Author
: Grachev Ilya Illarionovich
Editor
: Efremov Mikhail Mikhailovich
Date of publication: 05/13/2014 Date of update: 05/24/2021 All doctors of the clinic
- Elbow pain during/after coronavirus and ARVI
- Diagnostics
Pain in the elbow joint is not uncommon. It can be a consequence of injury, inflammation, tumor and a host of other diseases. Sometimes painful sensations occur against the background of various intoxications, previous infections and diseases of the internal organs. To figure out why elbow pain appears, you need to see a doctor. You can learn everything about the causes, symptoms and treatment of such conditions from this article.
What exactly hurts
The elbow joint is a complex joint consisting of three bones (ulna, radius, humerus) and interconnected joints: radioulnar, humeroulnar and humeroradial. The radial side of the joint is on the outer (lateral) side of the arm, the ulnar side is on the inner (medial). The complex joint is surrounded by a dense capsule that protects it from external influences.
The inner lining of the capsule is called synovial. It secretes synovial fluid, which is the “lubricant” of the joint and supplies nutrients to the cells of the hyaline cartilage that covers the articular surfaces of the bones. Around the joint between the bone and tendon-ligament tissues there are 3 bursae - articular capsules containing synovial fluid (interosseous ulnar, radioulnar and ulnar subcutaneous). They improve the process of sliding of joint tissues during movement and prevent injury.
The joint is strengthened by four ligaments: two lateral (ulnar and radial), annular (fixes the head of the radius) and quadrate (fixes the connection of the radius and ulna). In the area of the elbow, the tendons of the flexor and extensor muscles of the shoulder are attached and the tendons of the forearm, which are involved in the movement of the arm below the elbow joint, originate. Joint movements: flexion-extension, supination-pronation (rotation of the forearm in and out).
The structure of the elbow joint
The elbow is the elbow joint and the soft tissues surrounding it - tendons, ligaments, blood vessels, nerves, subcutaneous tissue and skin. Elbow pain can occur due to pathology in any of these structures.
What to do at home if your elbow hurts
Elbow pain can appear suddenly in a person or increase gradually. Their causes can also be obvious (trauma, inflammation) or completely unclear (slowly developing chronic inflammatory and degenerative pathological processes).
In any case, if you experience constant pain, you should not:
- treat yourself with folk remedies or medicines that helped a neighbor;
- panic – all this can be treated, but only by specialists; You will be helped in a medical clinic, Moscow - the clinic’s specialists have extensive experience in the treatment of pain syndrome of the elbow joint.
How to treat a sore elbow at home
There is no point in delaying a visit to the doctor. But sometimes circumstances develop in such a way that pain in the elbow needs to be relieved urgently, but there is no way to see a doctor. To temporarily eliminate pain in the elbow, you can use medicinal and non-medicinal means, but you need to remember that this will not cancel a visit to the doctor:
- Painkillers in tablets:
- paracetamol (trade names Efferalgan, Panadol, Paracetamol) – for pain you can take a 500 mg tablet; contraindications: severe liver disease, chronic alcoholism;
- medications from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - ketoprofen (Ketonal, Artrum) has the most powerful analgesic effect; You can take a 100 mg tablet once; contraindications: gastrointestinal ulcers, severe kidney and liver diseases;
- nimesulide (Nise) is a medicine from the NSAID group that does not cause significant side effects from the gastrointestinal tract; for pain, you can take a 100 mg tablet.
- Pain-relieving ointments, creams, gels – applied externally and can be no less effective than tablets; Moreover, they have no side effects (except for allergies) and contraindications:
- ointments with diclofenac : Voltaren emulgel, Diclofenac gel;
- ointments with ketoprofen : Bystrumgel, Artrum gel, Ketonal cream and gel;
- ointments with nimesulide : gels Nise, Nimulid, Nimesulide.
