Percutaneous puncture vertebroplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that is used for destruction and compression fractures of vertebral bodies. Using a needle, a special cement is injected into the damaged vertebra, usually polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA); less commonly, suspensions of phosphate and calcium sulfate are used. This helps relieve pain, restore movement, and improve the patient's functionality. According to some data, after vertebroplasty, about 75% of patients become more mobile and active.
Our expert in this field:
Sergeev Pyotr Sergeevich
Oncologist, surgeon, chemotherapist, Ph.D. Member of the international society of surgical oncologists EESG
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
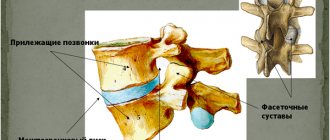
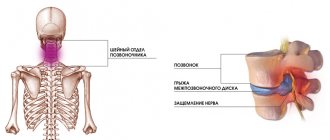
What is a vertebral compression fracture? This is a fracture caused by simultaneous compression and flexion. The load on the anterior part of the vertebra sharply increases, it breaks, deforms and takes on the shape of a wedge. Compression fractures are one of the most common spinal injuries, most often occurring in the lower thoracic and lumbar regions, as they experience the highest stress. Moreover, a serious injury is not at all necessary for this: pathological fractures often occur when the vertebral body is initially destroyed by a pathological process, and even a small applied force becomes traumatic. In this case, movements in the spine are limited, and compression of the nerve roots and spinal cord occurs. There is pain, impaired sensitivity, movement, up to complete paralysis.
A modification of vertebroplasty is kyphoplasty. During this procedure, a special balloon is first inserted into the body of the affected vertebra in a deflated state. It is inflated inside to restore the normal shape of the vertebral body and create a cavity. It is then filled with bone cement.
How is the procedure done?
During the operation, medical cement is injected into the spine with a needle. The procedure is performed under x-ray guidance and is considered minimally invasive as the work is performed through a small puncture in the skin. There is no open incision. The mandatory requirement is to administer the substance within six minutes. The entire operation takes about an hour and is performed under local anesthesia. After the cement has hardened, the patient can go home. If there is a risk of complications, observation for two days in the hospital is possible.
Hardened bone cement:
- Strengthens the damaged area;
- Eliminates pain;
- Restores back functions.
The procedure is carried out in areas where the vertebral body is covered only by skin and access to them is not difficult. Hence the name of the operation - percutaneous vertebroplasty . Due to the absence of large traumatic incisions, and access to the vertebrae through punctures and needles, the operation has a second name - puncture vertebroplasty .
Approximate cost of surgical intervention to strengthen the vertebrae
Not all medical institutions have the necessary equipment for performing vertebroplasty, as its cost is quite high. Also, the complexity of carrying out operations in government institutions free of charge is made difficult due to insufficient qualifications of specialists. Therefore, in most cases, surgical intervention to strengthen the vertebral bodies is carried out in private medical centers .
Vertebroplasty is an expensive procedure. Before you trust an unfamiliar specialist, make sure of his competence and high qualifications, find out about the number of operations he has performed and their outcomes. Pay attention to the quality of service in the medical facility itself and make sure that the necessary equipment is available.
On average, the cost of vertebroplasty on 1 segment of the spinal column can range from 30,000 to 70,000 rubles , depending on the degree of damage to the vertebra.
The indicated amount for the operation does not yet include the costs of the material used by the neurosurgeon.
In this case, a preoperative consultation with a neurosurgeon can cost 4000-5000 rubles. The use of local anesthesia will cost the patient approximately 1,000 rubles, and a day of hospital stay costs from 5,000 to 7,000 rubles.
Indications and contraindications
Spinal vertebroplasty is performed for spinal hemangioma in the acute stage, when the patient experiences discomfort when exposed to physical activity. The degree of aggressiveness is determined by the intensity of pain and the structure of the vertebrae (detected by CT and MRI).
