Causes
The spine is a complex structure consisting of vertebrae, connective tissue joints, muscles, and intervertebral discs. Regardless of the severity, any spinal injury is considered a serious illness. Spinal injuries occur as a result of:
- Falls from any height. Loss of stability and imbalance can lead to dangerous injuries. Even falling from your own height is dangerous, not to mention falling from more dangerous balconies, stairs, scaffolding, trees or roofs.
- Mechanical impacts as a result of road accidents. Bruises and fractures occur due to excessive compression and inertial forward movement of the head.
- Compression. Injury occurs when a heavy object falls on a person from above. Most often, compression of the spine occurs as a result of the collapse of any structures, industrial emergencies, or beatings.
- Pathological processes in the body. Damage to the spine is observed in older people as a consequence of the rapid progression of osteoporosis, degenerative bone diseases, and degenerative changes.
Risk factors for spinal injury
Did you know that...
Next fact
Such factors are divided into two types.
Fatal:
- Floor. Women are susceptible to osteoporosis, especially after giving birth. This disease negatively affects the skeletal system of the spine.
- Age. Men often develop osteoarthritis in adulthood.
- Genetic predisposition. The risk increases significantly if the parents have spinal problems.
- Dysplasia of joints and bones. Presence of congenital diseases.
Removable:
- Obesity. Overweight people always have serious problems with their knee and ankle joints. Large body weight affects the bone apparatus, which aggravates concomitant diseases and leads to bone deformation.
- Systematic excessive physical activity. This includes: heavy lifting, standing for long periods of time, active work that causes severe fatigue.
Pay attention to risk factors for spinal injury. Low activity. It is as harmful as a heavy load. Insufficient activity causes the development of muscle and bone tissue atrophy.- Professional sports. Sports that place stress on the spine significantly increase the development of joint diseases.
- Calcium deficiency. With a deficiency of this element, pathologies of the musculoskeletal system quickly develop. In addition, calcium is the main component of bone tissue. With its deficiency, bones weaken and become fragile.
- Smoking. This bad habit greatly increases the risk of osteoporosis.
- Alcohol abuse. Their excessive consumption reduces the ability to absorb calcium, which causes osteoporosis.
- Diseases of joints and bones. Such diseases lead to other problems that are no less serious.
- Serious injuries. It is advisable to prevent them, as they lead to significant disruptions in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system. Even full treatment will not help.
Risk factors for spinal injury must be completely eliminated. If injury occurs, treatment must be completed.
Video: “Sports injuries of the spine”
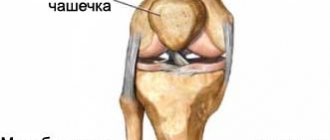
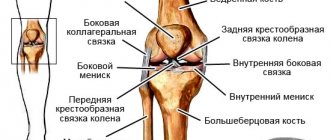
Types of spinal injuries
Injuries to the spinal column are divided into open and closed. Depending on the location - for injuries of the cervical, thoracic, lumbar spine. Based on the nature of the damage, the following are distinguished:
- spinal bruises;
- ruptures of joint capsules, ligaments without displacement of vertebral bodies - distortions;
- vertebral arch fractures;
- vertebral body fractures;
- fractures of the transverse, spinous processes;
- dislocations and subluxations;
- fracture-dislocations;
- spondylolisthesis is a displacement of the body of the superior vertebra relative to the inferior one as a result of a traumatic rupture of ligaments.
Of the total number of spinal injuries, stable and unstable injuries are distinguished. With stable injuries, the traumatic disorder does not get worse, but with unstable injuries, there is always a threat of developing a more severe condition. Most often, these injuries occur with combined damage to the posterior and anterior sections of the vertebrae.
Traumatological classification implies the division of all spinal column injuries into large groups:
- Uncomplicated - in which the integrity of the spinal cord is not compromised.
- Complicated – with spinal cord injury. Depending on the type of spinal cord injury, there are: reversible (concussion), irreversible (concussion, bruises), compression myelopathy (the result of hematoma, swelling).
06.08.2018
Author of the article: neurosurgeon Ermek Valerievich Kisaev
What is a spinal injury and why is it dangerous?
