Magnetotherapy (16) Infrared and phototherapy (10) Vibroacoustic therapy (6) Laser therapy (4) Quantum therapy (2) Thermotherapy (3) Electrophoresis and Galvanization (5) Electrical stimulation (3)
Magnetic therapy for fractures of the foot bones is an effective means of accelerating the rehabilitation process and preventing possible complications. The effect of magnetic therapy for fractures of the foot bones:
- The magnetic field causes the induction of weak currents in the blood, which increase the speed of cellular movement.
- There is an acceleration of metabolic processes.
- The supply of O2 and nutrients to cells increases, which contributes to the active restoration of damaged tissues.
One of the most significant therapeutic factors of magnetic therapy for fractures is the stimulation of callus formation processes.
For foot fractures, portable magnetic therapy devices are used, which are used even in the presence of a plaster cast after 72 hours from the injury.
The inductors are installed at right angles to the damage site, which ensures uniform distribution of magnetic field radiation.
Indications for magnetic therapy for a foot fracture:
- slow fusion of bone fragments;
- prevention of stiffness in the post-immobilization period;
- removal of puffiness;
- prevention of false joint formation;
- acceleration of recovery processes;
- reduction of pain.
Contraindications to magnetic therapy for a foot fracture are:
- purulent formations and acute inflammation;
- presence of a pacemaker;
- oncological diseases;
- period of post-infarction rehabilitation;
- severe hypotension;
- hyperthyroidism;
- severe heart disease;
- bleeding, etc.
Magnetic therapy devices for the treatment of fractures
[td]
Rules for conducting exercises
Doctors and physical therapy specialists give the following recommendations when recovering from a fracture:
- Charging must be done with caution, slowly, smoothly, listening to your own feelings.
- Each exercise is done 10-20 times (all individually).
- The main thing is not to overload your legs. If you feel tired, rest and continue later.
The rehabilitation period after a complex fracture of the metatarsal bones of the foot is very important. Requires the implementation of all actions prescribed by the traumatologist.
Recovery does not allow indulgences and laziness. How you treat it will directly affect the future functioning of your foot.
Exercise sets
To speed up the recovery process, you need to devote time to exercise therapy every day.
The complex includes exercises that are performed 10-20 times:
- Rotate the foot in a circle (clockwise and counterclockwise).
- Turns to the sides, down and up the feet.
- Compression, extension of toes.
- They place the ball under the foot, begin to roll it, roll it from toe to heel and vice versa.
- They sit on a chair, rise, transfer their body weight to their heels, smoothly rolling onto their toes. Over time, this exercise is performed leaning on a chair, and later – standing.
- They lie down on a flat surface and swing their legs (crosswise).
Additionally, you can do the following interesting activities:
Displaced fracture of the 5th metatarsal
Comminuted fractures occur at tendon attachment points. When there is a traumatic effect on the muscles, they undergo a sharp and excessive contraction. They may be subject to tearing and stretching. But often there is a separation of bone tissue at the site of attachment of tendon fibers. The metatarsal bone in most cases is injured in this way in the area of the diaphysis and base.
Any fracture of the 5th metatarsal bone of the leg in the second zone requires surgical treatment. If this is a displaced fracture of the 5th metatarsal bone, then the osteosynthesis method is used by introducing screws. They are installed inside the intramedullary canal until the bone is completely fused.
Proximal displaced metatarsal shaft fractures often occur in elite runners and jumpers. It can lead to instability of the intermetatarsal joint of the bones, which causes serious deformation of the foot. It is considered a stress fracture and requires a long period of rehabilitation before returning to sports. Often after this injury, a stable cavovarus deformity is formed. Sensory nephropathies of the foot and fingers may develop with loss of sensation and periodic paresthesias.
Fracture
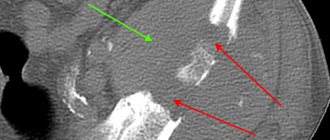
A metatarsal fracture is a rare occurrence. To accurately make this diagnosis, it is necessary to perform a thorough diagnosis.
Due to similar symptoms, a metatarsal fracture is often confused with a sprain or bruise.
Traumatology identifies the following symptoms:
- pain,
- inability to support the leg,
- hematoma,
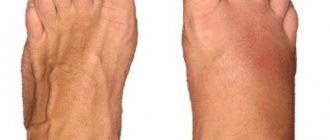
- edema.
Therapy and rehabilitation after healing a metatarsal fracture are quite serious. It is necessary to follow all doctor's instructions to avoid further deformation of the foot, arthrosis, and pain.
Application of massage procedures
The prescribed physiotherapy procedures are combined with massage.
Massage as a rehabilitation after a serious fracture of the 5th metatarsal bone is extremely useful and helps to quickly get your legs into shape. Usually this is a traditional or water massage.
Not everyone can attend massage courses in specialized places, so it is allowed to perform it at home. The main thing is to do this carefully, with caution.
The session goes like this:
- The foot is massaged with smooth, gentle movements in a circle, gently pressing on the site of injury.
- They also perform pinching, stroking, kneading.
- Knead the entire foot (outer, inner part), fingers.
In addition, after the massage it is a good idea to prepare a foot bath with medicinal herbs and sea salt. It will help relieve tension in the limbs and relax. Warm water up to 40 degrees is recommended.
Attention! Massage in combination with baths will quickly cope with swelling, relieve pain in the limbs, accelerate tissue regeneration and foot mobility.
