Osteochondrosis is one of the most common spinal diseases these days. Its cause is deformation of the vertebral discs, which occurs due to various injuries, insufficient blood supply to any area, hereditary defects, metabolic disorders, as well as as a result of a sedentary lifestyle or excessive stress (during sports or heavy physical labor, for example). Treatment of the spine always requires an integrated approach, including a whole range of means - from the use of medications to physical therapy. Physiotherapy is one of them.
What are the stages of this disease, and how do they differ?
Like any disease, osteochondrosis goes through several stages in its course, at each of which its own treatment methods are recommended. There are four such stages in total:
- The first is practically asymptomatic, but destructive processes already begin inside the spinal discs, and the spine itself becomes more susceptible to injury.
- The second is characterized by more pronounced disorders, which are revealed during examination. During this period, the intervertebral spaces narrow.
- The third is characterized by the appearance of obvious deformation, determined visually, and even a hernia. Pain syndrome may also occur. At this stage, the patient often seeks medical help himself with complaints of pain with sudden movements. Symptoms depend on the location of the diseased area.
- The fourth stage is the most difficult. As a result of pinched nerve endings, the patient experiences severe pain, which can lead to complete immobilization.
To avoid the occurrence of intervertebral hernia, treatment of osteochondrosis should begin as early as possible, at the first signs of disruption of the proper functioning of the spine, without waiting for the manifestation of severe pain.
How do physiotherapy methods work?
In the early stages, the use of physiotherapeutic procedures is especially effective. Their specific use depends on the location of the affected area. There are osteochondrosis of the cervical, thoracic or lumbosacral regions. It should be emphasized that during periods of exacerbation of the disease, it is better to suspend most procedures, but in each specific case this must be decided by the attending physician.
As a rule, physiotherapy is used not as an independent method of treatment, but in combination with others - medication, physical therapy. It not only helps to quickly restore a diseased organ, but also makes it possible to significantly reduce the unwanted effects of medications on the body, which are not always harmless. Physiotherapeutic procedures, in the absence of contraindications, have virtually no harmful side effects and consequences. When using them, the following happens:
- blood microcirculation in the diseased area increases;
- pain syndrome is eliminated;
- the immune system is activated;
- the supply of diseased areas with nutrients and oxygen improves;
- there is a general anti-inflammatory effect on the body;
- a therapeutic effect is provided not only on the affected area of the spine, but also on nearby tissues and organs.
Treatment of osteochondrosis with a magnet in Moscow
The Yusupov Hospital provides magnetic therapy (2 fields) and other physiotherapeutic procedures for the treatment of spinal osteochondrosis. Magnetotherapy refers to additional physiotherapeutic methods that help heal the spine in severe diseases of the musculoskeletal system. The hospital uses innovative drugs to treat osteochondrosis and uses effective methods of rehabilitation therapy. You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
What types of physical therapy are there?
Physiotherapeutic methods can be natural or artificial. Natural factors include exposure to natural factors - healing waters, mud, sun, sea bathing, etc. Artificial is a hardware effect that imitates the work of natural sources.
A person receives natural health treatments when undergoing spa treatment. Artificial - this is what, in fact, is called physiotherapy. Her patient has the opportunity to undergo treatment not only on vacation in a sanatorium, but also in a clinic at his place of residence. The most common methods of artificial or hardware physiotherapy are as follows:
- Electrophoresis. A procedure often prescribed for various lesions of the spine, during which the patient, under the influence of a weak current, penetrates the skin of medicinal substances.
- Magnetotherapy. The method is based on the effect of a magnetic field on the diseased area. Has a healing and analgesic effect.
- Ultrasound. The procedure provides micro-massage of the required areas using ultrasonic vibrations.
- Ultraviolet radiation. Simulates the effect of the ultraviolet spectrum of sunlight. Has an analgesic, bactericidal, anti-inflammatory effect, promotes the synthesis of vitamin D.
- Shock wave method. It is the use of an acoustic wave of a certain length and intensity, which has an analgesic effect.
- Laser therapy. Laser treatment gives several effects at once - pain relief, inflammation relief, stimulation of metabolic processes, wound healing.
- Detensor therapy. During this procedure, special mats are used to stretch the spine.
- UHF. It is the use of ultra-high frequencies for deep heating of soft and bone tissues.
- Electrotherapy. The method is based on the direction of electric current of various frequencies to the affected areas, which is usually used in combination with electrophoresis and the use of therapeutic mud.
Impact of magnets
The magnetic field has a positive effect on the human body:
- Elimination of the focus of the inflammatory process in the area of the affected vertebrae.
- Normalization of lymphatic drainage.
- Improved blood circulation.
- Pronounced analgesic effect due to blocking active nerve fibers.
- Reduced blood viscosity.
- Increased effect of other treatment methods (conduction effect).
- Normalization of metabolism and restoration of damaged tissues of the vertebrae and cartilage.
- General improvement in the functioning of blood vessels and muscle tissue.
- Relaxation of back muscles, improvement of overall mobility of the spine.
When identifying the cervical type of osteochondrosis, magnetic therapy helps eliminate such characteristic signs of the disease as dizziness, headaches, and chronic weakness. All this reflects favorably on the overall course of the disease.
Devices for magnetic therapy
To successfully perform magnetic therapy, a fairly large number of different medical devices have been developed. In the clinic, large stationary devices with remote control are used. By pressing the buttons, the doctor can adjust the intensity of the magnetic field and the duration of its influence to the required zone. The duration of one magnetic therapy procedure is 20 minutes. When using high-frequency exposure, the session can last up to 15 minutes.
