1. How does dizziness manifest in osteochondrosis?
2. How are dizziness and cervical osteochondrosis related?
2.1 The main causes of the development of osteochondrosis
2.2 The main causes of dizziness in osteochondrosis
3. Clinical picture
4. Diagnostics
5. How to treat?
6. Prevention
Without a doubt, one of the most common symptoms is dizziness. This symptom occupies a leading place in prevalence and is associated with a number of pathological conditions and diseases, which indicates its nonspecificity; however, there are some types of dizziness that occur only in certain conditions, for example, cervicogenic dizziness with pathology of the cervical spine. A symptom such as dizziness can occur with a wide range of neurological, vascular and mental diseases and require a mandatory diagnostic and therapeutic approach, as it is often a symptom of a serious and even life-threatening disease.
The appearance of systematic dizziness occurs in more than 35% of people living in large populated areas. Very often, dizziness accompanies neurological and vascular diseases and can be a harbinger of the development of transient or acute cerebrovascular accident. In more than half of the cases, the occurrence of constant sluggish dizziness is formed against the background of diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
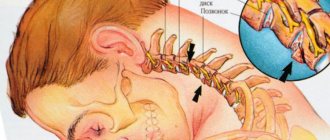
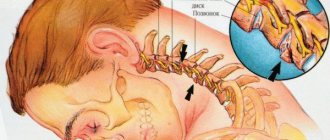
How does dizziness manifest in osteochondrosis?
Dizziness, or synonymous with vertigo, is a pathological feeling of uncertainty in assessing the position of one’s body in space, while the sick person feels as if the objects surrounding him are rotating around him, less often the sensations are of the opposite nature, i.e. the feeling of rotating your own body around surrounding objects. These sensations lead to uncertainty in one’s actions, disrupt motor skills and cause awkwardness in the patient’s movements. With fairly severe manifestations of dizziness, in addition to the main symptom - uncertainty in movements, neurological symptoms are added in the form of nausea and even vomiting with severe dizziness. The patient also experiences some autonomic disorders, such as:
- Increased heart rate and pulse;
- Unstable blood pressure;
- Increased sweating, especially of the upper extremities and face;
As dizziness increases, all of the above accompanying symptoms also progress proportionally and become more pronounced.
In neurological practice, it is very convenient to divide dizziness into several main types, depending on the pathogenetic mechanism of its formation. The following types of vertigo are distinguished:
- Systemic dizziness. Such dizziness has a vestibular cause and occurs when moving the head. The patient feels dizziness in the form of falling or continued rotation in response to head movement. Very often, systemic dizziness is complemented by severe hearing problems.
- Syncope or presyncope. Dizziness is a common symptom and warning sign of impending loss of consciousness. Dizziness occurs and increases along with a general deterioration in clarity of consciousness. The person becomes unstable, loses balance, and notices cloudiness or darkening in the eyes. If this condition occurs, the victim may fall and cause serious injury to himself.
- Neuralgic cerebrogenic dizziness. It occurs as a result of organic pathology with localization in the parts of the brain responsible for balance. For example, when the cerebellum is damaged in a person suffering from a stroke or traumatic brain injury, cerebellar ataxia occurs, one of the manifestations of which is constant dizziness. In other cases, cerebrogenic imbalance occurs due to paresis or paralysis, but in this case the feeling of dizziness is false.
- Cervicogenic dizziness. Such dizziness occurs with pathology of the cervical spine, most often with osteochondrosis. The formation of a feeling of awkward body position in space occurs as a result of a violation of proprioceptive sensitivity in the peripheral nervous system. It is the occurrence of dizziness of a cerebrogenic nature that is most often observed in patients.
How are dizziness and cervical osteochondrosis related?