Vertebral hemangioma can develop asymptomatically for a long time, and is detected by chance when a person consults a doctor due to severe pain. Such education requires a serious approach and a decision on the advisability of surgical treatment. The most modern technique is hemangioma vertebroplasty. As a rule, rehabilitation proceeds without complications and takes no more than 3 weeks. It is impossible to prevent the growth of spinal hemangioma, especially if there is an existing predisposition, but you can avoid excessive stress and injury.
The main indication for surgery is pain in the area of injury.
There is a need for surgery if there is a risk of fracture. In case of metastatic lesions, the introduction of bone cement has a cytotoxic effect. Effective vertebroplasty is possible provided that the vertebral body is destroyed by no more than 70%.
Absolute contraindications are:
- Inflammation of the bone tissue of the vertebra;
- Blood clotting disorder;
- Asymptomatic vertebral body fracture;
- Allergic reactions.
Relative contraindications:
- Systemic infection;
- Myelopathy or radiculopathy;
- Severe narrowing of the central canal.
Indications for the use of vertebroplasty
Surgical intervention to strengthen the vertebral bodies is used in cases:
Surgical treatment is prescribed if there is a risk of a compression fracture. The patient has hemangiomas (vertebral angiomas) - hemangiomas are benign tumors. They can affect most of the vertebral body and provoke pain in the spine during physical activity and even when walking. The location of pain is the part of the spinal column in which the vertebrae are damaged.- Active progression of osteoporosis - this disease is characterized by a violation of the bone structure of the components of the skeleton due to metabolic disorders in the body. Osteoporosis leads to disruption of the microarchitecture of bones, including the vertebrae.
- Back injuries resulting in the patient receiving compression fractures of the vertebrae (fall, road accident).
- The presence of metastases in the patient’s spine (can occur with breast cancer, lung cancer).
Note! Vertebroplasty provides the desired positive result in 90% of cases.
Rehabilitation after surgery
Recovery after surgery occurs in a short time, unless it was preceded by a spinal fracture. In this case, recovery from injury will be required.
During the first 24 hours after vertebroplasty, bed rest is recommended. Normal activities are resuming gradually. Pain at the puncture site is relieved by applying cold.
Over the next two days, the pain decreases and soon the person returns to normal life.
Vertebroplasty is used for compression therapy of the spine. In this case, the patient is given an antibiotic for prophylaxis. After the procedure you need to lie down for two hours. For osteoporosis, the procedure promotes recovery.
After surgery, the patient is required to:
- If necessary, wear a corset;
- Treat the underlying disease to avoid recurrence of the injury;
- Do not stand or sit for a long time;
- If pain occurs, take a horizontal position;
- Walk only until pain appears;
- Avoid carrying and lifting heavy objects;
- Perform therapeutic exercises.
Vertebroplasty for cancer
The spine is in third place among the organs to which malignant tumors most often metastasize, after the lungs and liver. At the same time, many patients are bothered by excruciating pain that does not decrease even during rest and at night, and pathological fractures of the vertebrae occur.
The pain can be treated with radiation therapy, but it does not help immediately (usually the effect is achieved after 2-3 weeks) and does not prevent further destruction of the vertebra.
After vertebroplasty, 70% of patients with vertebral metastases experience significant improvement within 1–3 days.
Enduring pain is life-threatening!
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Risks and complications
Risks include:
- Extrusion of cement solution, which provokes compression of nerves;
- Blood clot formation;
- Pulmonary embolism.
Practice shows that in most cases complications are associated with diseases of the spine:
- Oncological nature;
- Vertebral hemangioma;
- Osteoporosis.
Vertebroplasty is a safe operation, the successful outcome is close to 100%.
But complications are still possible in some cases (up to 5%).
Infection, tingling, severe soreness, and paralysis may occur.
- The main complication is the injection of too much cement, which causes compression of the nerve tissue, causing pain. In this case, the intervention is repeated and excess cement is removed.
- Infection due to poor hygiene. The likelihood of such a complication is almost zero, since the incision is small.
- Allergic reaction. Before the operation, tests are done for medications and bone cement.
- Lack of positive dynamics. In this case, the patient is given a thorough examination and the cause is determined.
