Arthritis and arthrosis - which doctor treats these inflammatory processes? What are they and how to identify them?
These are very painful and unpleasant diseases that occur in people of different ages. Although these diseases can sometimes be confused by the presence of similar symptoms, in fact they are different, and they need to be treated comprehensively.
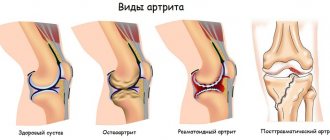
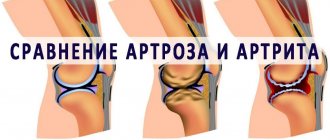
Osteoarthritis affects human joints, and arthritis is an inflammatory process that affects all organs. This is due to metabolic disorders, a malfunction of the immune system, or an infection that has affected the body.
Arthritis and arthrosis - which doctor treats these diseases? Where should a person go at the first symptoms?
How to recognize the disease?
Before looking for help in a clinic or hospital, you need to roughly understand what is happening to the body; it is advisable to know the signs of an emerging problem, so as not to trigger the disease and go to a specialist who treats arthritis. What kind of doctor is needed for this? After all, as everyone knows, it is much easier to be treated in the initial stage, and not in the advanced version.
With initial arthritis, joint pain is not very severe, only after serious physical exertion. Often people do not pay attention to this sign, thinking that the pain came simply from fatigue and overexertion. Later, the pain will not subside even with complete rest of the body, especially at night.
Simultaneously with the pain, a person hears a crunching sound and feels stiffness in the movements of the joint. With arthritis, you can experience many accompanying symptoms that affect the entire body. The temperature rises, the size of the tissue around the joint increases, there is drowsiness, weakness, unpleasant discharge from the genitals and even skin psoriasis may appear. Having such different symptoms of arthritis, a person does not always understand which doctor to contact.
Which doctor should I consult if I suspect arthrosis of the knee joints?
Pain in the joint and limitation of movement are observed quite often, but with such manifestations a person often does not know which doctor treats arthrosis of the knee joint. At different stages, certain specialists are involved in the treatment of this pathology.
Rheumatologist
This is a therapeutic doctor who should be contacted at the slightest sign of this disease. He is competent in matters of dystrophic and inflammatory lesions of the articular structure and connective tissues.
In the early stages, the following specialists are sometimes involved in its treatment:
- masseur;
- physiotherapist;
- arthroscopist;
- chiropractor;
- specialist in therapeutic exercises or physical education.
It should be noted that such a doctor uses only conservative methods of therapy. In this regard, he prescribes injections, medications and ointments to treat the pathology.
Arthrologist
This doctor treats arthrosis specifically. The difficulty is that it is quite difficult to get to a surgical specialist who deals specifically with joint disorders: such doctors are found only in highly specialized clinics.
- Which doctor treats arthrosis and arthritis of the joints?
Where to go for treatment?
Often, at the first sign of illness, patients are referred to their family doctor or general practitioner. This is a general specialist, in the end he will still refer you to another doctor, after making you run around the offices and take a bunch of tests, do a fluorogram, and will definitely refer the woman to a gynecologist. A lot of time will be lost, and the diseased joint will not receive treatment. Most clinics do not have a doctor who is a specialist who treats only joint diseases. Only a few private clinics or large treatment centers have arthrologists.
Often the therapist refers the patient to either a surgeon or an orthopedist. But the cause of the disease may be hidden inside the body. When choosing which doctor to see for arthritis, you need to understand that the problem needs to be solved comprehensively. Several specialists must take part at once. It all depends on the causes of arthritis or arthrosis. Let's take a closer look at them.
Treatment methods and follow-up features
The course of treatment by a rheumatologist depends on the specific disease and its severity. Unfortunately, in the case of degenerative and inflammatory diseases of bones, joints and connective tissue, treatment is usually long-term.
In most cases, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve rheumatic pain. Sometimes antibiotics and stronger analgesics may be prescribed. In severe cases, glucocorticosteroids are used, which suppress the immune system and have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect.
These and other drugs, which in addition to alleviating the symptoms of the disease, also inhibit the destruction of joints. Reception should be started as early as possible to avoid unpleasant complications and degenerative changes. It should be remembered that the nature of most rheumatic diseases is such that the pills must be taken constantly; withdrawal may cause a relapse.
Physiotherapy is also very important, thanks to which you can stop the progression of the disease, and sometimes even restore some motor functions of damaged joints. The doctor may prescribe procedures such as:
- Kinesitherapy . The technique is based on performing active and passive exercises that are designed to improve the functioning of diseased joints.