Osteochondrosis is one of the most common and frequent causes of dizziness. With this disease, damage occurs to the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs of the cervical spinal column as a result of a violation of their nutrition or trophism. As a result of disturbed metabolism, dystrophic processes are formed in cartilage tissue, which leads to a decrease in the volume of cartilage and its destruction, as a result of which the spinal column loses a significant degree of its shock-absorbing properties. The load on the bodies of the cervical vertebrae increases, which leads to their mechanical trauma and subsequent destruction. Bone growths or spines appear on the vertebrae, the mobility and mobility of the vertebrae is significantly reduced, and their height also decreases, which leads to the gradual involvement of spinal cord neurons and their processes in the inflammatory process, which exit through the lateral openings between the vertebrae in the form of sensory and motor nerve fibers as part of nerve roots. In the absence of timely diagnosis and treatment, osteochondrosis progresses and leads to the development of serious complications in the form of organic damage to nervous tissue, one of the symptoms of which is the development of cervicogenic dizziness.
The main causes of the development of osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a multifactorial disease and it is not possible to identify any specific factor leading to its occurrence. However, among a wide range of pathogenic factors, several leading factors can be identified, which include:
- Hereditary genetic predisposition;
- Systematic long-term physical inactivity or, conversely, increased load on the musculoskeletal system;
- Dysmetabolic disorders;
- History of chronic infectious diseases.
All of the above factors can lead to the development of osteochondrosis, both individually and in combination. When exposed to two or more factors from the above list, the risk of gradual formation of osteochondrosis increases significantly.
The main causes of dizziness in osteochondrosis
Whether dizziness can occur with cervical osteochondrosis is a complex question. Of course, in most clinical cases this symptom is present, but there are also situations when osteochondrosis progresses in a latent form without dizziness and other vegetative manifestations. It is important to immediately note that only osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is accompanied by the appearance of the symptom of dizziness. As mentioned above, osteochondrosis leads to a decrease in the area and volume of the intervertebral discs, which leads to its flattening and compression or compression of the spinal nerve endings, while in addition to the direct effect on the nervous tissue, compression of the vertebral or vertebral arteries occurs, which entails a chronic impairment of oxygenation nervous tissue of the spinal cord and medulla oblongata. The complex effect of chronic ischemia and trauma to nerve fibers leads to increased sensitivity and irritation of autonomic nerve endings, resulting in cervical dizziness.
Preventing the condition with medications
In addition to the course of taking balanced complexes of vitamins and microelements, doctors prescribe systemic chondroprotectors to patients. These are Teraflex, Dona, Arthra, Structum, Chondroxide, Alflutop, Chondrogard. The use of chondroprotectors at the initial stage of development of osteochondrosis allows for partial restoration of damaged discs. And in case of a disease of 2 or 3 degrees of severity, drugs are used to prevent its spread to healthy tissue.
Clinical picture
The symptoms of dizziness in osteochondrosis are specific. As a rule, awkwardness and impairment of motor activity are of minor intensity. The feeling of imbalance is stable and gradually increases as osteochondrosis of the cervical spine progresses. As mentioned above, dizziness is often accompanied by other neurological symptoms, such as headache, nausea and vomiting, hyperhidrosis or increased sweating, weakness and increased heart rate.
In some cases, patients may experience attacks of dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women
As a rule, symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women appear 5-10 years later than in men. First of all, this is due to the later onset of menopause and anatomical features (including a lighter bone structure).
Before the mass distribution of computers and the demand for “sedentary” professions, the average age of onset of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women ranged from 50 to 55 years. But now the disease has “rejuvenated” to 40-45 years.
Unlike a similar problem in men, symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women often include:
- sudden surges in pressure, especially due to the weather;
- pallor of the face, blue discoloration of the lips and skin;
- decreased sensitivity, up to numbness, of the skin of the face and cervical-collar area, which is accompanied by tingling or goosebumps;
- a feeling of nausea, which is especially intensified in stressful situations.
It should be remembered that cervical osteochondrosis is a disease of the whole body, so it can negatively affect conception and the course of pregnancy. Also, symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women can cause ovarian dysfunction and disruption of the monthly cycle.
Diagnostics
If dizziness appears, especially if the symptom increases, you should not sit idly by. Only a consultation with a qualified specialist and a full diagnostic study will help to conduct a differential diagnostic search and identify a specific pathology. At the Clinical Institute of the Brain there is an entire department dedicated to the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and related complications. An integrated approach to diagnosis allows you to accurately assess the severity of neurological disorders and the localization of the pathological inflammatory process. The following diagnostic methods are used at the Clinical Brain Institute:
- Computed tomographic or magnetic resonance imaging study, which allows a detailed assessment of the localization and degree of the inflammatory process in the intervertebral discs and vertebrae.