- Injections (injections of medicinal solutions). Many patients do not have a medical education, so it is better to replace injections with rectal (introduced into the rectum) suppositories (suppositories). In terms of absorption rate and effectiveness, this corresponds to intramuscular injections. The following rectal suppositories can be used:
- Diclofenac – at a dose of 100 mg; contraindications: peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- Ketonal – at a dose of 100 mg; contraindications as for Diclofenac;
- Indomethacin – 100 mg; contraindications, like Diclofenac.
Well, if you still know how to give injections, then you can administer 75 mg of Diclofenac intramuscularly (a medicinal solution of 3 ml is produced in ampoules, 25 mg in 1 ml, a total of 75 mg in an ampoule).
Drugs for treating acute pain in the elbows at home
Exercise therapy exercises will also help. If you experience significant pain before training, it is better to consult your doctor. But sometimes you can start doing the simplest light exercises on your own.
The main thing is to continue training every day, but do not overdo it, do not make sudden movements and do not continue training when the pain increases.
Effective exercises:
- bending all the way and straightening the arms at the elbows; repeat 15 times;
- rotational movements with arms bent at the elbows; do first 10 times to the left, then 10 to the right;
- simultaneous squeezing of a tennis ball with the right and left hands; repeat 10 times.
What not to do if you have elbow pain
If you have constant pain in your elbow, then you shouldn’t:
- lift weights;
- constantly perform the same professional movements with a load on the elbow joint; if this is not possible, then you should change your job or give up playing sports such as tennis, basketball;
- supercool;
- constantly expose yourself to stress and overload at work;
- smoking, regularly drinking alcohol;
- self-medicate.
When you need to see a doctor urgently
This must be done if you have pain in your elbow:
- accompanied by swelling and redness of the skin, increased body temperature;
- do not go away, despite eliminating stress and taking painkillers;
- accompanied by impaired movement and numbness of the hand;
- increase during movements in the joint;
- arise against the background of deformation of the elbow area.
If such symptoms appear, you cannot postpone visiting a doctor; this can lead to serious complications.
Methods of treating pathologies
Some of the diseases can be cured completely (epicondylitis, tendinitis, compression of the ulnar nerve, some arthritis) with timely treatment, others are incurable and constantly progress (arthrosis).
General principles of treatment (pain relief methods)
To treat all these diseases, means and methods are used that can relieve severe symptoms - pain, swelling, numbness, impaired mobility and sensitivity, etc.
The doctor prescribes:
- Non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs: Voltaren, Diclofenac, Nise.
- Hormonal drugs (corticosteroids): Kenalog, Dexamethasone, Prednisolone.
- Therapeutic gymnastics.
- Physiotherapy: paraffin therapy (exposure to heated paraffin), balneotherapy (mineral water baths).
Physiotherapeutic procedures promote rapid tissue restoration and help restore mobility to the joint.