Vertebroplasty: cost and quality analysis
Most often, osteoporotic fractures occur in the lower thoracic and lumbar (lumbar) spine, especially in elements T11, T12, L1, L2. Hemangiomas are found mostly in the thoracic area. Therefore, it is these anatomical objects that mainly need cementoplasty. The approximate cost of the operation is about 100 thousand rubles. However, everything depends on the characteristics of the diagnosis and the complexity of the case, the price of consumables, the number of defective segments and, of course, the skill level of the surgeon.
In Moscow, in some hospitals, according to our monitoring, the price sometimes reaches up to 150,000 rubles. Somewhere away from the capital, take Chelyabinsk as an example, the procedure costs an average of 85,000 rubles. As evidenced by reviews from patients who have undergone such spine treatment in our country, our cost does not always mean what the quality will be. This statement, of course, does not apply to all hospitals, but, unfortunately, there are a small number of worthy ones.
Another problem is that it is not always possible to find a clinic in your city. You have to undergo unsafe surgical intervention or limit yourself to unjustified conservative therapy, that is, the minimum that municipal medical institutions have. There is another option: travel to another city or, if it is important for a person to receive impeccable medical care, go abroad. The Krasnoyarsk residents were unlucky in this case. People are ready to accept any cost, but in Krasnoyarsk, in fact, it is impossible to undergo such an operation anywhere.
We also do not organize rehabilitation for such patients well enough, and everywhere. It is worth noting that, despite the low degree of surgical trauma, the operated person necessarily needs high-quality restoration of the spine, and the restoration program must be very thoroughly thought out. In Russian medical institutions, the patient undergoes physical rehabilitation at great expense, but does not receive proper care. Or it doesn’t go away at all. This leads to frequent complications and an additional “bouquet” of problems.
In fact, after this intervention, the risk of developing consequences should not exceed 1%-2%; in Russia it is increased to 4%-7%. This fact is explained by the fact that for the domestic territory this surgical technology is still a new, insufficiently mastered and practiced treatment tactic. Needless to say, we have a shortage of truly first-class specialists with a narrow focus, dedicated to their work and responsible to each patient. But the price in St. Petersburg and the main capital for the corresponding type of therapy is considerable. Therefore, many people choose foreign medical services.
Today, the country where all the tactics of minimally invasive spinal surgery are mastered is the Czech Republic. Prices here will be approximately 2 times lower than in any other prosperous state, and the quality will be the same, if not better. Why? Each surgical treatment program in Czech clinics necessarily includes full rehabilitation; this is a mandatory condition that operates at the legislative level in this country. The leader in demand and quality of services offered is the leading medical company Artusmed.
Among the Russian medical institutions that enjoy a good reputation, of course, within the Russian Federation, we can highlight the Research Institute named after. Vreden and DKB JSC Russian Railways (St. Petersburg), National Medical and Chemical Center named after. Pirogov and the Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics named after Priorov (Moscow).
Where is vertebroplasty performed?
For an effective operation, it is important to choose the right clinic and surgeon. Many patients choose the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow. Here, the best specialists – experienced neurosurgeons, who have the latest equipment at their disposal – restore the health of the spine.
You can find out more about the work of the clinic, the cost of diagnostics and treatment of the spine on the website; reviews of patients who have undergone surgery are also provided here. Many of them note that after vertebroplasty, the pain syndrome has decreased significantly and significant relief is felt.
Vertebroplasty is a sought-after procedure that is currently gaining popularity.
Patients in need of vertebroplasty can find out how much the operation costs by calling the clinic's telephone numbers.
Preparation for the procedure
Before vertebroplasty, blood and urine tests, blood coagulation tests, tests for infections (syphilis, HIV, viral hepatitis), fluorography, ECG are performed, and consultation with a therapist is required. The condition of the spine is assessed using radiography, computed tomography, MRI, and scintigraphy.
No special preparation is required. The patient should inform the doctor about what medications he is taking; some of them may need to be discontinued for a while (aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anticoagulants).
