The cartilaginous joints of the bones are covered with a synovial membrane, which provides protection and reliable “grip”. It also secretes synovial fluid, which performs 2 important tasks:
- provides nutrition that maintains cartilage in working condition;
- serves as a lubricant between cartilages to reduce friction.
Osteoarthritis affects the cells that produce the main element of synovial fluid - glucosamine. Due to lack of nutrition, cartilage loses its elasticity and cracks. The distance between them at the ends of the bones (articular space) decreases, and the lack of lubrication increases friction and accelerates the process of thinning of the cartilage tissue. As a result, the joint loses functionality. All these changes lead to pain, and then to the inability to move normally.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis (osteoarthritis)
The difficulty of timely diagnosis of the disease lies in the fact that in the early stages patients practically do not notice any deviations from the norm. There is no pain (or it is mild), movements are not constrained. You can find out about the development of osteoarthritis from the results of an x-ray or ultrasound. The cartilage begins to lose its smoothness, and bone growths appear.
The first symptoms of osteoarthritis for which you should consult a specialist are:
- Pain when moving or even just trying to perform any action;
- Limitation of mobility in the first time after sleep;
- Painful sensations when touching the joint.
Another option is possible: in some patients, pain appears immediately in the early stages of the disease. This is due to the inflammatory process in the joint. Broken pieces of destroyed cartilage irritate the joint lining, causing inflammation. This process does not go unnoticed and interferes with movement. Particularly severe pain occurs at night, closer to the morning.
As the disease progresses, osteoarthritis increasingly affects cartilage tissue. To compensate for the damage, the body tries to expand the surface of the joint, which is why bone spurs appear. At this stage, discomfort increases significantly. Every movement becomes difficult and painful. The joints cannot cope with the load, and bone growths only aggravate the situation, reducing mobility.
Ultimately, the disease leads to complete loss of joint functionality. The cartilage tissue is destroyed, the friction between the bones becomes maximum. In fact, a person loses the ability to move. In addition, the muscles next to the joint become damaged and lose their ability to contract (muscle atrophy).
Common symptoms of osteoarthritis are:
- Pain in the joint (when moving, at night, when trying to move - “starting pain”);
- Reduced mobility (heaviness when performing actions, restrictions due to acute pain);
- Characteristic crunching sound during movements;
- Stiffness or stiffness (in the morning);
- Loss of mobility (last stage of the disease).
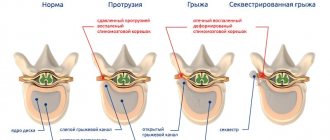
Osteochondrosis and uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine
Cervical osteochondrosis causes arthrosis over a long period of time without appropriate treatment. The gradual destruction of intervertebral discs leads to deformation of small joints. The process of bone tissue deformation begins. Growing osteophytes provoke the development of an inflammatory process.
Gradually developing arthrosis aggravates the course of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, and the rapid development of protrusion begins. There is a high probability of contractures and ankylosis if mobility is impaired. This will entail the formation of withers, hump, and other types of curvature of the spinal column.
Osteochondrosis and uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine in young patients causes serious pain, stiffness and crunching when moving. What is noteworthy is that with age this pathology does not give a clear clinical picture. Thus, in patients over the age of 40 years, osteochondrosis and uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine do not cause severe pain, the amplitude of mobility decreases, but this does not bother the patient much. A compensatory curvature of the spinal column occurs, posture changes, stooping appears and a sharp limitation in the mobility of the cervical spine appears.
Long-term osteochondrosis and arthrosis of the cervical spine inevitably lead to the formation of posterior vertebral artery syndrome. Blood pressure increases, visual and hearing acuity decreases, and prerequisites for cerebral circulation disorders and the development of stroke in the posterior lobes may develop.
Causes of osteoarthritis (osteoarthritis)
There is no specific cause of osteoarthritis. Most often, a combination of various factors leads to the disease. However, there are certain risk groups that are most susceptible to this disease. The likelihood of developing osteoarthritis increases in the presence of the following circumstances:
1. Aging. With age, all mechanisms of the body begin to lose their power. Most patients with osteoarthritis are people over 40 years of age. Age is not a necessary factor for the onset of arthrosis, but the presence of additional provocateurs increases the risk.
2. Injuries. One of the common causes of the disease. Bruises, fractures, and dislocations do not lead to the immediate appearance of osteoarthritis, but weaken the joint, which causes the development of the disease in the future.