- Medical massage . Reduces muscle tension and stiffness, improves local blood circulation and blood supply to tissues.
- Electrophoresis . The procedure is a method of delivering drugs directly to the affected organ. The technology is based on the use of weak electric current discharges and injections. Electrophoresis helps reduce swelling, reduce pain, and speed up cellular metabolism.
- Ultrasound therapy . The method promotes the resorption of swelling and helps in the restoration of damaged tissue.
- Acupuncture . The technique helps to get rid of pain and accelerates regeneration processes.
Along with therapy, the doctor will give recommendations regarding lifestyle. The topic of proper nutrition with limited salt and maintaining a healthy body weight, as well as other preventive measures will be discussed: quitting smoking, maintaining a drinking regime, minimizing stress, etc.
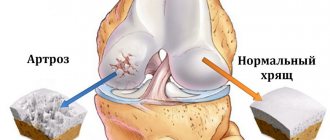
Causes of arthrosis
Arthrosis can occur in older people due to salt deposition and wear of cartilage tissue. But there is another type of arthrosis, which can often be observed in people involved in sports or heavy physical labor.
- Which doctor treats arthrosis of the joints?
But pathology occurs for many other reasons. Excess weight and improper metabolism, weakened immunity, poor nutrition and a violation of a healthy lifestyle contribute to the development of arthrosis. The joint can also become inflamed after severe hypothermia. The lesion can be caused by a number of infections, such as syphilis, gonorrhea, purulent arthritis, colds, severe toxin poisoning.
Various types of injuries, fractures and dislocations can contribute to joint inflammation. Diseases of the thyroid gland and blood also affect his condition.
Causes of arthritis
The causes of arthritis can be allergies, diseases of the nervous system, tuberculosis, gout, disruptions in the endocrine system, hormonal changes in the female body during menopause, lack of vitamins, alcohol and drug addiction. Arthritis can result from a simple bite of a poisonous insect into the joint cavity.
By analyzing all this, a specialist treats arthritis. Tests and studies will show which doctor the patient needs first. Therefore, it is impossible to answer this question unequivocally.
When choosing which doctor will treat the disease for arthritis, you need to correctly determine the cause of the disease and refer, in addition to the surgeon and orthopedist, to other necessary specialists.
Correct diagnosis
To determine the type of arthritis and arthrosis and which doctor treats this type of disease, you need to do a series of studies and collect anamnesis. The blood is checked for erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and the number of leukocytes and eosinophils is calculated. Based on the results, the doctor will understand whether a bacterial infection or allergy is present. For gout, a biochemical blood test is done. Checking immunological parameters will show the presence of rheumatoid arthritis.
X-ray examination will help determine joint degeneration and the stage of the disease. Ultrasound and computed tomography will show joints, especially large ones, in several positions, which will determine the condition of bone and muscle tissue. MRI is used in rare cases of spinal disc and ligament damage.
If necessary, arthroscopy is performed, taking a biopsy of tissue and fluid from the joint (usually the knee).
Kinesitherapy for joint pain
Pathological processes occurring in the joints for a number of reasons cause limited mobility, weakening of muscle tissue, and discomfort when performing normal movements and manipulations.
At the kinesitherapy center Doctor Osteochondrosis, treatment and restoration of joint mobility is carried out using special simulators. Rehabilitation under conditions of light local load allows you to strengthen the muscle corset and restore full mobility of the spine and joints. Such rehabilitation is absolutely safe, effective and painless for people with different types of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
The clinic has been operating since 1999, successfully treating pain of various locations. All classes are supervised by a specialist, and the load regimen is developed strictly individually.
The Clinic of Effective Kinesitherapy has centers in Zelenograd, Tver, Dubna and Klin.
Professional help for arthritis
Which doctor treats the patient is determined by the data obtained. A surgeon or orthopedist, rheumatologist or arthrologist may prescribe initial treatment. First you need to remove the inflammation and anesthetize the patient. Conducted anti-inflammatory drug therapy should be accompanied by ointments and gels that remove inflammation directly in the desired area of the body. Wearing products made from dog hair (knee pads, sleeves, belts, gloves) and special orthopedic devices will help.
- Arthritis 3 degrees
For bacterial arthritis, you need to take a course of antibiotics. Cartilage tissue is restored using chondroprotectors.
If a decrease in immunity is associated with poor nutrition or excess weight, then you will need to consult a nutritionist and endocrinologist. Proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle will help you recover faster from illness.
If the condition of arthritis or arthrosis is advanced, which doctor treats the patient is clear without any recommendations. This is a surgeon. During the operation, the destroyed joint is removed and a prosthesis is placed in its place.
