The term “radiculopathy” (literally a nerve disease) is used to refer to a radicular syndrome, which includes a number of symptoms that appear as a result of damage to the spinal nerves due to various reasons: compression, inflammation, infection, impaired blood supply, changes in metabolism, etc. It can manifest as pain sensations in various areas of the human body, starting from the neck and ending with the upper or lower limbs. Radiculopathy can occur in any part of the spine - just like the disease that caused it.
You can undergo a course of treatment for these symptoms at the CELT Pain Clinic. Our doctors have extensive experience in this area and have a range of tools that will help effectively eliminate it.
Causes
Clinical manifestations of radiculopathy arise as a consequence of a number of diseases, which are characterized by damage to nerves and roots;
- osteochondrosis;
- protrusion, prolapse or herniated disc;
- spinal canal stenosis;
- piriformis syndrome;
- spondylosis;
- injuries accompanied by displacement of the vertebrae;
- osteoarthritis.
- infectious lesion;
- impaired blood supply to the nerve, radiculoischemia;
- systemic, autoimmune lesions of the nervous system;
- toxic damage to the nervous system
- metabolic, hormonal disorders;
- diabetes mellitus, diabetic neuro-, radiculopathy;
Relevance of the problem
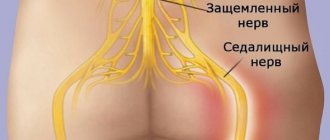
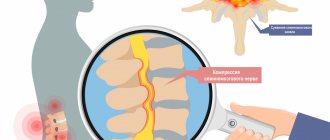
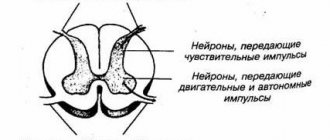
Radicular syndrome or radiculopathy is a symptom complex associated with compression of nerves at the level of the spinal column [5]. For various reasons, one or more nerves leaving the spinal canal become compressed by hard tissue. The spine consists of vertebrae of different sizes, in the center of each there is a hole, the combination of which forms the spinal canal. It contains the spinal cord, which consists of motor and sensory nerves that run toward or away from the brain. Nerves extend from the vertebrae to certain organs, muscles or areas of the skin. Together, the nerve fibers and their plexuses form the spinal part of the peripheral nervous system.
Rice. 1. Diagram of the peripheral nervous system
When the distance between the vertebrae changes or bone growths appear, these branches can be pinched, which forms radicular syndrome. The spinal root includes efferent motor axons (anterior root) and afferent sensory axons of the spinal cord ganglion. Sometimes compression affects isolated sensory or motor nerves (for example, with herpes zoster or polyradiculitis), but more often both branches of the spinal root are subject to compression [6]. Also, radicular syndrome is formed by compression of the cervicobrachial and lumbosacral nerve plexuses, which are the branching and connection of mixed axons of motor and sensory nerves [1].
Rice. 2. Vertebral structure
The main manifestation of radicular syndrome is severe back pain. The vast majority of the population encounters this symptom throughout their lives, which is why the relevance of the problem cannot be in doubt.
Discogenic and vetebrogenic radiculopathy
Discogenic radiculopathy is considered the most common and has a number of features and characteristic symptoms:
- thinning of the intervertebral discs, which ultimately leads to the formation of a hernia and compression of the nerve roots;
- irritation and compression by intervertebral discs of one or several nerve roots, which may be located in different parts of the spine.
Vertebrogenic radiculopathy is a secondary form of discogenic radiculopathy and consists of compression created by growths that have formed around the nerve roots; osteophytes, hypertrophy of ligaments, capsules of intervertebral joints.
How to diagnose
With a physical examination and special tests, the neurologist determines a preliminary diagnosis. Modern and most informative methods for confirming degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the musculoskeletal system include:
Computed tomography. CT allows you to visualize in more detail:
- vertebral column
- canal stenosis
- destruction of bone tissue
- osteophytes.