The following types of devices can be used:
| Device type | Peculiarities |
| Tape recorders | Create a constant influence of a magnetic field. Usually they are fixed to the affected area and left for a long period |
| Micromagnets | Microdevices are attached with adhesive tape to painful points. The doctor determines the attachment points and marks them with a marker. Such devices create an alternating magnetic effect |
For magnetic therapy, only special medical magnets are allowed to be used. Attaching homemade devices is strictly prohibited - this can only worsen the patient’s condition.
The effect of the procedures
Advantages of magnetic therapy for spinal osteochondrosis:
- Low price for medical procedures.
- Lack of habituation effect to magnetic therapy.
- The procedure is completely painless.
- The possibility of carrying out magnetic therapy at different ages for adults and even children (practice for children from three years old).
- Possibility of using procedures in combination with other types of therapy.
- The full course of treatment allows you to achieve lasting positive dynamics.
- The procedure is not contraindicated for patients with hypersensitivity (its tactile form).
- Strengthening the therapeutic effect of taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Safety of the procedure (subject to contraindications, magnetic therapy does not have a negative effect on other organs and systems).
After completing a course of magnetic therapy, the achieved effect of treatment lasts for 2-3 months. To prolong it, parallel treatment with physiotherapy and medications can be carried out.
Results after completing a full course of magnetic therapy:
- improved blood circulation;
- increase in working capacity;
- elimination of the inflammatory process;
- pain relief;
- relief of congestion in the spine;
- normalization of metabolism;
- elimination of the process of destruction of cartilage tissue and their restoration.
The general course of treatment with magnetotherapy for spinal osteochondrosis is ten sessions. To consolidate the achieved therapeutic effect, treatment can be repeated no earlier than a month after completion of the first course.
Physiotherapy methods used for osteochondrosis of different parts of the spine
Osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region is the most common type of disease. It is accompanied by a serious restriction of mobility of the entire body, when severe pain is caused by attempts to sit down or bend, as well as to assume a vertical position after a prolonged period of sitting or lying down. Often the advanced form of the disease leads to loss of sensation in the legs. Sometimes the patient is forced to move, relying on a stick. For this type of disease, the use of a laser has proven itself to be effective, quickly relieving the patient’s condition. Magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, ultraviolet irradiation and other procedures are also used.
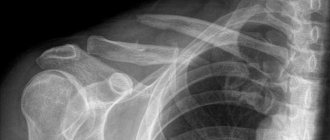
A distinctive feature of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is severe pain not only in this area of the neck, but also in the head, which manifests itself with any movement and can be accompanied by muscle spasms, dizziness and numbness of the tongue. For this type of disease, physiotherapeutic procedures are especially effective. Most often, when the cervical spine is affected, electrophoresis, laser exposure, magnetotherapy, and ultrasound treatment are used.
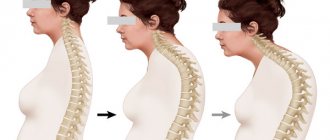
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is less common than its other two types. Symptoms include pain when breathing, chest numbness, and limited arm mobility. The causes of the disease are lack of movement due to a sedentary lifestyle, poor posture associated with spinal curvature, and obesity. This is a type of osteochondrosis that has the greatest number of contraindications for physiotherapy, which should be performed with great caution, since chest pain can have many other, very dangerous causes, for example, heart failure or pulmonary diseases. All this requires additional examination. The most commonly used physiotherapeutic methods are ultraviolet irradiation, ultrasound, magnetic therapy, detensor therapy, and electrophoresis. A history of a heart attack is a contraindication to PT procedures. Patients with pacemakers and other metal implants in the body are prohibited from undergoing magnetic therapy, electrotherapy and electrophoresis. Physiotherapy should be used with caution for coronary heart disease.
Despite the fact that today you can purchase a wide variety of equipment in pharmacies for carrying out physiotherapeutic procedures at home, it is not recommended to do this without consulting a doctor.
Features of osteochondrosis
When osteochondrosis is detected, magnetic therapy can be used exclusively as an auxiliary therapy and prescribed by a doctor in combination with drug treatment and physiotherapy. This is the only way to make progress in treatment and improve your general condition.
Magnetic therapy works most effectively when combined with hydrotherapy. When these types of therapies are used together, lasting improvement is evident after 3-4 months.
Osteochondrosis of the spine is an acute degenerative disorder of articular cartilage. The pathology can affect almost all joints, but most often acute inflammation is observed in the area of the intervertebral discs. Based on the specific affected area, in medical practice there are three types of spinal osteochondrosis: lumbar, thoracic and cervical.
The main reasons why spinal osteochondrosis may occur have not yet been fully studied and do not have scientific evidence. Prerequisites for the development of the disease:
- excess weight;
- individual genetic predisposition of the patient to osteochondrosis;
- presence of bad habits;
- a poorly balanced diet, in which cartilage tissue does not receive enough beneficial microelements;
- previous spinal injuries (impact, fall, accident, etc.);
- acute infectious lesion, which led to metabolic disorders in the body;
- curvature of the spine in different stages;
- living in unfavorable conditions;
- flat feet;
- sudden cessation of sports training in athletes;
- excessive physical stress on the spine;
- work that involves lifting heavy objects;
- prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position (sitting, standing);
- complete lack of active physical activity.
In recent years, doctors have noted a trend toward “rejuvenation” of osteochondrosis. This is justified by the fact that previously people from forty years of age suffered from back pain, but in recent years patients from twenty to twenty-five years of age are increasingly turning to the doctor. In many ways, this process is justified by the curvature of the spine since school years.