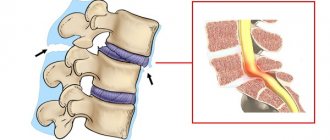
Vertebral instability is one of the common reasons for seeking medical help. This pathology causes a feeling of discomfort in the affected part of the spine and is caused by increased non-physiological mobility between the vertebrae due to degeneration of the intervertebral discs, sprain of the spinal ligaments, weakening of the muscle corset or as a result of gross mechanical impact on the spinal structures, i.e. trauma. At the same time, the spine, and more often one or more of its segments, are not able to remain in their normal physiological position and maintain it when a person is at rest and especially in motion.
Instability of the cervical and thoracic vertebrae is caused by their displacement in different directions. This pathological condition can appear at any age, and the lack of timely medical care can lead to serious complications in the event of compression of the spinal cord and to profound disability of the patient. You can undergo a course of treatment for instability of the cervical vertebrae at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic. Our highly qualified spine doctors and neurosurgeons have a whole arsenal of modern tools that allow us to return our patients to normal life.
At CELT you can get advice from a neurosurgeon.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Types of instability, their causes
Instability of the thoracic or cervical vertebrae can be caused by various reasons. In accordance with them, it is customary to distinguish the following types:
- post-traumatic - appears due to dislocations or fractures of the vertebrae;
- degenerative - appears due to the development of degenerative processes in the spine against the background of other diseases;
- postoperative - appears due to excessive load on the spine during rehabilitation after surgery;
- dysplastic - appears as a result of pathological processes in the connective tissue of the vertebrae, their joints and ligaments.
Clinical manifestations
Instability of the cervical or thoracic vertebrae has a number of clinical manifestations:
- pain symptoms localized in the affected part of the spine or spreading to the entire spinal column, accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and discomfort;
- increased pain when the body remains in an uncomfortable, forced position for a long time, after physical exertion or lifting heavy weights;
- limitation of mobility, which is expressed in difficulties when turning and bending the body;
- pain in the lower extremities when walking;
- headaches and dizziness;
- the appearance of crunching and clicking sounds when turning and bending the body;
- a feeling of numbness in the back muscles in the affected area.
Establishing diagnosis
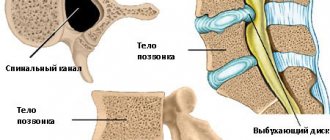
The most optimal action in diagnosing vertebral instability is fluoroscopy. Although, as already noted, it will not immediately and not always clearly show how displaced the vertebra is and whether it is displaced at all. But if mobility is pronounced, hypermobility will be detected in the flexion and extension positions of the patient. In a neutral position, it can only be confirmed indirectly.
The second diagnostic technique, more sensitive and revealing, is MRI. But even this method will only show structural instability.
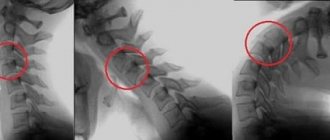
Displacement of the cervical vertebrae (example)
The most commonly used test is with the patient lying on their stomach. At the same time, the hips are lowered from the table and hang down, and the feet touch the floor. With maximum relaxation of the lower back in this position, the doctor palpates the area. The patient's legs are then raised up and palpation is performed again. The pain difference is taken into account.
Raising straight legs back while lying on your stomach on a bench
In a tense position, the pain should be minimal or absent; when relaxed (initial position), the pain is felt to a greater extent. Instability thus manifests itself in a resting posture when the muscles are unable to stabilize the vertebrae.
Complications
Often, the stability of the vertebrae can be a signal of the development of a disease such as osteochondrosis. At the initial stage, it may practically not manifest itself - however, as the pathology progresses, even one unsuccessful movement or a slightly more intense load than usual can cause severe pain. Due to the mobility of the vertebrae, the development of osteochondrosis occurs much faster and will ultimately lead to complications in the form of arthrosis of the intervertebral joints. Due to instability of the vertebrae, the load on the muscles and ligaments is significantly increased, which leads to impaired muscle tone and the appearance of pain symptoms when sitting for long periods and trying to perform simple movements. In the absence of proper treatment, pathology can lead to the following consequences:
MRI of the spine
- Cost: 16,000 rub.
More details
- neurological disorders;
- restriction of movements;
- spasms;
- headaches accompanied by nausea and weakness (with damage to the cervical vertebrae);
- development of spondylosis.
Lack of stability
In essence, instability is the absence of stability. And when it comes to the spine, it is its structural elements, in particular the vertebrae, that are unstable.
Noteworthy is the inconsistency of the term from a medical point of view. An unambiguous interpretation of the concept has not been finalized
In any case, in medical practice it means a disruption of the normal movement process of the vertebrae, which leads to pain and gives rise to neurological symptoms.
Varieties
A distinction is made between functional (or clinical) and structural (or radiological) instability. This means that the full term includes both clinical symptoms and radiographic findings of hypermobility.
Functional
Clinically, everything is simple - this is the inability of the vertebral structural elements to withstand normal loads, their failure to perform shock-absorbing functions. More precisely, they perform their functions without collapsing or offering resistance, but in this case pain occurs.
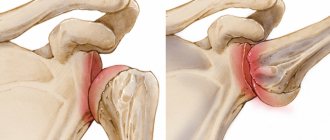
Impaired spinal stability
In fact, functional pathology is illusory in nature. For example, a person experiences stress and gets psychosomatic problems. The manifestation of the disease is present, but only in dysfunction, and not in changes in structure. In other words, no instability is visualized. X-rays do not show pathological changes; everything in the vertebrae and intervertebral structures is smooth and in its place. But changes have already begun in the nervous system, for example, multiple sclerosis has developed. The nerve does not control the muscle and is not able to give it a timely impulse to relax or contract. And at this time, the spine is constantly under load, and instability occurs, that is, the spine’s ability to withstand the load weakens. The body signals these changes with pain.
