Home > Pain in the arm
This article will describe a condition such as epicondylitis of the elbow joint, symptoms and treatment of this pathology.
So, this is the most common disease associated with overload of the muscles of the forearm, which is often also called “tennis elbow.” However, repeated wrist extension occurs not only in tennis players, but also in ordinary people. Most patients with so-called “tennis elbow” have never held a racquet in their hands.
What is epicondylitis of the elbow joint?
This is a common disease, which is characterized by gradual development, which, however, does not prevent it from becoming chronic. It manifests itself in the form of pain that regularly occurs in the area of the elbow joint. These manifestations may vary and depend on the type of disease. For example, pain can occur when a person simply bends his arm at the elbow or tries to grab or lift something with his hand.
Epicondylitis is one of the most common problems associated with the musculoskeletal system. However, there is no complete statistical picture, since not all people with elbow epicondylitis turn to specialists if the symptoms remain mild.
Types of disease
The disease is classified depending on the location of the inflammatory processes and their severity. The following types of illness are distinguished.
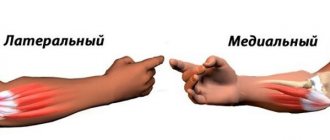
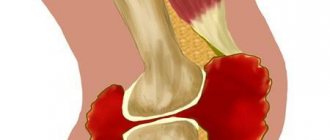
- External or lateral epicondylitis - the inflammatory process mainly spreads along the outer part of the elbow. This type of disease is also called “tennis elbow” because typical for professional tennis players. When performing grasping movements, carrying or lifting objects, there is a disturbance in the movement of the hands, which is accompanied by painful pressing sensations over the bones that enter the joint area.
- Internal or medial epicondylitis - localization of the inflammatory process occurs along the inside of the elbow joint. A person experiences discomfort in this area.
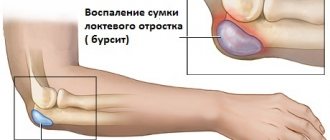
- Inflammation of the posterior area of the elbow - characteristic is the development of bursitis and damage to the mucous membrane of the bursa.
Security mode
Relevant for all types of disease, both during exacerbation and in remission. It consists of dosing loads and eliminating provoking factors:
- Change in the nature of activity or working conditions. Systematic muscle overstrain during work provokes the development of the disease; transfer to light work is recommended. For example, when working at a computer, it is desirable that the elbow joint is on the table, and the mouse pad is equipped with a special anatomical cushion that relieves the hand.
- The use of mechanized tools and process automation, alternating periods of work and rest.
- Dosing of sports loads and restructuring of the training program. Monotonous movements that require sudden movements of the hands are excluded. For example, in tennis, if symptoms of “tennis elbow” appear, it is recommended to reconsider the hitting technique, or select the optimal weight of the racket.
The protective regime should not be neglected. These simple measures will help stop the progression of epicondylitis.
Reasons for development
The main cause of epicondolitis is the loads that fall on the elbow area. This can include intense physical activity, power lifting, sudden movements, or not very intense, but regular and monotonous actions. They are usually associated with human activities - professional or amateur, sports. For example, they can be provoked by sports in which the hands are actively involved, and professions associated with carrying various heavy objects. It is the regular performance of monotonous movements, which are based on flexion and extension of the elbow joint with simultaneous load on the hands and forearms, that becomes a factor contributing to the development of the disease.
Another common cause is trauma and microtrauma. In particular, the cause of inflammation in the posterior area of the elbow is most often a fall on the elbow.
The risk group includes people with congenital connective tissue dysplasia. Often, people with thoracic and cervical osteochondrosis also develop epicondylitis.
Epicondylitis is more common in men. The risk of developing the disease is present in the more active hand, that is, right-handers are more likely to develop right-sided epicondolitis, and left-handers are more likely to develop left-sided epicondolitis.