Magnetic resonance scanning. MRI shows:
- disk status
- stage of hernia development, size of the protrusion
- changes to the facet joints, ligaments and nerves, including spinal cord compression
Cervical radiculopathy
Radiculopathy of the cervical spine is characterized by pain sensations ranging from pronounced intense to a feeling of discomfort in the neck, shoulder blade, shoulder girdle, shoulder, forearm, hand and fingers and can be of the nature of true pain and feelings of cold, heat, crawling, cerebral irritation, etc. qualitative, often subjective characteristics depending on the type of disease. They may decrease at rest and intensify when trying to turn or tilt the head. They are accompanied by the following clinical manifestations:
- painful sensations in the hand of a very different nature;
- decreased strength in the arm, hand, fingers:
- impaired sensitivity to pain, temperature, vibration, etc.;
- disturbance of the color of the skin of the hand: redness, pallor, formation of spots, local increase or decrease in skin temperature during the vegetative component;
- skin rashes
- hypotrophy, weight loss of arm muscles;
- trophic disorders, changes in nails, ulcers;
Therapeutic patch DORSAPLAST - increasing the effectiveness and quality of treatment of radiculopathy
It should be noted that NSAIDs are characterized by a relatively high risk of side effects such as dyspepsia, gastrointestinal bleeding, liver dysfunction, headache, kidney dysfunction, etc. Therefore, modern drugs that, when used in combination, make it possible to reduce the dosage of NSAIDs, shorten the time of their use, increase the effectiveness of treatment and do not cause side effects are of great interest to patients and specialists. One of these drugs is the new therapeutic anti-inflammatory patch DORSAPLAST.
The therapeutic plaster DORSAPLAST has shown high effectiveness in the treatment of various diseases of the spine. It allows you to relieve pain and inflammation, improve blood circulation in the affected area, reduce the dose of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, and increase the effectiveness of their action.
To relieve acute symptoms in the treatment of vertebrogenic cervical radiculopathy, a therapeutic patch is used for 3 to 5 days. The duration of the course of treatment for chronic disease is from 9 days. It is usually recommended to use the treatment patch in the morning for 12 hours, but it can also be used at night.
When treating cervical radiculopathy, the DORSAPLAST therapeutic plaster is applied to the disturbing area of the neck, avoiding the anterior surface, especially the area of the carotid arteries and lymph nodes. A course of treatment of 9 days or more is recommended. It is usually recommended to use the patch in the morning for 12 hours, but it can also be used at night.
High efficiency, unique composition, long-term (up to 12 hours!) therapeutic effects, ease of use and affordable price make DORSAPLAST the drug of choice in the treatment of various forms of radiculopathy.
Read more about DORSAPLAST
Thoracic radiculopathy
Radiculopathy of the thoracic spine is characterized by acute or chronic painful sensations of varying intensity, having various qualitative and subjective characteristics from acute piercing, unbearable pain to the sensation of a blow of wind and depends on the disease causing radiculopathy. Painful sensations can change depending on the position of the body, head, movements, time, day, climatic phenomena, the menstrual cycle in women, psycho-emotional status and many other reasons that a doctor can find out by carefully collecting an anamnesis. In addition, the following clinical manifestations can be objectively observed:
- muscle weakness of the arms and back;
- impaired sensitivity of the skin of the back, upper limbs, sternum, abdomen;
- shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat;
- increased muscle tone on the side of the affected nerve.
- discoloration of the skin on the body;
- skin rashes on the body;
- hypotrophy, weight loss of body muscles;
Incidence (per 100,000 people)
| Men | Women | |||||||||||||
| Age, years | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + |
| Number of sick people | 0 | 0 | 10 | 500 | 1500 | 5000 | 10000 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 500 | 3000 | 5000 | 10000 |
Lumbar radiculopathy
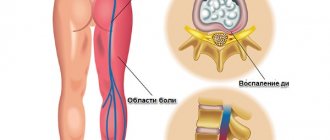
Radiculopathy of the lumbosacral spine is characterized by pain phenomena of varying nature and intensity, spreading to the leg or legs; it may be accompanied by motor disturbances in the lower extremities in the form of weakness, sensory disorders manifested by a feeling of numbness, burning, coldness, stiffness in the legs. With radiculopathy, it is possible to develop trophic disorders manifested by increased skin pigmentation, hair loss on the legs, deformation of the nail plates on the toes, maceration and the formation of ulcers; in rare cases, dysfunction of the pelvic organs is observed in the form of disturbances in urination, defecation, erection, and ejaculation. The following symptoms occur with lumbar radiculopathy.