Treatment methods for various diseases
| Pathology | Treatment methods |
| Injuries | First aid (cold compress for 24 hours, immobilizing the joint, applying a splint or plaster) If necessary, after an injury, the integrity of the tissues is restored by surgical methods (reduced, sutured), fluid is removed from the joint (puncture), drugs are prescribed that resolve hematomas and bruises: Heparin, Troxevasin, Lyoton. A few days later, vasodilators (Trental, Pentoxifylline), warming agents (Viprosal, Fastum-gel) are prescribed (help speed up healing) |
| Epicondylitis | The load is minimized, the elbow is immobilized (for 7 days) Anti-inflammatory drugs are used topically: Voltaren, Diclofenac |
| Arthrosis | In the early stages of arthrosis, long-term use of chondroprotectors (Dona, Structum, Artra, Teraflex) and the introduction of hyaluronic acid into the joint are effective - they help stop the destruction of cartilage and the progression of the disease |
| Tendinitis | The load is reduced or the elbow is immobilized (by applying a cast or splint for 10 days) |
| Carpal tunnel syndrome | Eliminate the cause that caused compression of the nerve (if there is a lack of nutrition or oxygen in the nervous tissue, vasodilators are prescribed (Trental, Actovegin); in case of injuries, the limb is immobilized) To relieve acute symptoms (pain, sensitivity disorders), diuretic medications are prescribed (reduce swelling): Canephron, Brusniver, kidney tea To restore nervous tissue - vitamins (Neurobion, Magne B6) and stimulants (aloe extract) |
| Arthritis | They use medications that eliminate or influence the causes of the disease (antibiotics - Cefepime, Amoxiclav, Metronidazole; antiallergic - Erius, Claritin, Suprastin; immunosuppressants - Methotrexate, Delagil, Remicade) |
1 – cold compress on the elbow joint; 2 – plaster cast; 3 – application of medicinal ointment; 4 – elastic bandage
What to do for pain in the elbow of various types
Elbow pain can have different origins and characters. To eliminate pain, you need to find out the cause of its occurrence. It is impossible to do this on your own; you will need to consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
Elbow pain during/after coronavirus and ARVI
Viral infections cause general intoxication of the body, which may cause pain in the joints, including the elbow. After recovery they go away.
But in some cases, viral infections become a trigger, triggering autoimmune processes in the joints. Experts note that coronavirus infection causes immunity disorders. In people with a hereditary predisposition, this can become a starting point (trigger) for rheumatoid arthritis. The disease does not develop immediately, but some time after the infection. Often the elbow joint is the first to be affected. What to do: consult a doctor immediately.
Elbow and arm pain
Painful sensations in the elbow and in the arm in general indicate the involvement of peripheral nerves in the pathological process. In the area of the elbow joint, the median, ulnar and radial nerves pass in narrow anatomical canals. With injuries, inflammation, overgrowth of bone tissue with arthrosis, the nerves are compressed, which is accompanied by pain in the elbow, radiating upward or downward, a crawling sensation, and movement disorders. These are the so-called tunnel syndromes, manifested by:
- pain in the arms from the elbow to the hand on the inside - indicates compression of the ulnar nerve; painful sensations on the outer side - a sign of compression of the radial nerve, in front of the forearm - the median; sometimes the clenching of the hand into a fist is disrupted;
- pain in the arm from the shoulder to the elbow indicates compression of the nerves in the brachial plexus, as well as pinched nerve roots in the neck.
What to do: take a pain reliever, immobilize the joint with a bandage and seek medical help. You may need the help of several specialists: an orthopedist-traumatologist or a rheumatologist and a neurologist. It is problematic to cure carpal tunnel syndrome on your own.
Elbow pain can spread throughout the arm - from the elbow to the shoulder and/or from the elbow to the hand
Pain in the right or left elbow
It could be:
- a consequence of acute injury or long-term microtrauma during habitual professional movements; with prolonged trauma, osteoarthritis develops in the joint - degenerative-dystrophic changes with periodically developing inflammation; the joint capsule, ligaments, and tendons may also be affected; what to do: contact an orthopedic traumatologist and carry out the treatment prescribed by him; You may have to change your profession or give up your favorite sport;
- acute arthritis - in addition to pain, swelling and redness of the skin over the joint appears, body temperature may rise; what to do: acute arthritis with a violation of the general condition requires immediate consultation with a doctor, since the process can become purulent in nature and threaten the patient’s life;
- chronic arthritis - asymmetrical damage to the left or right elbow may signal the onset of psoriatic or reactive arthritis; sometimes such an atypical onset appears in rheumatoid arthritis; pain can be of both joint and muscle origin (with muscle spasm), the course develops gradually, without pronounced symptoms; what to do: contact a rheumatologist and carry out all the prescribed treatment.
