Treatment of sciatic nerve sciatica at home
In most cases, treatment of sciatica is carried out at home, on an outpatient basis.
Inpatient treatment of sciatic nerve sciatica may be required in cases where surgical intervention to remove a hernia or tumor is necessary to relieve pain. In this case, the patient is placed in a surgical hospital. After the operation, his condition is monitored by a neurologist and surgeon. In all other cases, treatment of sciatic nerve sciatica is carried out at home. Official medicine uses the following scheme for this:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are administered intramuscularly to relieve pain and eliminate the inflammatory reaction;
- Vasodilators are used to increase local blood flow in the lesion;
- B vitamins help support the trophism of the affected nerve fiber;
- chondroprotectors are drugs that should hypothetically restore damaged cartilage tissue (in practice, this effect can only be achieved in combination with a course of injections with osteopathy, manual therapy and therapeutic exercises);
- local application of warming ointments;
- administration of muscle relaxants in the presence of symptoms of excessive muscle fiber tension.
Also, for the treatment of sciatica at home, massage, physiotherapy, and therapeutic exercises are prescribed. They are the ones who have the most pronounced therapeutic effect. Unfortunately, the volume that is prescribed to the patient according to modern standards is not enough to completely restore the damaged tissues of the spinal column. Therefore, it is recommended to independently look for manual therapy clinics and go there for full treatment of sciatica and the disease that caused it.
There are contraindications, consultation with a specialist is required.
B vitamins in the treatment of acute back pain: myth or reality?
Significant changes are taking place in the treatment of acute back pain. The main difference is the abandonment of strict immobilization of patients and the transition to rapid activation with the help of physical therapy. In this case, one of the conditions for successful therapy is pain relief, starting from the first day of the acute period. Traditionally, simple analgesics (Aspirin, Paracetamol), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle and epidural blockades are used for this. Along with these approaches, combination vitamin preparations containing thiamine (vitamin B1), pyridoxine (vitamin B6) and cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) have proven to be quite popular in the relief of acute pain.
Interest in the widespread use of a combination of B vitamins for pain came from practice. Since 1950, in many countries they began to be considered as analgesics. It is well known that B vitamins are neurotropic and significantly affect processes in the nervous system (metabolism, metabolism of mediators, transmission of excitation). In domestic practice, B vitamins are used very widely. Clinical experience shows that parenteral use of a combination of thiamine, pyridoxine and cyanocobalamin relieves pain well, normalizes reflex reactions, and eliminates sensitivity disorders. Therefore, for pain syndromes, doctors often resort to using vitamins of this group in combination with other drugs.
The popularity of B vitamins for acute back pain is also associated with other aspects. When working with patients suffering from such pain, one often encounters certain difficulties. Firstly, these are various complications of pharmacotherapy. The use of numerous NSAIDs is often rejected by patients themselves due to side effects, mainly from the gastrointestinal tract. Secondly, if any drug is ineffective, it is necessary to prescribe drugs from several groups simultaneously, which increases the risk of side effects and also, as a rule, increases the cost of treatment. Thirdly, many patients have contraindications to various pain-relieving physiotherapeutic procedures (electrotherapy, magnetic therapy, thermal procedures, etc.). Often, due to pain, they cannot leave the house, and accordingly, carrying out any procedures outside the home is excluded. In addition, it is not always possible to carry out the necessary muscle or epidural blockades due to the lack of appropriate conditions or specialists.
More than 90 studies have been published indicating clinical improvement with the use of B vitamins in patients with acute back pain [1–5]. However, many questions remain regarding the use of a combination of B vitamins in the treatment of acute back pain. How can B vitamins help with acute pain? What is their mechanism of action? How quickly does the effect occur? How safe is the combination of these vitamins? Can they be combined with NSAIDs? Is this combination treatment more effective than monotherapy?
The purpose of this work was a randomized, open-label comparative study of the effectiveness of Milgamma, diclofenac and their combination in the treatment of acute pain in the low back. The drug Milgamma is available in ampoules of 2.0 ml. One ampoule contains 100 mg of thiamine hydrochloride, 100 mg of pyridoxine hydrochloride, 1000 mcg of cyanocobalamin and 20 mg of lidocaine. The difference between Milgamma and other vitamin preparations is its release form: one ampoule contains large doses of vitamins B1, B6 and B12 in combination with a local anesthetic. A decisive role in the combined use of B vitamins is played by the fact that the areas of application of B vitamins overlap and complement each other.
The study included 60 patients suffering from acute back pain. Inclusion criteria were acute back pain with an intensity of at least 6 points on the visual analogue scale (VAS). Exclusion criteria were: cancer; back pain caused by pathology of the abdominal and pelvic organs, compression of the spinal cord. All patients were divided into three groups. The first group (“M”) included 20 patients who received 2.0 ml of the drug Milgamma for a period of up to 10 days, the second group (“D”) included 20 patients who took diclofenac 75 mg intramuscularly for the same period per day, the third group (“M + D”) also consisted of 20 people who received daily injections of Milgamma (2.0 ml) and diclofenac (75 mg). The drug diclofenac was chosen for comparison as the most popular painkiller from the NSAID group, widely used in our country to relieve back pain. No other pharmacological drugs and/or physical procedures were prescribed to patients of all three groups. Treatment was carried out on an outpatient basis. The maximum duration of drug use was 10 days. If the pain syndrome was completely eliminated before this period, treatment was stopped.
The average age in the “M” group was 42.8 ± 9.9 years, in the “D” group – 40.0 ± 9.8, in the “M + D” group – 43.1 ± 10 years. In the “M” group there were 40% men and 60% women, in the “D” and “M + D” groups, respectively, 30% men and 70% women. Thus, the study groups were comparable in age and gender (p > 0.15).