With the help of massage, the foot develops and blood circulation improves. The affected tissues begin to receive high-quality nutrients.
How long does it take for a fracture of the 5th metatarsal to heal?
How long it takes for a fracture of the 5th metatarsal to heal depends on a number of factors. First of all, this is the fracture site. If it is located in the second and third zones, then there is a high probability that the injury will not heal on its own without surgical intervention. Therefore, when diagnosing such fractures, experienced traumatologists immediately refer the patient to osteosynthesis surgery. When the base of the metatarsal bone is fractured, healing occurs within 3 to 4 weeks. Residual effects may be present for the next 6-7 months. This is mild pain in the metatarsal area, stiffness in the morning, muscle weakness, and a feeling of instability when placing the foot.
The second important factor is the state of calcium-phosphorus metabolism in the human body. Women who have entered menopause are at risk. They have decreased female sex hormones, which can result in a process of leaching of calcium from bone tissue. In such a situation, to successfully restore the integrity of the 5th metatarsal bone, correction of the hormonal balance and restoration of calcium-phosphorus metabolism are necessary.
Often, the patient is prescribed vitamin D and a complex of mineral supplements to accelerate the formation of callus.
The third factor on which the recovery period depends is the correctness of the treatment. As mentioned above, you should not expect successful restoration of the integrity of bone tissue if the fracture occurred in the second or third zone. There are virtually no resources for recovery here, since the zones are very poorly supplied with blood.
The patient must strictly follow all the recommendations of the attending physician. Only in this case is there a high probability of complete fusion of bone tissue in the shortest possible time. Please note that rehabilitation will be required to fully restore the functionality of the injured foot.
Types of fractures
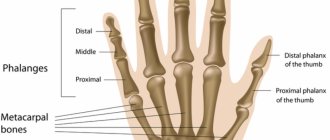
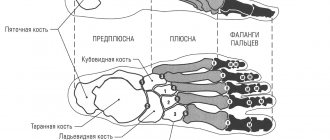
The metatarsal bones are the part of the skeleton that forms the “foundation” of the toes. It is with the head of the metatarsal bone that the phalanx of the finger is connected. The 5th metatarsal bone is located on the outer edge of the foot, its bony protrusion - the styloid process - is quite easy to feel under the skin. This bone has several features:
- The head of the 5th metatarsal bone is one of the three fulcrum points of the foot. When you walk, at least a third of your body weight presses on this tiny area.
- The short peroneal muscle and a strong ligament are attached to the base, or more precisely, the styloid process of the bone. When the foot deviates inwards, these structures become tense and pull the metatarsal bone along with them.
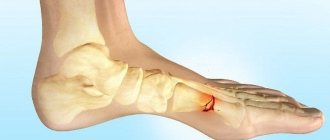
After injury or overload, the head, diaphysis (body) or base of the bone may break. Due to a number of features, a fracture most often occurs at the base of the bone - its widest part. In this case, the most typical are two types of injury:
- Jones' fracture or dancer's fracture is a typical base fracture, more unfavorable due to poor blood circulation in this area;
- fracture of the styloid process - separation of a small section of bone, more favorable due to good blood circulation and low load.
Causes of injury
Fractures of the base of the 5th metatarsal bone can be traumatic and stress-related.
A traumatic fracture is a consequence of a simultaneous overload of a bone during a fall, jump, or twisting of the foot. In an avulsion fracture, the styloid process is torn off by the pull of a powerful tendon and ligament. The diaphysis of the bone can break when a heavy object falls on it or a loss of balance occurs during excessive load on the outer edge of the foot.
Interestingly, the so-called dancer's fracture was first described by the English traumatologist Jones back in 1902. The doctor received the injury while dancing and at first believed that he had damaged a ligament or tendon. After taking an x-ray, he discovered that there was a fracture at the base of the 5th metatarsal. The doctor described all this in an article for a medical journal, after which the injury was named after Jones.
A stress fracture is a consequence of overload of the musculoskeletal system. In this case, microdamages accumulate, and a “crack” forms gradually. This type of injury is typical for athletes, manual workers, and military personnel. Sometimes the condition goes unnoticed, and its consequences are revealed during examination for a completely different reason.
Fracture of the head and diaphysis of the 5th metatarsal bone
A complete fracture of the head of the 5th metatarsal bone is common in women who prefer to wear high-heeled shoes. There is deformation of the joint between the metatarsal and phalangeal bones. With a slight traumatic impact on the joint, the head is displaced and a crack in the bone tissue occurs. This injury can be successfully treated with casting and does not require surgery.
Partial or complete fracture of the diaphysis of the 5th metatarsal bone is mostly observed near the head. This is due to the anatomical narrowing of this part. There is a very narrow intraosseous channel and blood microcirculation in the periosteum area is noticeably reduced. Therefore, bone density may be reduced.
A diaphysis fracture can occur when:
- high and long jumps;
- standing on your feet for a long time in shoes that compress the foot;
- running in shoes that do not absorb the load;
- long-term phenomena of osteomalacia and osteoporosis.
An undoubted risk factor is excess body weight and a sedentary lifestyle. Vascular pathologies such as diabetic angiopathy, atherosclerosis, varicose veins of the lower extremities, and obliterating endarteritis have a significant impact on the condition of bone tissue. In patients, a number of endocrine pathologies that can provoke bone tissue destruction should be excluded. Also, in order to prevent fractures of the small bones of the foot, you should avoid systematically taking hormonal drugs, including those used to treat diseases of the musculoskeletal system.