3. Regular increased load. Heavy physical labor leads to microtrauma of the joint. For example, football players develop arthrosis of the knee joint, and boxers develop arthrosis of the wrist.
4. Concomitant diseases. Any disease weakens the body. Osteoarthritis often affects people who are overweight, diabetes, and varicose veins.
5. Climax. During menopause, the production of important hormones that can protect the body decreases. This is a combination of two factors: age and weakened immunity. As a result, women get sick more often than men.
6. Flat feet. Flattening of the arches of the feet interferes with shock absorption when walking. The load from the foot is transferred to the knee joint, as a result of which arthrosis of the knee joint can develop.
7. Congenital abnormalities. Some congenital anomalies (connective tissue dysplasia, dislocations, scoliosis) significantly increase the likelihood of osteoarthritis. But with timely and correct treatment, the disease will not appear.
A general definition of the cause of osteoarthritis is a discrepancy between the load and the body’s capabilities.
Treatment of osteochondrosis and arthrosis
Conservative methods of treatment are mainly used to treat osteochondrosis and arthrosis. Pharmacological drugs without additional methods of manual therapy do not have any therapeutic effect. This is due to the fact that the development of osteochondrosis and arthrosis is based on a violation of the diffuse nutrition of cartilage tissue. Accordingly, the liquid and the medicinal substances dissolved in it do not penetrate the damaged cartilage tissue. With the use of manual therapy techniques, regeneration processes are launched and the use of chondroprotectors becomes effective.
In our manual therapy clinic, the following techniques are used for the complex treatment of osteochondrosis and arthrosis:
- traction traction of the spinal column allows you to eliminate compression, restore intervertebral spaces to physiological height, and relieve pain;
- reflexology (acupuncture, pharmacopuncture) – relieve pain, start the process of restoration of damaged tissues, increase the overall tone of the human body;
- kinesiotherapy and therapeutic exercises trigger the process of impaired diffuse nutrition and increase the performance of the muscular frame of the back;
- osteopathy and massage restore microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid, improve the elasticity of tissues (cartilage, tendon, ligament and muscle);
- laser exposure allows you to quickly restore the damaged structure of bone and cartilage tissue;
- Physiotherapy allows you to quickly restore the health of the spinal column.
If you need to undergo an effective and safe course of treatment for osteochondrosis and arthrosis, you can make a free appointment with a vertebrologist in our manual therapy clinic. During the consultation, the doctor will tell you about all the possibilities and prospects for using manual therapy methods in your individual case.
Gonarthrosis (arthrosis of the knee joint)
Despite the commonality of symptoms, the consequences of the disease vary depending on the location of the lesion. Therefore, let us dwell in more detail on the types of arthrosis.
One of the most common forms of arthrosis. The knee joint is under attack. Most often the disease manifests itself after 45 years. Additional provocateurs are excess weight, injuries or bruises.
The risk group also includes athletes: football players, track and field athletes, weightlifters, etc. At the same time, according to statistics, more women fall ill. The disease can affect both legs or one. In this case, painful sensations may appear only on one leg.
What is the diagnosis of joint osteoarthritis and which doctor is best to consult?
A rheumatologist diagnoses and treats diseases of the musculoskeletal system. To seek advice and receive a referral for treatment, you must first of all see a therapist who will conduct an examination, collect anamnesis and make the best decision on further actions.
Before starting treatment, each patient who seeks professional medical help with characteristic symptoms is sent for a comprehensive diagnostic examination, which involves the following stages:
- passing laboratory tests - conducting a general biochemical analysis allows you to get a fairly detailed picture of the existing disease and makes it possible to assess the level of substances contained, as well as the beginning of the development of pathological processes;
- X-ray examination - X-ray examination allows you to obtain images that clearly display the structure of the tissues and clearly visible damage to the bone or other elements of the joint, and bone formations (if any) are easily determined;
- arthroscopy is a minimally invasive diagnostic operation involving endoscopic examination of synovial fluid, the results of which provide the specialist with the opportunity to accurately assess the presence of any pathology, infection or inflammatory process.
Regardless of how intense the manifestation of the symptoms of a degenerative-dystrophic disease, in order to eliminate the possibility of making a false diagnosis, as well as to clarify the existing stage of development of pathological processes, each patient is required to undergo laboratory and x-ray examination.
Coxarthrosis (arthrosis of the hip joint)
Arthrosis of the hip joint is one of the most severe forms of arthrosis.