Elbow pain radiating to other areas
A feature of pain in the elbow area may be irradiation into nearby and relatively distant tissues. In case of irradiation:
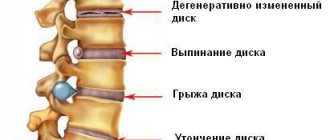
- in the hand and fingers - one can assume the presence of inflammation (neuritis) of the ulnar or radial nerve; pain along the peripheral nerves (neuralgia) can be a consequence of both direct damage to the nerves and compression at various levels in diseases of the elbow joint and osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic spine; with motor disorders, clenching the hand into a fist suffers; what to do: first you should contact a neurologist; you may need to consult a rheumatologist or orthopedist-traumatologist; acute short-term pain radiating to the left little finger may be of cardiac origin (angina attacks); if they appear for the first time, you need to immediately consult a therapist;
- to the scapula and back - the cause is most often cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, but sometimes irradiation can be transmitted along peripheral nerves in pathology of the elbow joint to the neck, scapula and back; short-term acute left-sided pain in the shoulder blade and back is always suspicious of diseases of the cardiovascular system; what to do: if there is pain on the left, it is better to start by consulting a therapist; if you have pain on the right side, you can immediately contact a neurologist;
- in the biceps (in the front side of the shoulder) - usually develops with osteochondrosis of the lower vertebrae of the cervical spine, as well as with neuritis of the branches of the peripheral nerves extending from the brachial plexus; what to do: contact a neurologist;
- in the chest - osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic spine, any pathology of the elbow joint leading to pinching of peripheral nerves, as well as diseases of the cardiovascular system, if the pain radiates to the left side of the chest; what to do: it’s better to start with a consultation and examination with a therapist.
Elbow pain on the inside
The inner side hurts when:
- injury to the internal collateral ligament of the elbow joint; this can be an acute injury (fall on the hand, blow) or long-term microtrauma; the result is a sprain, partial or complete rupture of the ligament; what to do: seek help from an orthopedist-traumatologist;
- tendonitis - inflammation of the muscle tendons attached to the inner surface of the joint; these are the longus palmar muscle, flexor carpi ulnaris and pronator teres; pain can be aching and acute, depending on the cause of the disease; what to do: contact an orthopedist-traumatologist.
Crunching in joints - when to worry
Joint pain at rest
Elbow pain with exertion
This kind of pain in the elbow most often occurs during excessive physical activity in athletes (tennis players, golfers, weightlifters), as well as in people with heavy physical labor. Pain in the elbow during exercise can occur when lifting weights, doing pull-ups, or doing push-ups - most often this is associated with microtrauma of the ligaments and tendons, accompanied by an inflammatory process. They cannot be tolerated, as the process can become chronic.
What to do: contact an orthopedist-traumatologist; if the soreness is associated with inflammation, you may need help from a rheumatologist.
Elbow pain when bending and straightening
Such pain indicates a pathology of the flexor and extensor tendons at the site of their attachment to the bone (epicondylitis). At rest, pain does not always occur. The cause is most often microtrauma, but sometimes inflammation associated with a chronic, silent inflammatory process in the joint.
What to do: to figure out why pain in the elbow appeared, it is better to contact a rheumatologist or orthopedic traumatologist as early as possible.
Pain often occurs when bending and/or straightening the elbow
Elbows and knees hurt
If symmetrical joints in the elbows and knees hurt at the same time, you need to consult a rheumatologist. Perhaps these are the first manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. In the future, the process is always accompanied by painful discomfort in the small joints of the hand and foot. You should not hesitate to consult a rheumatologist.
My elbow hurts and I have a lump
These symptoms are characteristic of bursitis - inflammation of the periarticular bursa of the joint. It is imperative to treat, otherwise the pain will intensify and become permanent. What to do: consult an orthopedist-traumatologist.
Elbow hurts when pressing
If there has been no acute injury, pain in the elbow when pressed is associated with inflammation in the joint or periarticular tissues. What to do: be sure to see a doctor. If you don’t know why there is pain when pressing on your elbow, then it’s better to start with a therapist, he will refer you to the right specialist.