Who treats osteoarthritis, which doctor will help
Osteochondrosis is an age-related, degenerative-dystrophic change in cartilage tissue in intervertebral discs and other large articular areas. If pain occurs, it is necessary to diagnose and prescribe treatment. To make a diagnosis of osteoarthritis, it is enough to consult a traumatologist. The competence of this doctor also includes monitoring the course of the disease of a particular patient. If there are no complications, then a regular therapist can monitor your health.
Treatment of osteoarthritis
Methods of treating osteoarthritis are predominantly conservative and are not much different from the tactics of treating other diseases of a degenerative-dystrophic nature. At the initial stages of development, exercise therapy and lifestyle modification are indicated. If the disease further progresses and provokes other complications, including the appearance of protrusion or hernia, complex conservative treatment is prescribed. In case of serious damage, manifested by extensive growth of a large number of osteophytes, a consultation with a surgeon is prescribed. This physician should consider options for surgical removal based on the specific clinical presentation.
Recovery after illness
For final recovery, a complex of procedures is carried out. This includes mud treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, acupuncture.
One of the main methods of additional treatment is physical therapy, namely joint exercises, which increases joint mobility and restores blood circulation in the right places.
With the help of such gymnastics, the world-famous circus performer and folk healer Valentin Ivanovich Dikul gives freedom of movement to many desperate patients every year. His treatment is based on active rehabilitation and kinesiology.
Prevention of arthritis and arthrosis
To avoid such problems or put them off for a long time, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat healthy and rationally, eating as many vegetables and fruits as possible. Preferably raw or after minimal processing. Cereals and dairy products, fish, poultry and lean varieties of beef are useful.
You also need to monitor your weight, then you won’t have to treat arthritis. Which doctor can help with this? Of course, a nutritionist. In reality, the diet is not so strict. You just need to get rid of the habit of drinking alcohol, fatty foods, salt, sugar, offal, and legumes. If necessary, you will need to take vitamins.
The most important thing is to move a lot, stay active until you are very old, then arthritis will not cause inconvenience and pain.
- Which doctor treats rheumatoid arthritis?
Joint diseases have become noticeably “younger”. And arthritis is not the least of them. But a person far from medicine cannot always distinguish it from other inflammatory lesions of articular tissues. To get medical help, you need to know what it is and which specialist to contact if you suspect this illness.
Causes of the disease
As paradoxical as it sounds, the disease affects older people much less often than young people and even children. This disease is quite insidious and difficult to diagnose, especially in the case of damage to the knee joints. And the reason is that it is an inflammatory process caused by various types of infections. Most often, the causative agents are staphylococci of various types, but there are also candida bacteria and other pathogens.
It seems that the immune system of young people is much stronger than the elderly, and they are much more active in movement and a priori should not suffer from joint pain. But doctors state that a tenth of young people have joint damage, and even children under one year of age suffer from it. Why is this happening? Modern doctors do not give a clear answer to this question. But the main causes of joint inflammatory infections are called:
- consequences of injury;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- hip dysplasia;
- diseases caused by infections;
- unhealthy food and extra pounds;
- hereditary predisposition;
- disruptions in the hormonal system.
To determine the type of arthritis, the doctor must prescribe a diagnosis and, based on the results, refer you to a doctor who treats these diseases.
These are just some of the causes of the disease. To determine the type of inflammatory infection, the doctor must prescribe a diagnosis and, based on the results, refer you to a doctor who treats these diseases.
Rheumatologist. What does it cure?
Let's look at the dictionary again. Rheumatologist is a doctor who diagnoses and treats diseases associated with damage to the musculoskeletal system, heart (acquired heart defects), as well as systemic connective tissue diseases, joint diseases - rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis, etc.
Thus, the rheumatologist
– a key specialist in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, gout, rheumatism.
But not arthrosis. There is a fundamental difference between arthrosis and arthritis. In arthritis, the soft tissue around the joint becomes inflamed. The main symptom of arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis is damage to the connective (soft) tissue around the joints, inflammation and swelling, pain and swelling of the joints, which are often accompanied by an increase in body temperature for no apparent reason. Arthritis, as a rule, is associated with other autoimmune diseases, for example, chronic tonsillitis, allergies, and can be caused by a staphylococcal infection, past purulent tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, or antibiotic treatment. Arthritis is, in fact, an inflammatory disease of the entire body, not just the joints
.