This type of osteoarthritis is the most difficult to treat. The disease manifests itself at retirement age, but in the presence of congenital anomalies, young people also become ill. Women tolerate this form of arthrosis worse, since the specific structure of the pelvic bones plays an important role in bearing and giving birth to a child.
The main symptom of coxarthrosis is severe pain in the pelvic area. It can cause lameness and changes in gait. Inflammations are outwardly invisible, but touching the sore spot is accompanied by painful sensations.
A serious side effect is spinal curvature. To reduce pain, a person begins to lean forward, which increases the load on the intervertebral joints. In addition, a change in gait.
What is the prevention of osteoarthritis of the joints?
The best way to treat pathologies of any type is, of course, their prevention. We share recommendations that will reduce the risk of developing such an unpleasant and difficult to treat disease.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and maintaining a level of regular physical activity
There is an opinion that physical activity contributes to the wear and tear of tissues, however, in practice, things are somewhat different. Indeed, excessive loads can have a detrimental effect on the condition of the joints, but measured ones will only be beneficial.
According to studies, activity of any type, aimed primarily at strengthening the muscular frame or improving coordination, primarily supports the motor function of the joints, enriching them with useful substances due to the activation of blood circulation.
It is known that people who prefer walking are less susceptible to the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
Monitoring optimal body weight and using adequate measures to reduce it (if necessary)
Excess body weight significantly increases the load on the body, which negatively affects the functionality of the joints. Over time, due to increased load, the lower limbs and spine of an obese person may be subject to degenerative-dystrophic pathologies. For this reason, regardless of the collected anamnesis, the severity of symptoms, and other factors, physical activity (visiting exercise therapy) is necessarily included in the treatment and rehabilitation protocol.
Work on the correction and elimination of congenital deforming conditions
By deforming conditions of the congenital type, it is customary to understand a large number of diseases, among which is flat feet.
The absence of proper measures to eradicate deformities of this type can lead to a confusion of the axis of the lower extremities, as well as improper distribution of the load on individual fragments of the joints.
Compliance with the principles of balanced nutrition
“You are what you eat” is a great saying that accurately conveys the importance and significance of a nutritious, balanced diet.
Refusal of a large number of useful microelements, diet, irregular nutrition, and other factors can become a point of development of pathological processes of the degenerative-dystrophic type.
Timely seeking qualified medical care
Since the times of the USSR, it was instituted to undergo medical examination, which made it possible to timely identify pathological conditions and begin their treatment. Today, this practice is more of a advisory nature, which inevitably leads to a deterioration in the health of patients.
Refusal to consult a doctor when the first signs of illness appear sometimes leads to irreversible consequences.
Preventive use of drugs from the chondroprotector group
Proper nutrition and an active lifestyle are certainly good. However, in a situation where the body is under increased stress or for some reason cannot absorb absorbed microelements, their preventive intake comes to the rescue.
An excellently proven drug is Artracam, which belongs to the category of chondroprotectors and is one of the most effective in its segment.
There are plenty of obstacles to a full, rich life. Only the person himself can ensure the desired level of quality of life, adhering to recommendations for the prevention of various types of diseases, as well as finding positive aspects in everything and enjoying every minute he lives.
Take care of your health from a young age!
Arthrosis of the interphalangeal joints of the hands
This form most often occurs in women after menopause. A clear sign of osteoarthritis are small lumps - nodules that can be felt on the fingers. Patients feel burning and tingling in their fingers. The functionality of the phalanges of the fingers is reduced. When diagnosing, it is important not to confuse it with rheumatoid arthritis. It also often affects the fingers, but with osteoarthritis these are the “end” joints, located closer to the tips of the fingers, and with rheumatoid arthritis, these are the “inner” joints, located at the base of the finger.
Clinical picture
Although the diseases are very similar to each other, their symptoms are significantly different. The main difference in the clinical manifestation of pathologies can be seen in the comparative table:
| Characteristics | Osteochondrosis | Osteoarthritis |
| Manifestation of pain | After sleep, when in a forced position for a long time | At night, after daytime physical activity |
| Localization of pain | In the affected area of the spine with irradiation to the sternum and limbs | Localized in the diseased joint |
| Feeling stiff | Has a long-lasting nature | Passes within an hour |
| Swelling | Applies to face, shoulders and limbs | Extremely rare |
| Temperature | Often accompanied by low-grade fever | An increase in local temperature is observed only in cases of complications |
| Major complications | Vertebral artery syndrome | Reactive synovitis |