The study used clinical neurological analysis, neuroimaging (MRI, CT, radiography), VAS to assess the intensity of pain (daily), a scale of patient impressions of the effectiveness of therapy, and analysis of side effects of drugs. Statistical analysis was carried out using parametric and nonparametric statistical methods (Statistica 5.0 program).
results
The pain syndrome was represented predominantly by muscle-tonic disorders in all groups (100% in all groups). Radicular pain due to discogenic compression was noted: in groups “M” and “D” - 10% each, in group “M + D” - in 20% of cases. At the same time, intervertebral disc herniation was detected on MRI: in the “M” group – in 10% (L5-S1), in the “D” group – in 20% (L5-S1), in the “M + D” group – in 20% cases (L4-L5, L5-S1). Osteochondrosis occurred in 95% of cases, in group “D” - in 100%, in group “M + D” - in 95% of cases.
The intensity of pain according to the VAS scale in the compared groups before treatment did not differ significantly. In groups “M” and “D” there was a statistically significant decrease in pain intensity on the VAS scale, starting from the second day of therapy and its subsequent highly significant decrease throughout the course of treatment (p < 0.001). In the “M + D” group, a significant reduction in pain was noted already from the first day of therapy. Comparing the overall effectiveness of treatment in the studied groups, one can note a significant and consistent reduction in pain during all days of therapy (Table 1).
To assess the dynamics of pain reduction, an analysis was carried out of changes on the VAS scale as a percentage in relation to the intensity of pain before treatment, taken as 100%. By the 3rd day of treatment, all groups achieved a clinically significant reduction in pain for patients (by more than 30%). It should be noted that the greatest changes (reduction of pain) were observed during the first 3 days, but these differences did not reach the level of significance.
There is a widespread belief among doctors that diclofenac is more effective than Milgamma for very intense pain. To test this hypothesis, we compared the effectiveness of treatment in three groups in patients with an initial pain intensity of 8–10 points on the VAS scale. When analyzing the dynamics of pain regression in these patients (8–10 points on the VAS scale), a significant decrease in pain intensity was observed in all groups within the first 5 days. However, if we evaluate the degree of pain relief by days of therapy, we should note a positive effect on the first day of therapy in the “M + D” group (p < 0.05), while in the “M” and “D” groups a significant reduction in pain was observed only with the second day of treatment (Table 2).
In our work, we analyzed the number of patients with varying degrees of pain regression: with complete relief by 100%, with regression by 50 and 30%, depending on the duration of therapy. It should be emphasized that a 30% reduction in pain is considered a clinically significant improvement. On the second day of therapy, clinically significant improvement was noted by 11 people in the “M + D” group, which is significantly more than on this day in the “M” and “D” groups (p < 0.05). In the M + D group there were more patients with complete pain relief during the first 5 days of treatment. However, it can be noted that starting from the 4th and 5th days of treatment, the number of patients with pain regression of more than 30% was approximately the same in the three groups.
Patients were also asked to independently evaluate the analgesic effect of the drugs on a scale of subjective impressions (Table 3). In general, following the results of 10 days of treatment, complete pain relief was noted by 45% of patients in group “M” and 35% of patients in group “D”, however, the largest number of patients with complete regression of pain was in group “M + D” (70%). The fact that pain decreased slightly was reported by 10% of patients taking diclofenac or Milgamma alone. In the group of patients receiving diclofenac, one person had pain that persisted throughout 7 days of treatment and the patient was hospitalized.
During treatment, a number of patients experienced adverse reactions: nausea, abdominal discomfort, stomach pain, diarrhea. Analysis of adverse reactions showed that most of them are associated with taking diclofenac. Their number was significantly higher in the group of patients taking diclofenac (35%), slightly lower in the group using two drugs (25%) and least in the group of patients receiving Milgamma (5%, p < 0.05, urticaria in one patient on the 7th day of therapy). Due to side effects, 20% in the “D” group (10% after the 5th injection, 10% after the 7th injection), 15% in the “M + D” group (after 5 days of treatment) abandoned therapy. 5% - in group “M” (after the 7th injection). Thus, a significantly larger number of patients discontinued treatment due to side effects associated with the use of diclofenac.
Discussion
With a normal and varied diet, the body receives enough vitamins to prevent any vitamin deficiency. With the advent of synthetic vitamins, a person can receive in one dose of the drug the amount of vitamins that comes from food throughout the year. However, at these pharmacological doses, vitamins should be considered as drugs. And what is very important is that at such doses the mechanism of action often differs from the well-known physiological effects of “natural” vitamins [6].
There are two groups of disorders for which vitamin therapy is unconditionally indicated. The first is vitamin deficiency conditions (beriberi disease, gout, alcoholism, malabsorption, cystic fibrosis, etc.). The second is genetic defects in vitamin metabolism. Moreover, both of these groups of vitamin deficiency conditions serve as the basis for only a very small part of all prescriptions of vitamin preparations. In medical practice, B vitamins are most often prescribed as adjuvants for conditions not accompanied by vitamin deficiency: pain syndromes, psychoses, asthenia, tunnel syndromes, alopecia. Very often, good treatment results are achieved. However, it remains unclear in which cases the positive effect is associated with the action of vitamins, and in which it may be random or due to placebo.
However, clinical and experimental studies are currently underway on the use of vitamins as active drugs, with new mechanisms of action [7–9]. Experimental work studying the effects of a combination of vitamins B1, B6 and B12 on pain showed inhibition of nociceptive responses caused by formaldehyde, which did not change after administration of naloxone. It has been suggested that the antinociceptive effect of the combined vitamin complex may be due to inhibition of synthesis and/or blocking the action of inflammatory mediators [7]. Many studies emphasize that both combination and separate use of vitamins B1, B6 and B12 have an analgesic effect. It has been shown that the B complex of vitamins enhances the effect of norepinephrine and serotonin, the main antinociceptive neurotransmitters. In addition, the experiment revealed suppression of nociceptive responses not only in the dorsal horn, but also in the thalamus optica [8].
Despite the fact that there are no large evidence-based studies in this regard, practice shows that B vitamins in large doses do have analgesic properties, and can also enhance the analgesic effects when used simultaneously with simple analgesics or NSAIDs. Positive results have been obtained in the treatment of both musculoskeletal and neuropathic pain [9]. In particular, there are studies showing the effectiveness of vitamin B6 in carpal tunnel syndromes. There are indications that B vitamins enhance analgesia when used concomitantly with diclofenac for acute back pain, which may shorten treatment time and reduce dosages of diclofenac, thus reducing the risk of side effects [10–13].