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- Ultrasound Doppler mapping of neck vessels;
- Comprehensive analysis of the patient’s vestibular function.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men usually appear at the age of 40-45 years. Patients often notice them during physical activity (for example, working out in the gym or lifting weights). Delayed self-diagnosis of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men is associated not only with a reluctance to go to the doctor, but also with physiological prerequisites. Men have stronger and thicker vertebrae than women, and the vessels are stronger. Therefore, they may notice discomfort only when changes have already affected the intervertebral discs. Characteristic symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men include:
- decreased overall strength and endurance;
- deterioration of libido and erectile dysfunction;
- irritability, sometimes neuroses;
- deterioration of motor skills (“awkward fingers”);
- headaches that do not go away after taking analgesics.
Vertebral hernias with symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are more common in men than in women.
How to treat?
I feel dizzy with cervical osteochondrosis, what should I do? First of all, you should consult a specialist for advice. Only after the examination can we talk about drawing up an effective treatment plan. Treatment of dizziness with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine consists of complex therapy using both medications and physical procedures. For the purposes of pharmacotherapy, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They can significantly reduce the amount of inflammation, relieve swelling and, accordingly, compression of the nerve roots and spinal cord. For a more effective effect at the time of therapy, a course of injectable forms of anti-inflammatory drugs is used. The main drugs in this group include: Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Nurofen and Meloxicam.
- Cerebroprotectors and nootropics are drugs that improve cerebral circulation and metabolic processes in nervous tissue. These drugs include: Piracetam, Cinnarizine, Cavinton or Vinpocetine.
- Chondroprotojectors are means that protect cartilage tissue from destruction. This group of drugs improves the elastic and shock-absorbing properties of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc, thereby relieving compression syndrome.
It is important to note once again that treatment must be comprehensive and complex; only in this case can one hope for a good effect from therapy. For this purpose, in addition to medications, physiotherapy is also used: therapeutic electrophoresis on the neck area, ultrasound and magnetic therapy. The systematic implementation of therapeutic exercises also plays a significant role.
Treatment methods for dizziness
Cervical osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease that cannot yet be completely cured. Therefore, its therapy uses methods that help achieve sustainable remission. At this stage, there are no significant symptoms, including dizziness.
At the beginning of treatment, patients are advised to wear Shants collars during the daytime for 3-4 hours. When using these devices, there is no compression of the vertebral artery by osteophytes or displaced discs. Doctors also recommend purchasing an orthopedic mattress and pillow for sleeping to prevent circulatory disorders in the brain at night.
Drug therapy
When choosing drugs to eliminate dizziness, the vertebrologist takes into account the cause of its occurrence - muscle spasm, inflammatory edema, hernial protrusion, irritation of nerve endings. The nature of the accompanying symptoms, the age of the patient, and the presence of chronic pathologies of internal organs are also important.
Muscle relaxants
Muscle relaxants are used for muscle spasms to reduce skeletal muscle tone. Treatment regimens include Sirdalud, Tolperisone, Baclosan (Baclofen). For severe pain, the Mydocalm injection solution, which contains the anesthetic Lidocaine, is especially in demand.
Painkillers
Intramuscular administration of Baralgin, Spazgan, and Ketorolac can quickly eliminate pain in the neck. These medications are then prescribed to the patient in tablet form. You can cope with pain with the help of acetylsalicylic acid, Paracetamol, Analgin. Analgesics are not intended for long-term course use. They are recommended to be taken only once to eliminate pain.
Vasodilators of the neutropic or myotropic group
To improve blood circulation in the cervical spine, eliminate oxygen and nutrient deficiency, Xanthinol nicotinate, Pentoxifylline, and Eufillin are used. Therapeutic regimens also include Vinpocetine and Cinnarizine (Stugeron). The drugs have a vasodilating effect, exhibit moderate antihistamine activity, and reduce the excitability of the vestibular apparatus.
Betahistine is used directly to eliminate dizziness. The drug affects blood flow, stimulating microcirculation and permeability of the capillaries of the inner ear.
