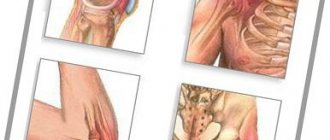
The upper limbs are made up of many bones, the largest of which are the humerus, radius and ulna. The hand contains the metacarpal, carpal and phalangeal bones. In total, each arm consists of 32 bone elements. They are connected to each other by joints.
The joints of the upper extremities are divided into large (elbow, wrist, shoulder and humeroscapular) and small (carpometacarpal, metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal). The joint is formed by the heads of bones and cartilaginous synovial tissue, which provides shock absorption and easy gliding during movement. Aching pain in the arm is often caused by the destruction of cartilaginous synovial tissue.
Around the joint there is connective, ligament and tendon tissue. With the help of the latter, muscles are attached. When ligament and tendon tissue are sprained, rough fibrin scars subsequently form. They put pressure on nearby nerve fibers. It can also cause severe aching pain in the arms.
Aching pain in the bones of the arms is often misunderstood by the patient. In fact, bone tissue is largely devoid of its own innervation. The exception is the periosteum - a thin layer in which capillary blood vessels are located. For innervation, nerve fibers pass nearby from muscle tissue. Therefore, when the periosteum is injured, pain may occur. The bone itself does not hurt. Pain is caused by inflammation of surrounding tissues.
So, if the ligamentous apparatus is deformed, it narrows the natural tunnels in which large nerve fibers are located (brachial, ulnar, radial, carpal, palmar, median and other nerves). When the tunnel passages narrow, compression of the nerve fiber occurs. This is precisely what can cause severe and extremely unpleasant aching pain in the hands.
In inflammatory processes, aching pain is complemented by other characteristic symptoms. This may include increased temperature (local), redness of the skin, pain at a local point during palpation, and limited mobility. When carrying out differential diagnosis, it is important to first determine the expected site of development of pathological changes. Then the doctor must establish the etiology of the process: trauma, inflammation, degeneration, dystrophy, tumor or infectious process.
For diagnosis, X-rays, RT examinations, ultrasound of soft tissues, and various blood tests are used. You can find out what potential causes can cause hand diseases with constant nagging pain in this article. It tells you what symptoms you should pay attention to and which doctor you should contact for diagnosis and effective treatment.
In Moscow, you can make an appointment with an orthopedist, vertebrologist or neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. Here, each patient is given the opportunity to receive a completely free initial consultation with a doctor. The doctor will conduct an examination, make a diagnosis and give individual recommendations for safe and effective treatment of the identified disease.
Causes of aching pain in the arms and hands
The causes of aching pain in the hands may be hidden in damage to the following types of tissue:
- nerve fiber, ranging from radicular syndrome due to cervical osteochondrosis and ending with damage to small nerve endings due to inflammatory or traumatic swelling of soft tissues;
- muscles - as a result of injury, cicatricial deformation, dystrophy and atrophy, impaired blood supply due to angiopathy, impaired innervation;
- tendons and ligaments - sprains and ruptures, scar deformation, inflammatory processes and tumor growth of their cells;
- synovial tendon tissue - for dystrophic degenerative and inflammatory diseases, this can be arthritis, arthrosis, osteoarthritis, synovitis, chondrosis, etc.);
- bone - osteoporosis, deformation of bone heads, cracks and fractures;
- other soft tissues due to the deposition of uric acid salts (gout), fibrin fibers (myogelosis), tumor cells (lipomas, fibromas, fibroids, etc.).
The most common causes of aching pain in the hands are tunnel syndromes. This may be a lesion of the carpal tunnel or carpal valve. These two diseases can be identified by their characteristic nagging, aching pain. She first grabs the hand and fingers. Then, if effective treatment is not carried out, the pain syndrome spreads to the forearm and shoulder. Secondary paresthesia, numbness, and decreased muscle strength in the fingers may occur.