The results obtained in our work confirmed the effectiveness and safety of the combined drug Milgamma in the treatment of acute back pain. A reliable analgesic effect is observed from the second injection of the drug. The effect of Milgamma, a drug not related to analgesics, turned out to be comparable to diclofenac, a “classical” pain reliever. This may indicate that the combination of B vitamins in Milgamma has a clear analgesic mechanism of action and is not the result of the usual traditional physiological effects of these vitamins. We think this provision is very important, since there is a widespread opinion among doctors that the use of B vitamins for acute pain is ordinary vitamin therapy aimed at “strengthening the nervous system.” Taking into account the new experimental data mentioned above, we can expect that in the future the analgesic properties will be studied in more detail and the mechanisms of action of large doses of B vitamins on humans will be clarified.
In our study, side effects and complications during and after the end of therapy were associated with diclofenac. In the group of patients taking this drug, a high percentage of side effects was obtained (35%), which, unfortunately, indicates that its level is not high enough.
As for combination therapy, it turned out to be more effective than monotherapy in terms of the dynamics of pain regression. A faster and more pronounced reduction in pain in the first days of therapy has been shown, which is very important especially for intense pain. It is likely that combination therapy shortens the treatment period, and also makes it possible to discuss the use of lower doses of NSAIDs when combined with Milgamma. The combination of Milgamma with diclofenac can be recommended for very high pain intensity for its rapid relief in the first days of treatment. It should be noted that the effectiveness of Milgamma monotherapy for intense pain was not inferior to diclofenac, and this fact, taking into account the better safety profile, allows us to classify the drug as universal for both mild and severe pain.
conclusions
The study confirms clinical experience of the high effectiveness of a combination of B vitamins in the treatment of acute back pain.
Monotherapy with Milgamma for acute back pain is accompanied by a significant decrease in the intensity of the pain syndrome from the second day and throughout the entire course of treatment with a virtual absence of undesirable side effects.
Milgamma is an effective pain reliever for both moderate and high intensity pain.
Treatment of acute back pain with diclofenac is effective, but in a third of cases it is accompanied by unwanted side effects, which should be taken into account when choosing medications.
Combination therapy with diclofenac and Milgamma provides a more pronounced analgesic effect than monotherapy (with Milgamma or diclofenac); a pronounced positive effect is observed already on the first day of therapy, which is important to consider if urgent pain relief is necessary.
It is likely that combination therapy (NSAIDs + B vitamins) will allow the use of lower doses of NSAIDs in order to prevent unwanted side effects. when maximum pain relief is achieved.
With a treatment duration of 7–10 days, combination therapy has no advantages over monotherapy with Milgamma or diclofenac in terms of the final result, however, monotherapy with Milgamma is better tolerated and safer.
The drug Milgamma in injections should be considered not as a component for the treatment of vitamin deficiency conditions or a general strengthening agent, but as an active agent, with special, not yet sufficiently studied, but obvious analgesic properties.
For questions regarding literature, please contact the editor.
A. B. Danilov , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of MMA named after. I. M. Sechenova, Moscow
Causes and symptoms
The sciatic nerve is responsible for physical activity in the legs. If there is no irritation, the fibers do not make themselves felt. Acute symptoms occur as a result of inflammation for some reason. Pain is considered the main symptom of inflammation of the sciatic nerve. Unpleasant sensations arise slightly below the lower back, are transferred to the buttocks, and pierce the entire leg.
When moving, the pain is unbearable. In a calm state, the symptoms become nagging, aching, and a feeling of heaviness rarely occurs. Sleep problems arise because it is difficult to determine a comfortable position. Weakness appears due to a painful syndrome, the leg goes numb, colic begins, and the joints give way when moving.
Pinching is one of the main causes of inflammation, caused by destructive processes in the spine:
- Hernias appear in the intervertebral discs.
- Osteochondrosis appears.
- The bones become deformed and growths appear on them.
- As a result, the nerve fibers are pinched, causing severe pain.
Prognosis and possible negative consequences
If the sciatic nerve is pinched, its symptoms should never be ignored, since the lack of timely treatment can lead to the development of undesirable consequences that significantly reduce the quality of life of patients.
First of all, when painful sensations occur, it is necessary to establish the true cause of their occurrence, since if therapeutic procedures are carried out incorrectly, sciatica can go into the chronic stage of development, and in some cases, paralyze the patient (especially if the tumor-like neoplasm is untimely removed or the hernia is reduced spine).
In addition, the following types of complications are possible if sciatica is not treated in a timely manner:
- constant intense pain syndrome;
- decreased libido levels;
- infertility;
- deterioration in the functionality of internal organs and systems;
- insomnia;
- disturbances in the menstrual cycle in women;
- a sharp decrease in physical activity;
- paralysis;
- disruption of the functioning of the intestines and bladder in the processes of emptying them.
Only timely seeking medical help and properly administered therapy can prevent the occurrence of the complications described above. In general, with proper treatment of sciatica, the pathological prognosis is positive and all the disorders in the body that it causes are completely reversible.
Comprehensive treatment of inflammation.
Treatment of sciatica is a complex of procedures; it is selected differently for each patient and depends on the specific symptoms and severity of the condition. Treatment includes:
- Bed rest during periods of acute pain.
- Medicines: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, vitamins are used, ointments and gels of irritating action are applied topically, which relieve pain and reduce spastic syndrome.
- Physiotherapy: prescribe warming compresses, heating, electro or phonophoresis.
- Massage begins after the acute process has subsided, it helps reduce pain, increases the conductivity of the damaged nerve, improves blood supply and lymph flow, and prevents muscle wasting.
- Therapeutic exercise: after identifying the cause of inflammation of the sciatic nerve, an exercise program is individually selected for the patient, some of which must be performed already in the first days of the illness, while lying in bed. As motor activity is restored, the load is gradually increased. Activities in the pool are also recommended.