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
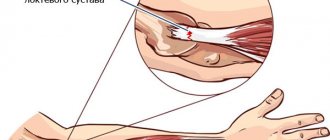
The elbow joint is formed by three bones: the humerus, as well as two bones of the forearm - the radius and ulna. In the distal part of the humerus there are two epicondyles: one is lateral, which is located outside, and the second is medial, it is located inside.
The area of maximum tenderness is usually the area at the lateral epicondyle, where the extensor muscles of the forearm begin. The extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle is most commonly affected, but the extensor digitorum muscle, extensor carpi radialis longus muscle, and extensor carpi ulnaris muscle may also be involved.
The radial nerve also passes in close proximity to this area, which here divides into the superficial radial nerve and the posterior interosseous nerve of the forearm.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms of epicondylitis can be divided into two main types.
The lateral form is characterized by pain and discomfort:
- locally in the outer area of the elbow;
- when moving;
- when twisting the arm with the elbow bent inward;
- when feeling the outer area of the elbow;
- when bending the hand or strongly clenching the palm into a fist.
The hand does not hurt when at rest or when performing passive movements.
The medial form is characterized by pain in the inner part of the elbow joint when the internal epicondyle is affected. Twisting the arm inward or bending it at the elbow leads to pain that radiates along the inner surface of the shoulder up to the armpit and towards the thumb.
It is not necessary to undergo heavy physical activity to develop internal epicondylitis. Loads can be relatively small, but regular. Therefore, people with the same type of constant loads fall into the risk zone - for example, seamstresses, machinists, golfers. This type of disease often occurs in women after lifting weights.
Are you experiencing symptoms of epicondylitis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Clinical picture
The most prominent symptom of lateral epicondylitis is pain, which can be reproduced by palpating the extensor muscles of the hand at their origin on the lateral epicondyle. The pain may radiate up the shoulder and down the outside of the forearm, in rare cases radiating to the middle and ring fingers. In addition, a common symptom of tennis elbow is decreased flexibility and strength in the extensors of the hand and posterior shoulder muscles.
Read about compression of the ulnar nerve here.
Based on the severity of symptoms, Warren described 4 stages of disease development:
- Mild pain a couple of hours after the provoking activity.
- Pain immediately after completion of the provoking action.
- Pain during inciting activity that increases after the activity ends.
- Constant pain that makes any activity impossible.
In addition, patients note that their grip strength decreases and they also experience difficulty carrying things in their hands, especially when the elbow is extended. This is explained by weakness of the extensor muscles of the fingers and supinators of the forearm. Some patients experience a feeling of paralysis, but this is rare.
Symptoms last on average from 2 weeks to two years. 89% of patients recover within one year without any treatment (the only thing they may do is avoid painful movements and avoid sports injuries).
When to see a doctor
Which doctor treats epicondylitis and in what case is it recommended not to postpone a visit to him? A specialist in the diagnosis and treatment of epicondylitis is an orthopedic traumatologist. Specialists from JSC “Medicine” (clinic of academician Roitebrga) provide consultations in the central district of 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane 10. Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya, Novoslobodskaya and Mayakovskaya metro stations are located nearby, within walking distance, which makes visiting the clinic as comfortable as possible.
Our main advantages are highly qualified specialists, high-quality equipment, affordable prices, the shortest possible time for conducting research, and an individual approach. Our specialists have accumulated invaluable experience in the successful treatment of epicondylitis.
Diagnostics
The basis of diagnosis for suspected epicondylitis is a thorough examination by a doctor and the presence of clinical manifestations of the disease. When compiling an anamnesis, it is imperative to find out the patient’s professional activity and his regular additional activities (for example, playing sports).
Changes in the elbow joint can only be detected as a result of a long course of the disease. In some cases, the doctor prescribes an x-ray or computed tomography to accurately diagnose epicondylitis. No laboratory tests are required for diagnosis.