Aching, pulling pain in the shoulder of the arm
Aching pain in the shoulder of the arm can be a symptom of many orthopedic and neurological diseases. Often in patients with such a clinical sign, a detailed examination of the examination results reveals serious dorsopathy in the cervical spine. Degenerative dystrophic changes in the cartilage tissue of the fibrous ring of intervertebral discs leads to the fact that the vertebrae lose the stability of their position. Their listhesis (displacement) leads to compression of large radicular nerves. This gives rise to referred pain syndrome in the shoulder area.
Other pathologies of the cervical spine that provoke shoulder pain include stoop and curvature, myogelosis, vertebral displacement, subluxation of the first cervical vertebra, muscle sprain, static tension of the muscles of the collar zone, spondyloarthrosis and ankylosing spondylitis.
Aching, nagging pain in the arm can be triggered by the initial stage of development of brachial plexitis, periarthritis of the glenohumeral joint, or deforming osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint. Particular attention to the appearance of this symptom should be paid to those patients who suffer from habitual shoulder dislocation. They experience gradual destruction of the articular labrum, as a result of which the process of deformation of the articular capsule begins. During which time a habitual dislocation of the shoulder can lead to complete disintegration of the tissues of the joint. In this case, only endoprosthetics surgery can help. Therefore, if you experience aching or nagging pain in the shoulder or arm area, immediately consult an orthopedist or neurologist.
How to treat hand joints?
All existing treatment methods, both the most modern and traditional, which the Alan Clinic Center for Neurology and Orthopedics uses in its work, are safe and exclude surgical intervention.
The treatment process is always a comprehensive program with an individual approach to each of our patients.
Most of our methods, which are essentially drug-free, are acceptable even for the treatment of infants, pregnant and nursing mothers. We have at our disposal the following methods:
- Manual therapy
- Osteopathy is treatment done by a doctor, with a gentle effect on the musculoskeletal system, nervous and vascular systems, and internal organs.
- Medical massage
- Acupuncture - exposure to biologically active points with microneedles.
- Laser reflexology is a painless effect on reflexogenic zones and points.
- Tsubotherapy is a gentle effect on the reflex points of the body.
- Pharmacopuncture is the introduction of medicinal drugs of natural origin to the source of the problem.
- Plasma therapy is the introduction of the patient’s own purified blood into the site of the disease.
- Isometric kinesiotherapy - individual gymnastic techniques/exercises, according to indications, with elements of joint massage.
- Kinesiotherapy using the Exart installation
- Kinesio taping
- Ozone therapy is treatment with active oxygen.
- Physiotherapy
- Physiotherapy with enzyme preparations
- Medical droppers
- Hirudotherapy - treatment with leeches.
- Botulinum therapy is treatment with botulinum toxin.
- Intra-articular injection of synovial fluid endoprostheses
- Intra-articular blockades
All methods are recognized by official medicine, and doctors using them have appropriate certificates. The decision on the need to use certain medications during the course of treatment is made by the doctor, based on the complexity and severity of the disease, concomitant diseases, as well as the diagnosis.
Aching pain in the wrist, hand and fingers
Frequent aching pain in the wrist may be a symptom of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. Quite often this is a sign of pain spreading along the ulnar nerve when it is compressed in the area of the cubital canal. It is located at the back of the elbow joint and is often subject to compression by external factors. So, if you have a habit of sitting with your head resting on your arm placed on your elbow, then there is a high probability of developing cubital syndrome in the near future. It is characterized by pain that extends to either the wrist or shoulder joint.
Aching pain in the hand can be caused by carpal syndrome, the consequences of traumatic damage to bone, ligamentous and muscle tissue. An experienced doctor should diagnose the pain. It is very difficult to identify the potential cause on your own. Laboratory tests will be required.