- Surgical treatment is indicated in cases where conservative methods do not work and severe pain becomes chronic, as well as in cases of severe dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Disease prevention
To prevent inflammation of the sciatic nerve, it is necessary to pay attention to maintaining the tone of the back muscles, you should do strengthening exercises and control correct posture during sedentary work, take regular breaks and warm-up, avoid injuries, do not lift heavy objects, and avoid hypothermia.
Treatment of the sciatic nerve - advice from a neurologist.
How to treat the sciatic nerve - advises 1st category doctor O.V. Antonovskaya. If you experience symptoms similar to those of inflammation of the sciatic nerve, you should consult a doctor to clarify the diagnosis before starting treatment. Similar symptoms can be caused by renal colic, which occurs when sand passes through the ureter, and acute inflammatory diseases in the pelvis. Sciatic nerve diseases are diagnosed using MRI and X-rays. Only after an accurate diagnosis can you begin treatment at home.
Treatment of inflammation of the sciatic nerve - what to do at home?
First of all, the patient should lie down on a flat bed and wrap a warm scarf around his lower back. Quickly apply any dry heat - it will only be beneficial.
Drug treatment of the sciatic nerve (sciatica).
To remove the symptoms of inflammation or pinching, complex treatment will be required.
- If the sciatic nerve hurts so much that it is impossible to tolerate, painkillers are used. Pain is very exhausting for a person, and this slows down the recovery process.
- Tablets and injections. In the first 3-4 days, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed in the form of injections to treat inflammation of the sciatic nerve: ibuprofan, declofenac, voltaren. Then they are replaced with tablets from the same group. For problems with the gastrointestinal tract, tablets can be replaced with corresponding suppositories, ointments, gels and patches with the same names.
- In especially severe cases, when the patient is bedridden, hormones are used in the treatment of sciatica under the supervision of a physician. They very effectively relieve swelling and inflammation of the nerve roots.
- Physiotherapy will help relieve sciatica pain and inflammation: Bernard currents, electrophoresis, phonophoresis, detensor therapy. Swimming, massage, and hirudotherapy are useful for sciatica.
Treatment of the sciatic nerve with folk remedies will complement the effect of medications and help you quickly cope with the disease at home. You will find recipes and reviews from those who were cured in this article.
We advise you to study - Back exercises to perform at home
Surgery
It will not be possible to do without surgery if conservative treatment does not bring positive results within 3 months or there are pathologies that cannot be eliminated non-surgically. Therefore, the help of a spinal surgeon is required when:
- spinal fractures;
- intervertebral hernias that compress the sciatic nerve or spinal cord and provoke the development of radicular syndrome;
- spondylolisthesis;
- scoliosis;
- tumors of different nature.
In each case, different types of operations are used, differing not only in the method of execution, but also in the level of trauma, the duration and complexity of the rehabilitation period, as well as the number of risks and possible complications.
The easiest, least traumatic and safest methods of percutaneous surgery are recognized, which can be used to remove intervertebral hernias and treat compression fractures. But such methods can only be used if there is a small hernia, otherwise they are ineffective.
Percutaneous surgery methods include hydroplasty and nucleoplasty. In both cases, operations involve destruction of the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc using instruments whose diameter does not exceed several millimeters. But when using hydroplasty, the nucleus pulposus is destroyed by liquid pressure, and when using nucleoplasty, it is destroyed by cold plasma, laser or radio waves. In both cases, the postoperative wound is so small that it does not require stitches. It is only covered with a sterile bandage, and the rehabilitation period proceeds almost unnoticed by the patient.
A somewhat more traumatic way to remove intervertebral hernias is endoscopic surgery, which involves resection using a lateral approach. The operation is performed using special endoscopic equipment equipped with a video camera. It is immersed into the patient’s body through pinpoint punctures, the diameter of which does not exceed 1 cm. In this way, hernias of different sizes can be removed, but when they are located in hard-to-reach places, the technique is ineffective.
For large, complex or even sequestered hernias that have led to spinal canal stenosis, the operation is performed through a soft tissue incision in the projection of the affected disc and is called microdiscectomy. It can be used in all cases with virtually no restrictions, with the exception of obvious contraindications to surgical intervention (respiratory or heart failure, pregnancy, etc.). Microdiscectomy uses special small surgical instruments. But since the operation is associated with injury to soft tissues, recovery after it is more difficult and longer than when using other methods of surgical treatment of intervertebral hernias.
If pain and inflammation of the sciatic nerve are caused by a compression fracture of the spine, the patient urgently requires vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Both operations have an almost identical technique, which consists in filling the flattened vertebra with a special, quickly hardening bone cement, which ensures the formation of a strong bone conglomerate. But kyphoplasty has broader indications for use and can be used for severe compression fractures with a significant reduction in the height of the vertebra, since it involves the initial restoration of its natural shape and size using a balloon inserted inside. It is gradually taken off, thereby restoring the parameters of the spine, and then deflated and removed.
If sciatic nerve pain is caused by scoliosis or spondylolisthesis, special metal structures consisting of plates and screws screwed into the vertebrae are used to fix the vertebrae in the correct position and restore the normal axis of the spine. They are introduced into the body through small incisions and remain in the human body for life.
Thus, pain and inflammation of the sciatic nerve can significantly poison life and deprive a person of his ability to work. But with timely treatment, they can be completely overcome and disability can be avoided. Therefore, if you experience regular pain, and even more so if you detect other of the above signs, we recommend that you immediately contact a neurologist or a spinal surgeon.
Only a qualified doctor can correctly diagnose and prescribe optimal treatment.
Physiotherapy
If the sciatic nerve is inflamed, you need to move carefully so as not to cause an attack of sudden pain. However, in the absence of severe pain, it is necessary to begin physical therapy exercises, which will improve the condition of the body, activate blood circulation, and eliminate congestion.
For sciatica, the following exercises are recommended.
