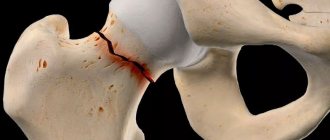
Pertrochanteric femoral fracture
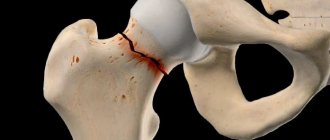
A pertrochanteric femoral fracture is a bone injury of the femur that is localized in its upper third in the area between the base of the femoral neck and the pretrochanteric zone. It occurs during the process of quickly twisting the leg or during a sharp fall to the side, followed by a strong blow to a hard surface.
This damage manifests itself in victims:
- pain of high intensity;
- hemorrhages in the fracture zone;
- inability to move the hip joint;
- pronounced swelling of the thigh.
The injury prevents the patient from moving due to the inability to rely on the limb. It is classified as one of the most dangerous injuries. This injury is treated by traumatologists and orthopedists.
Symptoms
The symptoms are not much different from a violation of the integrity of the femoral neck. With pertrochanteric fractures, pain and swelling are more intense. A hematoma forms, which can spread throughout the thigh. Support on the limb is impossible; light tapping in the area of injury causes sharp pain.
This indicates that the patient has not just a bruise, but a serious injury that requires emergency medical attention.
A characteristic sign is the shortening of the leg and its forced position, in which the foot is turned outward.
Causes of injury
Pertrochanteric femoral neck fractures in young people occur due to excessive mechanical impact on the femur as a result of road or work injuries. In older people, a pertrochanteric fracture of the femur often occurs as a result of everyday falls with a minor traumatic impact. This is explained by increased bone fragility in elderly patients as a result of increased leaching of calcium from bone tissue.
The main predisposing factors for fracture are:
- lack of calcium in bone tissue;
- pregnancy period;
- excess weight;
- road accident;
- unbalanced diet;
- acquired and congenital bone diseases that reduce the strength of bone substance;
- osteoporosis;
- falling onto the side surface of the body with a strong blow;
- twisting of the lower limbs;
- a strong blow to the hip joint with a hard blunt object;
- high-intensity mechanical impact on the bone in the area of the trochanter of the femur;
- decreased strength of bone tissue.
This list contains the most common causes of hip injuries, but other less common factors may also be involved.
IMPORTANT If there is a predisposition, it is important to conduct a bone density test in time to avoid damage.
Caring for patients with a hip fracture
- Content:
- What is a femoral neck fracture?
- Clinical picture
- Causes of fracture and risk groups
- Hygiene procedures and selection of diapers
- Types of femoral neck fractures and first aid
- Fracture treatment and possible complications
- Proper home care for an elderly person with a fracture
- Prevention of complications
What is a hip fracture in older people?
The femoral neck is located in the socket of the hip joint, formed by the pelvic bone. It connects the head and body of the femur. It is surrounded by a reliable sheath of muscles, so a fracture of the femoral neck at a young age is extremely rarely diagnosed.
The risk of this pathological condition increases significantly in old age, when bones become more porous and fragile every year. A femoral neck fracture can be caused by an accidental fall from a small height, in which the greater trochanter is bruised.
The main danger of this injury is that the bone fragment, due to the lack of blood supply due to rupture of blood vessels, can completely resolve over time. This will lead to the fact that the femur will not heal and the person will never stand on his feet again. A hip fracture is confirmed by x-rays and, in some cases, by MRI. This type of injury has clear symptoms and signs that require immediate medical attention.
Clinical picture of a femoral neck fracture in elderly people
A hip fracture in older people cannot go unnoticed. This type of injury to the femur is accompanied by vivid symptoms, forcing you to immediately seek emergency help, namely:
- severe pain in the groin;
- girdling pain around the hip joint of varying intensity;
- inversion of the limb outward, clearly visible along the foot;
- inability to keep the leg hanging straight;
- inability to tear the heel of the injured limb off the surface.
Almost immediately, the specific symptoms of a hip fracture are joined by general signs of severe limb injury - general weakness, dizziness, nausea, pale skin, swelling and bruises.
Causes of hip fracture in older people and risk groups
A fracture of the femoral neck provokes a severe bruise of the greater trochanter in an unsuccessful fall from a height. Elderly people need to be especially careful during icy conditions. The main factors that increase the risk of receiving this serious injury include:
- menopause;
- osteoporosis;
- oncopathology;
- physical inactivity;
- excess weight;
- vegetarianism;
- neurological pathologies in which there is a lack of coordination of movements.
People suffering from diabetes mellitus and other endocrine pathologies are predisposed to hip fracture.