Anti-inflammatory
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the first choice drugs in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis. They eliminate pain and swelling, relieve inflammation, and reduce temperature. Patients with mild discomfort are prescribed ointments and gels Voltaren, Fastum, Artrosilen. Intramuscular administration of Ortofen, Ketorolac, and Movalis helps relieve acute pain. And when they are moderate, tablets Nise, Ketorol, Diclofenac, Celecoxib, Nurofen are used.
Blockades
Drug blockades are indicated for patients with acute, piercing pain that cannot be eliminated with NSAID injections. To carry them out, glucocorticosteroids (Triamcinolone, Diprospan) and anesthetics (Lidocaine, Novocaine) are used. With the help of blockades you can get rid of pain for several weeks.
Vitamins and vitamin complexes
In the treatment of osteochondrosis, clinically manifested by dizziness, drugs with B vitamins are necessarily used. Milgamma, Combilipen, Neuromultivit improve the condition of the nerve pathways and restore innervation. To strengthen the immune system and replenish nutrients in the vertebral structures, balanced complexes of vitamins and microelements are prescribed - Supradin, Complivit, Vitrum, Selmevit.
Physiotherapy and manual procedures
For physiotherapeutic treatment of osteochondrosis complicated by dizziness, 5-10 sessions of magnetic therapy, laser therapy, UHF therapy, shock wave therapy, electrophoresis with anesthetics, analgesics are carried out. Applications with paraffin and ozokerite, hirudotherapy, and acupuncture are used.
It is often possible to avoid surgery by visiting a chiropractor. He presses his hands on the vertebrae, increasing the distance between them.
Physiotherapy
The most effective method of treating osteochondrosis is daily physical therapy exercises. Regular training helps strengthen the muscles of the neck and shoulder girdle and improves blood supply with oxygen to the brain. Exercise therapy doctors recommend that patients tilt and turn the head with resistance, and rotate it in a circular motion. All exercises are performed smoothly, without sudden movements.
Folk recipes
Folk remedies will not help cope with dizziness. But their use at the stage of remission will prevent relapses of osteochondrosis, in which they occur. Ointments, compresses, and applications with ingredients that have a local irritant effect are especially effective. And the use of herbal teas helps improve the quality of sleep and strengthen the body's defenses.
Compresses
A mixture for compresses is prepared from fresh leaves of burdock, cabbage, horseradish, plantain or dandelion. They are ground until a homogeneous mass is formed, a tablespoon of thick honey is added, a drop of essential oils of juniper, rosemary, and eucalyptus are added. Stir thoroughly and apply to the back of the neck. Fix with film, woolen cloth, gauze or elastic bandage. Leave for 2 hours, wash off the residue with warm water, rub any moisturizer into the skin.
Decoctions and infusions of herbs
To prepare a soothing, tonic tea, pour a glass of boiling water into a teaspoon of dry plant materials St. John's wort, chamomile, lemon balm, abalone or thyme. Leave covered for 30-40 minutes, cool, filter. Take the infusion before bed, after adding a little flower honey to it.
A decoction is prepared from a dry mixture of equal parts of calendula, eucalyptus, elecampane and peppermint. Pour 3 tablespoons of plant material into a glass of hot water, bring to a boil and simmer for 20 minutes. Cool and filter. Soak a bandage folded in several layers in the broth and apply it to the back of the neck for an hour.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development or progression of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and associated dizziness, as well as other neurological manifestations, the same complex of physiotherapeutic methods is used. To avoid the development of this disease, it is important to understand that only the absence of pathogenic factors can eliminate the unnecessary risk of developing osteochondrosis and its complications. To do this, you need to change your lifestyle and attitude towards your own health. Such simple things as an active lifestyle, proper nutrition, alternating work and rest significantly reduce the risk of osteochondrosis and its manifestations. Take good care of your body and be healthy.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 127 votes
Share article on social networks
Features of treatment during pregnancy
During pregnancy, dizziness caused by cervical osteochondrosis is eliminated mainly through physiotherapy, massage, and daily physical therapy exercises. Pharmacological drugs are also used in therapy. Vertebrologists prefer ointments, gels, and balms. The ingredients of external agents almost do not penetrate into the bloodstream and do not have a teratogenic effect.