Usually the intervention is performed under local anesthesia. Sometimes, if sedation or general anesthesia is planned, you are not allowed to eat or drink for several hours before surgery.
Some patients are prescribed a course of antibiotics to prevent infectious complications.
If a woman who is prescribed vertebroplasty is pregnant or does not rule out the possibility, she should inform the doctor. During pregnancy, X-rays and CT scans should not be used, and MRI should only be used in extreme cases and with caution (although there is no evidence that the strong magnetic field during this study can harm the unborn child).
Feedback on vertebroplasty of the lumbar vertebrae
The patient came to the clinic due to constant pain in the lumbar spine. She had difficulty walking and could not stand up or sit down normally. An examination showed she had a compression fracture of the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae. Percutaneous vertebroplasty was performed. The patient was activated and was able to walk two hours after surgery. “At first I was very afraid of this operation, but it went well... Read full review
International clinic Medica24 is the only place where they could help
Our clinic became the only place where they could help the patient. All the others refused it due to age and concomitant diseases. The reason for hospitalization was the threat of a fracture of the first lumbar vertebra due to a secondary lesion. The patient underwent CT-guided vertebroplasty and the first course of immunotherapy. Further treatment is ahead. “The only clinic where we found help and very good specialists. I express my gratitude to the doctors... Read full review
After spinal surgery, mom already tried to dance
Maria Lvovna’s mother could not walk due to severe back pain. Diagnostics revealed damage to five vertebrae, which caused excruciating pain. Andemir Olegovich Akhov came to the rescue, who performed vertebroplasty in three stages, during which bone tissue was restored. Thanks to the technique used and the professionalism of Andemir Olegovich, the recovery period was short and, as the patient’s daughter, mother, notes... Read full review
Feedback on the treatment of spinal hemangioma 12/12/2019
The patient presented with a hemangioma of the first thoracic vertebra. She complained of instability and heaviness when getting out of bed. She underwent vertebroplasty surgery. The patient was able to walk the same day. The problems she complained about disappeared! “It’s just wonderful to spend it here. Very fast, very professional. The condition recovers very quickly after this. So don't be afraid of anything. Just relax and trust your doctor. Everything will be... Read full review
Testimonial from a patient after treatment of hemangioma of the first thoracic vertebra
The causes of certain symptoms may lie far from the place where they appear. Therefore, there is a high probability of medical error and incorrect diagnosis. Some doctors, not understanding the causes of symptoms, refuse treatment. This is possible everywhere, but not in the international clinic Medica24. Here is a case where our specialists were able to help a person even when others refused. The patient came to… Read full review
Vertebroplasty for risk of pathological fracture
The patient was admitted to the clinic in serious condition due to the underlying disease. The patient’s relatives chose the clinic on the recommendation of a friend who had previously been treated here. A CT scan showed the presence of distant metastases in the bones of the spine. At the medical consultation, a decision was made to carry out staged vertebroplasty in two parts of the spine: In the cervical spine for the purpose of fixation and stabilization. In the lumbar… Read full review
Vertebroplasty at the international clinic Medica24
Patient Yuri Pavlovich came to the clinic with complaints of complications after a course of chemotherapy. A routine CT scan revealed foci of destruction of the bone tissue of the spine and ilium. This threatened the patient with a pathological fracture. Yuri Pavlovich underwent osteo- and vertebroplasty. Operating surgeon Andemir Olegovich Akhov. Read full review
Percutaneous vertebroplasty: stages of the operation
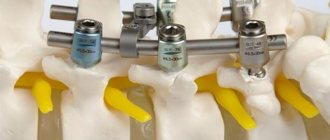
During the operation, a puncture technique is used to create access for the introduction of medical cement. For stabilization, there is no need to install any internal metal fixators at all, which are not biodegradable implants. And this fact is an undeniable advantage of vertebroplasty.
32 years have passed since the creation of the method, so it can be safely called a proven and guaranteed effective method of augmenting partial and weak vertebrae. The intraoperative process takes place on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia; in some cases, it is additionally possible to administer intravenous sedatives for the patient’s psycho-emotional comfort.