Constant aching pain in the fingers is almost always associated with polyarthritis or polyarthrosis. It is important to understand whether one interphalangeal joint is affected or several at once. Polyarthrosis requires an integrated approach to treatment. It is important to exclude negative impact factors. If the pain affects only one finger, then this is most likely monoarthrosis. Also, during the initial diagnosis, the doctor also excludes contracture of the fingers due to a functional limitation of their mobility. This may be a consequence of long-term cervical osteochondrosis, brachial plexitis, etc.
Why do my hands hurt?
To answer this question, you need to undergo a competent and comprehensive diagnosis at the Alan Clinic Center for Neurology and Orthopedics, which, with its comprehensive approach to identifying joint problems, will help establish your diagnosis. It includes the following research methods:
- consultation with a specialist;
- special orthopedic tests;
- dynamic active and passive tests;
- local palpation examination of damaged joints;
- assessment of the condition of the musculoskeletal system, posture, gait, uniform distribution of load on joints, range of motion, stability and strength of the joint;
- making and explaining the diagnosis;
- selection of individual complex motivated treatment.
If necessary, the doctor may also prescribe:
- MRI;
- Ultrasound;
- X-ray;
- lab tests;
- diagnostic puncture of the joint.
Dull aching pain in the joints of the hands
Prolonged or periodically occurring dull aching pain in the arm is a symptom of a chronic degenerative dystrophic process. During periods of remission, any clinical symptoms may be absent. And during an exacerbation, aching pain occurs in the joints of the hands, which becomes more acute with each episode of exacerbation.
For diagnosis, please consult an orthopedist. He will prescribe an x-ray, which will reveal pathological changes in bone tissue. This is usually how deforming osteoarthritis is diagnosed (by the size of the joint space, the height of the cartilaginous synovial tissue, the presence or absence of bone growths). Also, using an X-ray image, you can exclude a fracture or crack of bone tissue, the formation of osteophytes, including corner ones against the background of destruction of the end articular plates.
If an X-ray image fails to establish the cause of the aching pain in the arm, an ultrasound of soft tissues and angiography with preliminary administration of a contrast agent are prescribed. In this way, angiopathy, tumors, and nerve impulse conduction disorders can be detected. In complex diagnostic cases, an MRI examination or CT scan, arthroscopy, etc. are required.
Pain in the joints of the fingers: treatment, causes
Pain in the joints of the fingers is most often caused by the following diseases:
- polyosteoarthrosis of the fingers;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- psoriatic arthritis;
- gout, gouty arthritis;
- de Quervain's tenosynovitis;
- rhizarthrosis.
In addition, pain in the joints of the fingers, accompanied by numbness, may be associated with carpal tunnel syndrome and Raynaud's syndrome.
Pain in the joints of the fingers with polyosteoarthrosis
In 40% of cases, pain in the joints of the fingers is associated with polyosteoarthrosis, which is diagnosed mainly in people over 40 years of age, most often in women.
Characteristic signs of polyosteoarthrosis are special nodules (the so-called Heberden's nodes) on the dorsal or lateral surfaces of the joints, localized near the nails. The development of Heberden's nodes occurs symmetrically, simultaneously on the left and right hands, with the same localization. Similar formations can occur on any finger.
In some people, Heberden's nodes form, accompanied by burning and pain, swelling and redness. In others, this pathology develops asymptomatically, pain and burning are absent.
In addition, polyosteoarthrosis is characterized by the appearance of mildly painful Bouchard nodes on the proximal interphalangeal joints located in the middle of the fingers. The shape of these nodules is spindle-shaped, development is slow, and there is no pain.
Pain in the joints of the fingers with rheumatoid arthritis
About 5-8% of cases of pain in the joints of the fingers are caused by rheumatoid arthritis. Most often, this disease occurs in people over 30 years of age, mainly in women. As a rule, rheumatoid arthritis is caused by severe stress, flu, severe colds, infectious diseases or hypothermia.
Early in the development of rheumatoid arthritis, the metacarpophalangeal joints of the middle and index fingers become inflamed and swollen. Most often, against the background of their inflammation, the wrist joints of the hand also become inflamed and swollen.
