Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic systemic disease of connective tissue with predominant damage to peripheral (synovial) joints of the type destructive-erosive polyarthritis. Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis has ICD code No. M05.8, seronegative rheumatoid arthritis – M06.0. Probable rheumatoid arthritis in the ICD is defined with codes M05.9, M06.4, M06.9. Rheumatologists at the Yusupov Hospital, using the latest research methods, establish an accurate diagnosis and promptly prescribe adequate treatment.
To avoid unnecessary examinations, adhere to the following tactics:
- The true localization of the lesion is clarified (joint or periarticular structures);
- The nature of the lesion is determined (the predominance of the inflammatory or degenerative process);
- Determine the extent of the lesion (local, limited or generalized);
- Carry out differential diagnosis.
Doctors solve these diagnostic problems before settling on a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. During treatment, patients are kept in rooms with a European level of comfort. They are provided with dietary food and individual personal hygiene products. Severe cases of rheumatoid arthritis are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council. Candidates and doctors of medical sciences, doctors of the highest category take part in its work. Leading specialists collectively develop patient management tactics.
Causes
Primary gonarthritis develops more often after injuries, operations and infection of open wounds. Secondary - against the background of other diseases: gout, rheumatism, psoriasis.
Other factors influencing the development of the disease are:
- hypothermia, frostbite;
- excess weight;
- changes in joints due to tumors;
- disturbances in metabolic processes and the endocrine system;
- uncomfortable shoes.
People over 25 years of age are at risk, but 70% of cases of the disease are diagnosed in elderly patients. The negative impact of arthritis extends to other organs: kidneys, heart, liver.
Diagnosis of knee arthritis
Diagnosis of knee arthritis is possible at the earliest stages of the disease, when cartilage erosion is completely reversible with the help of drugs for the treatment of knee arthritis. Therefore, if you experience the slightest discomfort in your knees, it is better to consult a doctor. Late diagnosis is the main reason why the disease enters the chronic stage.
To evaluate symptoms and treat knee arthritis:
- initial examination of the patient (visual assessment, joint palpation, mobility testing, gait observation);
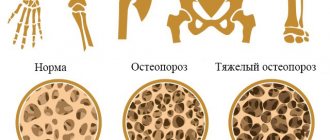
- radiography (detects the presence of osteoporosis, microcracks, osteophytes and neoplasms, narrowing of the joint space, disruption of the natural position of bones in the joint and other characteristic signs);
- Ultrasound of the knees (determines changes in cartilage tissue, fluid accumulation in the joint);
- general and biochemical blood test (to assess the inflammatory process);
- blood test for rheumatoid factor (to diagnose or exclude rheumatoid arthritis);
- arthroscopy (a minimally invasive technique for examining a joint from the inside through a microscopic incision);
- joint fluid sample (to identify pathogenic microorganisms, reduce viscosity, assess specific cellular and protein composition);
- computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (to collect information about the condition of soft tissues);
- scintigraphy (demonstrates disease activity and bone tissue condition).
Using these methods, a doctor (rheumatologist, traumatologist or orthopedist) excludes bursitis, arthrosis, muscle pain, cysts and other symptomatically similar diseases, and prescribes highly specialized medications for the treatment of arthritis of the knee joint.
Since various factors can provoke the inflammatory process, differential diagnosis is important, with the help of which the type of arthritis is determined.
Cost of arthritis treatment
| Services list | Price, rub |
| Initial consultation with ORTHOPEDIST | 1600 |
| Repeated consultation with ORTHOPEDIST | 1200 |
| Consultation with an ORTHOPEDIST in a cycle | for free |
| Therapeutic puncture of the joint and joint capsule | 5500 |
| Intra-articular administration of drugs, without consumables | 4400 |
| Plasmolifting (Orthoplasma) into the joint | 7000 |
| Intra-articular injection (diprospan) | 5500 |
| Complex taping (joints) 1 zone | 1600 |
| Complex taping (joints) 2 zones | 2200 |
| Intra-articular blockade | 5500 |
| Paravertebral plasma | 6500 |
| Initial consultation with a kinesiotherapist | 1600 |
| Interim consultation with a kinesiotherapist | for free |
| Session with a kinesiotherapist (1 patient) | 3900 |
| Individual lessons with a personal trainer | 2700 |
| Intra-Articular PRP Injection | 7000 |
| Manual therapy 1 department (15 min.) | 2700 |
| Soft manual techniques (30 min.) | 4500 |
| Osteopathic techniques (30-75 min.) | 7000 |
| Kinesio taping 1 zone | 1100 |
| UVT 1 procedure | 2000 |
Contact us
Call now
8 (495) 803-27-45
Make an appointment through our service
Make an appointment
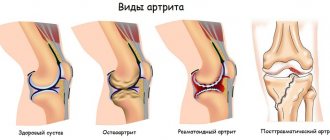
Degrees and stages of knee arthritis
There are 4 stages of the pathological process:
- Arthritis of the knee joint 1st degree. There are usually no obvious symptoms. There may be slight morning stiffness of the joint, slight swelling, and increased fatigue. With grade 1 arthritis of the knee joint, the pain is not severe and is periodic and irregular (“pinched”). At this stage, doctors usually give a positive answer to patients' questions about whether knee arthritis can be cured. A complete cure is possible.