- During the surgical session, the person lies on his stomach. To avoid neuropathic consequences, the operating doctor places cushions under certain parts of the body.
- The skin is extensively treated with an antiseptic, after which the doctor makes the correct anatomical markings on the skin. It is needed so that you can accurately introduce the anesthetic agent and correctly insert the puncture needle, through which, in fact, the strengthening solution will be supplied.
- Next, infiltration anesthesia is injected into the tissues of the surgical field, which will have a strong analgesic effect, and the patient will not experience any discomfort during surgery.
- Then, under powerful intraoperative fluorographic control, a thin needle is inserted parapendicularly or transpedicularly along its entire length into the affected vertebra. When the high-precision insertion of the needle is completed, the specialist begins preparing the cement mortar.
- After mixing the PMMA well, the resulting creamy mass is immersed in a special piston, which is connected to a conductor needle. Then the viscous mixture is immediately squeezed into the intravertebral structures in strictly dosed quantities.
- At the end of the manipulations, the instruments are carefully removed, and the wound is disinfected, and a sterile bandage is attached over it. Sutures are not required, since such a miniature puncture (size is approximately 3 mm) heals safely on its own without suture tying the edges of the skin. The entire session takes 40-50 minutes.
After 10 minutes, the introduced mixture completely hardens. As a result, the once defective segment acquires correct proportions, integrity and strength. The operated person does not get up immediately; he needs to maintain a horizontal, motionless position for another 2 hours. Afterwards you are allowed to get up and move around. If the condition is satisfactory, the patient is usually sent home on the same day (after approximately 6 hours). If the specialist considers it necessary not to rush into discharge, you may be hospitalized for 2-3 days.
Important! In most cases, the use of support devices in the form of corsets and bandages is not necessary. A person can walk normally immediately. However, do not neglect an orthopedic device if your doctor prescribed it for you! Remember that the complexity of the clinical picture is different for everyone, and on an individual basis it is possible that for your adequate recovery you will need to wear a certain type of fixation belt.
Russian Oncology Research Center named after. N.N. Blokhin RAMS, Moscow
Abstract. Vertebroplasty is indicated as a method that improves the quality of life of patients with metastatic lesions of the spine. From 2001 to 2009 at the Russian Cancer Research Center named after. N.N. Blokhin performed 235 vertebroplasty procedures in 168 patients with metastatic lesions of the spine. Vertebroplasty was most often used in patients with metastases of kidney cancer, breast cancer and multiple myeloma. The main clinical indication for vertebroplasty in cancer patients is pain caused by tumor damage to the spine and a decrease in its supporting function. An improvement in the quality of life after vertebroplasty was observed in the majority of patients. The comparative simplicity of the method, high efficiency and safety allow it to be widely introduced into clinical practice.
Key words: metastases in the spine, percutaneous vertebroplasty, treatment of pain, interventional radiology.
Introduction
The current state of medical science allows us to successfully solve the problems of radical and palliative treatment of patients with tumor lesions of various organs and systems, improve the five-year survival rates of patients with cancer, and use new diagnostic and treatment methods.
However, among patients suffering from spinal tumors, the majority are patients in whom multiple metastatic lesions of the vertebrae are a consequence of dissemination of primary malignant neoplasms of other organs. Metastatic lesions of the skeletal bones develop in 50-70% of patients with cancer. Metastatic lesions of the spine occur in 37-84% of patients with disseminated cancer of the breast, prostate, lung, thyroid gland, and kidney. These are those patients for whom, due to the significant prevalence of tumors and short life expectancy, extensive surgical interventions are not indicated, but only symptomatic treatment is possible [1, 2].