Spinal injuries are damage to the structures that make up the spinal column. This could be a bruise, dislocation, fracture, sprain of the ligamentous apparatus. It is necessary to understand and separate the concepts: spinal injury and spinal cord injury. Because a spinal injury is damage to the musculoskeletal system. A spinal cord injury is damage to the nervous system. These are not the same thing, although very often they accompany each other due to anatomical proximity. There may be a spinal fracture and no spinal cord damage. And in some cases, there is a spinal cord injury without damage to the spine.
Spinal injury is a common injury, accounting for 2-12% of the total number of musculoskeletal injuries. In young and middle age, men are more likely to suffer; in old age, women are more likely to suffer. Spinal injuries are detected less frequently in children than in adults. Usually the cause is intense traumatic impact, but in older people, spinal injuries can occur even with minor trauma (for example, from a simple fall at home or on the street).
The consequences depend on the characteristics of the spinal injury. A significant proportion of injuries are severe injuries. According to statistics, about 50% of the total number of injuries result in disability. With spinal cord injuries, the prognosis is even more unfavorable - from 80 to 95% of patients become disabled, and in approximately 30% of cases there is death. The higher the level of damage, the greater the likelihood of death. Injuries in the upper cervical region, at the level of 1-2 cervical vertebrae, more often lead to death due to the proximity of the brain stem. The brain stem contains centers that control the heart and breathing. Treatment of spinal injuries is carried out by traumatologists and neurosurgeons.
What are the causes of spinal injury?
In most cases, spinal injuries occur as a result of: road accidents, falls from a height, collapses (for example, collapses of building ceilings during earthquakes, blockages in mines). Severe injuries, accompanied by a high incidence of death and a high percentage of disability, occur during diving. Doctors call this category of patients “divers.” While diving in an unfamiliar place, in shallow water, when hitting the head, a fracture or dislocation of the cervical vertebrae occurs. This happens quite often due to the anatomical features of the cervical spine. Such as greater mobility of the cervical spine, weakness of the joint system of the neck and narrowness of the spinal canal, which increases the likelihood of damage to the spinal cord. If the cervical spine is severely damaged in such a “diver,” paralysis may immediately occur and the person will drown. If they manage to pull him out of the water, the spinal injury is aggravated by drowning, which worsens the prognosis. In addition, careless resuscitation measures and transportation can lead to additional secondary displacement of bone fragments with damage to the spinal cord.
Terminology used to define spinal injury
The simplest classification, sufficient to understand the problem among a wide range of the population, includes such concepts as stability-instability, complicated-uncomplicated, compression and spinal cord injury. I will try to explain these terms in simple words. With a stable spinal injury, there is no risk of displacement of bone fragments. With unstable damage, displacement of bone fragments and secondary damage to nerve structures is possible. This is important to determine the risks and feasibility of transportation. Complicated spinal injury is damage to the spinal column with complications from the nervous system. That is, the victim has motor, sensory and pelvic disorders. Such patients are treated by neurosurgeons. Traumatologists treat uncomplicated spinal injuries. I would like to note that traumatologists and neurosurgeons have different approaches to treatment. A spinal fracture can occur with or without spinal cord compression. Compression can be caused by bone fragments, post-traumatic disc herniation, or hematoma. In this case, the spinal cord itself may not be damaged. And if the compression is quickly removed, there is a chance of restoring spinal cord function. If the compression is not removed in a timely manner, the spinal cord dies, since in addition to the compression of the brain, the blood vessel feeding it is also compressed. Spinal cord injury is a post-traumatic disruption of the anatomy of the spinal cord. Everything is bad here, and even timely surgical intervention may not help restore function.
What is important to know?
It is important to deliver the victim to a medical facility as soon as possible. The time factor is a very important factor. It is generally accepted that 80% of irreversible changes in the spinal cord due to compression occur in the first 8 hours.
It is important to immobilize the damaged area during transportation to prevent secondary damage. Transportation in case of suspected spinal injury on a backboard (flat, hard surface). If there are no special fixing means, then improvised ones are used, made from scrap materials.
What is the treatment for patients with spinal injury?