- Starting position – lying on your back, hands behind your head. Bend your leg at the knee, and then press it to your stomach. Repeat the exercise at least 8 times. Carry out similar actions with the second leg. Movements should be smooth, but with maximum amplitude.
- Lying on your back, spread your arms to the sides. Bend your knees, place your feet on the floor. Place both legs to the left, then return to the starting position and place your legs to the right. Do the exercise until you feel warmth in your lower back. However, you should not repeat the movements more than 10 times.
- First lie on one side, bend your leg at the knee and pull it towards your stomach. The same must be done on the other side. The number of movements on each side is at least 5 times.
- Sit on the floor, placing your hands on the floor behind your torso. Bend your leg at the knee, pull it towards your stomach, straighten it and smoothly lower it in this position to the floor. Repeat these steps for each leg at least 5 times.
- Get on your knees, place your hands palms on the floor in front of you. Slowly moving your hands, without lifting them from the floor, move your body so that your hands touch the heel of one of your feet. Also moving your hands, return to the starting position, and then continue moving in the opposite direction, touching the heel of your foot with your hands on the other side.
- Lie on your stomach, place your palms on the floor, push off the surface with them, pushing your pelvis up. You need to hold this position for about 25 seconds. Your arms should be straight. Do at least 8 repetitions.
- Get back on your feet. Make circular movements with your pelvis with maximum amplitude, from the beginning in one direction, then in the other.
- The last exercise not only stretches the leg muscles, but also checks for nerve pain. Stand up straight, raise your arms up, bend your back slightly, and then slowly, without sudden movements, bend down as deeply as possible. Ideally, you need to touch not only your palms to the floor, but also your forehead to the lower part of your legs. However, the exercise must be done until the first sensation of pain.
By regularly performing all these basic exercises, you should gradually feel less and less pain in your lower back and back of your legs.
The importance of exercise for sciatic nerve pain
Exercises for sciatic nerve pain are a mandatory step in the treatment of the inflammatory process. The importance of therapeutic exercises is explained by a number of reasons:
- exercises allow you to relax your muscles and relieve spasms;
- normalization of blood circulation;
- increased muscle strength, which prevents the re-development of sciatica;
- strengthening the spinal column, improving the condition of ligaments and joints.
It is recommended to perform it when severe pain subsides a little. Otherwise, gymnastics will only bring unpleasant sensations.
Types of ointments for illness
All external use products, which are produced in the form of ointments, can be divided into several large categories, differing in their composition and mechanism of action.
Table. Review of the main groups of ointments used for sciatica.
| NSAIDs | First of all, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to quickly and effectively relieve pain. |
| Irritating/warming agents | They help improve blood supply and nutrition of tissues in the body. |
| Chondroprotectors | They, as the name suggests, are used to restore cartilage tissue. |
| Homeopathic medicines | They are aimed at gently relieving the inflammatory process. |
| Combined products | Such ointments have a comprehensive effect on the disease. |
Ointments for sciatica
The doctor’s prescription in this case will depend on the disease that sciatica is associated with, how severe the patient’s pain is, and whether he has any contraindications.
Treatment of the sciatic nerve
NSAIDs
They are rightfully considered the most popular group of ointments used for pinched sciatic nerves. This includes the following:
- "Diclofenac";
- "Piroxicam";
- "Nise";
- "Ibuprofen";
- "Ketaprofen" and others.
"Diclofenac"
Pain and inflammation after using such ointments are eliminated almost instantly. NSAIDs are often prescribed if sciatica was caused by hypothermia or injury. However, drugs in this group have numerous contraindications, including:
- liver/kidney diseases;
- childhood;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- period of pregnancy or breastfeeding.
In addition, the course of taking NSAIDs should be no more than three to four days.
"Piroxicam"
Irritating/warming agents
Such products are made from turpentine, hot pepper, snake/bee venom and other irritants. Helps improve tissue nutrition and blood circulation, help cope with swelling and inflammatory processes. After application, a burning sensation occurs, distracting from the unpleasant sensations caused by pinching of the sciatic nerve.
The most common representatives of this group are the following:
- "Capsicam";
- "Betanikomilon";
- "Viprosal";
- "Nicoflex";
- "Apizartron";
- "Finalgon"
As a rule, the duration of treatment with warming ointments varies between five and ten days.
Chondroprotectors
Helps restore connective tissue in the body. In case of intervertebral hernia, osteochondrosis, protrusion, causing sciatica, chondroprotectors not only eliminate the symptoms, but also prevent new attacks of nerve inflammation.
Chondroprotectors include:
- "Chondroitin";
- "Sofia";
- "Teraflex M";
- "Chondroxid" and other drugs.
All of them are low-toxic, and therefore treatment can last up to 3 months. However, such ointments are used in tandem with analgesics, since they do not eliminate pain after the first use.
Homeopathic medicines
The effectiveness of these remedies is not recognized by all experts, since homeopathic ointments contain very few active ingredients. As for research on this topic, their results are also contradictory.
But do not forget that these drugs, unlike their stronger analogues, have practically no side effects or contraindications, and therefore ointments can be used for children, pregnant women and other diseases that accompany pinching of the sciatic nerve.
As a rule, “Zel T” or “Traumel” is used for sciatica. They are made from animal and plant components, as well as from sulfur, a trace element that is very important for cartilage tissue. All these components have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Combined products
They consist, as you might guess, of several components that act not only on the symptoms, but also on the causes of the pathology. The most famous drug is Dolobene; it eliminates not only pain, but also inflammation and swelling. Analogs of this drug are “Dimexide” and “Dexpanthenol”.
We advise you to study - Spinal hernia - treatment without surgery with folk remedies
"Dolobene"
"Dimexide"
It is also worth noting that when treating a pinched sciatic nerve, the main thing is an integrated approach; without it, you are unlikely to be able to get rid of the disease once and for all.
Therefore, drug therapy should be combined with other methods - massage, therapeutic exercises, making adjustments to lifestyle (for example, increased caution should be exercised during physical activity).