Types of femoral neck fractures and first aid
In modern traumatology, the following types of femoral neck fractures are most often diagnosed in elderly people:
- open;
- closed, with or without offset;
- hammered in;
- pertrochanteric.
All types of hip fractures require emergency medical attention. Before the doctors arrive, it is recommended to place the patient on a flat surface, fix the injured limb with a splint, placing it on the area from the hip to the heel. The patient may only be carried on a hard surface.
Treatment of hip fracture in older people and possible complications
Conservative treatment of a hip fracture in older people is extremely rare, since it does not always have the desired effect. A more common surgical method, which in some situations can literally save a person’s life by restoring his ability to move independently. Elderly people facing this formidable injury are advised to:
- osteosynthesis of the femoral neck, that is, fastening damaged joints with screws;
- hip arthroplasty, which involves complete replacement of the joint.
Surgical treatment will have to be abandoned if the patient has serious concomitant pathologies, for example, a recent myocardial infarction. In this case, the only choice will be conservative therapy, sometimes requiring immobilization of the patient, that is, immobilization of the limbs to save his life.
Both surgical and therapeutic treatment of a hip fracture in older people can be accompanied by complications. Their likelihood increases if medical assistance was not provided immediately. These include:
- bedsores;
- pneumonia;
- amyotrophy;
- thromboembolism;
- urinary tract inflammation and enuresis.
Post-traumatic stress and forced bed rest can lead to a sharp deterioration in health in elderly patients, so it is extremely important to provide them with proper and complete care. It is extremely difficult for untrained people to cope with it on their own.
Medical statistics are disappointing - in more than 50% of elderly patients, death after a hip fracture occurs several months later. Its cause is complications resulting from improper care. To prevent this, the right decision would be to place the patient in a boarding house, where he will be provided with round-the-clock care, regular medical supervision and adequate rehabilitation.
Proper home care for an elderly patient with a hip fracture
If you decide to care for your elderly relative with a hip fracture on your own, get ready for the fact that you will have to radically change your life and routine. People with this injury are completely helpless - the injured joint cannot be bent or unbent.
To care for such a patient at home, you need to properly equip the bed in order to minimally disturb him while performing the necessary actions. An orthopedic mattress should be placed on it to prevent bedsores, and a longitudinal arch with a movable handrail should be installed, on which the patient will lean if necessary, to substitute a bedpan, remake the bed, or change a shirt. Later, the installed arch will be needed to perform physical therapy exercises.
Proper home care for an elderly patient with a hip fracture includes:
- regular massage, during which the patient should be lifted and turned over onto the healthy side;
- massaging the injured leg - foot, leg and thigh muscles, holding it in an elevated state;
- regular replacement of underwear and bed linen, especially if the patient suffers from uncontrolled urination;
- treatment of bedsores when they appear;
- proper nutrition and ensuring optimal drinking regime;
- regular wet cleaning of the room in which it lies and quartzing it.
Psychological support that can be provided to the patient by loved ones, aimed at preventing apathy and falling into a depressive state, is extremely important. In particularly severe cases, you may need the help of a specialist.
Prevention of complications
Proper care for a patient with a hip fracture includes the prevention of complications that can seriously worsen life and even lead to death. These include:
- Severe pain syndrome.
To relieve it, oral and injectable drugs approved for use at home are recommended.
- Urinary incontinence.
This phenomenon with such injuries is most often temporary. During enuresis, it is recommended to use diapers and nappies, which should be changed regularly.
- Bedsores.
To prevent them, the patient must be constantly moved and regularly massage the injured limb, with the exception of the injured area.
- Pulmonary complications.
They are dangerous because when infections occur they turn into pneumonia, which is extremely dangerous in old age. To prevent this, the patient is prescribed drugs to thin the sputum, it is recommended to regularly ventilate the room in which he is lying, and do breathing exercises and chest massage.
After 3.5 months, in the absence of contraindications, the patient is recommended to resume physical activity without putting stress on the injured joint. Initially, you should begin to move your body on the bed, leaning your hands on the arch installed above the bed, then carefully sit down, stand up and gradually move around the room, holding on to the support, and then switch to crutches.
Caring for elderly patients with a hip fracture in a private boarding house in the Leningrad region
Caring for an elderly patient with a hip fracture requires serious time investment - one of the relatives will have to quit their job to do it. A patient with this severe injury cannot be left alone and must be cared for around the clock. This is very difficult to do alone; turning over, pulling up, bathing, changing clothes of a helpless person requires special skills and physical strength.
