The feet are a part of the body that receives tremendous stress throughout the day, as the soles serve as support during walking, running, strength training and normal standing. Pronation and supination ensure proper functioning of the foot.
Thanks to the mechanisms of pronation and supination, the foot is cushioned, the impact on the surface is softened, and balance is maintained. This is taken into account in the production of sports shoes. It is recommended to select sneakers taking into account the type of pronation.
Foot work when running
The feet provide support for the entire body while standing, running, and walking. The image shows the range of movements that can be performed in a healthy foot.
Work of the foot while running (source: Faller A., Schuenke M., Eds. The Human Body. Thieme, 2004, 710 p.)
In the work of a normal foot during running, as a rule, there are 3 phases:
- repulsion phase;
- flight phase;
- landing and amortization phase.
Each of the movements in the image is involved in providing stability, support, shock absorption upon landing and imparting rigidity and the correct vector of load distribution when repelling from the surface.
When considering the work of the foot, it is worth highlighting its dynamics. These dynamics include the interaction of forces acting on the foot, as well as the loads and stresses that arise when these forces act. The foot is an integral part of the entire biomechanical system of the musculoskeletal system, and its dynamics should be considered in connection with this system.
A runner's feet endure high cyclic loads. The speed at which the foot lands on the surface when running ranges from 30 to 70 km/h. In a year, walking 10,000 steps a day, the average person takes more than 3.5 million. These are colossal loads that no endoprosthesis can withstand for more than 4-5 years. The durability of a healthy athlete’s foot is determined by the perfection of the mechanical design and the properties of the tissues of our body.
How to choose the right running shoes: 6 main criteria
Introduction
Over the past couple of million years, the process of evolution has made man a one-of-a-kind, upright, unique bipedal primate, capable of running only on his hind legs.
With this ability came unique difficulties and tasks that our brain and our body successfully solve. The main factor that influenced and influences the formation and structure of the human body is the force of gravity, in other words, the force of gravity. It was she who forced our spine to take the shape of the letter S, it was she who created for us the largest muscles in our body - the thigh muscles, small, parallel toes, straight legs and tendons that were increased in length when compared with other primates.
The human foot is that part of the body that significantly distinguishes us from other living beings inhabiting our planet; in the process of evolution, it acquired a complex mechanism consisting of levers (bones), springs (tendons) - there is no analogue of this system in nature. It’s hard to imagine, but the human foot consists of 26 bones, 33 joints, more than a hundred muscles and tendons, and this entire system perceives and withstands the load that occurs when running, 4 times the weight of the runner!
What is pronation
Pronation is the opposite movement of supination. It consists of raising the outer edge of the foot with turning the sole towards the inner arch of the foot relative to the supporting surface.
Pronation-supination mechanisms occur around the horizontal anterior-posterior axis of the foot.
In the normal state of the foot, these two movements complement each other and bring the foot to a neutral position after the movement. But this is not always possible and not for every person. Thus, both mechanisms, in addition to the neutral state described above, can be in excess (overpronation) and insufficiency (hypopronation, hypersupination). Hypersupination and hyperpronation are the causes of chronic diseases of the legs and lower back, as well as regular injuries.
Hypopronation or hypersupination of the foot is a fairly rare phenomenon. With such violations, the support during landing passes to the outer parts of the feet. As a result of movement, the load simply does not come to the arch of the longitudinal arch (the place where the main shock absorption is carried out), but is absorbed by the tissues and ligamentous-muscular apparatus of the outer surface of the foot and overlying joints.
Such a violation during long running and regular running will cause overload, resulting in damage and pain in the foot. This happens in people with a varus alignment of the calcaneal bone axis.
Insoles and sneakers for flat feet
Incorrect ankle positioning can lead to pain in the knees and back, periosteum and Achilles tendon. Insoles and sneakers for flat feet are designed to help the body with disturbances in natural shock absorption. To put it bluntly, insoles and running shoes for overpronation are a runner’s crutch. They do not cure, but help to avoid more severe injuries.
To correct deviations, perform special exercises to strengthen your feet.
Overpronation or excessive pronation of the foot
A much more common phenomenon is overpronation or overpronation. In this case, the longitudinal arch of the foot is either excessively flattened or is initially in a flattened state. This phenomenon occurs due to longitudinal flatfoot or valgus alignment of the heel bone axis.
In this condition, the foot does not return to a neutral position after landing, which subsequently leads to insufficient shock absorption on the muscular-ligamentous system. When running on feet in a position of hyperpronation, the joints of the foot are overloaded and the tibia rotates inward, which also affects the condition of the menisci and ligaments of the knee joints.
Varus and valgus deviations. Source: synertech.spb.ru
What do foot defects lead to?
Deformations cause a lack of shock absorption during movement. Most often this affects the joints, as well as the spine, as the load on the skeleton increases. The body has to look for ways to adapt and protect all organs from functional failure.
Such a restructuring can lead to the development of clubfoot, flat feet, hallux valgus, plantar calluses, and damage to the Achilles tendon. The most serious pathology caused by foot deformity is arthrosis. With the disease, degenerative processes in the joints are observed as a result of impaired blood circulation caused by overpronation.
