surgery is only necessary if the ligament is torn.
Physiotherapy
With exercises you can train muscles and increase joint mobility. Exercise can speed up the healing process if done regularly. Usually a set of exercises is recommended by the attending physician. Depending on the diagnostic findings, ultrasound therapy, electrotherapy, transverse massage, manual therapy, etc. may be prescribed.
Stretching
Regular muscle stretching exercises reduce tension in the tendon.
Bandages
Specially designed bandages stabilize the knee joint. Bandages with straps, such as Genumedi PSS, are particularly effective because the straps secure the tendon and thereby reduce tension on the tendon fibers.
Cooling
Cold compresses and coolant packs reduce pain (their temperature should be around 7°).
Warm
Warming and massaging with a warm towel improves blood circulation in the area where the tendon attaches.
Drug therapy
If necessary, the doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen or diclofenac, for 1-2 weeks.
Local treatment
Anti-inflammatory ointments and gels can be used topically several times a day. This speeds up recovery.
Insoles
Orthopedic insoles, such as igli Allround, optimize the biomechanics of the knee joint.
Massage
Massage reduces pain. An experienced massage therapist can relax muscles and improve blood circulation in the area of inflammation in several sessions.
Treatment is selected individually in accordance with the clinical picture and the individual needs of the patient.
How to treat vocal cords?
Traditionally, inflammation of the pharynx and larynx is treated by an ENT doctor. If dysphonia is associated with an infectious disease, the treatment regimen may include taking antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal drugs, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agents, lozenges and lozenges for coughs and sore throats, gargling, inhalations and a course of physiotherapeutic treatment. An ENT doctor will also help if voice loss is associated with burns to the larynx or exposure to harmful substances.
A phoniatrist treats strained ligaments. After the examination, the patient will be prescribed a treatment regimen, which, in addition to traditional treatment methods, includes special exercises so that the problem does not recur in the future.
If dysphonia is a consequence of an allergic reaction of the body to an irritant, treatment should be carried out under the supervision of an allergist. Neurological disorders and the consequences of stress are treated by a neurologist and a psychotherapist. If laryngeal tumors were discovered during the examination, further treatment must be continued with an oncologist.
Thus, treatment tactics will depend solely on the cause of dysphonia or aphonia!
Primary joint pain:
Arthritis
The most common joint disease. Arthritis develops against the background of advanced trauma, infectious and autoimmune diseases. There are two subgroups of arthritis: acute and chronic. In acute arthritis, pain in the joints is sharp, accompanied by severe swelling, redness and increased temperature of the joint. In chronic cases, the joint constantly aches, but there is no severe swelling or redness. The patient quickly gets used to it and stops paying attention to the pain until the joint completely collapses. With arthritis, the joints often hurt constantly, and over time, problems with flexion and extension appear.
Arthrosis
Wear and destruction of joint cartilage. With arthrosis, cartilage loses its elasticity, becomes thinner, and metabolism in the cartilage tissue is disrupted. Most often it affects the knee joints. Arthrosis is characterized by aching pain, weaker after sleep and intensifying during the day. The intensity of the pain increases with tension in the leg and pressure on the joint. With advanced arthrosis, the pain does not subside even after rest. Other symptoms of arthrosis are clicking and crunching sounds in the joint.
Bursitis
Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the joints most often occurs as a complication of injuries. Bursitis is characterized by painful swelling due to abnormal enlargement of the joint sac. The pain varies depending on the stage of development of the disease, it can be aching, severe, shooting and throbbing, and can radiate beyond the joint. Often worsens at night.
Prevention
In many ways, the appearance of dysphonia is a signal that somewhere they haven’t looked after something and haven’t taken care of their health. To avoid having to subsequently be treated by an ENT doctor:
- treat infectious diseases in a timely manner;
- do not get too cold, do not breathe through your mouth in the cold and do not drink ice-cold drinks;
- do not shout, do not speak in a raised voice;
- take breaks if you have to talk a lot and for a long time;
- do special exercises recommended by phoniatrists to avoid strain on the vocal apparatus;
- avoid contact with allergens;
- wear masks if you work in unfavorable conditions;
- stop smoking.
If a problem does arise, do not engage in self-diagnosis or self-medication: a timely visit to an ENT doctor will help avoid complications and speed up the recovery process.
At the ENT Clinic of Doctor Zaitsev, consultations are conducted by highly qualified ENT doctors and phoniatrists with extensive practical experience. When the first signs of voice problems appear, please call the following numbers: +7 (926) 384-40-04 and come!
We will be happy to help you!
Treatment of pain in the joints of the legs
If you have pain in your leg joints, do not self-medicate under any circumstances. Due to improper treatment, complications can arise, which are much more difficult to cure than the primary disease. Make an appointment with a neurologist or orthopedic traumatologist. The doctor will listen to complaints, perform palpation, and prescribe additional examinations: ultrasound, MRI, arthroscopy and laboratory tests.
Once the diagnosis is made, the doctor will create a treatment plan. Treatment of joints includes taking various medications: anti-inflammatory, antibiotics, chondroprotectors or hormonal. Almost all patients are prescribed physical therapy and physiotherapy. In advanced cases, prosthetic surgery is performed.