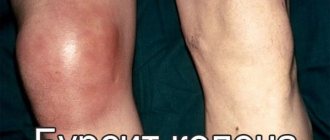
- Arthritis of the knee joint 2 degrees. The pain syndrome is noticeably expressed, swelling of the joint is clearly visible. An unpleasant crunching sound may occur when bending your legs. With grade 2 arthritis of the knee joint, redness of the skin and a local increase in temperature begin.
- Arthritis of the knee joint grade 3. From the side, the deformation of the joint is noticeable, the patient’s gait changes. The pain is felt constantly, interfering with normal daily activities and significantly limiting the patient even when taking medications for knee arthritis.
- Arthritis of the knee joint 4 degrees. The joints become ankylosed (fused) and almost completely lose mobility. Irreversible changes affect the bones. The leg muscles suffer from contractures, and the ligaments shorten. At this stage, surgery is required.
Features of the disease
The very name of the disease indicates a serious change in the shape of the joints.
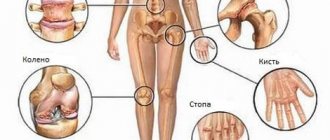
Deforming arthritis of the elbow, knee or other joint is a disease that is caused by its inflammation. Doctors distinguish several types of pathology, namely monoarthritis and polyarthritis. In the first case, inflammation and deformation of only 1 joint is observed. With polyarthritis, several connections are affected at once. Often, with this course of pathology, the hands and fingers of the upper and lower extremities suffer. Monarthritis usually affects the shoulder, hip, knee or elbow joints.
The international classification ICD 10 contains information about deforming arthritis. The designation of the pathology varies. It depends on the location of the lesion and the cause of the development of the disease itself. The stage of arthritis and the characteristics of its course are also taken into account.
For deforming arthritis, the following designations are highlighted in ICD 10:
- Acquired deformities of the fingers on the lower or upper extremities – M20.0-M20.6;
- Joint contracture – M24.5;
- Osteophytes – M25.7;
- Other limb deformities – M21.0-M21.9.
A special code for arthritis deformans allows you to find it in the international classification of diseases, which greatly simplifies the task of studying the characteristics of joint disease.
Folk remedies as auxiliary therapy
Unconventional methods of therapy will help reduce symptoms, but they are not able to cope with the disease
Treatment with folk remedies is allowed. In order to eliminate deforming arthritis, many patients use unconventional methods of therapy. The best way to cope with this task is:
- Warm baths with the addition of decoctions based on medicinal herbs and pine needles;
- Compresses with burdock (wrapping a sore joint with its leaves);
- Camphor-turpentine rubbing with vodka and vegetable oil.
When applying compresses and lotions, it is recommended to carefully wrap the sore joint. Leave them for several hours. It is optimal to keep the lotion on the affected area throughout the night.
It must be remembered that folk remedies are not able to stop the development of deforming arthritis. They are designed to relieve painful symptoms that haunt a person. Therefore, unconventional methods should not be taken as the main therapy. Recovery is brought only by a course of treatment prescribed by a qualified specialist in the clinic.
We understand the terms: arthrosis, arthritis and arthrosis-arthritis
Arthrosis-arthritis of the knee joint – inflammation of the joint and destruction of cartilage tissue
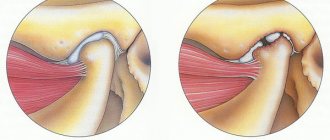
Arthrosis-arthritis of the knee joint is a disease associated with simultaneous inflammation of the joint capsule and degeneration of cartilage tissue. The pathology is characterized by the symptoms of these two diseases, which makes its course very difficult. To accurately understand the essence of the problem, you should understand the specific terminology.