Not everyone can afford the services of a private nurse, but there is a way out - a private boarding house for the elderly “Vita” in St. Petersburg or the Leningrad region. This is not just a nursing home, but a full-fledged rehabilitation center, where there is everything that is needed to meet the needs of elderly people with a serious injury to the hip joint. At your service:
- bright, spacious and equipped with all necessary rooms;
- polite, friendly and well-trained medical staff;
- comfortable living conditions;
- full nursing care;
- proper and nutritious nutrition;
- carrying out rehabilitation according to an individually designed program, including physical therapy and massage.
Full professional care in a boarding house will provide a patient with a hip fracture with a quick recovery. Your elderly relative will be able to walk and care for himself again. Trust our qualified staff to care for you after a serious injury.
Don't know how to provide quality care for a loved one?
We will help!
8
In the network of boarding houses "Vita" we guarantee you complete care.
We help with transportation to the boarding house.
We offer
- Accommodation in a room for one, two, three or four guests to choose from.
- Dietary balanced nutrition. Only high-quality and fresh products.
- Games, sports, outdoor walks, concerts and much more.
- Monitoring your well-being and taking medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Full medical care and health monitoring 24 hours a day (accompaniment, assistance in eating, carrying out hygiene procedures).
- Providing specialized equipment and technical care.
- Regular change of bed linen, washing of clothes.
- Assistance in carrying out hygiene procedures.
- Optimal price-quality ratio for you and your loved ones.
Classification
In traumatology, there are two classifications of fractures: the classic division of intertrochanteric femoral fractures and Evans. Therefore, the authors divide hip injuries into stable and unstable. A stable fracture is characterized by the ability to compare fragments without surgical intervention. This is possible in the absence of trauma to the cortical bone. Healing of a pertrochanteric femoral fracture without displacement occurs quite quickly. With an unstable fracture, deep damage to the bone occurs with damage to the cortical layer. It is characterized by an oblique passage of the fracture line. Restoring the damage is very difficult. The classic division of this pathology includes seven types of intertrochanteric and pertrochanteric femoral fractures.
The following are distinguished:
- The first type includes pertrochanteric femoral fractures with little or no displacement. The bone fracture occurs outside the joint capsule. The neck-shaft angle is normal or slightly changed.
- Second, these include intertrochanteric non-impacted fractures with significant displacement. Refers to rare injuries of the femur. The neck-shaft angle is significantly changed.
- The third type includes impacted pertrochanteric fractures without pronounced displacement. No displacement of the neck-shaft angle is detected.
- The fourth is an impacted pertrochanteric fracture of the femoral neck with significant displacement. Sometimes it is accompanied by destruction of the greater trochanter of the femur. This type of fracture is quite common. A significant violation of the neck-diaphyseal angle is revealed.
- The fifth type is characterized by a non-impacted closed pertrochanteric fracture of the femur with significant displacement, combined with a violation of the neck-shaft angle.
- The sixth type includes non-impacted pertrochanteric fractures without significant displacement. It is characterized by a helical line of damage with preservation of the configuration of the neck-shaft angle. Damage is common.
- The seventh type is diaphyseal-pertrochanteric fractures with significant displacements with the formation of several fragments. Typically the fracture line is helical. There is no change in the shape of the neck-shaft angle.
Symptoms of a pertrochanteric fracture
The signs of injury resemble those of a femoral neck fracture, but in this case the signs are more pronounced.
When a fracture occurs, the following symptoms are identified:
- high-intensity increasing pain in the hip joint, shooting into the leg;
- with pressure on the heel, the pain increases;
- hematomas and bruises in the thigh area;
- loss of the ability of the lower limb to move;
- with impacted fractures, the leg is turned outward;
- inability to flex and extend the leg at the knee joint;
- shortening of the damaged limb;
- in case of displaced fractures, deformation of the trochanteric region is revealed;
- swelling of the thigh is noted;
- When palpating the damaged area, the pain syndrome intensifies.
When bone fragments rupture the vessels in this area, internal bleeding develops. It can be suspected if the victim becomes pale, cold and sweats. With an open intertrochanteric fracture of the femur in the hip region, severe bleeding and a state of shock are noted. The victim is unable to walk. Loss of consciousness as a result of painful shock is possible.
First aid
If it is possible to call an ambulance to your home, it is better not to disturb the victim - changing the position of the body without fixing the sore leg is fraught with divergence of bone fragments and worsening the health condition. If the patient needs to be transported independently, first you should immobilize the injured leg:
- Apply two splints: one on the outside of the area from the waist to the heel, and the second on the inside from the groin to the foot.
- Using a bandage, secure the pads in the area of the knee joint and lower back.