I would like to note right away that when the spinal cord is traumatically damaged, it is not sutured or glued together. All treatment is aimed at creating conditions for the restoration of the spinal cord. The basic principles in spine surgery are decompression (elimination of compression of nerve structures) and stabilization of the damaged spinal motion segment. The capabilities of modern medicine in treating spinal injuries have expanded. For stable spinal fractures, minimally invasive surgeries such as vertebroplasty are possible. The operation consists of strengthening a broken vertebra by injecting bone cement into it. It is performed under local anesthesia. The approximate operation time is half an hour. After 2 hours you can walk. In case of severe spinal fractures, complete removal of the damaged vertebra is possible. Such operations are carried out in 1 or 2 stages, depending on the situation. Much depends on the technical equipment of the clinic and the experience of the specialist.
Rehabilitation of patients with spinal injury
Most often, a person does not die from the spinal injury itself. He may die from bedsores (30%), pneumonia (30%), urological complications (30%), thromboembolism and other causes. These are approximate figures. To reduce mortality and improve a person’s recovery after a spinal injury, a set of rehabilitation measures is necessary. The sooner you start this, the better the result will be. It is better to carry out all these actions together with relatives. So that they can learn all this and continue at home on their own, since recovery can take months and years. After surgery to stabilize the spine, you can start the next day.
Let us consider the example of a victim with a complicated injury to the cervical spine, as the most difficult case. In order to prevent congestive pneumonia, breathing exercises are performed. To do this, the patient inflates balloons. If this is difficult, then you can blow bubbles in a glass of water through a straw. To prevent the development of bedsores, it is necessary to turn the patient from side to side every 2 hours, with rubbing and kneading the back. It is necessary to ensure that the bed linen is free of folds and foreign objects (crumbs, etc.). Bedsores appear very quickly and heal very poorly. Therefore, it is easier to prevent their occurrence. Daily massage and passive joint development are needed if the patient himself is unable to move. The development of joints should be carried out daily, regularly. If this is not done, contractures arise, mobility in the joint is limited or disappears, and even if the motor function of the spinal cord is restored in the future, there will be no movement due to the joint. Passive development must be done carefully. Often patients may not feel what you are doing and this can lead to damage to the ligamentous apparatus and even fractures. If defecation is disrupted or stool is retained, it is necessary to empty the intestines at least once every 3 days with the help of medications and cleansing enemas. If feces accumulate in the intestines, they will be absorbed into the blood and poison the body. In addition, the passage of gases will be disrupted, there will be bloating, which will interfere with normal breathing and aggravate the condition of the victim. Impaired urination, when urine is retained, it accumulates. The body continues to produce urine, but cannot empty the bladder. Bladder pressure increases, the outflow of urine from the kidneys is disrupted, which leads to kidney problems. When a urethral catheter is installed, urine flow is restored, but other problems arise with the catheter. First, the catheter is a foreign body and the development of urethritis, cystitis, and pyelonephritis is possible. Secondly, if the catheter is installed for a long time, a urethral bedsore may develop. To exclude this, an operation is often performed - epicystostomy, when a catheter is installed through the anterior abdominal wall into the bladder cavity. It is not advisable to do this. The fact is that with constant emptying of the bladder (it is always empty), the bladder shrinks and it loses the ability to stretch and contract. And it is possible to restore urination. The fact is that in the lumbar region of the spinal cord there is a lumbar thickening, in which the center of spinal automatism is located. If you interrupt the flow of nerve insults above this level (even with a complete anatomical break of the spinal cord), then after some time spinal automatism will begin to work. The intestines and bladder will work independently of the brain and empty as they fill. But for this, something needs to irritate the receptors of the bladder and intestines. Bladder training is carried out by closing the urethral catheter or periodically removing it. The patient may not feel it, but there will be emptying of the bladder and bowels. Men can even have an erection. There may be no sensitivity, but the ability to have sexual intercourse will remain.
Spinal injury is a serious big problem for the injured person and his relatives, for doctors who, by the nature of their work, are involved in solving this problem, for a state that is losing its population of young, productive age, who die or become disabled. It's better to avoid this. To reduce the likelihood of such problems, it is necessary to wear seat belts in transport, follow safety precautions while working and playing sports, and do not dive in unfamiliar places. And if a disaster does happen, the treatment results and outcome will be better if the medical staff and loved ones work together. Relatives must learn the specifics of caring for the patient if they want to avoid major problems and improve the outcome. Psychological support means a lot. It will not be replaced by medicine and social services.
