The knee joint has a rather complex structure compared to other joints. It is formed by several bones: the upper part is the femur, the lower part is the tibia and the anterior part is the patella (kneecap). It consists of 2 halves (the larger is the inner one), which is ensured by paired bony protrusions and a special arrangement of internal ligaments. What role does the special functional structure of the knee play?
Firstly, such a device is associated with the need to withstand body weight and transferred loads. This is ensured by thick and strong tendons that cover the joint on all sides from the outside, and cruciate ligaments that strengthen it from the inside. Therefore, apart from flexion and extension, other movements in the knee do not normally occur.
Secondly, occupying a central position on the leg, the knee experiences greater motor load. Consequently, the fairly round shape of the joint and the extensibility of the cruciate ligaments (anterior and posterior) provide small rotational movements in it. Since these are the most mobile and fragile formations, they are damaged most often.
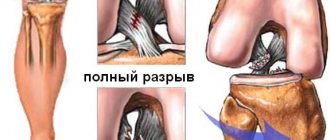
From 70 to 92% of all tendon injuries of the knee joint are complete or partial ruptures of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL).
Causes of anterior cruciate ligament rupture
Most common mechanism of anterior cruciate ligament rupture
is a rotational twist in the knee with a fixed shin, i.e.
twisting at the knee. This situation is not uncommon when playing team sports (football, basketball, etc.). of anterior cruciate ligament rupture
during skiing
is increasing every year Another cause of ACL injury
is a lateral blow to the knee (for example, in football or in a contact sport - karate, judo, other martial arts).
Causes
The anatomical features of the structure of the ACL already predispose to a higher frequency of injuries - it is much longer and thinner than the posterior cruciate ligament. Its function is also affected - to prevent hyperextension of the lower leg. And if bending back is limited by the hip, then the absence of a barrier in front with excessive load leads to frequent stretching and tearing of the ACL. There are 4 mechanisms for the occurrence of rupture.
- With the knee bent, a sharp attempt to straighten is made, but the joint deviates outward. This is most common when lifting heavy objects, such as in weightlifters.
- It appears again with a sharp strain on the ACL, but the lower leg bends and falls onto the knee. It is typical for falling from a small height onto straight legs or while intoxicated.
- As a consequence of excessive extension, it usually occurs when running, when people try to brake sharply.
- Occurs after a strong blow to the front surface of the knee with a heavy object. Typical for work-related injuries and car accidents.
A single rupture of the ACL is a rare occurrence, so its injury is always combined with tears of other ligaments or the internal meniscus.
How does anterior cruciate ligament rupture occur?
Quite common during anterior cruciate ligament rupture
Patients note an audible crunch in the knee, but the torn anterior cruciate ligament does not cause pain as such.
Pain in the knee joint is associated with injury to other intra-articular structures (meniscal tears, intra-articular fractures, etc.), which can be combined with damage to the anterior cruciate ligament.
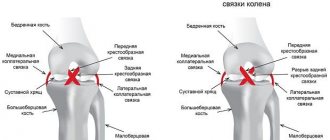
In orthopedic practice, the so-called triad is often encountered: damage to the anterior cruciate ligament + damage to the internal collateral ligament + damage to the medial meniscus.
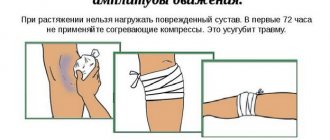
What to do immediately after a knee injury
- Try to adequately assess the situation.
- Do not continue playing sports under any circumstances; this may result in additional trauma to the knee joint.
- Limit movement in the knee joint, do not step on your leg.
- Secure the knee with at least an elastic bandage.
- Cold applications are required: you need to put ice or other frozen product on your knee. Cold applications should be done for 20-30 minutes, several times with an interval of 1 hour.
- Be sure to consult a doctor.
Clinical picture of anterior cruciate ligament rupture
When the anterior cruciate ligament ruptures
An accurate diagnosis will be made only by an experienced orthopedic traumatologist who directly deals with injuries of the knee joint. Sometimes clinics diagnose a normal knee bruise and send you home, which is unacceptable.
The doctor should carefully conduct a clinical examination of the knee joint. The presence of knee swelling and effusion (fluid) in the knee joint must be assessed. Meniscus tests and ligament tests are checked. The Lachman test and the anterior drawer test are used to clinically evaluate anterior cruciate ligament injury.