Exercise therapy for sciatica
Patients often ignore or underestimate prescribed exercises for sciatica. Many patients find that medications are more effective than therapeutic exercises. This opinion is clearly erroneous.
A set of properly selected exercises improves blood circulation, relieves inflammation and activates metabolism . Therapeutic exercises speed up recovery, and pain can be relieved in a few days.
In addition, other spinal problems that may cause sciatica are eliminated. All exercises are performed only in the absence of pain; during periods of exacerbation, training is strictly prohibited. The main thing is to do the exercises correctly.
Doing exercises is prohibited during the acute phase of sciatica. For gymnastics to be effective, you should adhere to certain recommendations:
- It is better to master the complex under the supervision of a doctor.
- Exercises will be beneficial if done twice a day.
- All exercises for sciatica are done on a hard surface.
- During an exacerbation of the disease, breaks are allowed, but then you need to continue performing the complex, taking into account your state of health.
- Gymnastics should be done regularly. If there is no desire or strength, then you should not cancel the training, you need to do at least 2-3 exercises at half strength.
If the disease is in the acute phase, then the exercises are not performed until the pain disappears.
Physical activity is also undesirable in some pathologies:
- Mental disorders.
- Epilepsy (frequent seizures).
- Serious spinal injuries.
- Oncology.
- Heart diseases.
- Viral infections that are accompanied by fever.
Due to these restrictions, you should first consult a doctor or undergo a full examination.
Video: “The most effective exercise for pinched sciatic nerve”
Find out more about spinal neuralgia:
- Radicular syndrome with osteochondrosis in the cervical spine
- You can find out how to give injections for sciatica here
- A list of ointments for sciatica is posted on the page
Rubbing
You can cure a cold sciatic nerve at home with the help of rubbing, which is carried out using the following means:
- bear lard (total duration of therapy – at least 4 weeks);
- agave juice (the plant is thoroughly washed, the thorns are cut off and cut in half; the cut is rubbed on the inflamed area several times a day for 2 weeks);
- vodka and salt (the ingredients are mixed in the ratio of 1 glass of vodka to 1 tablespoon of salt, add 1 glass of honey and the same amount of radish juice; after thoroughly mixing the ingredients, rub the sore spots with the prepared product several times a day for 1-2 weeks);
- Kalanchoe (plant juice in a volume of 100 ml is mixed with liquid honey (200 g) and vodka (1 glass); rubbing is carried out before bed, after the procedure, wrapping the affected area with a plastic bag and a warm blanket; a total of 7 sessions are required daily);
- hot pepper and aloe (crush a small leaf of the plant, add 1 tablespoon of celandine flowers and red hot pepper (pod); mix all ingredients and pour vodka (1 glass); after infusing for 1 week, rub the sore area with the product daily within 2–3 weeks);
- lilac (the buds are thoroughly crushed and mixed with interior fat in a ratio of 1:4; then the mixture is placed in a water bath and kept until a homogeneous mass is obtained; the resulting product is rubbed into sore spots several times a day for 1 week).
How to help yourself
During an attack of acute pain due to sciatica, you need to know how to properly help yourself and your loved ones to alleviate the condition: - lie on your stomach, in a position that will be comfortable. You can place a pillow or cushion under your head or chest; - take a pain reliever, such as ibuprofen; - when the first symptoms have gone, lie on your back and put a pillow on your lower back or buttocks. Only after the condition has eased can you begin to treat sciatica.
If these simple manipulations do not alleviate the condition or remove the pain, you should urgently call an ambulance.
Massage and reflexology
The massage complex effectively helps relieve sciatica pain. It is carried out in the usual way or using cans. There are options using rubbing ointments. Traditional Chinese medicine recommends acupuncture and acupressure to target acupuncture points and relieve pain.
Acupuncture normalizes local metabolic processes and stimulates the entire body. Treatment is carried out through complex sessions. The targeted effect improves blood circulation, and natural recovery processes are launched.
How long does home treatment last? Stable positive results occur no earlier than after 2 weeks/month of using infusions and decoctions, and local application of compresses.
Traditional methods and herbal recipes are especially useful for pregnant women, since any analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs are contraindicated during pregnancy.
Care should be taken in selecting treatment during the period of breastfeeding. To prevent pinched nerves and support the abdomen, expectant mothers are recommended to wear a prenatal bandage in the form of a belt or a hood bandage.
What caused sciatica to appear?
Sciatica is not an independent disease, but appears as a complication caused by other, often neurological diseases. Diseases that can cause sciatica:
- intervertebral hernias are one of the main causes of sciatica;
- osteochondrosis is the main cause of the disease;
- lumbar spine injuries;
- viral and infectious diseases;
- tumors on the spine;
- arthrosis;
- hypothermia;
- lumbar radiculitis.
Traditional medicine as a way to combat sciatica
Time-tested folk recipes have proven themselves very well and give a quick and guaranteed effect. But still, treatment of sciatica at home should be carried out as an addition to other methods of therapy. There are a whole variety of traditional medicine suitable for the treatment of sciatica, including decoctions, infusions, compresses and rubs, and ointments.
Decoctions and infusions for the treatment of sciatica
- mix thyme, calendula, viburnum color (1.5 tablespoons each), horsetail (3 tablespoons). 2 tbsp. spoons of herbal mixture pour 0.5 l. boiling water, boil for 2 minutes, turn off, let cool and take 0.5 cups 3 times a day before meals;
- Brew beans and beans as tea and drink;
- aspen leaves (1 tablespoon), add water (1 liter) and boil. Drink before meals, 4 rubles/day, 250 g;
- calendula roots (1 tbsp.) and water (250 g.) Calendula infusion is often used, boil for 5 minutes, strain and drink 125 g. 2 rubles/day.
Compresses for the treatment of sciatica
- rub the problem area, apply hot beeswax and wrap the area;
- grate horseradish root and potatoes in a ratio of 1.1, mix, add a spoonful of honey. Place the mixture in a cloth and apply it to the sore spot. You definitely need to wrap yourself up.
- cabbage leaves are applied to problem areas and insulated with woolen cloth.