If it is impossible to achieve a radical therapeutic effect in patients, special treatment carried out for palliative or symptomatic purposes can significantly increase the life expectancy of patients and ensure its satisfactory quality [3, 5]. Pain syndrome and instability of the musculoskeletal system lead to disability of patients, and in some cases do not allow further therapy. Treatment of patients with metastatic lesions of the spine is a complex, multidisciplinary problem that lies at the intersection of oncology, neurology, and orthopedics. Prevention of the development of serious neurological complications due to tumor compression of the spinal cord or as a result of a pathological fracture of the spine, prevention or elimination of pain are the main tasks that must be addressed first. Pain syndrome of varying severity in 95% of patients with metastatic lesions of the spine is its first clinical manifestation. Pain as a manifestation of sensory disorders indicates the appearance of neurological symptoms; Subsequent tumor progression leads to more serious neurological disorders - movement disorders, more often observed with compression of the spinal cord by a tumor or with a pathological fracture of the spine. The duration of the pain syndrome before the development of movement disorders is on average 4-6 weeks [4, 2].
The introduction into clinical practice of special minimally invasive interventional radiological techniques, which make it possible in a short time to significantly reduce pain and improve the quality of life of patients, has significantly changed the tactics of treating such patients in specialized medical institutions, gradually replacing traumatic and technically complex surgical interventions on the spine. One such method is percutaneous vertebroplasty. During this manipulation, percutaneous strengthening of the vertebral body is performed with special bone cement. For the first time, percutaneous vertebroplasty was successfully used by neurosurgeon R. Galibert and interventional radiologist N. Deramond in 1984 in France in a patient with hemangioma of the C2 vertebra. The authors also identified indications and contraindications for performing this type of treatment. In 1989, Lapras and Kaemmerlen were among the first to publish the results of vertebroplasty; The work noted a decrease in pain in 80% of patients. In 1997, Cortet et al. presented the results of using the method: 97% of patients with metastatic lesions of the spine obtained a positive treatment result in the form of a decrease in the intensity of pain of varying degrees. Currently, percutaneous vertebroplasty is widely and successfully used in the treatment of patients with metastatic lesions of the spine. The essence of the percutaneous vertebroplasty method is the percutaneous injection of special bone cement based on polymethyl methacrylate into the destruction cavity in the vertebral body. By filling the destruction cavity, the anterior supporting complex is stabilized, and pathological micromovements in the vertebral body disappear, causing irritation of the richly innervated periosteum, which is clinically manifested as a decrease in pain in the affected segment. The adequacy of the needle insertion into the pathological lesion and the filling of the pathological cavity are controlled by radiological methods (fluoroscopy, X-ray CT).
Indications and contraindications for vertebroplasty
There are two types of fundamental indications: clinical and radiological. The main clinical indication for percutaneous vertebroplasty is pain caused by vertebral instability.
X-ray indications are a threat of a pathological fracture or a pathological fracture of the vertebra. Stable pathological vertebral fractures without clinical pain syndrome are not an indication for vertebroplasty. Such patients receive conservative treatment: wearing a corset and analgesic therapy. If conservative treatment is ineffective and/or the risk of a pathological fracture develops, percutaneous vertebroplasty may be performed. The principal contraindications are an inflammatory process (spondylitis, discitis, osteomyelitis), diffuse pain syndrome, severe coagulopathy that cannot be corrected, the general severe somatic condition of the patient, and severe neurological deficit. The vertebroplasty procedure itself does not improve the neurological picture, but it can prevent the development of compression of neural structures by preventing pathological fracture. Also, vertebroplasty is not a method of treating radicular pain syndrome, since the method itself does not eliminate compression of the nerve structures.
Material and methods
At the Russian Oncological Research Center named after. N.N. Blokhin Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, interventional radiological percutaneous vertebroplasty has been used since 2001. During the period from 2001 to 2009, 235 vertebroplasty procedures were performed on 168 patients. Average
The age of the patients was 56.3 years (from 17 to 73 years), men - 79 (49%), women - 89 (51%). Data on the level and morphological variant of tumor lesions of the spine are presented in the table.
In all observations, the neurological status, severity of pain, quality of life before and after puncture vertebroplasty were assessed. Pain syndrome, which is the main criterion for the effectiveness of the procedure, was assessed using the Watkins scale and visual analogue scale (VAS). Neurological status was assessed using the Frankel scale, quality of life - using the Karnofski scale.