The rheumatologist offers very strict drug treatment - corticosteroid hormones, immunosuppressants, and all this, of course, together with antibiotics. At the same time , rheumatologists admit that it is impossible to completely recover from the disease, and medications only temporarily suppress inflammatory processes in tissues (and at the same time the immune system) . And such temporary relief, which is perceived as “treatment,” is very expensive for the body, the liver is destroyed, and the kidneys suffer. There is simply a gradual destruction of the human body, without any absolutely real chance of regaining health.
Autoplasmotherapy for the treatment of inflammation (arthritis) of joints
Autoplasma therapy is most effective for inflammatory joint diseases, pain, swelling, effusions (fluid accumulation), arthritis and arthrosis...
Symptoms of the disease and choosing a specialist
Arthritis is an inflammatory process and its threat is that not only the joints are affected, but also other organs, especially the liver, kidneys, and heart. The disease is divided into several categories, but each has common symptoms:
- Swelling.
- Redness of the diseased organ.
- Pain that gets worse at night.
All these indicators indicate the presence of infection and a malfunction of the immune system when it begins to fight against its own body.
The ideal option if you suspect the development of the disease would be to visit an arthrologist.
Arthritis can be primary or secondary, as a consequence of other diseases.
Primary is characterized as an independent disease, without obvious pathological damage to the body by other diseases.
- Rheumatoid – affects small joints, constraining them and limiting movement, a “tight glove” effect, accompanied by pain, swelling, and morning stiffness.
- Juvenile – covers elbows, knees, ankles. Children under 16 years of age are susceptible to it. Dangerous due to impaired development of skeletal bones and growth.
What kind of doctor treats these diseases? Of course, the ideal option would be to visit an arthrologist. This doctor specializes exclusively in the diagnosis and treatment of joint pathologies, as well as their prevention.
If you suspect rheumatoid type or lupus, then you need to go to a rheumatologist. But, given that this specialization is quite narrow, and not every clinic has doctors of this profile, then first of all you need to go to a therapist, and in childhood, to a pediatrician.
If the disease is primary, it is treated by one of the above-mentioned specialists. Rheumatoid and juvenile arthritis require consultation with an immunologist, since the root cause of its development is the body's autoimmune reaction.
If you suspect the rheumatoid variety or lupus, then you need to go to a doctor - a rheumatologist. Gout is the accumulation of salts in the joint tissues with the formation of tophi. It most often affects the big toe.
Gout requires treatment in parallel with the nephrologist’s prescriptions, due to the fact that its development is provoked by kidney disease. In addition, you will need to go to a doctor-nutritionist, since uncontrolled consumption of chocolate products, natural coffee, strong tea, alcoholic drinks, and protein foods can trigger a relapse.
- Spondylitis is inflammation of the vertebrae. It is characterized by limitation of the motor function of the spine, up to paralysis, changes in the physiological structure of the spinal column and its deformation.
- Osteoarthritis is the destruction of cartilage on the surface of a joint. It is fraught with irreversible restrictions on motor activity.
If the source of pain is concentrated in the area of the spinal column, then consultation with a vertebrologist is necessary. He is the one who treats spinal pathologies. But such doctors are also quite rare. If it is not possible to see a specialist doctor, then the first step is to visit a therapist who will determine the further course of treatment.
When is it time to see a specialist?
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a chronic disease, the main symptom of which is the thinning and gradual destruction of cartilage, which causes deformation of the joint and disruption of its function. Gonarthrosis, as the pathology is also called, is divided into several groups according to severity. The main manifestations of the disease are the following:
- pain in the knee when walking;
- pain in the joint during movements;
- crunching in the sore area;
- stiffness in the knee in the morning.
The cause of gonarthrosis is various factors, including the following:
- Injuries: in youth, this type of arthrosis often occurs due to dislocations and fractures.
- Increased stress: overly active sports can lead to microtraumas and sprains. Such conditions, especially with age, cause thinning of the cartilage tissue.
- Excess weight: It increases pressure on the knees and can cause meniscus damage.
- Varicose veins: in combination with excess weight, it often leads to a severe form of gonarthrosis.
- Joint diseases: arthrosis is often a consequence of arthritis. The inflammatory process during such a disease greatly affects the structure of cartilage tissue and contributes to its destruction.
- Problems with metabolic processes: if the body suffers from a lack of certain substances, this immediately affects the condition of the cartilage.
Old age can also be a cause of the disease, since over time the joint structure wears out and cannot withstand the loads that it could handle before.
For reference! Gonarthrosis is more often observed in women and is caused by a combination of excess weight and varicose veins.
Symptoms and treatment of pathology are interrelated and depend on the degree of development of gonarthrosis.