Basic treatment methods
Current question: how to cure epicondylitis? If the disease has already been established, all further actions should be aimed at preventing exacerbation. Treatment methods are mostly conservative. These include:
- local use of drugs - treatment of epicondylitis with ointments is prescribed;
- ensuring rest in the area of the elbow joint - use an orthosis or bandage for epicondylitis;
- physical therapy – special exercises for epicondylitis help relieve pain, have a positive effect, and speed up the healing process;
- in case of severe pain, an injection for epicondylitis may be prescribed with the administration of corticosteroid hormones with anesthetics;
- in cases of advanced stage of the disease, extracorporeal shock wave therapy is prescribed.
This disease is characterized by a chronic course. Provided you follow all the doctor’s recommendations and gradually return to exercise, the treatment is quite successful. However, it should be understood that there is a high risk of relapse under conditions of heavy loads or injuries.
Exercises for epicondylitis often involve the mill and scissors. In addition, movements when the arms are bent at the elbows and the fists are alternately clenched and unclenched help improve blood circulation.
You need to bend and straighten your elbows, keeping your hands together. Movements must be performed extremely slowly and carefully. Another exercise: extend the forearm area using circular movements outward and inward.
In addition to simple exercises, there are exercises with strength loads on the arms. However, all of them must be prescribed by a competent doctor, taking into account the patient’s condition, the stage of development of the disease, general well-being, and level of athletic training. Exercises chosen incorrectly can simply harm the patient!
Remember that self-medication can be very dangerous. Most often, it leads to the disease reaching a severe stage, and the patient requires long-term, complex, and often expensive treatment. That's why you shouldn't delay seeing a doctor.
Therapeutic exercise (physical therapy)
It is recommended to perform special physical exercises only after the inflammatory process has stopped. The complex of therapeutic exercises helps restore muscle tone, tendon elasticity, and improves blood supply to tissues. Even in severe cases, exercise therapy should not be excluded. It is necessary to devote at least 20-30 minutes a day, and for people whose work involves monotonous workload, such exercises should be performed regularly, even in the absence of pain.
Postisometric muscle relaxation (PIR) is carried out by a physical therapy specialist, or a chiropractor, and consists of smooth stretching of the tendons and muscle groups of the forearm, alternating periods of resistance and rest, as well as performing special resistive exercises.
Before performing exercises, you should consult your doctor. Exercising during an exacerbation or premature training leads to muscle overstrain and worsening of the condition.
| Hand exercises | Hand exercises |
Prevention
Most often, tennis players, painters, carpenters, and massage therapists are exposed to the disease. If you belong to a risk group, you should definitely know what prevention should be for epicondylitis. Preventive measures include:
- primary actions are aimed at preventing the disease;
- secondary – the goal is to prevent exacerbation of an existing disease.
Both types of activities are based on the same recommendations.
- You should try to avoid or at least limit monotonous, stereotypical movements that will increase the load on the joint.
- To protect your elbow, you should wear an elastic bandage or elbow pad. This way you can ensure proper fixation of the tendons and distribute pressure evenly on the muscles. In addition, a light massage will be performed as you move.
- Before you play sports, you need to warm up your muscles. It is important to pay attention to warming up the joints, which will help improve blood circulation.
- It is necessary to perform exercises, maintaining adequate intensity and frequency, and give the body time for breaks.
- Sports equipment must be selected correctly, the load must be feasible.
- Shock absorbers and suitable protective pads and dressings should be used.
If, due to your chosen profession, you are at risk for epicondylitis of the elbow joint, then:
- try to be in a comfortable position while working;
- avoid monotonous movements;
- change your activities from time to time;
- be sure to take regular massage courses;
- watch out for spinal diseases;
- take mineral complexes;
- the diet should contain the required amount of vitamin D, as well as calcium (include cottage cheese and fatty fish in the menu);
- If you experience discomfort or pain in a joint, do not self-medicate with folk remedies, consult a doctor.
As for the prognosis, we can say: it is favorable if the patient consults a doctor on time. With proper treatment, relief occurs after 3-4 days. If the patient follows the doctor's instructions, long-term remission can be achieved.