- To prevent the development of painful shock, give the victim an oral painkiller or inject an anesthetic into the thigh area.
- If you suspect internal bleeding, apply an ice bag to the injured area.
Long boards or metal slats can be used as a splint, which would provide not only fixation, but also simultaneous traction of the limb. The patient must be transported very carefully without unnecessary shaking, as this can lead to fragments breaking off and penetrating into soft tissues.
Diagnostics
To diagnose intertrochanteric fractures, you must contact a specialized medical institution, the traumatology department of a medical institution or an emergency room. The examination is carried out by a traumatologist or surgeon. The doctor interviews the patient about the circumstances of the injury, finds out complaints and medical history. It detects swelling of the thigh, limited mobility in the hip and knee joints on the affected side. Detects bruising in the fracture area and determines the boundaries of the spread of edema.
The following additional types of research are prescribed:
- X-ray of the femur in two projections;
- computed tomography of the hip joint;
- if a hematoma is suspected, an MRI is prescribed.
If there is damage to blood vessels, vascular surgeons are involved in the examination.
First aid
Open and closed pertrochanteric fractures of the femur are life-threatening injuries. Therefore, assistance to the victim should be provided as early as possible. First you need to call an ambulance. Then it is necessary to immobilize the damaged limb. Without this, the victim cannot be transported. If this is ignored, bone fragments damage blood vessels and internal bleeding begins. Soft tissue ruptures occur. To immobilize the injury area, apply a splint to the limb or splints. To make homemade tires, use any hard objects that reach the heel and shoulder (boards, pieces of plywood, etc.). This object is fixed to the side of the entire body, the leg is completely immobilized. The bandages should not be tight and not put pressure on blood vessels and muscles. Cold is applied to the damaged area (a bottle of cold water, ice in a plastic bag). It helps reduce swelling and prevent bleeding.
IMPORTANT Ice should be wrapped in cloth and not applied directly to the skin. This can cause tissue frostbite.
The patient is given painkillers and transported to the hospital. The victim should lie motionless in a comfortable position. When transporting this person, avoid excessive shaking, which provokes displacement of bone fragments.
Treatment
These patients are treated by orthopedic traumatologists. They are necessarily hospitalized in specialized trauma departments of hospitals. This pathology is treated with conservative and surgical methods.
Conservative treatment
Uncomplicated pertrochanteric femoral fractures are treated without surgery. Patients without significant somatic pathology undergo skeletal traction. The staples are attached to the epicondyles of the femur or behind the tuberosity of the tibia. The traction period is on average up to two months. A load of four kilograms is suspended from the rod, then gradually increased to six or more. This depends on the patient’s age, the condition of his musculoskeletal system and the presence of somatic diseases. Traction is carried out under x-ray control and continuous supervision of the attending physician. After the formation of a callus, the patient is put in a cast for an average of three months. He is allowed to walk with the help of crutches.
Pertrochanteric femoral fracture in the elderly
For a pertrochanteric femoral fracture in elderly people with skeletal traction, a lesser load is used than in young people. Its duration is reduced to one and a half months, since a prolonged position in a stationary state increases the likelihood of developing somatic complications (congestive pneumonia, bedsores, muscle atrophy, etc.). The use of a derotation boot helps reduce this period. This plaster cast limits movement in the hip joint. The use of such tactics helps to allow the elderly patient to move earlier and reduces the likelihood of complications. The rate of fusion at this age lasts up to six months. If the elderly need surgical treatment, only gentle techniques are used. During the operation, a small incision is made, and through it the fragments are fixed with one pin.
Recovery after a fracture
Rehabilitation is a very important part of a patient’s recovery, if not the most important one. Since during it the entire course of treatment is consolidated. This is done with the help of special therapy. Rehabilitation takes place over a long period of time. It includes the following procedures:
- exercise to restore hip motor function;
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- a course of medications, which includes taking vitamins, as well as medications containing the required amount of calcium and minerals needed to strengthen the bone structure.
Rehabilitation depends entirely on the patient himself and his desire to recover. If he strictly follows all the rules of the course, takes medications on time and performs all the above-mentioned procedures, recovery will be easy and without any consequences.
Recovery period
The recovery period afterward is often prolonged. Its duration depends on the complexity of the injury, the age of the patient and the condition of the musculoskeletal system. The older the patient, the more time he will need to recover from injury. With conservative management of the patient, the recovery period is extended to eight months. Recovery after surgery for a pertrochanteric hip fracture takes up to four months. At this time, measures are being actively taken to rehabilitate the patient.
