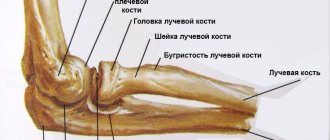
Flexion and extension are two multidirectional movements in the elbow joint that a person performs every day and does not think about it. However, as soon as pain appears, the patient begins to think about whether to bend the elbow or not, and performance and activity are impaired. Often the symptom indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the joint involving its medial structures. It is difficult to independently determine the cause of the pathological condition. This process must be entrusted to specialists. Traumatologists working at the Shifa clinic will quickly help identify pathology and eliminate its manifestations.
What is the severity of pain when bending the elbow?
Discomfort developing in the area of the elbow joint may indicate local inflammation. Due to the stretching of the joint capsule, the receptors that transmit pain information to the brain are irritated.
Characteristics of the symptom:
- moderate intensity - an exception may be traumatic injuries with a violation of the integrity of soft tissues;
- chronic course - most inflammatory diseases are sluggish with a gradual increase in the clinical picture;
- increased discomfort with physical activity and/or twisting of the arm.
Pain when bending the elbow may spread to nearby tissues. Most often, the patient also indicates discomfort along the muscles on the medial side of the forearm, shoulder, and thumb area. Rest and temporary peace reduce the intensity of discomfort.
The most common elbow injuries are throwing.
When athletes repeatedly throw at high speeds, the repetitive stress can lead to various types of injuries. Problems most often occur on the inside of the elbow because the most stress is placed on the inside of the elbow when throwing.
Flexor tendinitis
Repetitive throwing can cause irritation and inflammation of the flexor/pronator tendons where they attach to the humerus on the inside of the elbow joint. Athletes in such cases note pain on the inside of the elbow when throwing, and if the tendinitis is severe, pain will also be noted during rest.
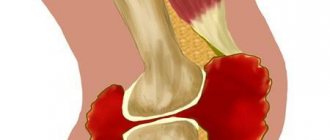
Ulnar collateral ligament injury
The ulnar collateral ligament is the most commonly injured ligament in throwing activities. Injuries to the UCL can range from minor damage and inflammation to complete rupture of the ligament. Athletes in such cases report pain on the inside of the elbow, and often notice a decrease in throwing speed.
Valgus overload during extension
During a throw, the ulna and humerus twist and push against each other. Over time, this can lead to valgus overload, a condition in which the protective cartilage of the olecranon wears away and excess bone growth (osteophytes) occurs. Athletes with valgus stress report swelling and pain at the point of maximum contact between the bones.
Stress fracture of the olecranon
Stress - fractures occur when the muscles are overworked and are unable to absorb the vector of force and absorb the blow. And, therefore, tired muscles transfer the load vector to the bone tissue, which leads to microcracks, which are called stress fractures.
The olecranon is the most common site of stress fracture in throwers. Athletes report aching pain along the surface of the olecranon process on the underside of the elbow. This pain is worse during throwing or other vigorous activity, but sometimes pain can also occur during rest.
Ulnar nerve neuritis
With the elbow flexed, the ulnar nerve runs along the bony eminence at the end of the humerus. When throwing, athletes experience repeated stretching of the ulnar nerve and sometimes displacement of the nerve from its location, which leads to the fiber slipping. This stretching or slipping causes irritation and inflammation of the nerve and is called ulnar neuritis.
With ulnar nerve neuritis caused by throwing, patients note a sharp pain (like an electric current) that begins on the inside of the elbow and radiates along the nerve into the forearm. Numbness, tingling or pain in the pinky and ring finger areas may occur during or immediately after throwing, and may also persist during rest.
Ulnar neuritis can occur not only with throwing injuries, but also with other conditions. Patients usually notice similar symptoms, usually in the morning, after the elbow has been bent for a long time.
What diseases may be associated with pain when bending the elbow?
About 70% of cases of elbow pain when bending are associated with chronic inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Arthritis, arthrosis (degenerative disease) most often cause discomfort when bending the elbow joint.
Other causes of the symptom in question are:
- systemic connective tissue diseases with damage to peripheral joints;
- injuries, sprains, cuts;
- pathology of the cervical spine with compression of the roots that innervate the upper limbs;
- congenital connective tissue dysplasia with dysfunction of the elbow joint.
Traumatologists and orthopedists at the Shifa clinic diagnose and treat pathologies accompanied by pain in the elbow when bending. Extensive practical experience, the use of modern treatment methods and an individual approach to the treatment of each patient help make recovery faster and more effective.
Training and stretching muscle structures
To improve the mobility of the elbow area, you can perform therapeutic exercises . If the disorders are associated with illnesses or injuries, physiotherapeutic methods . Therapeutic exercise differs from other exercises in its reduced range of motion and simplified pace:
- sitting on a chair, place your hands in front of you on the table, bend and straighten your fingers 8-12 times;
- sitting on a chair, bend and straighten the palms at the wrist joint 8-12 times;
- bend the arms at the elbow joint 10-12 times so that the elbows lie on the table;
- turn the forearm left and right, keeping the elbows at one point, repeat 8-10 times;
- put their shoulders on the table, point their arms up, bend them at the elbows, first holding the right hand with the left hand, then changing hands;
- sitting across the chair, place the left hand on the back, dangling the forearm, perform pendulum-like movements in the joint;
- hands lie on the table: press the surface with each finger for 2-3 seconds and relax, repeat 5-7 times;
- From the same position, bring and spread your fingers 6-8 times.