Pain after falling on your elbow (bruises, fractures, dislocations)
In case of acute elbow injury (fall, blow), the victim must be given first aid. Algorithm:
- if the wound is open, then you need to treat it with an antiseptic: hydrogen peroxide, miramistin, any alcohol solution (only the edges of the wound can be treated with alcohol) and apply a sterile bandage;
- immobilize the limb; if the elbow bends, it may be a bandage; in case of dislocations and fractures, it is better to leave the limb in a position that causes a minimum of pain and apply a splint - any board or stick, bandaging it so as to completely limit movement in the joint;
- give the victim any painkiller - Analgin, Pentalgin, Nise, etc.;
- call an ambulance and do not refuse hospitalization: in case of a dislocation or fracture, surgical assistance may be required.
Causes of elbow pain
Elbow pain can be a consequence of many diseases and injuries:
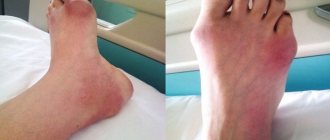
- Acute and chronic arthritis (inflammatory processes) of the elbow joint. The reason is infection entering the joint cavity, autoimmune (allergy to one’s own tissues) processes. In acute arthritis, redness, swelling, increased skin temperature over the joint, pain, and sometimes fever and general malaise appear. When arthritis takes a chronic course, the pain becomes moderate and aching, the swelling is insignificant, and there is no redness. You need to start treatment as early as possible; for this, in case of acute arthritis of one joint, you need to consult a surgeon; if several joints are affected at once or the process is erased, then consult a rheumatologist.
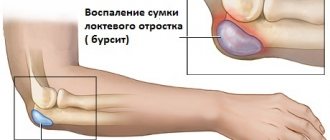
- Bursitis is an inflammation of the periarticular bursa (bursa). The disease develops against the background of microtrauma during constant performance of certain movements. Bursitis most often develops in the subcutaneous ulnar bursa (see Fig.), but can also occur in the radioulnar and interosseous ulnar bursa. It manifests itself as moderate pain and the appearance of a lump of dense elastic consistency in the elbow area. Bursitis is treated by an orthopedist-traumatologist.
- Epicondylitis, an inflammation of the muscle tendon where it attaches to the bony joint structure, can also cause elbow pain. Ulnar epicondylitis is divided into internal - with damage to the tendons of the flexor muscles attached to the inner surface of the head of the humerus and external - with pathology of the extensor muscles attached to the outer surface of the head of the humerus. Pain in this case appears respectively when flexing and extending the arm in the right or left elbow, as well as when pressing on the outer or inner surface of the head of the humerus. The reason for the development of epicondylitis is microtrauma during regular performance of monotonous work (painters, cooks) and sports activities (tennis, golf). Treatment consists of limiting exercise and anti-inflammatory therapy.
- Arthrosis is degenerative-dystrophic changes in the elbow that develop after injuries, inflammatory processes and in the second half of life, after the age of 50 years. Painful sensations of an aching nature, it is difficult to bend and straighten the arm at the elbow.
- Joint dislocation is a complete or partial (subluxation) divergence of articular joints. A dislocation develops when you fall backwards or forwards onto a straight arm, as well as from a direct strong blow to the joint. Symptoms: severe sudden pain, aggravated by moving the hand and clenching it into a fist, increasing tissue swelling. If such symptoms appear, you need to provide emergency assistance to the victim (see above) and call an ambulance. Reducing a dislocation on your own is strictly contraindicated: this can lead to a bone fracture, pinched nerves and blood vessels. In the hospital, diagnostics are first carried out, and then, under local or general anesthesia, the dislocation is reduced with the application of an immobilization bandage.