Signs of an ACL tear
- pain at the time of injury, which intensifies with any movement of the affected leg;
- swelling of the knee;
- the sound of a crack when the ligament ruptures;
- development of limb instability, dislocation of the lower leg;
- development of hemarthrosis (bleeding into the joint cavity);
- bruises, scratches, hemorrhages, cyanosis, redness of the knee;
- increase in local temperature.
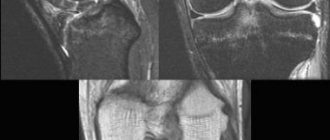
An accurate diagnosis can be established only after examination by a traumatologist and instrumental methods of MRI and ultrasound examination.
Diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament rupture
For any knee injury, an x-ray of the knee joint is required. The anterior cruciate ligament is not visualized on the x-ray; only the bone structures are visible. X-rays are performed only to exclude bone injury (fracture).
Ultrasound is a completely ineffective method for diagnosing anterior cruciate ligament injury
.
The most optimal method for diagnosing anterior cruciate ligament rupture
is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee joint.
Treatment of anterior cruciate ligament rupture
Practice shows that many patients do not immediately consult a doctor, believing that it will “go away on its own.” However, in the future, swelling of the joint persists, pain becomes more intense, and knee instability progresses. In most cases, a visit to a specialist occurs 1-2 months after the injury to the knee joint.
Some patients try conservative treatment, which consists of pumping up the thigh muscles, thereby noting that the knee becomes stable, but this is self-deception.
No matter how pumped up your thigh muscles are, intra-articular instability of the knee joint remains. Unfortunately, the fact remains that the anterior cruciate ligament is torn
does not grow together on its own.
A damaged anterior cruciate ligament
does not perform its functions, and this leads to chronic anterior instability of the knee joint, which, in turn, leads to the appearance of
arthrosis
with constant pain and irreversible destruction of the knee joint.
Surgical treatment is aimed at stabilizing the knee joint and consists of arthroscopic repair of the anterior cruciate ligament,
arthroscopy
of the knee joint
.
Why is damage dangerous?
The cruciate ligament is an important stabilizing element that ensures the functioning of the knee joint; they are located in its central part and are the axis of rotation. It is the two crossed ligaments that ensure the absence of excessive displacement of the articular structures along the surface of the tibia plateau. They also support the physiological movement of the knee joint.
Note! Damage occurs by tearing away from the place of attachment to the bone, in some cases together with a bone fragment. Injury can also be caused by rupture (full/partial option is possible).
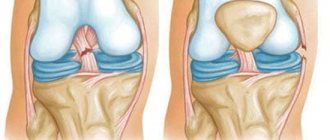
The main danger in case of injury is disruption of the stability of the knee joint. As a result of the resulting instability, the structures of the knee are displaced, which leads to dysfunction of movement and a sharp limitation of the range of motion in the joints of the lower limb.
Due to the rupture, the functional elements of the knee are greatly overloaded. Statistics provide the following data:
70% of cases of ACL injury lead to meniscus injury. 64% of all cases of meniscus injury occur precisely at the moment of ligament rupture. This type of injury occurs more often in women than in men.
The following facts are interesting:
Rupture, sprain and other injuries - these pathological changes are often observed in athletes. Treatment can be conservative or surgical. Surgery is often used as an emergency procedure when a sports injury occurs. The structure of the ACL is restored not by stitching the tear, but by plastic surgery using fragments of other tendons and ligaments. During postoperative rehabilitation, special exercises are used.
Arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament repair
Arthroscopic reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament
- a high-tech operation.
During the operation, an arthroscopic diagnosis of the knee joint
to assess the condition
of the anterior cruciate ligament
.
The most common finding is a separation of the anterior cruciate ligament
from the femur.
Along with diagnosing the anterior cruciate ligament,
a thorough examination of the entire joint is carried out and the condition of the menisci, posterior cruciate ligament, articular cartilage, etc. is assessed.
With a confirmed rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament
proceed to the second stage of the operation - direct
plastic surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament
.
Since it is impossible to stitch the damaged ligament, reconstructive surgery on the anterior cruciate ligament
, i.e. essentially creating a new anterior cruciate ligament.
For this purpose, anterior cruciate ligament grafts are used. There are autografts (from your own tissues) and allografts (synthetic). Today, autografts are preferred in arthroscopic surgery. There are several types of autografts: from the patellar ligament (BTB), from the quadriceps tendon, from the popliteus and gracilis tendons (HAMSTRING). In their practice, GUTA CLINIC specialists give preference to an ACL autograft from the tendons of the popliteus and gracilis muscles, since this graft meets all the strength characteristics of the ligament, various fixation options are possible, and this is the least traumatic method of reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament
.