Secondary arthritis as a concomitant pathology
Against the background of some underlying disease that is not diagnosed and not cured in time, or is difficult to treat, inflammation of the joints may begin, as a result of weakened immunity and the inability of the body to independently produce antibodies to suppress infectious bacteria. Such pathologies include:
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- psoriasis;
- granulomatosis;
- tuberculosis;
- hepatitis;
- borreliosis.
In addition to the three characteristic symptoms, with secondary damage, rashes, rashes, and plaques appear.
If arthritis develops against the background of psoriasis or systemic lupus erythematosus, you will need a dermatovenerologist. When fighting a disease caused by hepatitis, tuberculosis or borreliosis, you will need the help of a therapist and an infectious disease specialist.
In the most severe cases, the disease can only be treated surgically, or even with the help of prosthetics. In these cases, the patient is treated by a surgeon, physiotherapist, orthopedist, and traumatologist. Considering that the disease also affects the internal organs of a person, sometimes it may be necessary to involve doctors such as a cardiologist, urologist and other specialists. The condition of the affected bones and the detection of the disease are monitored by ultrasound doctors and radiologists.
Treatment methods for arthrosis and arthritis are different. Arthritis is characterized by the presence of a focus of inflammation, causing symptoms such as:
- redness of the skin;
- pain, swelling of the affected joint;
- local and general high temperature;
- general malaise;
- increased sweating;
- rarely conjunctivitis.
How to treat joint arthritis and what tactics to choose is determined by a highly specialized doctor, depending on the causes of the disease.
Which doctor treats arthritis depends on the type of disease
Treatment involves the use of complex therapy, which includes:
- Medication.
- Physiotherapeutic.
- Physiotherapy.
- Spa treatment.
- Ethnoscience.
- Diet.
- Surgical methods of treatment.
Some types of arthritis, such as infectious, have a very favorable prognosis and can be cured, subject to timely diagnosis and early proper therapy.
Arthrosis is a secondary type of disease caused by changes in bones and joints:
- as an outcome of a pathological inflammatory process;
- previous illnesses or due to age-related changes;
- disturbances in the body's metabolic processes.
Often the occurrence of arthrosis is associated with excessive mechanical stress, as a result of which the spongy, loose substance of the bones is damaged, the integrity of the blood vessels is disrupted, and a characteristic crunch appears in the affected joint. With further development of the disease, deformation and destruction of the affected bones and changes in their structure occur.
Leading doctors for patients diagnosed with gouty arthritis can be a rheumatologist, endocrinologist and nutritionist
In the later stages, arthrosis is incurable. However, with the right treatment regimen, it is possible to stop the further development of the disease and avoid irreversible changes in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system.
The following have proven themselves well in the treatment of arthrosis:
- corticosteroids prevent bone destruction;
- Chodroprotectors that stimulate the regeneration of cartilage tissue;
- NSAIDs that inhibit the process of inflammation;
Painkillers, sometimes by intra-articular injection.
Most often, when treating a disease, you will have to consult several doctors.
As a rule, after diagnosis, the therapist, depending on the form of the disease, refers the patient to doctors with a narrow specialized focus:
- Traumatologist
- Orthopedist
- Rheumatologist
- Surgeon
- Arthrologist
If the test for C-reactive protein is positive, and the quantitative indicator indicates that the cause of inflammation of the joints was rheumatism, then you should contact a rheumatologist.
This doctor prescribes therapy for rheumatoid arthritis, the characteristic manifestations of which are:
- general and local (in the affected area) increase in temperature;
- history of illness of viral or bacterial origin;
- deformation of the articular cavity, changes in the composition of the joint fluid;
- limited mobility of affected bone joints.
The specialist draws up a treatment regimen, including the use of cytostatics, NSAIDs, immunosuppressants, and vitamin and mineral supplements.
As the inflammatory process progresses, arthritis is subject to surgical treatment in a hospital. Observation and treatment of traumatic, purulent and other forms of severe stage disease is carried out by a surgeon. When a joint is deformed or fragmented, surgical intervention is necessary, after which a long period of rehabilitation under the supervision of a specialist is required.
You should contact a doctor of this specialization if:
- the synovial cavity and ligamentous apparatus are affected;
- with deformation of bone joints under the influence of destructive factors or genetic predisposition;
- the occurrence of prolonged painful manifestations in the affected area;
- surgical treatment with the use of prostheses and synthetic joint lubricants is necessary;
- it is necessary to select the type of reduction in limb mobility, special means that reduce the load on the diseased joint.