Nutrition
To speed up the recovery processes in damaged tissues, you must adhere to a balanced diet. They must be provided with sufficient quantities of the substances necessary for this. The diet of a patient with a fracture should consist of foods rich in proteins, collagen, vitamins and microelements. The daily diet of a person recovering from a fracture should contain at least one and a half grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. The patient's need for antioxidants increases. Vitamins D, C, K, B6 play a special role in this process. The food must contain a sufficient amount of minerals: calcium, copper, phosphorus, silicon, zinc.
The patient’s menu should contain the following products:
- dairy products;
- nuts;
- legumes;
- garden greens;
- hard cheeses;
- vegetables;
- sea fish;
- white poultry meat;
- fruits;
- products made from whole grain flour.
You should avoid drinking coffee, as caffeine leaches calcium from bone tissue. It is necessary to limit sweets, alcoholic drinks, canned food and marinades.
Exercise therapy and massage
The exercise therapy complex is prescribed to the patient by a rehabilitation specialist, and is carried out under the supervision of an experienced instructor. Gymnastics for a pertrochanteric femoral fracture begin immediately after repositioning the fragments. From the third day after the injury, body movements are allowed.
Therapeutic exercise solves the following problems:
- restoration of blood circulation in the injury area;
- preventing complications;
- strengthening the muscles of the pelvis and torso;
- prevention of muscle atrophy;
- restoration of functions of the damaged lower limb.
While the patient is in skeletal traction, exercises are aimed at relaxing the muscles. The patient is allowed to rise on his elbows to prevent bedsores. You can bend and straighten your knees. Flexion and extension of the ankle joints is considered a useful exercise. After removing the patient from skeletal traction and a plaster cast, intense exercises begin to prepare him for walking.
IMPORTANT To start walking fully, you should do gymnastic exercises daily for at least two hours. When patients are allowed to stand on their feet, active rehabilitation begins.
The following movements are performed:
- lying down, bend your leg at the knee joint with your hands;
- while sitting on a stool, move your leg forward and backward;
- leaning on the healthy leg, swing forward and backward with the injured leg, while holding onto the wall;
- also standing and holding the handrails, do flexion and extension of the leg at the hip joint;
- Balance exercises and stepping over barriers are useful;
- performing half squats while holding the handrails.
Prevention
There are no specific measures, except for caution when walking, playing sports and heavy physical labor. Pregnant women and the elderly need to undergo treatment courses to replenish the necessary vitamins and microelements.
The medbooking.com portal provides addresses of public and private medical centers where the best specialists work. On the website you can make an appointment with a specialist doctor, choose a suitable clinic, read customer reviews and prices for services.
Possible complications and their consequences
The most common complication after a pertrochanteric fracture of the femur near the trochanter is incomplete union. In this case, the patient loses the ability to walk and needs outside care. It occurs more often in old age.
The following complications are possible at the site of injury:
- necrosis of the femoral head;
- formation of a false joint;
- development of post-traumatic arthrosis and arthritis;
- formation of subluxation in the hip joint;
- the formation of blood clots in the pelvic veins and blockage of the lumen of the vessel.
In old people, the following complications are possible: shortening of the lower limb, lameness, inability to support the leg.
Systemic complications may develop, especially in old age. They arise due to the patient staying in a stationary position for a long time.
Prolonged immobilization contributes to the following:
- congestive pneumonia;
- development of soft tissue necrosis;
- the occurrence of infectious and inflammatory pathologies;
- increased thrombus formation and a high probability of blood clot detachment (pulmonary artery blockage, stroke).
Prolonged stay in a supine position and the ability to get up contribute to the development of severe depressive disorders.
Isolated trochanteric fractures
A fracture of the greater trochanter most often occurs as a result of a direct mechanism of injury and is characterized by local pain, swelling, and limitation of limb function. Palpation can reveal crepitus and a mobile bone fragment. Then x-rays are taken.
20 ml of 1% procaine solution is injected into the fracture site. The limb is placed on a functional splint with 20° abduction and moderate external rotation.
A fracture of the lesser trochanter is the result of a sharp contraction of the iliopsoas muscle. In this case, swelling and tenderness are found along the inner surface of the thigh, and impaired hip flexion is a “symptom of a stuck heel.” The reliability of the diagnosis is confirmed by an x-ray.
After anesthetizing the fracture site, the limb is placed on a splint in a position of flexion at the knee and hip joints to an angle of 90° and moderate internal rotation. In both cases, disciplinary cuff traction is applied with a load weighing up to 2 kg.
The period of immobilization for isolated trochanteric fractures is 3-4 weeks.
Restoration of working capacity occurs after 4-5 weeks.