- pain in the buttock, thigh, leg, foot or both lower extremities;
- development of weakness, decreased strength in the leg or legs;
- decreased or increased sensitivity in the leg, legs; in the perineum, anus, external genitalia;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs: urination, defecation, disorders in the sexual sphere;
- lameness.
Doctors at the Pain Clinic, neurologists, chiropractors, algologists, neurosurgeons, traumatologists and orthopedists at CELT will conduct the necessary diagnostic studies, on the basis of which they will develop a treatment plan. By following the latter, the patient will get rid of pain, inflammation and muscle spasms and return to his normal lifestyle!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Treatment of cervical radiculitis at the MART clinic
For the treatment of radiculitis, the MART clinic has a large arsenal of means. And most of them are aimed at slowing down the pathological process that leads to the occurrence of radicular syndrome and relieving patients of pain. Basic treatments:
I. Drug treatment of radiculitis
Medicines for the treatment of cervical radiculitis eliminate pain, improve tissue trophism in the area of the pathological process, and restore the structure of damaged nervous tissue. For this pathology, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- analgesics (analgin, paracetamol),
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Voltaren, naproxen, diclaberl),
- neuroprotective vitamin therapy (milgamma, neurobex),
- diuretics to relieve swelling in the area of inflammation (Lasix, hypochlorothiazide),
- diuretics to relieve swelling in the area of inflammation (Lasix, hypochlorothiazide),
- means for activating metabolism in damaged tissues (mildronate, aminophylline),
- corticoids eliminate inflammation (prednisolone),
- centrally acting myolaxants (tizanidine, sirdalud) do not affect neuromuscular transmission, while the force of voluntary contractions increases,
- blockade of damaged roots with local anesthetics,
- Local application of ointments or gels (Voltaren-gel, Nise-gel, indomethacin) is prescribed if it is impossible for some reason to use certain drugs.
II. Physiotherapeutic treatment of cervical radiculitis
The use of physiotherapeutic treatment for cervical radiculitis is always indicated, but only a neurologist decides on an individual basis which method is suitable for the patient:
- transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) improves recovery processes in nervous tissue,
- ultraphonophoresis, magnetophoresis, laser phoresis provide a deep effect of drugs on inflamed tissues,
- laser therapy for cervical radiculitis can reduce cell damage in the area of the inflammatory reaction,
- Vacuum therapy is aimed at increasing the speed of lymph movement and reducing tissue swelling,
- diuretics to relieve swelling in the area of inflammation (Lasix, hypochlorothiazide),
- means for activating metabolism in damaged tissues (mildronate, aminophylline),
- corticoids eliminate inflammation (prednisolone),
- centrally acting myolaxants (tizanidine, sirdalud) do not affect neuromuscular transmission, while the force of voluntary contractions increases,
- blockade of damaged roots with local anesthetics,
- Local application of ointments or gels (Voltaren-gel, Nise-gel, indomethacin) is prescribed if it is impossible for some reason to use certain drugs.
III. Manual therapy methods
- Massage is very effective during the period of relief of the acute phase of cervical radiculitis. Lymphatic drainage massage as one of the massage methods effectively eliminates tissue swelling at the site of inflammation and stimulates the flow of oxygen-rich blood.
- Manual therapy as a method of deeper impact is indicated for patients with cervical radiculitis with relieved pain. This procedure is performed by a qualified doctor.
- Osteopathy, like manual therapy, is intended to have a profound effect on the human skeletal system. A sufficient number of sessions will reduce most symptoms of cervical sciatica.
IV. Methods of physical therapy in the treatment of cervical radiculitis
- Kinesio taping is a method of physiotherapy that is based on strengthening muscles with special patches. Elastic tapes (tapes) do not restrict movement, helping to reduce or completely eliminate pain in cervical radiculitis. This allows us to move on to such an effective method of rehabilitation as physical therapy.
- Physical therapy is an integral component of the treatment of cervical radiculitis. Moreover, all exercises should not cause pain. Special exercises have been developed for patients with cervical radiculitis. They must be performed strictly regularly and every day. Stabilization of the cervicothoracic spine is paramount in limiting pain and preventing future exacerbations. The first part of the stabilization process aims to achieve the full pain-free range of motion that can be achieved with stretching exercises. Subsequently, the exercise program should be aimed at restoring and strengthening the weakened muscles of the neck, shoulder girdle and upper body.