Now you can move on to exercises for the muscles that extend the arms at the elbow from a standing position. The limbs are spread apart and perform circular movements with the wrists, keeping the elbows strictly parallel. Repeat 10 times.
you can take a dumbbell weighing 400-600 g in the injured hand They lift it up and hold the elbow with their free limb. Bend the hand with a dumbbell and move it behind the head. It is necessary to touch the opposite shoulder joint with the projectile and return to the starting position. If it is difficult to perform while standing, sit on a chair without a backrest.
All movements must be slow and careful. If you experience sudden or severe pain during exercise therapy, it is important to consult a doctor.
Stretching - stretching for the elbow
Stretching is used in fitness and sports to increase the elasticity of weak or damaged muscle fibers . The technique is also necessary to improve the condition of tendons, which often cause limited joint mobility.
To improve the flexibility of the flexor radialis, the following exercises :
- Standing facing the wall, place your palm on it with your fingers up.
- Move your hand, without lifting it from the wall, up and down, move your fingers clockwise.
- The body is kept in a straight and motionless position, moving the hand as low as possible. Hold the position for 10-30 seconds.
Additionally, stretch the entire arm and wrist . This exercise is very useful in the development of tennis elbow pathology:
- The hand is extended in front of you.
- With the second limb, bend the wrist, bending it into a fist, towards the floor.
- Hold for 10-30 seconds.
Instead of your hand, you can use a wall, resting against it with the bent back of your hand.
The “tennis elbow” stretch can also be performed this way: the arm is extended in front of you, the second, together with the first, forms a loose lock, clasping only the fingers. The wrist of your top hand should point your fingers down. The injured limb is fully extended, the helping limb is slightly bent. Rotate your wrists in this position for 10-30 seconds.
Triceps stretching is also used when training arms. Place the limb on the upper back with the elbow bent. Pressing the second limb on the elbow, lower it as low as possible and hold for 20-30 seconds. You need to press lightly.
Why you shouldn't ignore pain when bending your elbow
Ignoring any disease leads to further progression. Pain when bending the elbow is no exception. The pathology that provokes the symptom can last for years. Many patients tend to endure discomfort, limiting their full range of movements. However, this gradually leads to loss of functional activity of the elbow with wasting of the corresponding muscles.
Secondary joint deformation in such situations is rare. The prognosis for the patient if adequate therapy is selected is favorable. Therefore, specialists at the Shifa clinic recommend not delaying treatment and seeking help as early as possible.
Causes
Elbow injuries occur in athletes and are the result of excessive and repetitive throwing stress. In many cases, the pain disappears after stopping the load (throwing or throwing). Typically, these injuries are rarely seen in other types of physical activity.
In baseball players, the rate of injury is highly dependent on the number of pitches, the number of innings pitched, and the number of games pitched over a given period of time. The heavier the ball and the speed of the throw, the greater the risk of such injuries. Additionally, athletes who continue to play baseball while experiencing pain are at greatest risk for injury.
Which doctor should I see?
Pain when bending the elbow is a problem that is usually dealt with by traumatologists and orthopedists. However, other specialists are also involved. Family doctors or local therapists carry out the initial diagnosis of diseases that cause discomfort.
In cases where the cause of the pathology is osteochondrosis, consultation with a neurologist or vertebrologist is recommended. Doctors help you choose a combination treatment aimed at eliminating both problems with the spine and isolated problems with the joint. If necessary, the patient is referred for consultation to related specialists (cardiologist, endocrinologist).
The Shifa Clinic is a medical center where doctors of all these specialties are admitted. You won't have to wait in long lines. Just call the contact number and make an appointment at a convenient time. Our specialists will do everything necessary to ensure that you live an active, pain-free life!
Diagnostics
Disease history
At the doctor’s consultation, first of all, the athlete’s health is discussed, the characteristics of sports activity, symptoms, the time of their appearance, and their relationship with stress. Medical checkup
During the examination, the doctor checks the range of motion, strength and stability of the elbow joint. The shoulder girdle is also assessed.
The doctor evaluates the elbow's range of motion, muscle development, and appearance, and compares the affected elbow with a healthy other elbow. In some cases, sensitivity and muscle strength are assessed.
The doctor finds out from the athlete the exact localization of pain and palpates both the painful area and neighboring areas to clarify the location of the pain.
To recreate the stresses on the elbow during throwing, the doctor performs a valgus stress test. During this test, the doctor holds the arm and applies pressure on the side of the elbow. If the elbow is weak or if this test causes pain, it is considered a positive test. It is also possible to use other functional tests.
The results of these tests help the doctor decide whether additional testing is needed.
Radiography makes it possible to clearly visualize changes in bone tissue and diagnose stress fractures, osteophytes and other changes in bone tissue. Computed tomography (CT). This diagnostic method is generally rarely used to diagnose throwing-related elbow problems. CT scans provide three-dimensional images of bone structures and can be useful in diagnosing osteophytes or other bone changes that may limit movement or cause pain.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This diagnostic method makes it possible to clearly visualize the soft tissues of the elbow (including the condition of the ligaments and tendons). MRI allows you to determine the degree of ligament damage (presence of partial damage or ruptures). In addition, high-quality visualization of all tissues makes it possible to diagnose microcracks in stress fractures, which are not always possible to detect with radiography.