Structural
As for the structural variety, this problem is directly related to the inability to provide passive support to the spine. It can involve all structural elements - from ligaments to bones.
An example is destruction, damage, deformation of a vertebra with spondylolisthesis or a disc with osteochondrosis. Sooner or later the final range of mobility will be limited, and the patient will experience pain when crossing the restrictive threshold.
Instability of the cervical vertebrae
Unlike the functional appearance, structural immobility is very clearly visible on an x-ray (which is why it is called x-ray).
To identify this type, it is enough to take an x-ray, which will clearly show hypermobility of the segment.
Image of the spinal column
To diagnose structural instability, a series of photographs are taken in which the patient alternately bends back and bends forward from a sitting position.
That is, during X-ray diagnostics, for the first image the patient leans forward, and for the second, he leans in the opposite direction.
Functional images
Signs of structural instability are as follows.
- The discrepancy in the X-ray images of the angles of the edge plates is 10° or wider.
- The vertebrae are displaced in relation to each other by 5 mm or more.
Obviously, hypermobility of the spinal segment manifests itself visually. Clinically, it may not reveal itself in any way. And functional lumbar instability can occur without manifestations of hypermobility if the load effect is normal. Pain occurs as a clinical symptom only when either the intervertebral disc or the nerves located in it are overstressed.
Pain syndrome occurs during hyperexertion
Diagnostics
Before starting treatment for instability of the thoracic vertebrae, our specialists conduct diagnostic examinations to correctly determine the cause and make a diagnosis. This is very important because it ensures that the treatment will bring the desired results. In addition to the examination and history taking, the following is prescribed:
- traditional and functional radiography of the spine, which allows you to determine the location of displaced vertebrae, the degree of displacement, the severity of the curvature of the spine and a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs; the presence of congenital anomalies of insufficiency of the posterior supporting complex - spondylolysis.
- Magnetic resonance imaging, which allows you to detect the presence/absence of damage to the discs, nerves and spinal cord.
Pathogenesis
Most often, the fifth lumbar vertebra is subject to displacement; this happens much less often with the fourth.
Failure of the connection of the vertebrae as a result of a violation of the integrity of their arches or underdevelopment of the articular processes leads to pathological mobility. As the disease progresses, destructive changes occur in the intervertebral disc: the nucleus pulposus is absent, and the annulus fibrosus dissects. Over time, a gap forms in the disc, into which nearby tissues penetrate.
In addition to the disc, the structure of the bodies of the displaced and underlying vertebra also suffers. The terminal plates become thin, the spongy substance loses its beams, and many cystic formations appear. All these changes contribute to the destruction of the vertebral body. In the terminal stages of the disease, the intervertebral disc may be completely absent. And the resulting joint is subject to arthrosis, which is quite severe.
The aggravation of the process leads to a narrowing of the spinal canal, which at this level contains the “cauda equina” - the final section of the spinal cord.
The basic principle of the biomechanics of displacement of the lumbar vertebrae is that the pelvis gradually tilts backward, and the lumbar lordosis (natural curvature, forward deflection) increases.
Reviews of doctors providing the service - Vertebral instability
In 2000, Andrei Arkadyevich performed spinal surgery on me.
Four days in the clinic and I have been living a full life for 20 years without restrictions on movement and I remember with gratitude Dr. A.A. Khodnevich. God bless him. And in 2000 he could walk no more than 10 meters. Read full review Viktor Alexandrovich
20.05.2020
Low bow to Alexander Semenovich Bronstein and Andrei Arkadyevich Khodnevich. I arrived at CELT on July 2, 2021 with extreme pain that I endured for 10 days. Hernia C6-C-7. I was given two blockades in Ivanovo, about 9 complex IVs, I lost 6 kg in a week and was in a panic, I didn’t see a way out and nothing happened to me... Read full review
Elena Nikolaevna L.
20.10.2019
Treatment
The treatment plan for vertebral instability is drawn up taking into account the patient’s individual indications and the results of diagnostic studies. The following treatment methods are distinguished:
| Methodology | Description |
| Conservative treatment |
|
| Treatment with medications |
|
| Surgical techniques |
|
Operations for diseases of the spine
- Cost: 100,000 - 250,000 rubles.
- Duration: 40-60 minutes
- Hospitalization: 2-3 days in hospital
More details
It is worth noting that surgical intervention is practiced only in the most extreme cases, when the following indications exist:
- conservative methods did not produce any effect;
- there is vertebral subluxation;
- neurological symptoms are present;
- frequent relapses of the disease.
Surgical intervention involves fixing unstable vertebrae using special metal structures or implants.
Prevention
In order to minimize the risk of developing vertebral instability, the following rules must be followed:
- perform exercises aimed at strengthening the muscular frame of the back;
- Healthy food;
- eliminate intense stress on the spine;
- Lead an active lifestyle and exercise regularly.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Spondylosis - clinics in
Choose among the best clinics based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment
Family
Oriental Medicine Clinic "Sagan Dali"
Moscow, prosp. Mira, 79, building 1
Rizhskaya
+7
- Consultation from 1500
- Diagnostics from 0
- Reflexology from 1000
Write your review
Family
Center for Chinese Medicine "TAO"
Moscow, st. Ostozhenka, 8 building 3, 1st floor
Kropotkinskaya
+7
- Consultation from 1000
- Massage from 1500
- Reflexology from 1000
Write your review
Family