The fingers and wrist joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis become inflamed symmetrically: when the joints on the left hand are affected, the same joints on the right hand are affected.
In most cases, there is involvement in the pathological process of other joints of the upper and lower extremities, as well as large joints - knees, elbows, ankles, etc.
As a rule, the above symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are accompanied by general weakness, fever, weight loss and chills. Thus, the disease is the cause of a general deterioration in the patient’s well-being.
Pain in the joints of the fingers with psoriatic arthritis
About 5% of cases of pain in the joints of the fingers are also associated with psoriatic arthritis, which can be diagnosed in people aged 20 to 50 years, most often when they have skin psoriatic manifestations - dry, scaly reddish spots (psoriatic plaques) on the body or hairy area. parts of the head.
Psoriatic arthritis is characterized by so-called “axial” inflammation with swelling of all joints on a particular finger, which turns red and looks like a sausage.
Pain in the joints of the fingers due to gout or gouty arthritis
In less than 5% of cases, pain in the joints of the hands occurs due to gout or gouty arthritis. In persons suffering from these ailments, the big toe is deformed. Women most often experience arthrosis of the thumb, and men, as a rule, develop “classic” gout – gouty arthritis.
The disease can manifest in people from 20 to 50 years of age. It begins with inflammation of the joints of the toes, knees or ankles. Most often, inflammation and pain appear in the joint of the thumb, but sometimes the inflammatory process affects other fingers, both the right and left hands.
Gout attacks happen completely unexpectedly, most often at night. The pain in the joints of the hands during gout attacks is quite intense. Redness of the affected joint is observed.
Women usually have a milder course of attacks, there is no acute pain, and the joint, as a rule, does not redden.
A gout attack is characterized by a sudden onset, duration from three to ten days and relapses after some time.
Pain in the joints of the fingers with de Quervain's tenosynovitis
Pain in the joints of the fingers may occur in patients with de Quervain's tenosynovitis. With this disease, the ligaments and “small” muscles of the thumb become inflamed. Inflammation of other fingers with de Quervain's tenosynovitis is excluded.
De Quervain's syndrome affects both men and women equally and can occur at any age. The pathology is characterized by pain in the joint of the thumb - at its base and at the point of contact of the thumb with the wrist joint.
Pain in the thumb joint with rhizarthrosis
Another cause of pain in the fingers is rhizarthrosis, which is characterized by damage to the joint located at the base of the thumb and connecting the thumb to the wrist joint.
Rhizarthrosis can be a manifestation of polyosteoarthrosis of the fingers, but sometimes it is an independent disease, the development of which is associated with heavy loads on the thumb.
Rhysarthrosis and de Quervain's tenosynovitis have similar symptoms. The only difference between rhizarthrosis is that with this disease, the bones of the diseased joint are deformed in patients, which can be detected during examination and on x-rays. With de Quervain's tenosynovitis, only the soft tissues surrounding the joint change, and even then in rare cases.
Severe aching pain in the arm muscles
Severe aching pain in the arm can be caused by pathological changes in the muscle structure. Muscular dystrophy and replacement of myocytes with fibrous cells, ischemia of muscle tissue, and myofascial pain syndrome are often diagnosed.
If you experience aching pain in your arm muscles, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible and undergo a full examination. There is a danger that muscle pain is endocrine or cerebral in nature. In some patients, muscle pain often becomes the primary symptom of such dangerous blockages as:
- atherosclerosis of blood vessels (often causes the development of myocardial infarction or cerebral stroke);
- diabetic angiopathy and neuropathy due to high blood sugar (in advanced cases, complete blindness and diabetic coma are possible);
- obliteration of blood vessels by tumors and lymphadenopathy;
- spread of dangerous infections;
- parasitic forms of muscle tissue damage.
It is not possible to identify most of these pathologies on your own. Be sure to see a doctor.