An orthopedist is able to provide emergency assistance in case of exacerbation of the disease, injuries, defects and deformations of the human movement apparatus.
A doctor with a narrow specialization aimed at performing diagnostic operations and treating diseases of the joints, ligaments, and periarticular soft tissues. This specialist is able to perform surgery through a micro-incision to diagnose joint disease - arthroscopy. Carries out the selection of medications for drug treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures and preventive measures.
The clinical picture at the onset of the disease is not always clear. Symptoms are weak and uncharacteristic, which makes diagnosis difficult. Early seeking competent help increases the chances of recovery.
Diagnostics is based on general data:
- initial examination;
- familiarization with the medical history and clinical picture;
- X-ray results;
- laboratory test data (urine, blood, synovial fluid punctate);
- cytological studies;
- ultrasound, MRI, CT data;
- arthrography results;
- examination of the patient.
A detailed examination is based on the patient’s specific complaints. Areas of concern are examined through palpation and tapping, determining tenderness, swelling, stiffness, and lameness.
After the initial examination, laboratory tests necessary to make an accurate diagnosis are prescribed:
- general detailed blood test with leukocyte formula;
- clinical urine analysis;
- biochemical blood tests;
- rheumatic factor test;
- tuberculosis test;
- complex of allergy tests;
- examination of synovial fluid punctate;
- histological examination of tissues;
Laboratory tests alone are not enough to determine the extent of the disease and predict its development.
Modern methods of hardware diagnostics make it possible to extremely accurately determine the form of the disease, the degree of pathological processes, deformation and other changes in the normal picture of the area under study.
To do this, the following diagnostic procedures are performed:
- X-ray - allows you to detect pathological changes in tissues.
- Ultrasound, CT - allow you to determine the stage and clarify the nature of damage to joints and soft tissues.
- MRI is also prescribed for suspected damage to the ligaments, tendons and nerve endings.
- Arthroscopy is a study performed using an endoscope inserted through a microscopic incision to diagnose the affected tissue.
- Based on the research, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient, the scheme and type of therapy are determined.
The effectiveness of the treatment process depends on when the disease was diagnosed and the correctly selected therapeutic regimen.
Therapy for this disease consists of several methods:
If other methods of therapy are ineffective, surgical interventions are used, for example, endoprosthetics, arthroscopy for therapeutic purposes, and others.
- Traditional medicine, which includes decoctions, tinctures, compresses, rubbing, acupuncture, treatment with medicinal leeches, bee stings.
- Spa treatment.
- Maintaining a proper lifestyle and nutrition.
Arthritis is a disease that is difficult to cure, but can be controlled. With timely diagnosis and proper therapy, it has a favorable prognosis. However, treatment can take a long time and require patience from the patient.
Treatment tactics depending on the stage of the disease
Since the course of arthrosis of any joint has a clear stage, characterizing the degree of involvement of the joint in the pathology, the treatment methods and the choice of the doctor differ significantly. With the initial manifestations of arthrosis of any joint, the main direction of help for the patient is conservative therapy. Principles of treatment at stage 1 of arthrosis:
- improving blood flow in the joint;
- increased production of synovial fluid;
- increased activity of movements;
- strengthening the muscles and ligaments involved in the functioning of the joint;
- stabilization of the joint and prevention of progression.
“Doctors are hiding the truth!”
Even “advanced” ARTHROSIS can be cured at home! Just remember to apply this once a day...
Basic therapy methods:
- taking medications: chondroprotectors, NSAIDs, peripheral vasodilators;
- weight loss to ease stress on the joint, especially in the limbs;
- correction of concomitant diseases, in particular cardiovascular and endocrine pathologies;
- use of exercise therapy and massage courses;
- conducting acupuncture;
- appointment of physiotherapy sessions.
Therefore, the following specialists participate in the complex treatment of arthrosis:
- therapist;
- endocrinologist;
- physical therapy doctor;
- physiotherapist;
- rheumatologist;
- in the presence of concomitant severe pathology - a cardiologist.
A therapist supervises treatment for stage 1 arthrosis of any joint . He acts independently, but with the support of specialized doctors. It is with a visit to the local therapist at the clinic that the diagnostic and treatment process should begin.
Stage 2 arthrosis is borderline regarding further tactics of helping the patient. Initially, conservative therapy is always carried out, especially in the presence of systemic inflammation in the body. The leading specialist who corrects the treatment is a specialized doctor . It is extremely important to stop the progression of the disease, since when it moves to the next stage, surgery will be inevitable. The patient is usually prescribed:
- enhanced drug therapy, including chondroprotectors, NSAIDs, hormones, and sometimes cytostatics;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- exercise therapy;
- injection of drugs into the joint cavity.