Spinal surgery is evolving very rapidly. Treatment results are constantly improving. Doctors are not gods, but maybe someday we will learn to treat this too.
Symptoms
The severity of the clinical picture is determined by the type of injury. Spinal bruise is characterized by:
- extensive subcutaneous hemorrhage in the area of traumatic impact;
- diffuse soreness;
- swelling of the skin over the corresponding section;
- restriction of physical activity.
When fractures of the transverse processes of the vertebrae occur:
- severe pain in the soft tissues around the injury site;
- painful sensations intensify when turning the body;
- stuck heel syndrome - the patient lying on his back cannot lift his straightened leg off the surface.
Damage to the cervical spine is manifested by intense pain in the head, a feeling of numbness in the arms and legs. The patient reports memory impairment. Neurological symptoms immediately appear: vomiting, ringing in the ears, impaired tendon reflexes. In severe cases, paralysis occurs.
When the atlas (I cervical vertebra) is damaged, the following is observed:
- impaired movement in the neck area;
- pain in the upper neck radiating to the back of the head;
- nausea;
- loss of consciousness;
- visual impairment;
- convulsions.
In severe cases, when fragments are displaced, the patient dies as a result of compression of the medulla oblongata.
Fractures, fracture-dislocations, subluxations are manifested by an increase in the interspinous spaces, and sometimes bulges appear in the area of injury. There is always a limitation of mobility. The back muscles are tense. All types of sensitivity are impaired.
Spinal injuries accompanied by spinal cord injuries present with severe symptoms. In case of damage at the level of the IV cervical vertebra, the victim rapidly develops diaphragmatic paralysis, which leads to respiratory arrest and death.
In some cases, patients with spinal injuries experience dysfunction of the pelvic organs. Spinal cord rupture causes massive intestinal bleeding. Pathological changes in local blood flow and lymph movement quickly lead to the formation of bedsores.
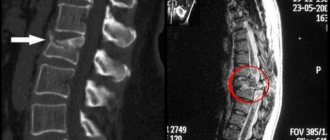
Osteochondrosis
Over time, the spine is subjected to daily stress and minor injuries, which ultimately leads to wear and tear of the intervertebral discs and their degeneration. The fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc is damaged under load, micro-tears of fibrous tissue occur, and then the damaged area is replaced by scar tissue, the elastic properties of which are much worse than those of fibrous tissue. Such changes in the annulus fibrosus lead to decreased shock-absorbing function of the disc and a greater risk of recurrent disc ruptures. As the annulus fibrosus becomes scarred, the gelatinous part of the disc (nucleus) also gradually shrinks, which in turn leads to a decrease in disc height. As the height of the disc and shock-absorbing functions decrease, the vertebrae begin to exert more pressure on each other under load, which leads to the formation of bone growths (osteophytes). Violation of the integrity of the fibrous ring leads to the formation of disc herniations. Disc herniations and osteophytes can cause compression or stenosis, leading to neurological symptoms.
Consequences
The severity of post-traumatic complications depends on the characteristics of injuries to the spine and spinal cord, the timeliness of first aid and the usefulness of subsequent treatment. The most common negative consequences are:
- acquired instability of the spine;
- intense pain syndrome;
- chronic inflammation in the area of injury;
- post-traumatic osteochondrosis;
- decreased muscle tone;
- muscle fiber atrophy;
- decreased physical strength and endurance;
- reduction of the lumen of the spinal canal;
- combined deformation of the spinal column in the form of kypholoscoliosis;
- disorder or complete loss of sensitivity;
- spastic manifestations;
- complete paralysis of the body;
- insufficiency of functions of internal organs.
In addition to physical changes, patients often experience psychological disorders. After spinal injuries, patients need long-term treatment and rehabilitation, which entails a complete change in their usual lifestyle, giving up sports and hobbies.
The inability to independently care for one’s needs and perform simple hygienic procedures causes neuroses and depressive disorders.