After harvesting the graft, using special guides, canals are formed in the tibia and femur. A new ligament is passed through the created bone channels and fixed. For fixation we use various designs: ENDO-BUTTON, RIGID-FIX system, BIO-INTRAFIX system, BIO-RCI interference screws.
, arthroscopic control of the isometricity of the new ligament is mandatory.
. The duration of the operation is 1.5-2 hours, the operation ends with drainage of the knee joint (vacuum drainage system "Redon" (B.BRAUN)), a cosmetic suture is applied to the postoperative wounds.
For the purpose of thromboprophylaxis, we must fix the lower extremities either with elastic bandages, or use postoperative compression stockings. We fix the operated knee with an orthosis (splint). Walking is allowed only with the help of crutches without putting any weight on the operated leg.
The hospital stay at the clinic is 2 days. Inpatient treatment is carried out under the round-the-clock dynamic supervision of orthopedists, resuscitators, and therapists and consists of antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anticoagulation and symptomatic therapy. Further observation and treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis.
Recommendations for the patient after arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament repair
- Walking without putting weight on the leg with the help of crutches – up to 5 days after surgery.
- Dosed load on the leg with support on crutches - from 5 days.
- up to 3 weeks after surgery.
- Full weight bearing on the leg (without crutches) – 3 weeks after surgery.
- Fixation of the knee joint with an orthosis (splint) - 2 weeks after surgery, later - development of movements in the knee joint.
- Antibacterial therapy.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy.
- For pain syndrome - analgesics.
- In order to prevent thromboembolic complications - elastic bandaging of the lower extremities or the use of postoperative compression + anticoagulants.
- Cold applications on the knee (to reduce swelling of the knee).
- Dressings: 2-3 dressings will be required (you need to go to the clinic).
- Sutures are removed 14 days after surgery.
- 3 weeks after the operation - active rehabilitation: restoration of full movements in the knee and hypotrophy of the hip muscles (rehabilitation at home (ORTHORENT) or in a rehabilitation center is possible).
- Start of sports activities (running) – 3 months after surgery.
- Sports without restrictions – 5-6 months after arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament repair.
Treatment
Depending on whether the gap was complete or partial, different methods of therapy are chosen. If a tear occurs, only conservative treatment and short rehabilitation are performed. If the ACL is completely damaged, urgent surgery is necessary, followed by a long recovery.
Conservative methods
Cruciate ligaments, due to their structure, have little ability to recover. This is due to the stretching of the ends of the tendon after the tear, and since they do not touch, scar tissue does not form between them. Damage to the synovial membrane, the main source of power for the ACL, plays a significant role. Therefore, surgery can only be done if it is partially damaged. Treatment options:
- Adequate pain relief is provided using analgesic injections or novocaine blockades. By relaxing tense muscles, the cruciate ligaments stop stretching.
- An ice pack wrapped in a towel or a bandage with chloroethyl is applied to the knee joint area. The cold is left for 2 hours, after which a break of 30 minutes is taken and then repeated. The positive effect is to reduce swelling and the amount of hemorrhage in the joint capsule.
- A fixed position of the limb is created (in an extended position) using a plaster cast up to the inguinal fold. The plaster can be removed after 2 weeks.
- Joint punctures are performed to remove excess fluid and blood clots from its cavity.
- Tissue repair stimulants (aflutop, actovegin, solcoseryl, chondroitin with glucosamine) are used in the form of injections or tablets.
All of these methods are combined with an early start of rehabilitation, good nutrition and vitamin therapy.
Surgical methods
To carry out the operation, there must be clear indications. They are divided into two main groups: for the period after injury and long-term. Immediately after damage, the operation is performed in the following cases:
- Complete rupture of the tendon at the point of attachment to the bone site.
- Absolute immobility in the joint and the ineffectiveness of other treatment methods.
In the long term, surgery is resorted to in cases of severe instability and pain in the knee, which are accompanied by periodic inflammation.
The surgical intervention is plastic, that is, it is aimed at restoring the damaged cruciate ligament. Its essence is to remove the remains and replace the ACL with an artificial tendon. At the site of its attachment, holes are made in the bone and the “renewed” ligament is secured with screws.
After the operation, a fixed position for the knee joint is created with an orthosis with a hinge or a plaster cast for up to 6 weeks. Currently, most of these interventions are done arthroscopically, that is, through small holes. This greatly simplifies patient care and reduces recovery time.