- propolis and beeswax are mixed in a 1:1 ratio, after which they are applied to the affected area for several hours;
- Mix egg white with 20 ml of turpentine, apply to the sore area every five hours and hold until a strong burning sensation appears.
Rubs for the treatment of sciatica
Therapy using rubbing is done by the following means:
- fir oil;
- badger fat;
- alcohol tincture on birch buds;
- agave leaves;
- St. John's wort tincture.
Ointments for the treatment of sciatica
- Mix ground iris root (3 tablespoons) with vegetable oil (1 cup). Rub into the sore spot 2 times a day.
- Vodka (250 gr.), black radish juice (5 glasses), 1 glass of honey, salt (1 tablespoon). Stir and refrigerate. Shake before use.
Baths for the treatment of sciatica
- steam pine shoots (1 kg) with water (3 liters), strain and pour into the bath in a ratio of 1:15. Take no more than 10 minutes, water temperature no more than 37°.
- add angelica decoction to the water;
- make a paste of mustard powder (400 g) with water and add to the bath. The water should be cool.
There are many folk recipes for treating the disease; the main thing is not to let the disease take its course.
Massage at home
To treat this ailment at home, you can also do acupressure, which will help the spinal tissues recover more easily. Massage can be done only when the inflammation has passed. It needs to be done in three stages:
- Determine the most painful point.
- Massage this point and the point behind the hip joint on the buttock.
- Sedative massage of the meridian points of the bladder.
New pain should not appear during the massage. If discomfort is felt, then this method should be stopped.
Gymnastics at home for the treatment of sciatica
Gymnastics is an effective method of treating inflammation of the sciatic nerve. There is no need to do complex and time-consuming exercises. The main thing to remember is that you should start doing gymnastics only after the acute stage of the disease has ended - the exercises should not cause you discomfort. Here are some exercises (all done while lying on your back on a hard surface):
- pull your legs to your chest and grab your buttocks, lower your legs to the starting position. Repeat 10 times.
- with your knees bent, try to pull your legs towards you, return to the starting position. Repeat 10 times.
- lie on your stomach, lift your body as if doing push-ups, without using your hands. Repeat 5 times.
We advise you to study - Exercises for chondrosis: a complex of effective gymnastics at home
Do exercises without fanaticism! It is advisable that your attending physician knows about your treatment methods and approves them. Your main priority is your well-being and health!
https://youtube.com/watch?v=2oesyhMg2PI
Symptoms of the disease
The first and obvious sign of sciatica is pain in the lower back, “radiating” to the legs and buttocks. The pain syndrome intensifies with any movement. Since neuritis of the sciatic nerve most often occurs in middle-aged people (30-55 years), this significantly complicates life, deprives one of the ability to work and the ability to move freely. Symptoms of sciatica may also include:
- increased body temperature over 38°C;
- an increase or decrease in sensitivity may be observed in the affected area of the body;
- change in gait, lameness, body tilt changes;
- muscle flaccidity, sometimes atrophy.
In case of inflammation of the sciatic nerve - sciatica - it is possible to relieve symptoms and treatment at home, but it is advisable to do this only after consultation with a doctor. Before you begin treating sciatica with folk remedies at home, you need to find out the original source of the disease and, in addition to fighting the symptoms of sciatic neuralgia, you need to eliminate its cause. Perhaps for a more effective and long-lasting result, it is necessary to use complex treatment.
Causes of inflammation of the sciatic nerve
Elimination of pain is not the main criterion in the treatment of sciatica (the medical term for damage to the sciatic nerve). If the cause of nerve compression is left unattended, pathological abnormalities will worsen, and painful discomfort will become a constant companion. Over time, chronic pain will affect your psycho-emotional state and performance.
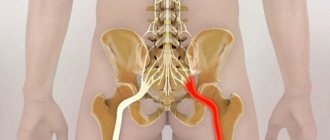
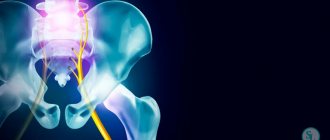
The sciatic nerve branches off from the central organ of the nervous system at the lumbar level, runs along the inner wall and posterior surface of the pelvis, and covers the ischial tubercle. Continuing its path, it innervates the muscles of the thighs, which are responsible for the flexion-extension function of the knee joints. Dividing in the area of the popliteal fossa into the tibial and tibial, through the lower leg it reaches the feet and toes.
Provocateurs of inflammation of the sciatic nerve are damage, pinching, and infectious lesions of its fibers in the innervation zone. Most often, sciatica (pain radiating along the nerve) manifests itself as a clinical symptom:
- degeneration and dystrophy of cartilaginous intervertebral layers - osteochondrosis, hernia, protrusion;
- injuries to the musculoskeletal system - bruises, dislocations, fractures;
- infectious diseases - herpes, measles, rubella, tuberculosis, HIV;
- formation of neoplasms – malignant and benign tumors, exostoses:
- piriformis syndrome.
An incorrectly administered injection into the buttock area provokes inflammation of the sciatic nerve.
Diagnostics
For an experienced specialist, determining the presence of damage to the sciatic nerve is not difficult by the presence of characteristic pain, the addition of neurological disorders or movement disorders. But finding the reasons that triggered this may take some time.
To do this, the doctor must conduct a general examination and interview the patient. This allows you to assess the condition of the spine, the functionality of the nervous system, muscle tone, conduct specific tests and detect local changes in the skin. Having formed a general impression of the nature of the existing pathological changes, and sometimes having a preliminary diagnosis, the doctor refers the patient for a comprehensive examination. It allows you to obtain objective data about the condition of the patient’s body, diagnose the slightest pathological changes in the spine and other organs, and formulate a prognosis.