- Joint fracture - develops during acute injury, can be open (with a violation of the skin and protrusion of bone fragments onto the surface) and closed. Bone fragments may remain in the same position as normal (undisplaced fracture) or move (displaced fracture). Symptoms: severe sudden pain in the elbow, dry cracking, change in joint configuration and increasing swelling. After emergency assistance is provided, the victim is hospitalized and urgently examined. In case of a non-displaced fracture, an immobilization bandage is applied. A displaced fracture is operated on, the bones are connected, and only after that immobilization is carried out.
Elbow fracture a) without displacement of fragments, b) with displacement
Types of painful symptoms
The types of pain in the elbow are as follows:
- Referred pain. Present in disorders of the musculoskeletal system, in particular in cervical osteochondrosis. The development of atrophic syndrome of the biceps muscle is possible. It often causes numbness in the fingers. The nature of the pain is nagging.
- Projected. Appears when spinal nerves are compressed, with a herniated disc or after an injury.
- Pulling.
- Neuropathic. It is provoked by inflammation of the nerve endings in the presence of arthrosis or due to a bruise. When bending, a sharp pain is felt, accompanied by a burning sensation when straightening.
- Spicy. Mainly appears with injuries, bursitis or arthritis. Very strong, sharp, limits physical activity.
- Burning. Appears during inflammatory processes or when nerve endings are compressed. In this case, straightening the arm causes an intolerable burning sensation in the joint.
- Dull and aching. Talks about chronic diseases such as arthrosis and bursitis. It is constantly present, even when the hand does not move, but becomes stronger at the moment of flexion and extension.
How to treat elbow pain
Adequate treatment of elbow pain syndrome is possible only after a preliminary examination. It is impossible to carry it out at home. Non-severe patients are examined on an outpatient basis, but for acute illnesses and injuries, patients with elbow pain often require hospitalization.
Diagnostics
First, the doctor conducts a clinical examination of the patient, then he is sent for additional examination, including:
- Laboratory diagnostics - clinical, biochemical and immunological blood tests reveal inflammatory, metabolic and autoimmune processes.
- Instrumental studies:
- X-ray of the elbow joint - reveals dislocations, fractures and bone changes in inflammatory and degenerative diseases;
- MRI and CT are more accurate studies needed in doubtful cases when clarification of the diagnosis is required;
- Ultrasound – changes in soft articular and periarticular tissues;
- Diagnostic arthroscopy - performed according to indications when a purulent inflammatory process and the presence of blood in the joint cavity are suspected.
Methods for treating elbow pain
Specialists at the Moscow Paramita clinic treat diseases of the elbow joint only based on the results of the examination. Patients who require surgical care are hospitalized with a recommendation for rehabilitation in our clinic after discharge from the hospital.
If the patient does not require hospitalization, he is provided with qualified medical care. An individual treatment plan is drawn up for each patient, taking into account his underlying and concomitant diseases. Complex therapy includes:
- modern Western methods of treating diseases and injuries of the elbow joint, including drug therapy, effective complexes of therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy;
- traditional oriental treatment methods that help restore energy potential and eliminate pathological foci (courses of acupuncture, moxibustion, acupressure;
- various types of joint immobilization to eliminate additional injury to the elbow area, for example, taping; fixation with adhesive elastic tape, etc.
The Paramita Clinic has extensive experience in treating and restoring the function of the elbow joint. Carrying out preventive courses of conservative therapy allows our patients to forget about pain in the elbow and lead a normal life.