Description of the percutaneous vertebroplasty method
To perform percutaneous vertebroplasty, special sterile disposable kits are used: needles and bone cement based on polymethyl methacrylate (Fig. 1). As a rule, each kit already contains all the necessary components: needles, cement and solvent, injector. For different levels of damage (cervical, thoracic or lumbar), bone needles of appropriate diameter and length are selected.
The procedure is performed under radiological guidance using an electron-optical converter (EOC) or computed tomography (CT) scanner, since both access and direct injection of bone cement require radiological imaging. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and only in rare cases, if it is impossible to achieve an analgesic effect, is anesthesia required.
Immediately before the procedure, a radiological examination of the affected part of the spine is performed. The level or levels of the lesion are visualized, access trajectories are determined, and horizontal and vertical markings are performed at all levels of the proposed intervention at once (Fig. 2).
Infiltration anesthesia is performed with local anesthetics on the skin and access areas to the affected vertebrae.
Next, under X-ray control, needles are inserted into the foci of destruction of the vertebral bodies (Fig. 3). At this stage, all the needles required for the manipulation are inserted.
The next step is the introduction of bone cement (Fig. 4). After mixing the bone cement components (bone cement + solvent) and time exposure (4-5 minutes), the cement reaches the required consistency. Provided the viscosity and fluidity are suitable, polymethyl methacrylate is injected under real-time X-ray control. Under such conditions, the risk of bone cement entering the venous system or the lumen of the spinal canal is minimal.
The final stage is a control X-ray examination of the adequacy of filling the pathological lesions and an assessment of possible complications. After complete polymerization of the bone cement, the needles are removed.
In case of multilevel lesions of the spine and multiple compression fractures of the vertebrae, simultaneous multilevel percutaneous vertebroplasty is recommended. In this case, the choice of vertebroplasty levels will depend on the topic of pain and the x-ray picture.
In the absence of complications after vertebroplasty, patients are mobilized after 2-4 hours. In some cases, on the first day after the procedure, the need for analgesic therapy remains.
Complications of vetebroplasty
Clinical complications of percutaneous vertebroplasty are quite rare and occur in 1-3% of cases. The most common occurrence is compression of the foraminal opening by a fragment of bone cement with the development of radiculopathy and a short-term increase in pain, observed in 10% of patients in our work. In 8% of patients, the pain syndrome is relieved by conservative therapy. Surgical treatment of complications of vertebroplasty was required in 2.3% of cases.
The most serious complication is the entry of cement into the spinal canal with compression of the spinal cord and the development of lower paraplegia and pulmonary embolism with fragments of bone cement (Fig. 5). These complications are extremely rare, occurring in 0.5-1% of cases.
A feature of the percutaneous vertebroplasty method is the extravertebral penetration of bone cement into the soft tissue, which, according to the literature, occurs in 17 to 73% of cases (Fig. 6). These are so-called radiological complications that do not cause clinical manifestations or the danger of bone fragment migration. In such cases, no therapeutic measures are required, but only dynamic observation.
Results and its discussion
Before vertebroplasty, pain syndrome was observed in 146 (87%) patients. After vertebroplasty, a decrease in pain was noted in 141 (84%) patients, including pain cessation in 72 (43%) patients.
Before vertebroplasty, the quality of life was impaired in 144 (86%) patients; after surgery, an improvement in the quality of life was noted in 124 (74%) patients. Neurological disorders were observed in 20 (12%) patients before surgery; after vertebroplasty, neurological deficit regressed in 11 (7%) patients.
The average follow-up period after vertebroplasty was 11 months (from 1 to 46 months). The average life expectancy of patients with metastatic tumors was 10.9 months. Relapses were observed in 45 (27%) patients within a period of 6 to 36 months.