Therefore, patients are usually prescribed:
- radiography of the spine, pelvis and legs in two projections - allows you to assess the condition of bone structures, detect signs of osteochondrosis and its complications, displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other, which will be the reason for further examination with other instrumental methods;
- CT is a more advanced method for studying the condition of bones, allowing one to visualize the slightest changes in them, the presence of tumors of various natures;
- MRI is the most informative method for diagnosing diseases of soft tissues and cartilage, which, in fact, are intervertebral discs; with its help, even the smallest protrusions and hernias, vascular tumors, aneurysms, spinal stenosis and a number of other common spinal diseases are detected;
- electromyography – used to assess the quality of nerve impulses to muscles and the intensity of their contraction;
- Ultrasound is used to diagnose gynecological, urological and a number of other diseases of internal organs, which can cause the development of an inflammatory process.
Often, instrumental diagnostic methods are complemented by laboratory tests. Depending on what diseases the doctor suspects, the patient may be prescribed a general blood and urine test, biochemical blood test, etc.
Baths
Baths with the addition of medicinal decoctions, infusions and other folk remedies help alleviate the general condition of a person suffering from sciatica. By taking a daily bath, you can reduce the intensity of the symptoms that arise, and over time, get rid of them altogether. In order for such a treatment technique to bring positive results, you need to know how to carry it out correctly:
- the total duration of the procedure is no more than 1 hour;
- course of therapy – no longer than 2 weeks;
- the water should have a temperature no higher than 40 degrees;
- It is recommended to take a bath before bed.
You can add mustard powder (no more than 300 g) to the baths, which is pre-diluted in water until a paste-like state is obtained. You can also add an infusion of angelica root, which is prepared in this way: the root is finely chopped, poured with boiling water in a volume of 1 liter and left to infuse for 1 hour.
For such a disease, you cannot limit yourself to folk remedies alone. That is why it is necessary to treat sciatica comprehensively, with the combined use of medications prescribed by the doctor.
What can't you do?
To prevent exercise from doing more harm than good, there are several tips on what not to do:
- It is not recommended to carry out exercises before consulting with a specialist and making an accurate diagnosis;
- When doing exercises, you need to take into account your own feelings, and not just follow the instructions;
- exercises are contraindicated in advanced forms of osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernia;
- Do not perform exercises with severe pain;
- It is not recommended to overexert yourself.
If physical therapy is approved by a specialist, it will only bring benefits and quickly eliminate discomfort. Otherwise, it can only aggravate the condition and increase pain.
Pinched sciatic nerve - exercises and gymnastics.
To quickly cure the sciatic nerve at home, you need to do exercises. Recommendations from the newspaper “Bulletin of Healthy Lifestyle” 2013, No. 19 pp. 12-13. Basic set of exercises.
Lie on your stomach. Leaning on your hands, slowly lift your upper body until your arms are straight. Stay in the top position for a few seconds, and then just as slowly lower to the floor. Lie on your back, bend your knees, arms along your body. Slowly lift your pelvis, then slowly lower it. Lie on your back, bring your knees to your chest. From this position, try to reach your knees with your forehead. Get on all fours, extend your right leg and left arm, count to 10. Return to the starting position, do the same with the opposite arm and leg. Sit on your heels, extend your arms in front of you. Slowly bend down and touch your palms to the floor. Sit on your heels, spread your arms to the sides, and, without bending, move them behind your back as far as possible. Return to starting position.
How to get rid of a pinched sciatic nerve with exercises.
When a woman’s sciatic nerve became inflamed, she first turned to a neurologist. The doctor prescribed her injections of milgamma and movalis, as well as nicotinic acid, massage and magnetic therapy, and advised her to swim more. The patient swam every day for 1-1.5 hours, tried to move more, despite the pain, and tried to assume the fetal position while sleeping. After this course of treatment, the neurologist looked at the pictures and said that medications would not help, and that surgery would be necessary. But the patient refused. Then the doctor said that all she had to do was endure the pain, maintain her spine with constant exercise and swim in water temperatures above 23 degrees. This is what the patient did: she selected a set of exercises for herself that increased blood circulation in the spine, strengthened the back muscles, and created a muscle corset. I started with simple ones, gradually increased the number of repetitions, and increased the amplitude. These exercises will help relieve a pinched sciatic nerve:
- Lying down after sleep, massage your head, gather your fingers in a bun, and rub your ears.
- Lying down, arms extended along the body, toes extended, do “scissors”
- Rotate the “bicycle” in the same position
- Lying down, bend your knees, rest your feet on the bed and slightly raise your pelvis, holding this position for 2-3 breaths.
- Holding the headboard of the bed with your hands, raise your straight legs at an angle of 90 degrees, hold them for 2-3 breaths.
- Raise your legs bent at the knees, placing your hands under them, pull your knees to your chest, lower them slightly and pull them up again. Focus on stretching the spine in the sacral area. This exercise protects against pinched nerves for the whole day.
- Get out of bed and massage your entire body using a hand massager.
- Do push-ups on the table or floor several times to improve blood circulation.
- Sit down several times, holding door handles or a stick.
- The most important exercise for stretching the spine: stand on outstretched arms and legs, raise your pelvis high, arch your back, lower your head. In this position, walk around the entire room.
- This exercise strengthens the muscles adjacent to the spine and stimulates the restoration of intervertebral cartilage.
- Sit on the floor, lean on your arms spread behind you, bend your legs. Raise your pelvis, trying to position your body parallel to the floor. Then lower to the starting position.
- Exercise "guardsman". Stand at attention. Pull the back of your head up while inhaling and after 3 inhalations and exhalations, return to i. P.
What exercises are contraindicated
Therapeutic exercises for sciatica always begin with a warm-up. Then they do stretching, gradually making the movements more difficult.
What exercises are prohibited to perform with this disease? Do not approach the bar under any circumstances . Excessive stress will further compress the intervertebral discs and can completely destroy them.
What not to do:
- Tilts and turns with weight . Friction occurs between the vertebrae, and this leads to disc injury.
- It is forbidden to squat with weight if the simulator is set to a rigid trajectory of movement, which does not always correspond to the anatomical structure of the spine.
Oddly enough, the most harmful thing for the spine is lying for long periods of time. To avoid pain in the lumbar region, the spinal column must have a strong muscular corset.
Video: “What exercise therapy exercises to do for sciatic neuralgia”