Arthritis is an inflammation of the joint, the joint capsule and the tissues around it. Arthritis varies due to its development and nature. Reasons for the development of pathology:
- joint injuries;
- infectious diseases;
- hypothermia;
- immunity disorders;
- genetic predisposition.
Arthritis can develop against the background of chronic diseases such as gout and psoriasis. This pathology primarily affects small joints, but can also spread to large joints.
Arthrosis is a degenerative disease that affects cartilage tissue. Reasons for its development:
- excess weight;
- strong systematic loads on the joint;
- injuries;
- salt deposits;
- posture disorders;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes.
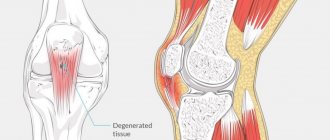
With arthrosis, cartilage tissue loses its elasticity, becomes covered with cracks and gradually collapses.
With arthrosis, particles of cartilage get into the joint and irritate it. This also increases the friction between the bones of the joint, which causes pain and impaired motor function of the joint.
Osteoarthritis is a disease in which the knee joint becomes inflamed and cartilage tissue is destroyed. In this case, there is an increase in pressure inside the joint due to increased production of synovial fluid due to arthritis, and increased bone friction due to the destruction of cartilage tissue.
Thus, the disease is accompanied by severe symptoms, due to which the motor function of the knee joint deteriorates.
Osteoarthritis is a complex joint disease. This requires timely diagnosis and therapy. This disease requires an integrated approach to treatment. As a rule, middle-aged and older people experience arthrosis-arthritis; the disease practically does not occur in young people.
Exercise therapy - physical therapy
Physiotherapy consists of laser irradiation, ultrasound (to reduce the inflammatory process). To improve blood circulation and develop muscles, it is recommended to undergo a course of massages, hydrotherapy, and electrical stimulation. Recently, cryotherapy has become popular, aimed at relieving pain and activating metabolic processes in tissues. In some cases, doctors insist on immobilizing the limb and applying a splint during the recovery period.
In cases where treatment of post-traumatic arthritis does not produce any results, the doctor insists on surgical intervention. When pus appears in the joint capsule, synovial fluid is aspirated. If the joint is deformed, then endoprosthetics is performed. When areas with dying tissue of the periarticular region appear, necrectomy is performed.
Nutrition for knee arthritis
A diet for knee arthritis includes low-calorie and low-carbohydrate foods, excluding foods that can cause allergies. It is advisable to eat food with a minimum amount of salty and smoked foods, but with an increased amount of calcium and vitamin D3.
For knee arthritis, nutrition should include fatty fish, animal cartilage, jellied meat, jelly and other sources of collagen, antioxidants and fatty acids.
We hope this material helped you understand how to cure knee arthritis! Be healthy!
Physical therapy for knee arthritis
Daily therapeutic exercises for knee arthritis help slow the progression of the disease and reduce the load on the joint by strengthening the muscles and connective tissue. It also reduces pain and discomfort, helps maintain and even restore mobility in the joint.
Examples of exercises for knee arthritis:
- Stand straight, with your back to the wall. Raise your leg to the side so that your shin is touching the wall and your big toe is facing forward, then lower it.
- With your arms folded across your chest, sit on a chair, keeping your back straight. Slowly rise from the chair, and then slowly lower yourself down.
- Standing straight, lift your ankle behind your back so that your heel touches your buttocks. Do not help yourself with your hands unless this is indicated in the exercise for knee arthritis! After 3 seconds, lower your leg.
- Lie on your side on the floor and place your bent arm under your head. Bend your knee and hip joint approximately 90° and lift your knee as high as possible.
- Lying on your stomach, rest your forearm on the floor in front of you. Bend the knee opposite your forearm and, grabbing your ankle with your hand, slowly pull your leg up. During exercises for knee arthritis, the muscles on the front of the thigh should stretch. Then roll over onto your back and, holding your leg under your knee, pull it towards your chest, feeling the stretch in your back muscles.
- Perform the “lying bicycle” exercise until noticeable signs of fatigue appear. Avoid suddenly throwing your leg forward - if the leg muscles are not strong enough for prolonged work, it is better to return to the exercise later.
All exercises for arthritis of the knee joint should be performed 15 times on each leg or (for example, “bicycle”) for at least 1 minute.
Creating an individual set of exercises for knee arthritis and teaching the correct technique should be carried out by a qualified instructor.
Please note that exercise therapy for knee arthritis is only allowed in a state of remission. When arthritis worsens, rest is advisable.