Usually, treatment does not end with outpatient care; At least 3 courses per year of active inpatient influence on the joint are required. Oral therapy is combined with parenteral therapy, and often intra-articular administration of drugs is indispensable.
At stage 2, the disease is already fixed, and it is almost impossible to reverse the process. Therefore, it is extremely important to seek medical help at the earliest manifestations of the disease. If the patient’s quality of life and ability to work cannot be restored by conservative measures, then the question arises of radical surgical correction using endoprosthetics. The patient is monitored by a rheumatologist and therapist, but regular consultative contact with an orthopedic traumatologist is necessary to choose the best tactics for helping the patient.
There are situations when conservative treatment is ineffective at stage 2. Among the pathologies:
- rapidly progressing process;
- necrosis of the femoral head;
- intra-articular fractures;
- the presence of vascular insufficiency due to injury or varicose veins;
- gross aesthetic defect;
- inability to perform daily work;
- a sharp deterioration in the patient’s quality of life;
- contraindications for taking maintenance medications.
In these cases, the doctor who treats arthrosis becomes an orthopedic traumatologist, since prompt assistance to the patient is necessary.
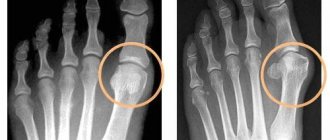
Stage 3 on x-ray.
At stage 3 of the disease, conservative measures have only a symptomatic effect. With their help, you can reduce pain, but it is no longer possible to establish activity in the joint. Therefore, with the consent of the patient and the absence of contraindications, the patient undergoes a radical operation - joint replacement. If it is impossible to install a prosthesis for technical or other reasons, then an orthopedist can also help the person.
Another operation is performed - fixation of the affected joint - arthrodesis. This does not cure the patient, but it improves his quality of life. If possible, a patient with stage 3 arthrosis is monitored by an orthopedic traumatologist, who decides on the advisability of radical intervention. This decision is often made, since endoprosthetics is the only way out for the patient’s rehabilitation.
Diagnosis of diseases
When the first signs of the disease appear, you must immediately contact a specialist who can correctly diagnose and prescribe therapy. First you need to decide which doctor treats arthritis and who to go to to get help. If this is your first time experiencing this problem, you should contact your GP. The specialist will prescribe a comprehensive medical examination and tests, based on the results of which he will refer you to a doctor with a more specialized profile.
Differential diagnosis includes:
- blood chemistry;
- x-ray of joints and sacroiliac joints;
- UAC;
- rheumatic tests;
- MRI and CT;
Depending on the symptoms and diagnostic results, the patient is referred to a rheumatologist, nutritionist, orthopedist, surgeon, traumatologist or arthrologist.
IMPORTANT! Before starting treatment, it is necessary to find out the cause of the disease and differentiate arthritis from other diseases.
Warning signs of the disease
Arthrosis is a disease that has a number of nonspecific signs that make themselves felt during the development of the second stage of the disease.
What are the signs to suspect the disease:
- Prolonged crunching in the joints that does not stop during movements. If you start walking slowly but continuously, your condition may improve slightly.
- Feeling of morning stiffness when moving. It takes 10 to 60 minutes for mobility to improve.
- Periodic manifestations of pain that occur when the affected area is loaded.
- The pain subsides or weakens during a period of rest.
- The joint may swell and become red if there is inflammation there.
- Gait and coordination are impaired.
Depending on the location of the lesion, there are diagnostic tests that can be used to understand the degree of stiffness in a certain area. Example - if it is difficult for a patient to bend forward in the morning, and he feels pain and stiffness in the lower back, then this indicates signs of spondyloarthrosis. Limitation of hip mobility when flexing the knee joint indicates gonarthrosis. If there is pain in the pelvis that prevents you from moving your leg forward when walking, this may indicate coxarthrosis.
How to distinguish arthrosis from arthritis of the joints
Arthrosis is an age-related disease that results in joint deformation. The disease affects only the joint membrane; the rest of the body does not suffer from this disease. Most often, arthrosis affects the hip and knee joints, as well as the joints of the big toes. The pain is not severe and appears after physical activity or movement. Therefore, patients do not rush to see a doctor, but begin to self-medicate. Very often the disease is advanced arthritis.
ATTENTION! Self-medication can further aggravate the disease.