Clinical manifestations of complications of vertebroplasty in the form of radiculopathy and short-term increase in pain were observed in 16 (10%) patients. In 13 (8%) patients, pain was relieved by conservative therapy. Surgical treatment of complications of vertebroplasty was required in 4 (2.3%) patients: in one case, emergency decompressive laminectomy was performed due to compression of the spinal cord with bone cement and the development of lower paraplegia, in 3 (2%) cases - corpectomy with replacement of the vertebral body with an endoprosthesis in due to the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment of pain syndrome that intensified after vertebroplasty. Interventional radiological percutaneous puncture vertebroplasty is a modern effective method of treating pain in patients with tumor lesions of the spine, allowing to reduce pain in 84% of patients and improve the quality of life in 74% of patients.
Literature
1. Anselmetti, G.C. Pain Relief Following Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Results of Series of 283 Consecutive Patients Treated in Single Institution / G.C. Anselmetti, G. Corrao // Card. Vasc. and Int. Radiol. - 2007. - Vol. 30, No. 3. - P.441-447.
2. Deramond, H. Percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethyl metacrylate. Technique, indications and results / H. Deramond, C. Depriester, P. Galibert // Radiol. Clin. North Am. - 1998. - Vol. 36(3). — P.533—546.
3. Sundaresan, SN Hughes JEO Metastatic tumors of the spine / SN Sundaresan, G. Krol, GV DiGiacinto // Tumors of the Spine. Diagnosis and Clinical Management / SN Sundaresan, HH Scmidek, AL Schiller eds. - Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1990. - P.279-304.
4. Weill, A. Spinal metastases: indications for and results of percutaneous injection of acrylic surgical cement / A. Weill, J. Chiras, JM Simon // Radiology. - 1996. - Vol. 199. - P.241-247.
5. Wingo, PA Cancer incidence and mortality, 1973—1995: a report card for the US / PA Wingo, LA Ries, HM Rosenberg // Cancer. - 1998. - Vol. 82. - P.1197—1207.
What is bone cement for vertebroplasty?
In order to fuse a weak vertebra, restore its shape, give it reliable rigidity and eliminate pain, a kind of polymethyl methacrylate drug (PMMA) is used for orthopedic purposes. In medicine, it is called bone cement, the price of which is high, which explains the high cost of the treatment procedure. The drug is represented by two main components: a liquid monomer and a powdery polymer. They are combined using a special mixer immediately before the puncture.
Cement.
When two substances are mixed, a polymerization reaction occurs, accompanied by the release of heat for 8-10 minutes. Without exceeding this time threshold, the neurosurgeon specifically introduces the resulting mass (55° Celsius), which resembles a semi-liquid paste, into the problem segment. The cementing composition permeates the spongy bone tissue, filling all defects from the inside and connecting the separated bone fragments into a single whole. What happens to the cement after the time is up? After about 10 minutes, it will harden into an impenetrable solid conglomerate that can withstand pressure of as much as 100 Pa. Thus, the restored segment also receives powerful prevention from the occurrence of fractures in the future.
For VP, special types of non-toxic cement are used, which have the following characteristics:
- high viscosity, which ensures uniform filling of bone tissue with cement mortar and prevents it from leaking beyond the vertebra;
- optimized thermal effect, thereby eliminating the likelihood of burn damage to anatomical structures;
- excellent biocompatibility with biological bone structures, which does not allow the body to react negatively to the substance introduced into the spongy tissue and trigger a rejection reaction;
- radiopacity, in other words, clear visualization of the drug during its implantation, which ensures high control over the process of injection of bone cement;
- antibacterial qualities due to the optimal content of antibiotics in the composition of the drug, which prevents the development of infectious and inflammatory processes;
- impeccable biomechanical properties, while sufficient strength, even of a very fragile element with severe osteoporosis, is achieved after the introduction of only 3.5-4.0 ml of cement.
Tecres product line.
As you may have noticed, polymethyl methacrylate is additionally enriched with a radiopaque additive and an antibiotic agent. As a rule, barium sulfate (BaSO4) acts as a contrast agent. The antibiotic is gentamicin or vancomycin.