Diagnostics
Pathologies of the elbow joint are diagnosed using various methods:
| Diagnostic method | Purpose of the event |
| Inspection, survey, testing | The doctor finds out the possible cause of the disease, accompanying symptoms, and conducts tests to clarify the preliminary diagnosis. |
| Radiography | Allows you to identify displacement of parts of the joint during dislocations, damage, changes in bone density during arthritis, deformation during arthrosis and arthritis |
| MRI, ultrasound or CT | Prescribed if it is necessary to confirm damage or changes in the soft tissues of the joint, to determine where they are located |
| Arthroscopy (examination of the joint cavity from the inside through a puncture using a special endoscopic instrument) | Allows you to examine the intra-articular cavity in case of arthritis, arthrosis |
| Electromyography (assessment of muscle contractility), electroneurography (recording of an electrical signal as it propagates along a nerve) | Help determine the speed of the nerve impulse, the location of nerve compression, and the degree of its damage |
| Puncture (puncture of the joint followed by collection of synovial fluid in its cavity) | A therapeutic and diagnostic procedure is necessary if, after an injury, blood or a lot of fluid has accumulated in the joint, which prevents you from moving your arm |
| Laboratory examination of intra-articular fluid | Helps confirm a pre-established diagnosis, identify causative agents of the process or changes characteristic of certain diseases |
| Blood tests for rheumatoid factor, autoantibodies for arthritis, C-reactive protein, etc. | Directly or indirectly indicate the presence of inflammation |
Additional research methods: 1 – radiography of the elbow joint; 2 – arthroscopy; 3 – puncture study; 4 – electroneuromyography
FAQ
Why can pain radiate to the elbow from the neck area?
Most often, this is associated with cervical osteochondrosis.
Why does pain appear in the bend of the elbow?
The reasons may be different. This is often associated with tunnel syndrome - compression of the ulnar nerve by swollen tissue due to injury or inflammation.
If you have pain in the elbow joint, which doctor should you contact?
It is worth starting with a therapist, and after the examination he will refer the patient to an orthopedic traumatologist or rheumatologist.
Could soreness in the elbow area be muscle related?
Maybe. In case of injuries or hypothermia, muscles are injured and inflammatory processes develop in them - myositis. Muscles can also be damaged by various joint pathologies; they develop spasms and atrophy (decrease in volume), which is accompanied by pain.
What are the causes of redness and pain in the elbow area?
Redness and swelling of tissue are signs of inflammation - arthritis, bursitis, synovitis or epicondylitis.
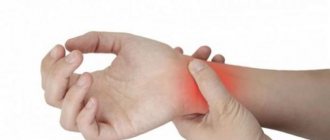
Cubital tunnel syndrome - what is it?
This is compression of the ulnar nerve in a narrow anatomical canal. Normally, the nerve passes freely through such channels, but when the surrounding tissues swell due to various inflammatory processes, it becomes compressed, accompanied by pain.
Elbow pain is not a death sentence. If it doesn’t go away, then you shouldn’t endure it. It is better to consult a doctor as soon as possible, find out what caused the pain and undergo a course of treatment. You can consult a doctor even with long-term pain, he will help you in any case.
Literature:
- Zorya V.I., Babovnikov A.V. Elbow joint injuries: a guide. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2010; 464.
- Mironov S.P., Burmakova G.M. Damage to the elbow joint during sports. M.: Lesar-art, 2000; 192.
- Hotchkiss R. Epicondilitis – lateral and medial. Hand clin., 2000;16; 505–8.
- Graham RG, Hudson DA, Solomons M. A prospective study to assess the outcome of steroid injections and wrist splinting for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Plast Reconstr Surg. Feb 2004;113(2):550–6.
Sign up for a free initial appointment
Which doctor should I see?
Pain when bending the elbow is a problem that is usually dealt with by traumatologists and orthopedists. However, other specialists are also involved. Family doctors or local therapists carry out the initial diagnosis of diseases that cause discomfort.
In cases where the cause of the pathology is osteochondrosis, consultation with a neurologist or vertebrologist is recommended. Doctors help you choose a combination treatment aimed at eliminating both problems with the spine and isolated problems with the joint. If necessary, the patient is referred for consultation to related specialists (cardiologist, endocrinologist).
The Shifa Clinic is a medical center where doctors of all these specialties are admitted. You won't have to wait in long lines. Just call the contact number and make an appointment at a convenient time. Our specialists will do everything necessary to ensure that you live an active, pain-free life!