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease that affects not only the joints, but the entire body as a whole. Most often the kidneys, heart, and liver are affected. The disease can begin to manifest itself at a fairly young age - after 30 years. Inflammation is expressed in joint swelling, redness and severe pain that worsens at night. This inflammatory process is explained by the presence of an infection or a malfunction of the immune system, which directs all forces against its own body.
Among the types of arthritis, the most common are: rheumatoid, arthritis of the lower extremities, in particular, arthritis of the knee joint and foot, as well as arthritis of the fingers. A doctor who treats these diseases can distinguish between arthritis and arthrosis.
IMPORTANT! If arthritis of the lower extremities is treated incorrectly, complications may arise in the form of gonarthrosis or coxarthrosis.
Risk factors
Arthrosis is considered natural and inevitable from the point of view of aging of the body, but with appropriate treatment its progress and the degree of damage to the joint can be reduced. There are a number of factors that contribute to the early onset of this degenerative disease:
- hereditary factor (the risk of vulnerability of the knee joint is higher if similar pathologies have been observed in the family);
- increased load on the lower limbs due to excess weight;
- atrophy or dystrophy of the muscles of the lower extremities;
- knee injury, trauma or surgery in this area in the past;
- systematic microtrauma of the structural elements of the knee (in athletes, miners and representatives of other professions);
- a large number of births and menopause in women;
- age after 40 years;
- impaired metabolism;
- other dysfunctions of the spine or the entire musculoskeletal system.
People who have one or more risk factors should see their doctor for a follow-up consultation at least once every five years.
Causes of the disease
The disease can develop very slowly (chronic form) or quickly and unexpectedly (acute phase). The cause can be any pathological process in our body. That is why it is very important to seek help from a specialist and find out which doctor treats the disease.
Medical research identifies several main causes of arthritis:
- infectious diseases;
- hypothermia;
- limb injuries;
- specific lesions of articular tissue;
- gout;
- immune system disorder;
- heredity.
Treatment
The main therapy is aimed at relieving pain, inflammation, restoring motor function, and identifying the cause of the disease. Often, after treatment of the underlying disease, remission and complete recovery occur.
The classic treatment regimen for arthritis of any etiology includes:
- Drug therapy.
- Exercise therapy.
- Diet.
- Orthopedic devices.
- Physiotherapy.
- Taking vitamin complexes.
IMPORTANT! Treatment with folk remedies is allowed, but only during a lull in the disease.
Drug therapy
Nonsteroidal drugs, antibiotics, and chondroprotectors are used in the treatment of arthritis. Anti-inflammatory drugs relieve inflammation, reduce swelling and pain. If necessary, a puncture of the inflamed area is performed, and antibiotics and steroid hormones (Dexamethasone, Kenalog) are injected into the joint cavity. The affected cartilage tissue is restored with the help of chondroprotectors. Arthritis of the feet and fingers can be successfully treated with ointments, gels, and creams with anti-inflammatory and cooling effects.
In advanced cases, surgical intervention is possible to replace the diseased joint using artificial materials. Thus, for arthritis of the knee joint, replantation or reconstructive surgery will help restore the diseased joint and prevent further development of the disease.
IMPORTANT! During treatment, it is necessary to reduce the load on the diseased joints as much as possible: long walking and heavy lifting are excluded.
Exercise therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures
Drug treatment should be carried out in combination with physiotherapy and exercise therapy.
Physiotherapeutic procedures include:
- diadynamic;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- mud - and paraffin treatment.
IMPORTANT! All activities are carried out during the remission process. For arthritis of the foot, exercises are performed only in a lying position.
Orthopedic devices
Treatment of arthritis of the knee joint and feet never takes place without auxiliary orthopedic devices and shoes. A regular cane, knee pad, and tight bandage will help reduce the load on the inflamed area and reduce pain.
Special energy-absorbing shoes should have hard or convex soles.
Diet
An important aspect of treating arthritis is proper nutrition. A nutritionist will help you create the right daily diet, which will include vegetables, fruits, cereals cooked in water, as well as foods rich in calcium. It is better to avoid eating fatty, salty foods, meat, and offal.
Diagnostic features and general treatment strategy
Diagnosis of gonarthrosis is carried out using the following main methods:
- X-ray: helps to see bone deformations - changes in the shape of the knee joint and the width of its gap. However, it is quite difficult to identify the first degree of pathology using radiography.
- Ultrasound: provides information about thinning of cartilage tissue and damage to the menisci. This type of diagnosis is usually combined with some other.
- MRI: allows you to detect the disease at the earliest stages. This method makes it possible to detect any degenerative changes, including swelling in the muscle area.
These types of diagnostics do not exclude a comprehensive examination of the patient.