Subsequently, the joints are destroyed. Leg pathologies are characterized by latent progression. There are no symptoms for a long time; exacerbations are usually provoked by active physical activity. Treatment of the disease is aimed at preventing changes and relieving pain during walking or sports training.
Causes of foot overpronation
The main causes of foot overpronation are longitudinal flat feet and weakness of the lower leg muscles, especially the tibialis anterior and posterior muscles. In most cases, these deviations in the position of the heel bone are formed in childhood and must be corrected by physical therapy and wearing correct shoes and insoles until the age of 12-14 years. It is much more difficult to correct this later.
When using special shoes or individual orthopedic insoles, it is often possible to return the foot to a position of neutral pronation and avoid excessive overload of the musculoskeletal system when running and jumping. But the use of these products must be combined with constant physical therapy and massage for the muscles of the feet and legs.
Training the lower leg muscles: 9 simple exercises for every day
Normal pronation is up to 5 degrees while standing and up to 15 degrees at the moment of maximum load on the foot when landing while running. In order to determine the degree of pronation while running, special video or photo recordings are used in specialized shoe stores and clinics.
Sneakers for flat feet
Shoes for overpronators have a special rigid insert on the inside of the midsole. It prevents the foot from falling through and puts the ankle in the correct position.
Important components of running shoes for flat feet:
- stable sidewall
- Achilles support
- heel with good cushioning
- special insert for stabilization
Here's a comparison of foot placement in regular soft running shoes and overpronating running shoes.
Foot pronation test
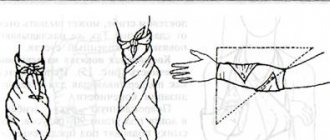
At home, you can determine the degree of pronation using a test of the axis of the heel bone and shin in a photo of the ankle joint from behind, standing at rest, and also at the moment of support on the foot when running, by calculating the angle between them, to assess the degree of pronation.
You can use the “wet test”: stand with wet feet on a sheet of cardboard or paper and trace the footprint with a marker. But you need to understand that such results will be approximate, so it is better to seek help from specialists.
Example of wet test results. Source: Orthopedic diagnostics, Marks V.O., 1978, p. 271
How to tell if there is a problem
The first, not the most accurate, but the easiest way to check your pronation is to see how the sole of your sneakers wears out.
With neutral pronation, the area under the base of the toes and the outer part of the heel will wear away.
For hypopronation , the outer part of the sole.
For moderate overpronation , the area under the ball of the big toe and the outer part of the heel.
With severe overpronation - the inner part of the sole.
The second, more accurate method is video recording, or gait analysis. A special camera is installed on a treadmill, and then leg movements are observed on a still frame. These cameras are available in stores that sell running shoes. For example, at Runlab or Adidas.
Some tips for choosing running shoes
When answering the question of how to choose running shoes for safe running, you need to adhere to the following tips:
- the choice of shoes also depends on the surface on which running training will take place;
- it is better to conduct a special analysis of the structure of the foot to identify all its defects;
- When buying running equipment, it is worth remembering that sneakers are the largest part of the expense;
- running shoes must be tried on before purchasing and be a little larger in size (about half a size, it all depends on the size of the distances);
- Along with running shoes, it is also better to immediately buy special running socks that will quickly remove moisture, hold the necessary parts of the foot well, and also prevent chafing.
It is also worth remembering that for each brand, technology with a specific function may have completely different names, so when you come to a sports store, explain to the consultant what kind of sneakers you need and he will help you choose not only the optimal size, but also the necessary technology that will protect your feet from excess load.
A small life hack for choosing sneakers.
Choosing sneakers that suit you perfectly is not an easy task, but it is still doable, let’s look at some criteria:
- Determine the type and style of your running, whether it's sprinting or long-distance running.
- Select the shoe category and features that suit your needs, such as trail running, pavement, etc.
- Take your old sneakers (if you have them) to the store and compare how the old and new ones feel. Of course, they will not be the same, but this will give you an understanding of what comfort should be.
When it comes to shoe size, things are not so simple. The fact is that despite a more or less uniform size grid, sneaker manufacturers use different shapes to make their products. Therefore, if you order sneakers online, be extremely careful. And first familiarize yourself with the sizing chart of a specific manufacturer.
You should also remember that your feet can swell during the day, so try to try on new shoes at the end of the day. Moreover, if you have not previously been involved in running and are buying sneakers specifically for this activity, then immediately buy them half a size larger, since while running, the foot tends to swell, and a perfectly selected sneaker in the store will turn into hellish torture while jogging.
By the way, one of the next articles will be about sports insoles, subscribe to our social media. networks and don’t miss new articles.
Another variant
Now some experts are of the opinion that even if an athlete has deviations from the norm in pronation, it is not necessary to interfere with the biomechanics of his body and urgently order insoles. This is due to the fact that almost a third of athletes have deviations within the normal range - up to 8 degrees.
Nike physiotherapist Lance Walker also believes that in this case, nothing needs to be changed: “The best way to remain a healthy runner is to choose shoes that are comfortable, rather than shoes that fit your specific parameters but cause discomfort. Science supports this point of view. If you give up the subjective factor (feeling of comfort), you can get into a lot of problems.”
In other words, it is better to listen to your body, not theoretical prescriptions.