Spinal cord injury
Sometimes a spinal injury extends to the spinal cord. This may be due to external factors such as a severe contusion or a compression fracture of the cervical spine, although the injury can occur in any part of the spine.
The following signs usually indicate a spinal cord injury:
- numbness or tingling in the limbs;
- pain and stiffness in the spine;
- signs of shock;
- inability to move limbs;
- loss of urinary control;
- loss of consciousness;
- unnatural head position.
Spinal problems are often the result of accidents or violent acts. Main causes of injuries:
- a fall;
- diving in shallow water (consequences of hitting your head on the bottom of a reservoir);
- trauma after a car accident;
- jumping;
- head injury during a sporting event;
- electric shock injuries.
Treatment of spinal injuries in Naberezhnye Chelny
To treat spinal injuries, a set of measures is used, which includes:
- medications;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- surgery.
At the Center for Rehabilitation Medicine in Naberezhnye Chelny, a neurologist draws up individual therapeutic programs for each patient. Depending on the degree of stability and severity of the injuries, the patient is prescribed:
- bed rest;
- immobilization of the spine, which involves maintaining the position of the body on the backboard, wearing special fixing collars and corsets;
- according to indications – realignment of the vertebrae;
- skeletal traction;
- thermal procedures.
A mandatory element of therapy is adequate pain relief, the prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs, and agents to accelerate regenerative processes.
In severe cases, patients who have sustained a spinal injury are advised to undergo surgical treatment and reconstructive operations.
Closed reduction
This method is used for dislocations of the cervical spine. The principle of this method is to use heavy weights for traction so that a slow maneuver can be performed to reduce the spine. This is a completely safe method. Neurological deterioration during reduction is a risk that is extremely rare, especially if the reduction is carried out carefully.
This method requires the installation of Crutchfield or Gardner-Wells traction forceps.
Unconscious patients should undergo an MRI scan before reduction.
Reduction is not performed for injuries such as craniocervical dissociation or cervical spine injury with signs of distraction.
Advantages of closed reduction
- Reduces the need for complex surgical procedures
- Improves stability, prevents neurological deterioration, or may improve neurological status
- Reduction in the first few hours of injury can lead to significant improvement in neurological status.
But there is no effective closed reduction method for the thoracolumbar spine yet.
Prevention
Unfortunately, spine and spinal cord injuries are unpredictable, but the risk of injury can be greatly reduced by following simple safety precautions.
- You should always wear a seat belt while riding in a car.
- When playing sports, you must wear appropriate protective equipment.
- Do not dive in unfamiliar bodies of water
- Strengthen the muscular system to provide proper support to the spine.
- Do not drink alcohol while driving.
How to help the victim?
So, the first thing is not to panic, but to reasonably assess the situation and do everything possible before the doctors arrive. The main consideration to be followed is “do no harm.” Here are the rules of first aid to the victim:
- If possible, ensure his body is in a stable position, do not move the patient anywhere until the ambulance arrives;
- Make sure the victim's breathing is not difficult. Unbutton your collar, free your neck from the scarf or tie;
- If a person is wearing a helmet or other protective equipment, it is not advisable to remove it. This should be done only as a last resort - for example, the victim does not regain consciousness and you suspect that he has stopped breathing;
- if the patient’s breathing or pulse has stopped, perform artificial respiration with pressure on the sternum;
- if you still need to move an injured person, carefully place him on a stretcher, carry him and lay him on a hard, flat horizontal surface. If there is no stretcher, call a few more people for help and move the patient together as carefully as possible, keeping his back straight. Pay special attention to the cervical region - the neck should under no circumstances be thrown back or, conversely, bent towards the chest;
- if you don’t have such special equipment as a neck brace on hand, wrap a jacket, sweater or towel around your neck so as to support the patient’s head;
- If a person is nauseous and there is a need to turn him on his side, do not do it alone. Ask others for help. Agree among yourself at what point to move the patient - for example, on the count of “three” - and act at the same time. Your task is to ensure that when turning, the head, neck and back of the injured person are on the same line;
- if possible, give the victim painkillers, cover him with a blanket and remain nearby until doctors arrive.