By contacting the MART center, you can be sure that as a result of a comprehensive examination, using modern diagnostic equipment, an optimal treatment strategy for cervical radiculitis will be developed, taking into account all individual characteristics. Using the treatment methods and procedures we offer, experienced specialists will help you successfully overcome the causes of cervical radiculitis, get rid of pain and return to your normal lifestyle.
The article was reviewed by Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Grigory Isaakovich Shvartsman, Northwestern Medical University. I.I. Mechnikov.
Sign up at the MART medical center in St. Petersburg (see map) by phone, or leave a request on the website.
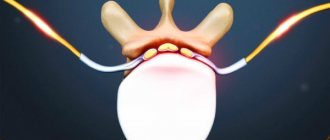
General clinical picture of radicular syndrome
General clinical signs of radicular syndrome:
- acute onset;
- intense pain syndrome;
- changes in sensitivity (paresthesia, hypersensitivity or numbness);
- limited mobility in the damaged segment of the spine;
- >muscle tension in the area of injury;
- muscle wasting of the innervated area;
- the development of paresis of the muscles innervated by the affected root is possible;
- paravertebral increase in muscle tone;
- local increase in temperature;
- decreased reflexes;
- with a long course, changes in the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid [1,3,5].
Rice. 4. Clinic of radicular syndrome
Forecast and prevention of the disease
It is necessary to recommend that the patient return to normal daily activities as quickly as possible, since maladaptive pain behavior is the main barrier to recovery. In addition, comorbid depression also negatively affects treatment outcomes. If pain persists for >4–6 weeks, it is advisable to add antidepressants to analgesic therapy. Pathogenetically, it is most justified to use antidepressants that act on both neurotransmitter systems (serotonin and noradrenergic) for the treatment of pain symptoms. Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), which block the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, have greater potential than selective antidepressants. TCAs are more successful in treating pain symptoms and leading to more complete remission of depression. A new class of drugs, dual-action antidepressants that block the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, have high analgesic efficacy and a more favorable spectrum of side effects than TCAs. The effectiveness/safety ratio is optimal for dual-acting antidepressants (duloxetine, venlafaxine). During the recovery period, active exercises are recommended to strengthen the muscle corset.
Diagnosis of radicular syndrome
The main clinical manifestation of radicular syndrome is pain. Pain syndrome is determined using a visual analogue scale (VAS pain). The patient subjectively evaluates the intensity in points, where 0 is no pain, and 10 is unbearable pain.
The main diagnostic value is a neurological examination performed by a neurologist.
Inflammatory activity is assessed based on the results of clinical and biochemical blood tests: C-reactive protein, ESR, leukocyte formula shift [1,7].
Instrumental diagnostics are aimed at detecting the cause of compression using imaging methods: radiography, CT or MRI of the spine. In difficult cases, myelography is performed (spinal puncture with the introduction of contrast and CT or radiography, as well as sampling of cerebrospinal fluid) [5].
Treatment of radicular syndrome
In the most acute and acute periods, rest is prescribed, for which orthoses are used (collar, reclinator, fixing belt and semi-rigid corset).
Drug therapy includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, chondroprotectors, antispasmodics, muscle relaxants, as well as warming ointments and gels. In cases of very severe pain, spinal blocks are performed. Physiotherapeutic treatment is used: diadynamic or sinusomodulated currents, electrophoresis, laser therapy, magnetotherapy, mud applications, massage, acupuncture, sometimes hirudotherapy (leech treatment), underwater horizontal spinal traction with underwater phototherapy. In the subacute period, physical therapy and manual therapy are added. Transcranial electrical stimulation, ozone therapy and EHF puncture are used [1,7].
Endoscopic puncture (percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy) can be used, and in particularly complex cases that are not amenable to conservative treatment, neurosurgical intervention must be resorted to [3].
We take a comprehensive approach to treating pain associated with radicular syndrome. The clinic has an impressive arsenal of methods and approaches to the treatment of acute and chronic pain: various methods of physiotherapy, medical massage, manual techniques and exercise therapy, methods of regenerative medicine, various types of blockades and the dry needling method, medical botulinum therapy, pharmacotherapy.
Recently, we have successfully used the shock wave therapy method as one of the most effective methods as part of complex therapy.